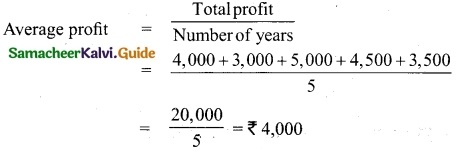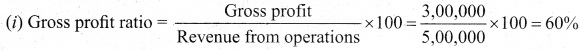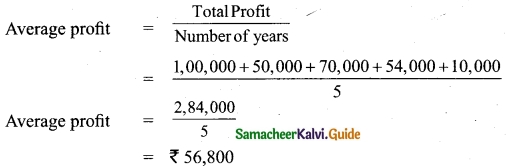Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Accountancy Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Accountancy Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 12th Accountancy Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II. III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 150 words.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 250 words. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2.30 Hours
Max Marks: 90
PART – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [Answers are in bold] [20 x 1 = 20]
Question 1.
Companies cannot keep books on single entry system because of……….
(a) tax properties
(b) legal provisions
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) legal provisions
Question 2.
Bills receivable endorsed are debited to………
(a) Bills receivable A/c
(b) Debtors A/c
(c) Creditors A/c
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Creditors A/c
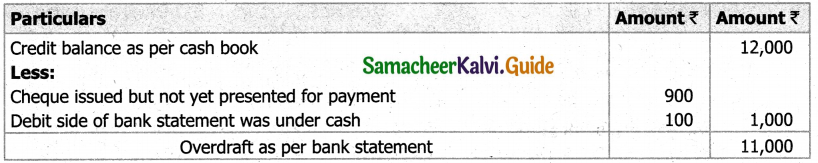
![]()
Question 3.
The amount or property received by a non-profit organisation as stated by the will of a decreased person is commonly referred to as……….
(a) Donations
(b) Honorarium
(c) Legacy
(d) Endowment
Answer:
(c) Legacy
Question 4.
In non-profit organisation the sale of old newspapers is generally considered as a/an …….
(a) Revenue Receipts
(b) Expenditure
(c) Income
(d) capital Receipt
Answer:
(c) Income
Question 5.
Which of the following method, the capital of the partners is not altered and it remains generally fixed?
(a) Fixed capital method
(b) Fluctuating capital method
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Fixed capital method
Question 6.
All the transactions between the partner and the firm are recorded in the……..
(a) Capital A/c
(b) Drawing A/c
(c) Profit and loss A/c
(d) Revaluation A/c
Answer:
(a) Capital A/c
Question 7.
Which of the following method goodwill is calculated by multiplying the weighted average – profit?
(a) Super profit method
(b) Annuity
(c) Weighted average profit method
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Weighted average profit method
Question 8.
Self-generated goodwill should not be shown in the……….
(a) Journal
(b) Ledger
(c) Balance sheet
(d) Books of accounts
Answer:
(d) Books of accounts
Question 9.
When A and B sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2 they admit C as a partner giving him 1/3 share of profits. This will be given by A and B………
(a) Equality
(b) In the ratio of their capitals
(c) In the ratio of their profit
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) In the ratio of their profit
Question 10.
In order to maintain fair dealings, at the time of admission it is necessary to revalue assets and liabilities of the firm to their………
(a) Cost price
(b) True value
(c) Selling price
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) True value
Question 11.
In both types of policies the insurance premium is paid by the……….
(a) Sale tradership
(b) Partnership firm
(c) Hindu undivided family
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Partnership firm
Question 12.
The policy amount received from the insurance company, is used to settle the amount due to the………..
(a) Increased partner
(b) Decreased partner
(c) Partnership at will
(d) Partnership deed
Answer:
(b) Decreased partner
Question 13.
The capital of a company is divided into small units of………..
(a) Current amount
(b) fixed amount
(c) Capital amount
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) fixed amount
Question 14.
Equity shares do not enjoy any ………..
(a) Equity rights
(b) Preference rights
(c) Dividend of rights
(d) Ordinary shares
Answer:
(b) Preference rights
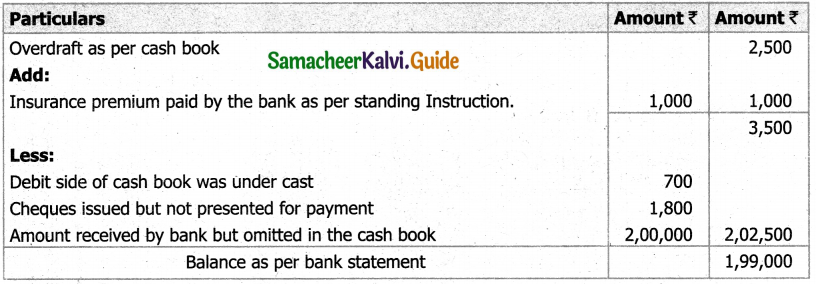
![]()
Question 15.
Comparative statements and trend percentages are examples of …………
(a) Cash flow analysis
(b) Trend analysis
(c) Horizontal analysis
(d) Vertical analysis
Answer:
(c) Horizontal analysis
Question 16.
Preparation of common size statements and computation of ratios are examples………..
(a) Ratio analysis
(b) vertical analysis
(c) Horizontal analysis
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) vertical analysis
Question 17.
Which ratio is the proportion, of fixed income bearing funds to ………..
(a) Debt, equity ratio
(b) Capital gearing ratio
(c) Propreetory ratio
(d) Profitability ratio
Answer:
(b) Capital gearing ratio
Question 18.
Which ratio indicates the efficiency of utilisation of fixed assets ……….
(a) Inventory turnover ratio
(b) Trade receivables turnover ratio
(c) Trade payable turnover ratio
(d) Fixed assets turnover ratio
Answer:
(d) Fixed assets turnover ratio
Question 19.
All transactions related to receipt either in cash or through bank are recorded using……….
(a) Payment voucher
(b) Centra voucher
(c) Receipt voucher
(d) Sales voucher
Answer:
(c) Receipt voucher
Question 20.
All transactions related to payments either in Cash or through bank are recorded using………..
(a) Journal voucher
(b) Centra voucher
(c) Receipt voucher
(d) Payment voucher
Answer:
(d) Payment voucher
PART – II
Answer any seven questions in which question no. 30 is compulsory. [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 21.
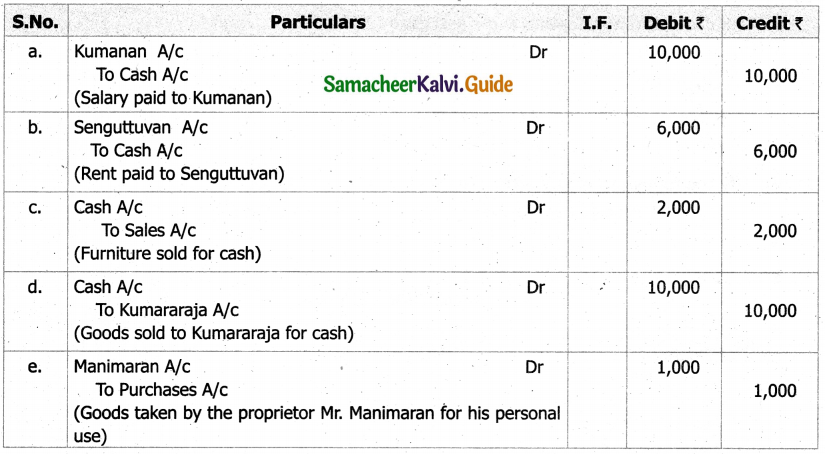
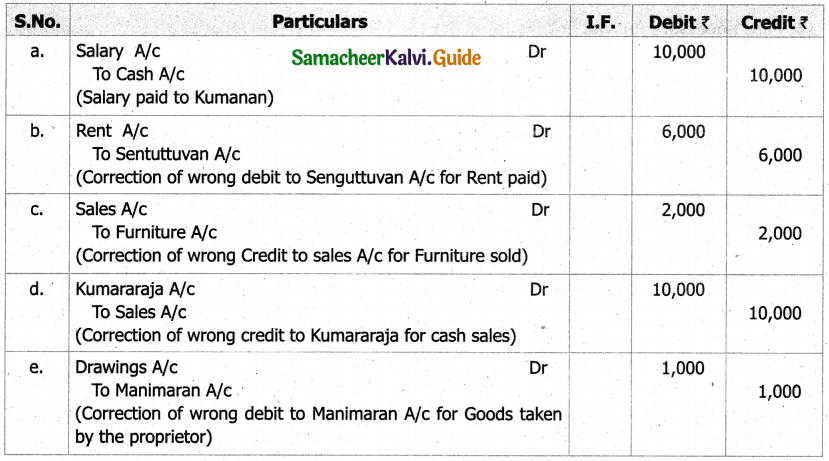
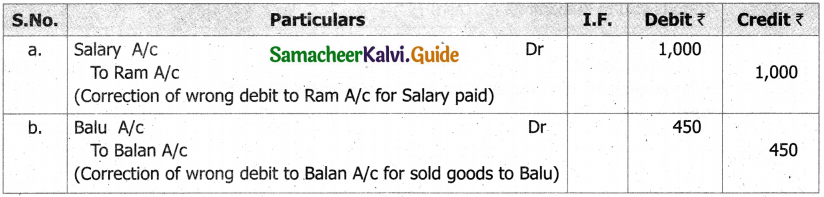
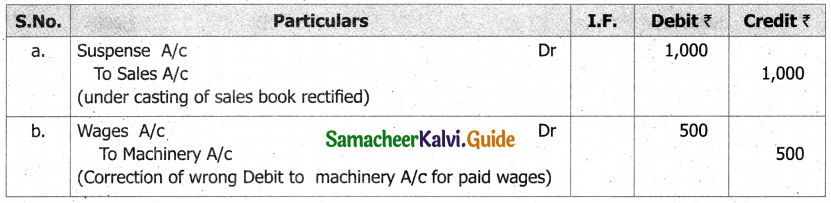
What is a statement of affairs?
Answer:
A statement of affairs is a statement showing the balances of assets and liabilities on a particular date. The balance of assets are shown on the right side and the balance of liabilities on the left side. This statement resembles a balance sheet. The difference between the total of assets and total of liabilities is taken as capital.
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Question 22.
How will the following appear in the final accounts of Marthandam woman Cultural Association.
Stock of sports materials on 1.4.2018 16,000
Sport materials purchased 84,000
Stock of sports materials on 31.3.19 10,000
Answer:
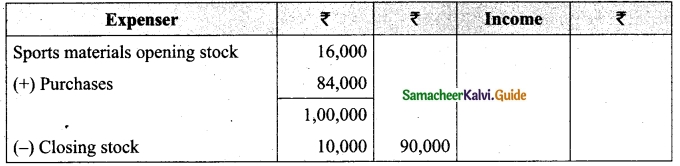
Question 23.
Mani is a partner, who withdrew Rs 30,000 on 1st September, 2018. Interest on drawings is charged at 6% per annum. Calculate interest on drawings on 31st December, 2018 and show the journal entries by assuming that fluctuating capital method is followed.
Answer:
Mani:
30,000 × \(\frac{6}{100}\) x \(\frac{4}{12}\) = Rs 600
Interest on drawings of Mani = Rs 600
Question 24.
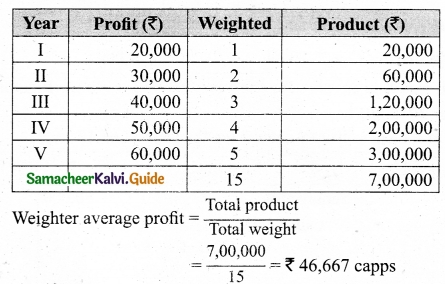
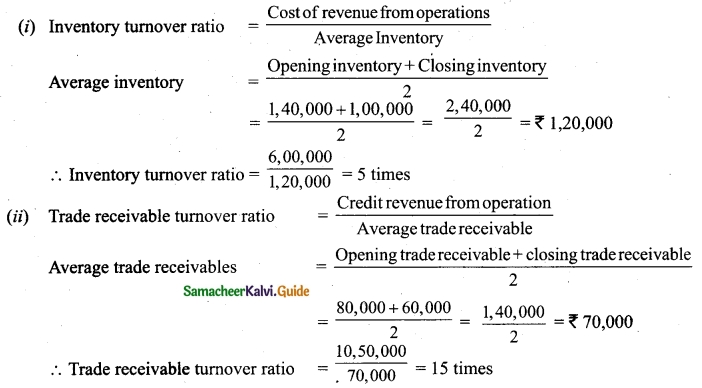
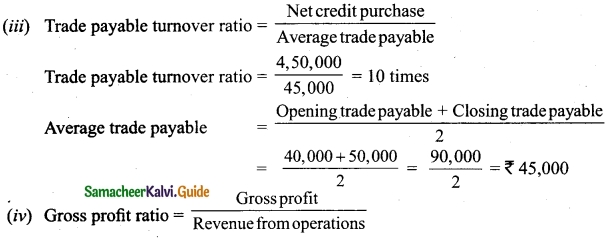
The following are the profits of a firm in the last five years: 2014: Rs 4,000; 2015: Rs 3,000; 2016: Rs 5,000; 2017: Rs 4,500 and 2018: Rs 3,500. Calculate the value of goodwill at 3 years purchase of average profits of five years.
Answer:
Goodwill = Average profit × Number of years of purchase
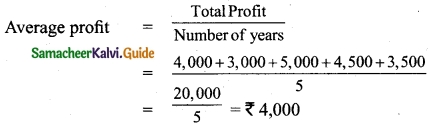
Goodwill = Average profit × Number of years of purchase
= 4,000 × 3 = Rs 12,000.
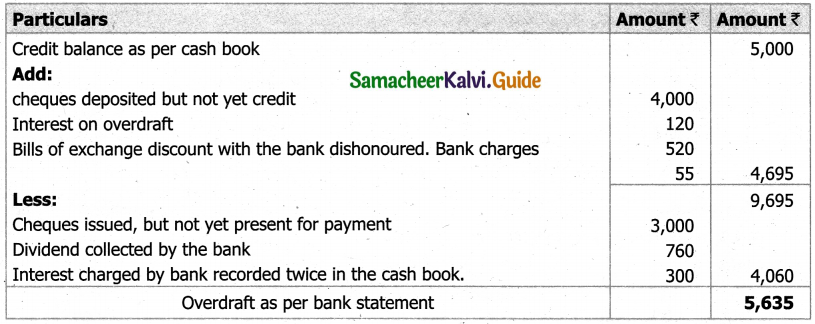
![]()
Question 25.
What is goodwill?
Answer:
Goodwill is the good name or reputation of the business which brings benefit to the business. It enables the business to earn more profits. It is the present value of a firm’s future excess earnings.
Question 26.
Anbu and Raju are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. Akshai is admitted as a partner. The new profit sharing ratio among Anbu. Raju and Akshai is 5 : 3 : 2. Find out the sacrificing ratio.
Answer:
Old ratio of Anbu and Raju = 3 : 2 that is, \(\frac{3}{5}\) : \(\frac{2}{5}\)
New Ratio of Anbu, Raju and Akshai = 5 : 3 : 2 that is, \(\frac{5}{10}\) : \(\frac{3}{10}\) : \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Share sacrificed = Old share – New share

Question 27.
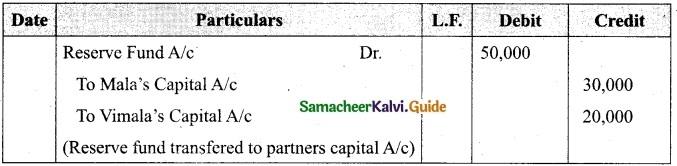
Vivin, Hari and Joy are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. On 31.3.2017, Hari retired. On the date of retirement, the books of the firm showed a general reserve of Rs 60,000. Pass the journal entry to transfer the general reserve.
Answer:
Journal Entry
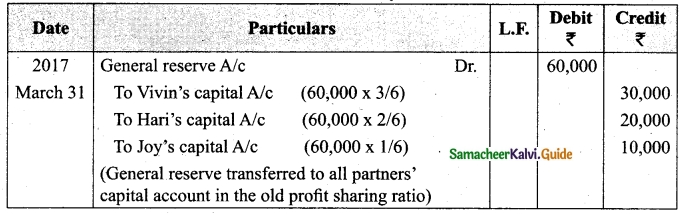
Question 28.
List the tools of financial statement analysis.
Answer:
- Comparative Statement
- Common size statement
- Trend analysis
- Funds flow analysis
- Cash flow analysis
Question 29.
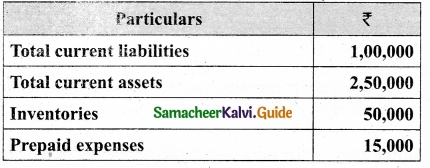
Calculate quick ratio of Ananth Constructions Ltd from the information given below.
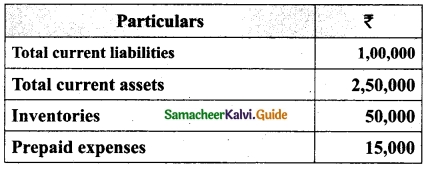
Answer:

Quick assets = Current assets – Inventories – Prepaid expenses
= 2,50,000 – 50,000 – 15,000
= Rs 1,85,000
Question 30.
What are the pre-defined ledgers available in Tally.ERP-9.
Answer:
Tally has two-predefined ledgers cash and profit and loss A/c. The user has to create various other ledgers based on their requirements. Pre-defined group/ledger cannot be deleted.
PART-III
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 × 3 = 21]
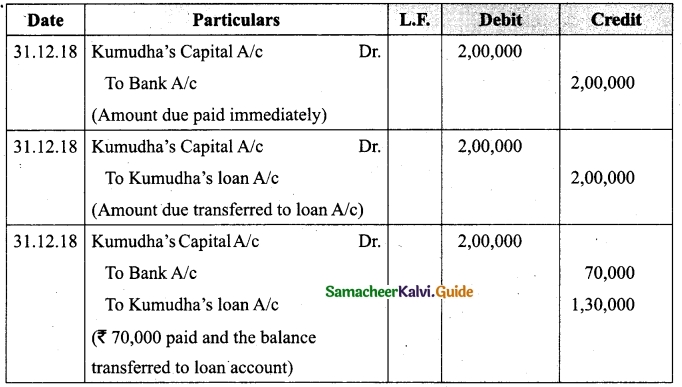
Question 31.
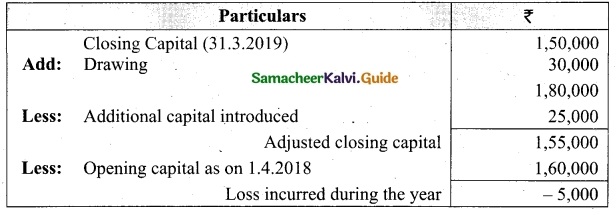
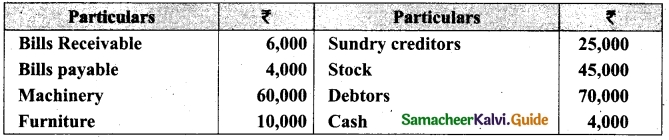
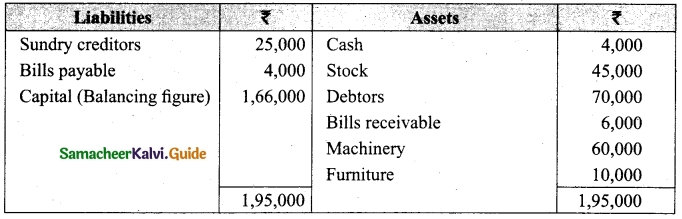
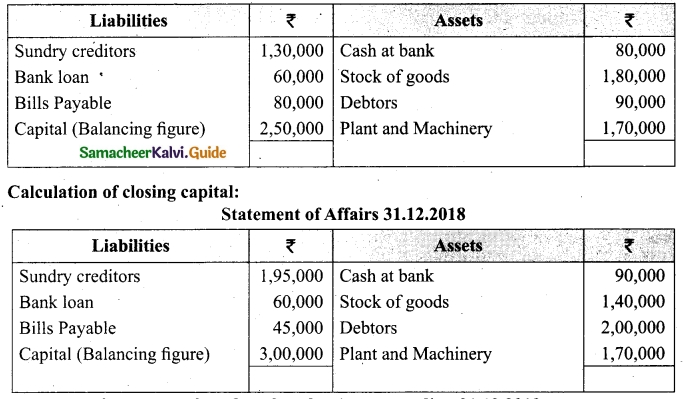
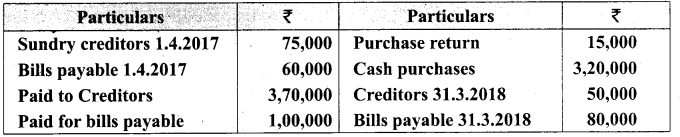
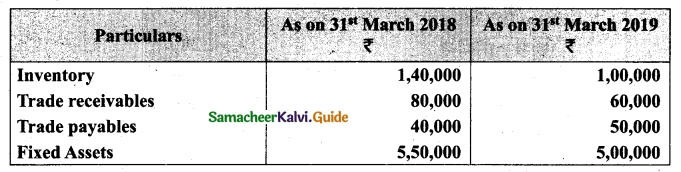
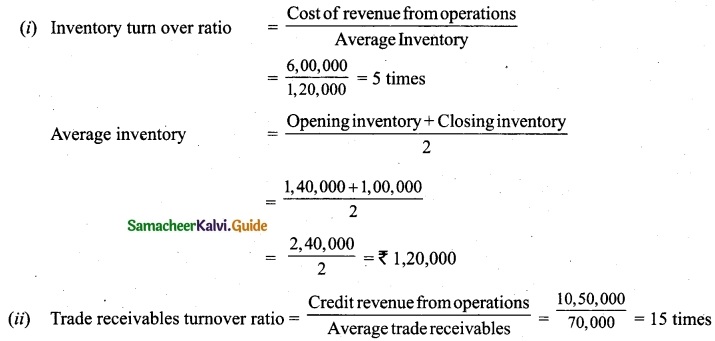
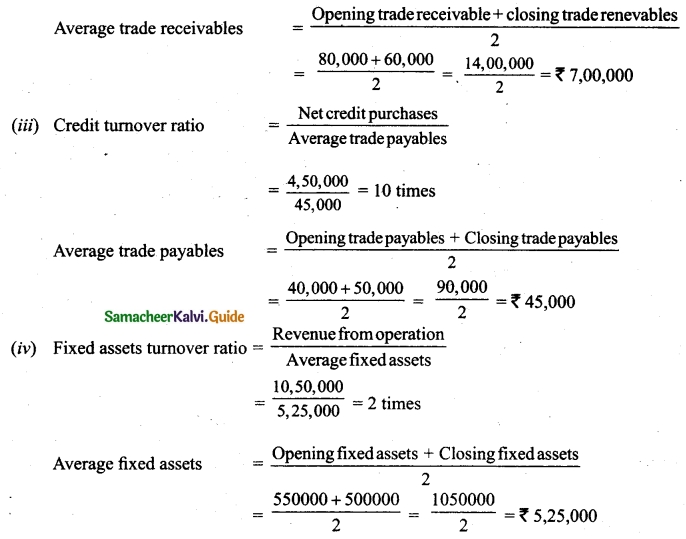
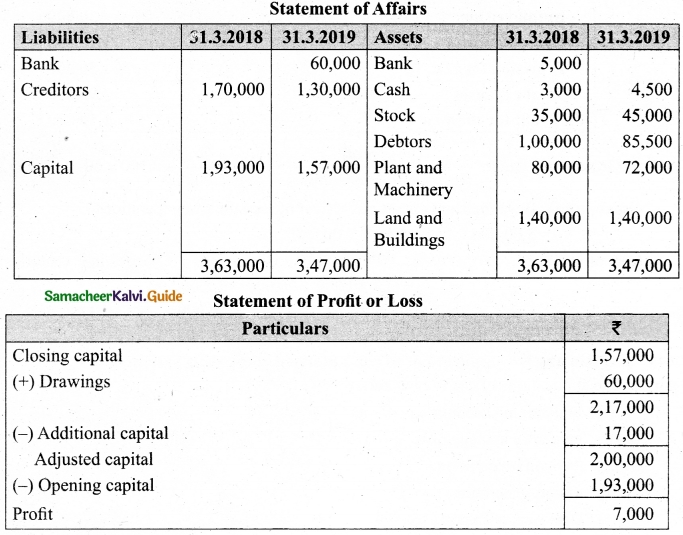
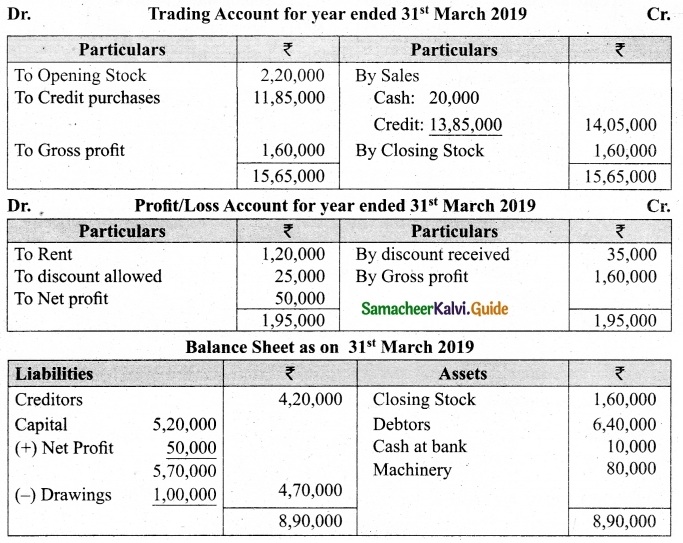
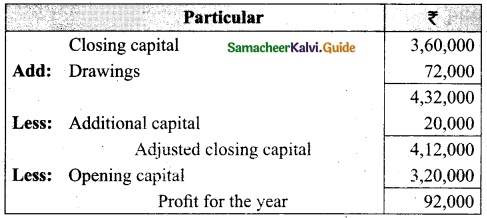
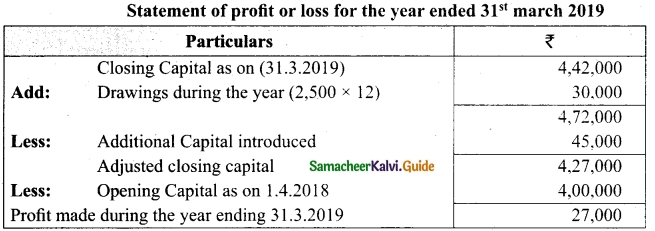
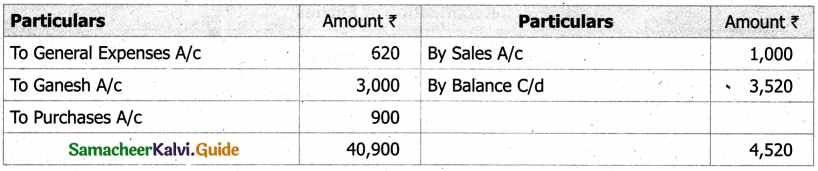
On 1st April 2017, Ganesh started his business with a capital of Rs 75,000. He did not maintain proper book of accounts. Following particulars are available from his books as on 31.03.2018.
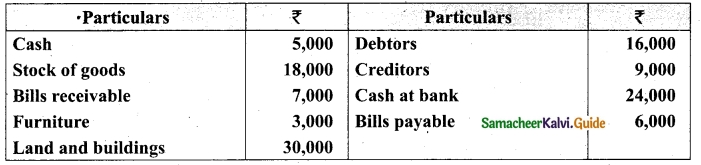
During the year he withdrew Rs 15,000 for his personal use. He introduced further capital of Rs 20,000 during the year. Calculate his profit or loss.
Answer:
Statement of affairs of Ganesh as on 31st March, 2018
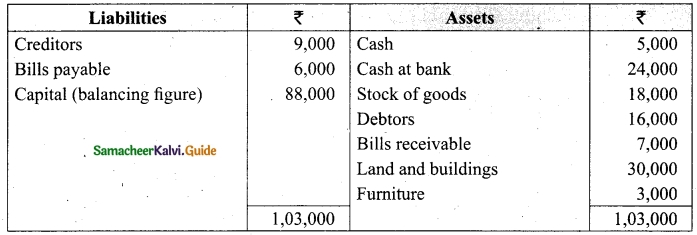
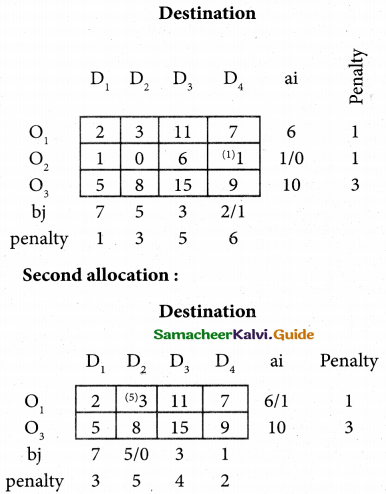
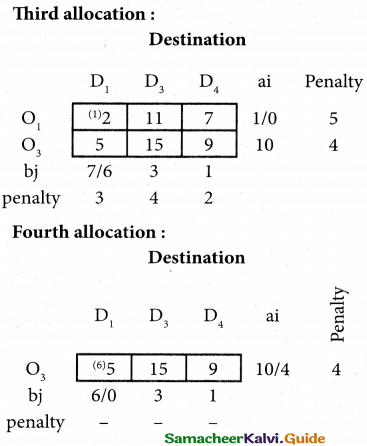
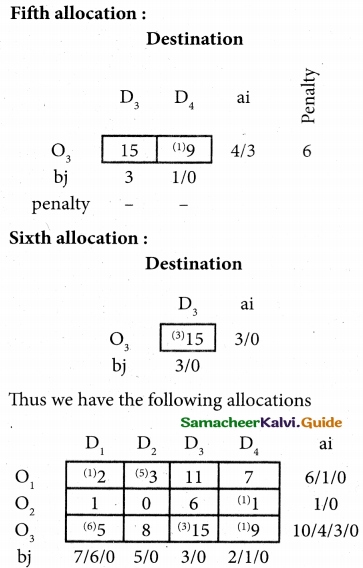
For finding out the closing capital, Statement of affairs as on 31st March, 2018 is prepared. Statement of profit or loss for the year ending 31st March, 2018

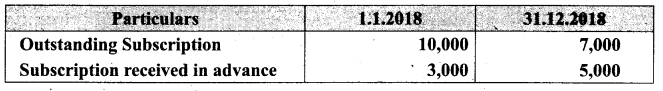
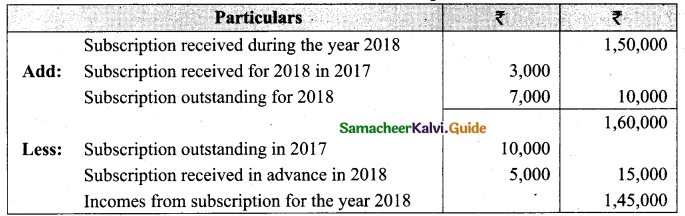
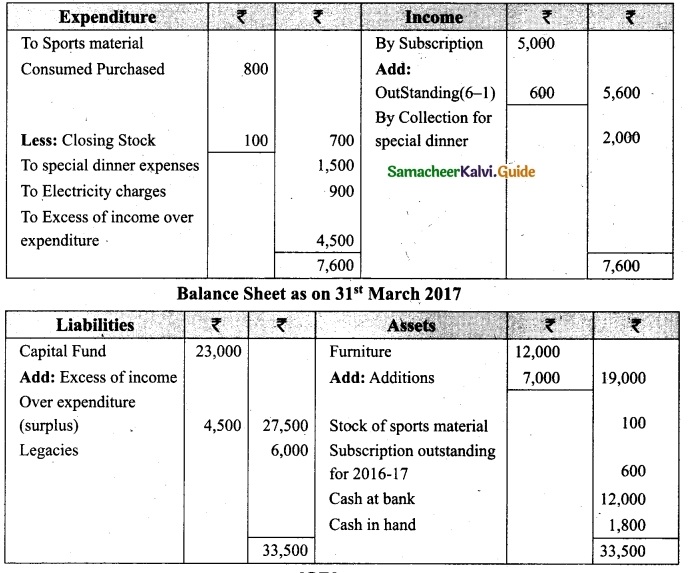
Question 32.
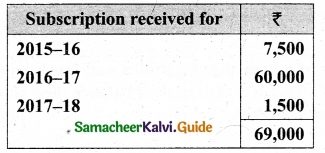
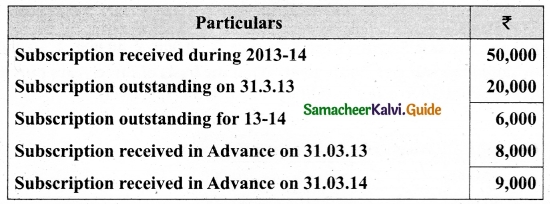
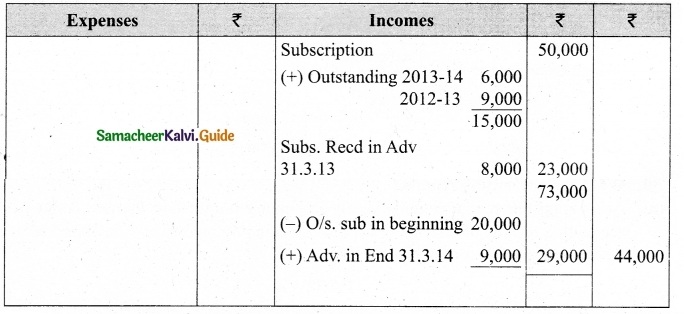
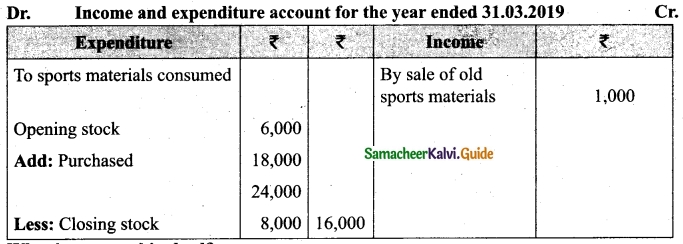
Compute income from subscription for the year 2018 from the following particulars relating to a club.

Answer:
Subscription received during the year 2018: Rs 45,000.
Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31.03.2019
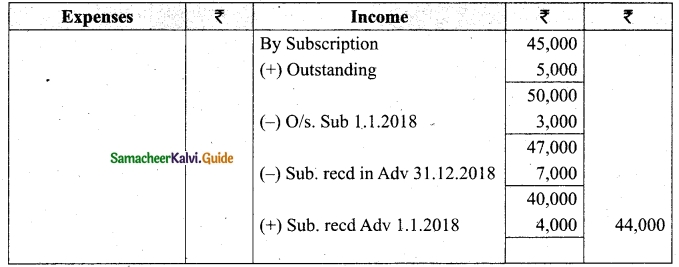
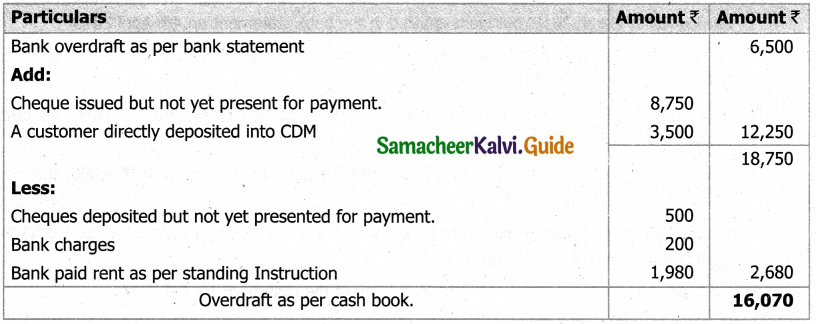
![]()
Question 33.
State the difference between fixed capital method and fluctuating capital method.
Answer:
| S. No. | Basis of distinction | Fixed capital method | Fluctuating capital method |
| 1. | Number of accounts | Two accounts are maintained for each partner, that is, capital account and current account. | Only one account, that is, capita] account is maintained for each partner. |
| 2. | Change in capital | The amount of capital normally remains unchanged expect when additional capital is introduced or capital is withdrawn permanently. | The amount of capital changes from period to period. |
| 3.
| Closing balance | Capital account always shows a credit balance. But, current account may show either debit or credit balance. | Capital account generally shows credit balance. It may also show a debit balance. |
| 4. | Adjustments | All adjustments relating to interest on capital, interest on drawings, salary or commission, share of profit or loss are done in current account. | All adjustments relating to interest on capital, interest on drawings, salary or commission, share of profit or loss are done in the capital account. |
Question 34.
From the following information, calculate the value of goodwill based on 3 years purchase of super profit
(i) Capital employed: Rs 2,00,000
(ii) Normal rate of return: 15%
(iii) Average profit of the business: Rs 42,000
Answer:
Normal profit = Capital employed × Normal rate of return
= 2,00,000 × 15% = Rs 30,000
Super profit = Average profit – Normal profit
= 42,000 – 30,000 = Rs 12,000
Goodwill = Super profit × Number of years of purchase
= 12,000 × 3 = Rs 36,000
Question 35.
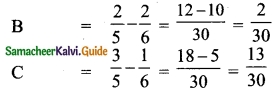
Govind and Gopal are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 4. They admit Rahim as a partner. Govind surrenders 2/9 of his share in favour of Rahim. Gopal surrenders 1/9 of his share in favour of Rahim. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio and sacrificing ratio.
Answer:
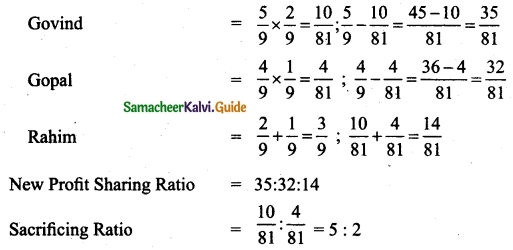
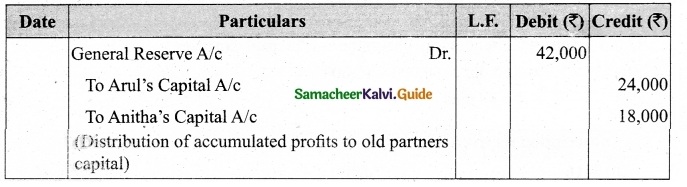
Question 36.
Balu, Chandru and Nirmal are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5 : 3 : 2. On 31st March 2018, Nirmal retires from the firm. On the date of Nirmal’s retirement, goodwill appeared in the books of the firm at Rs 60,000. By assuming fluctuating capital account, pass the necessary journal entry if the partners decide to
(а) write off the entire amount of existing goodwill
(b) write off half of the existing goodwill.
Answer:
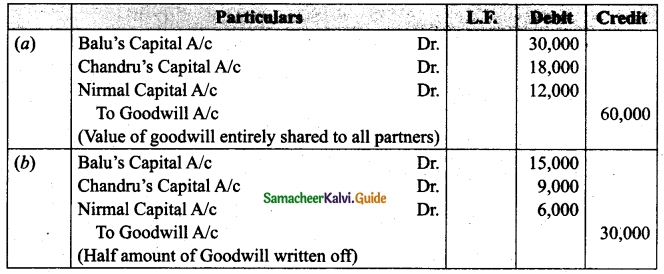
![]()
Question 37.
State the different between preference shares and equity shares?
Answer:
| S. No. | Points to Distinct | Preference Shares | Equity Shares |
| 1. | Rate of Dividend | Rate of Dividend is fixed. | Ratio of Dividend varies from year to year depending upon profits available. |
| 2. | Redemption | These are redeemed after stipulated period but within period of ten years from the date of issue. | These shares are not redeemed during the lifetime of the company. At the time of winding up |
| 3. | Participation in management | They have no right to participate in management. | These shareholders have the right to participate in management. |
Question 38.
Briefly explain any three limitations of financial statements.
Answer:
(i) Lack of qualitative information : Qualitative information, that is non-monetary information is also important for business decisions. For e.g. Efficiency of the employees and efficiency of the management. But this is ignored in financial statements.
(ii) Record of historical data : Financial statement are prepared based on historical data. They may not reflect the current position.
(iii) Ignores price level changes : Adjustments for price level changes are not made in the financial statements. Hence financial statements may not reveal the current position.
Question 39.
State any three advantages of ratio analysis.
Answer:
(i) Measuring operational efficiency : Ratio analysis helps to know operational efficiency of a business by finding the relationship between operating cost and revenues and also by comparison of present ratios with those of the past ratios.
(ii) Intra firm comparison : Comparison of efficiency of different divisions of an organisation is possible by comparing the relevant ratios.
(iii) Inter firm comparison : Ratio analysis helps the firm to compare its performance with other firms.
Question 40.
Explain any five applications of computerised accounting system (CAS).
Answer:
The applications of CAS are as follows
- Maintaining accounting records
- Inventory management
- Pay-roll preparation
- Report generation
- Data Import/Export
- Taxation
![]()
PART – IV
Answer all the following questions. [7 × 5 = 35]
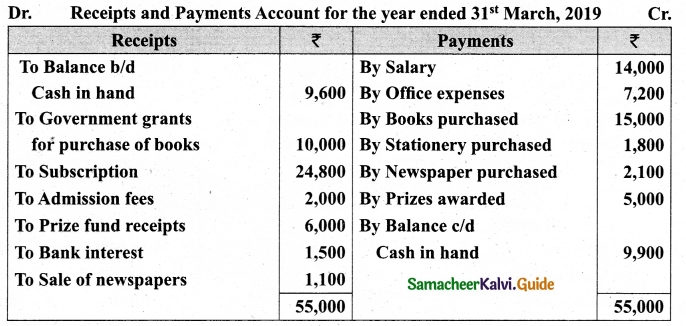
Question 41(a).
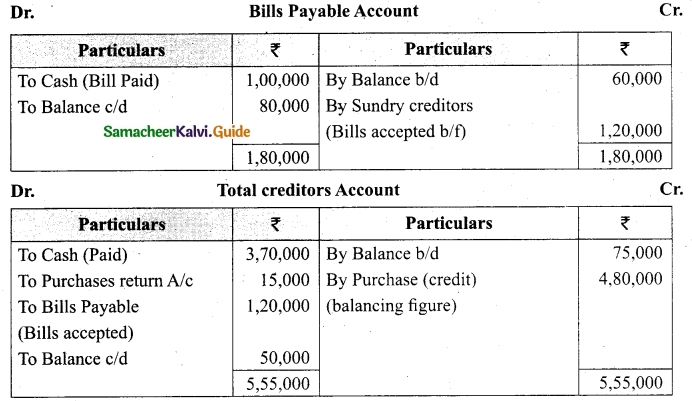
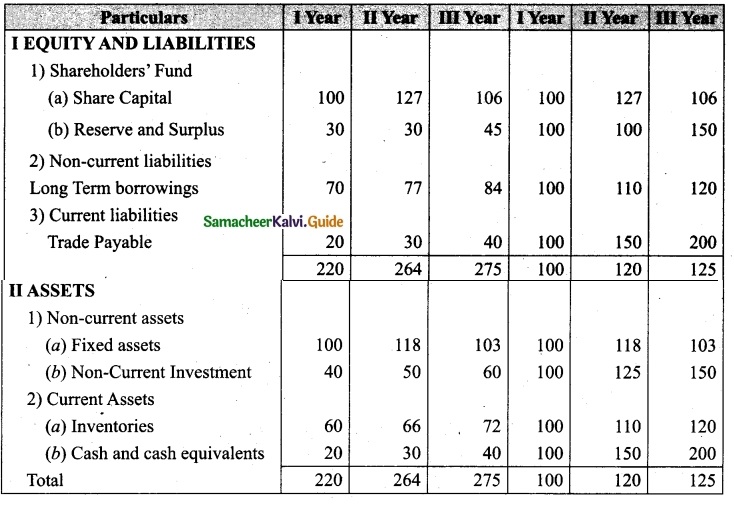
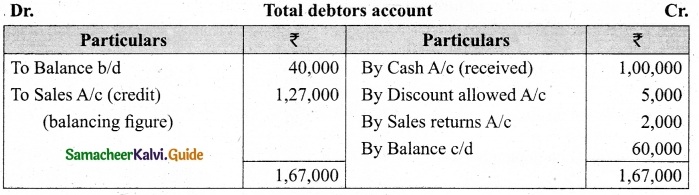
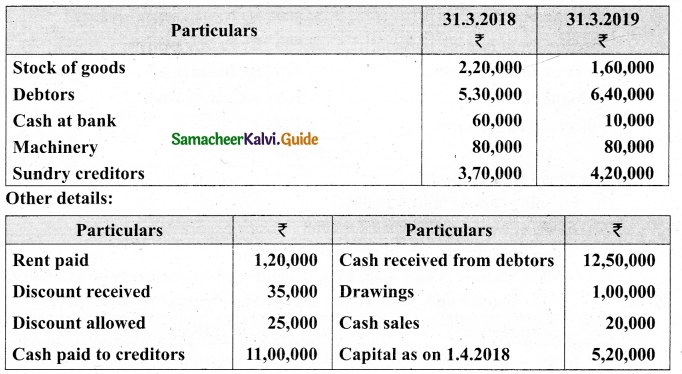
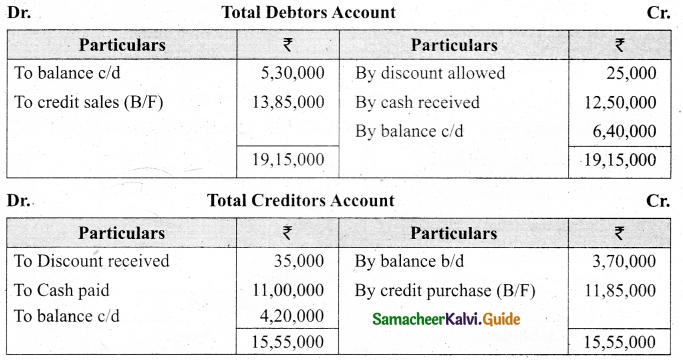
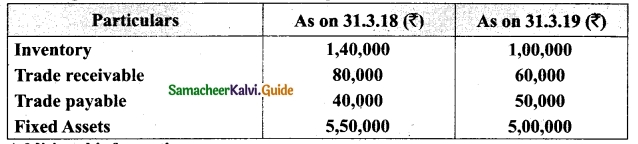
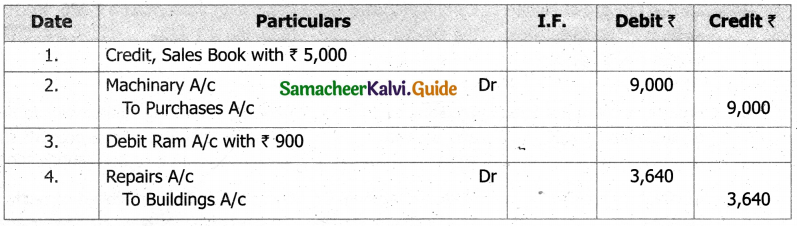
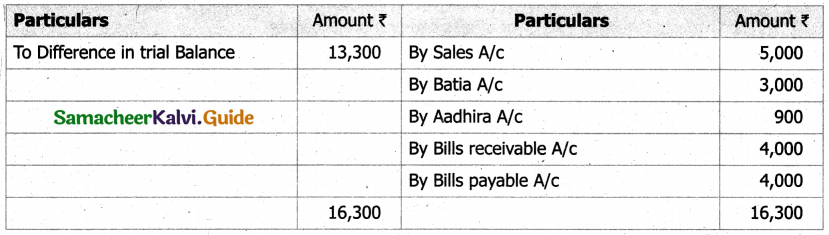
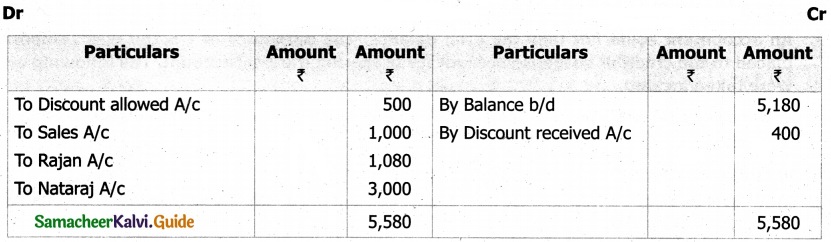
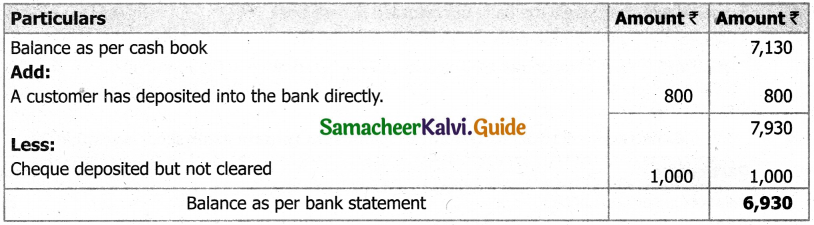
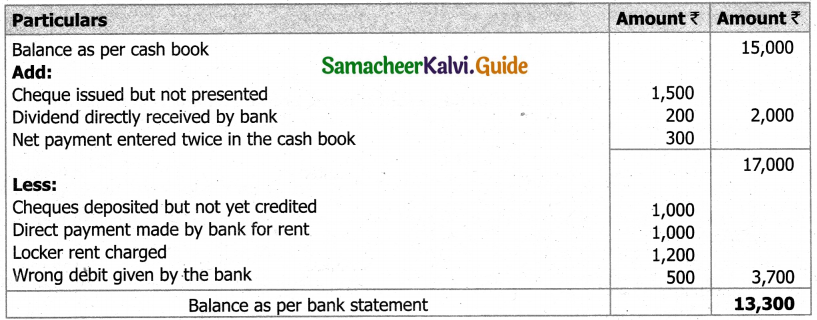
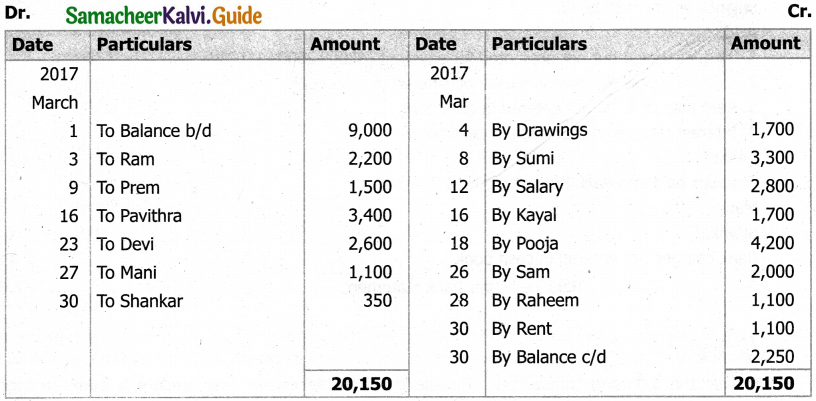
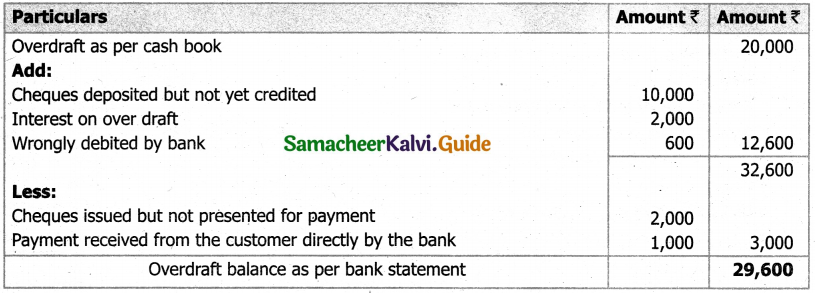
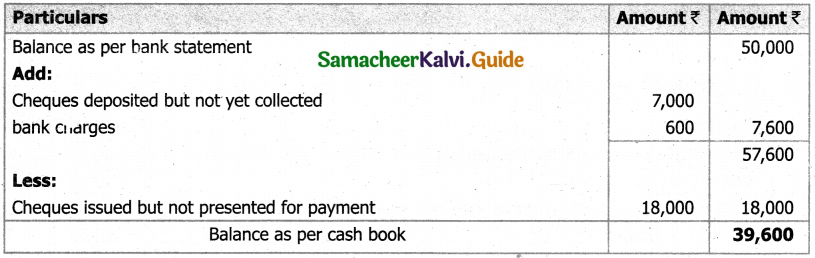
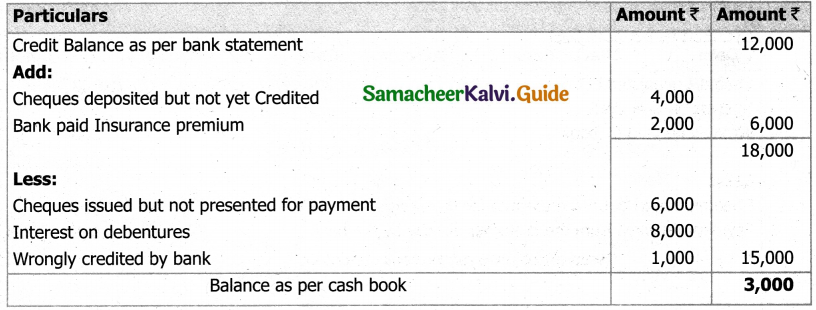
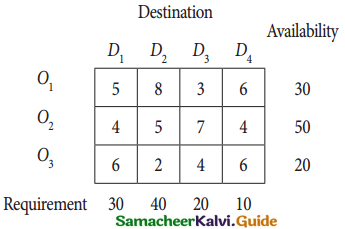
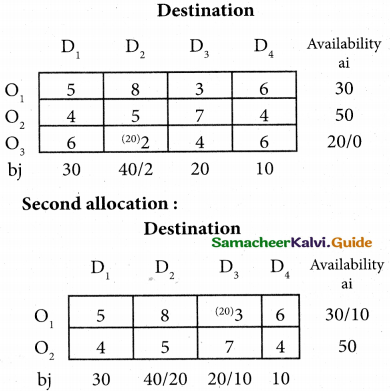
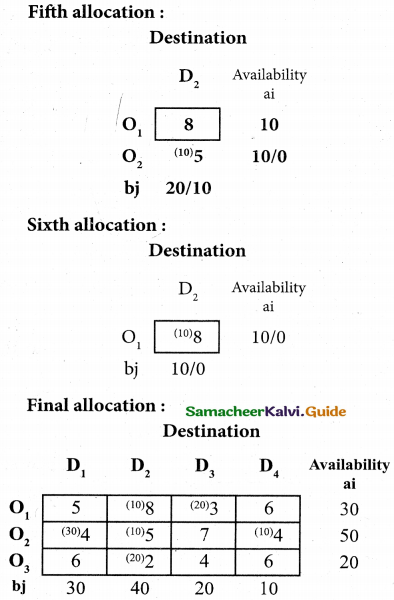
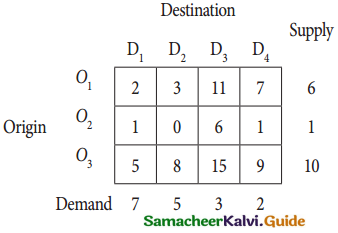
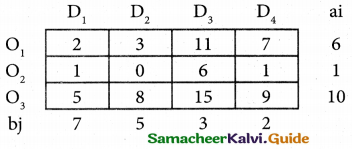
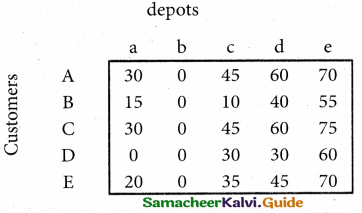
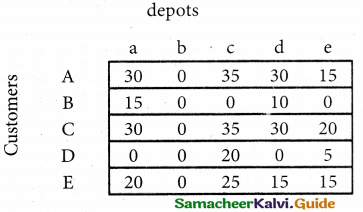
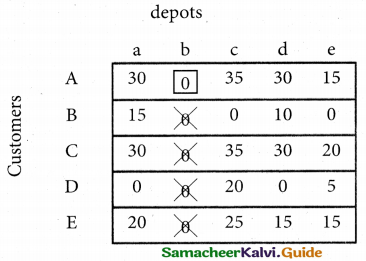
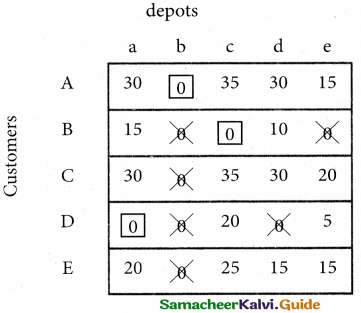
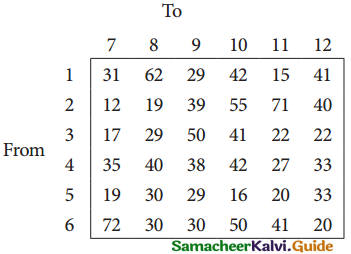
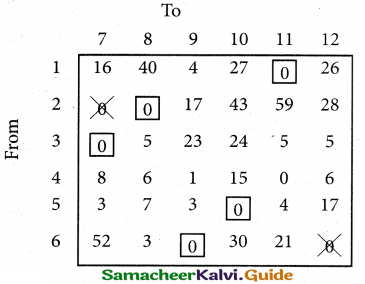
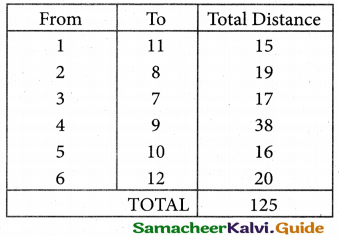
From the following details you are required to calculate credit sales and credit purchases by preparing total debtors account, total creditors account, bills receivable account and bills payable account.
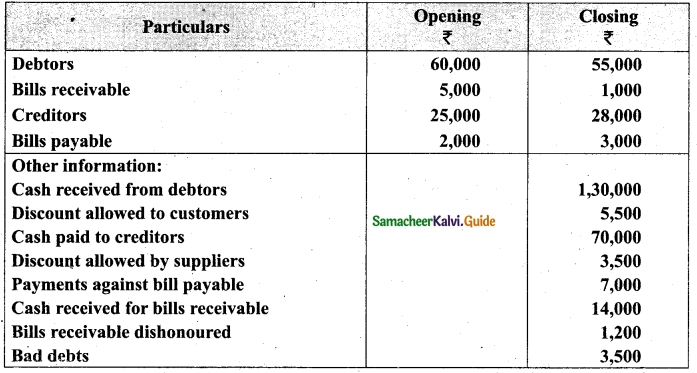
Answer:
[OR]
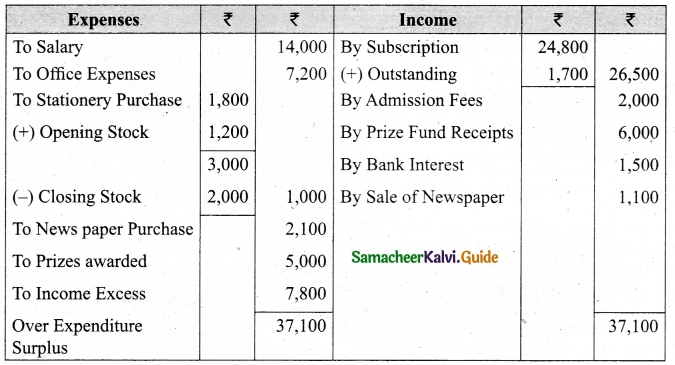
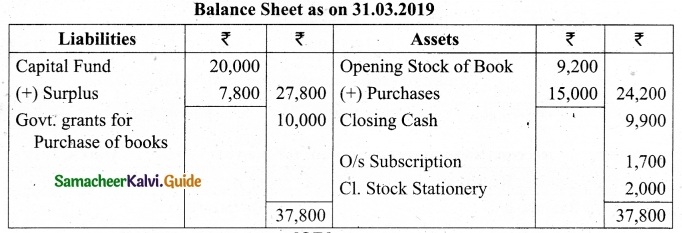
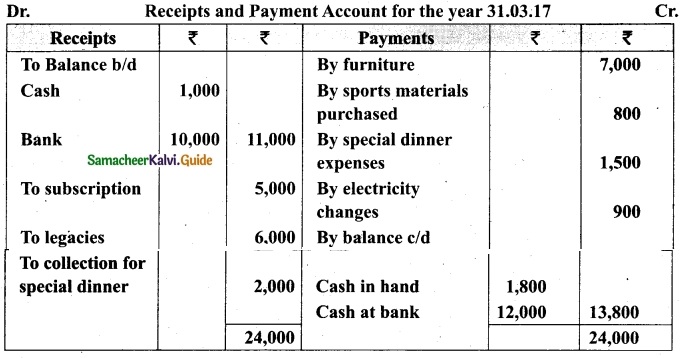
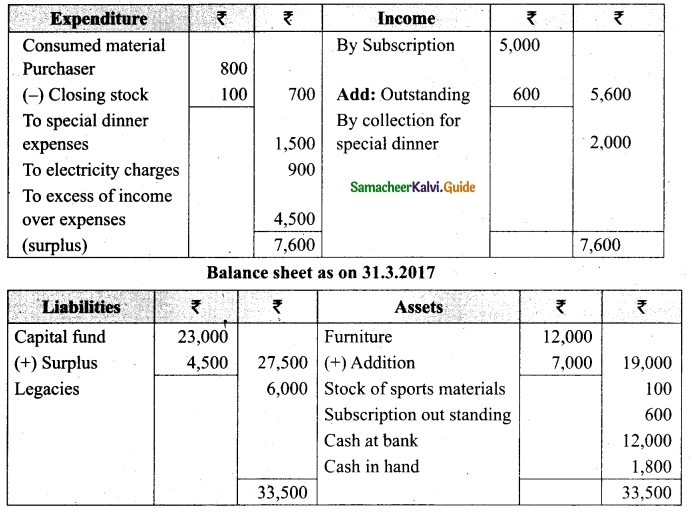
(b) From the following Receipts and Payments account of Yercaud Youth Association, prepare Income and expenditure account for the year ended 31st March, 2019 and the balance sheet as on that date.
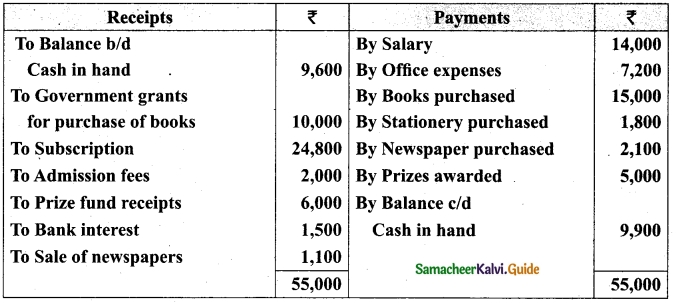
Additional information:
(i) Opening capital fund Rs 20,000.
(ii) Stock of books on 1.4,2018 Rs 9,200.
(iii) Subscription due but not received Rs 1,700.
(iv) Stock of stationery on 1.4.2018 Rs 1,200 and stock of stationery on 31.3.2019, Rs 2,000
Answer:
Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31.03.19
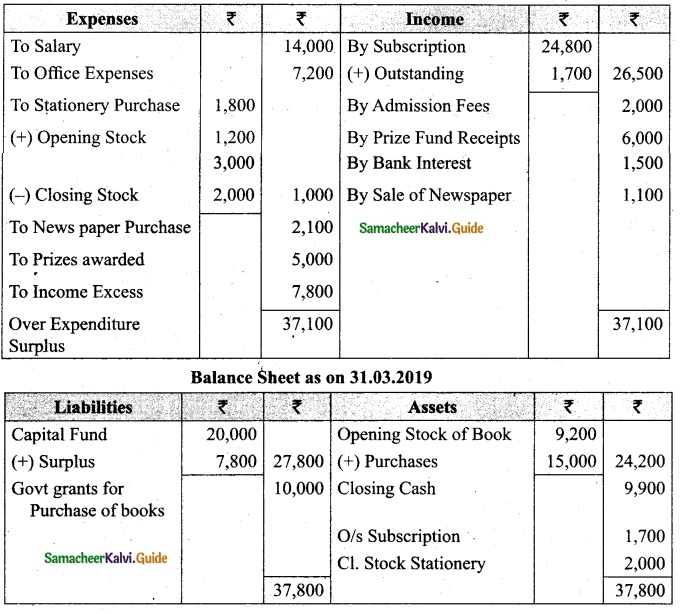
![]()
Question 42(a).
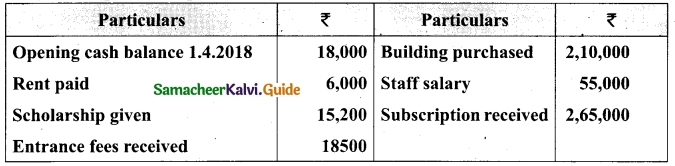
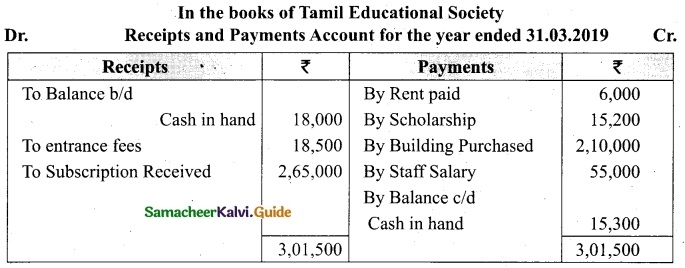
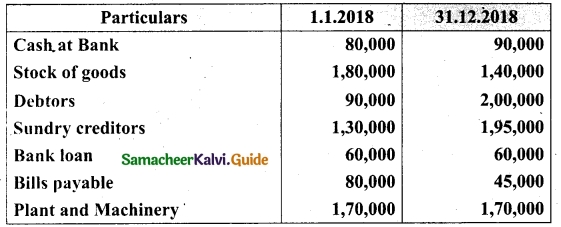
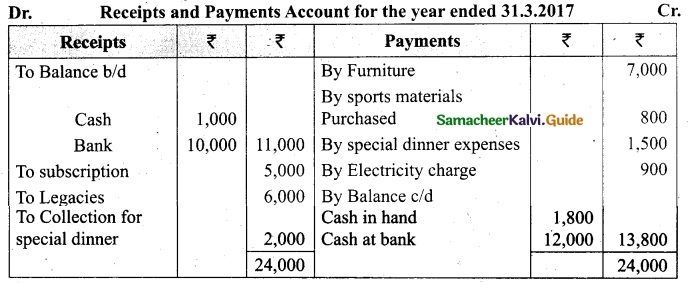
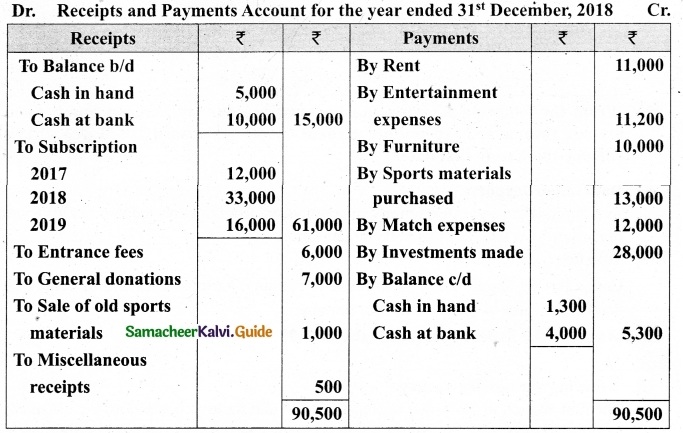
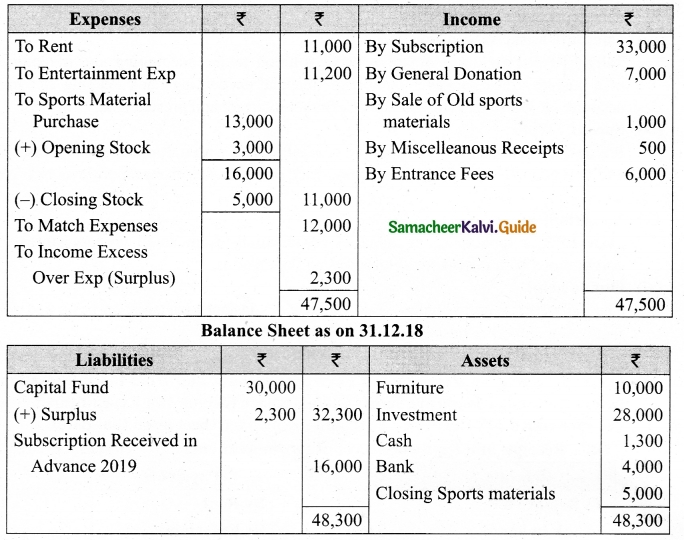
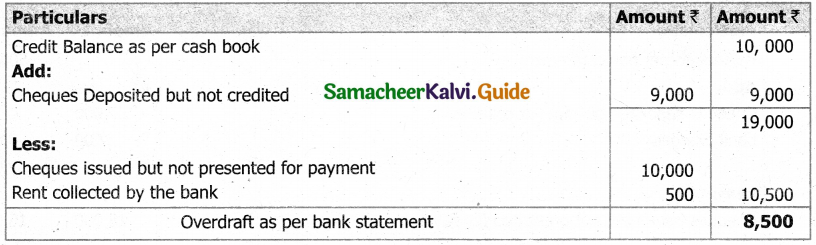
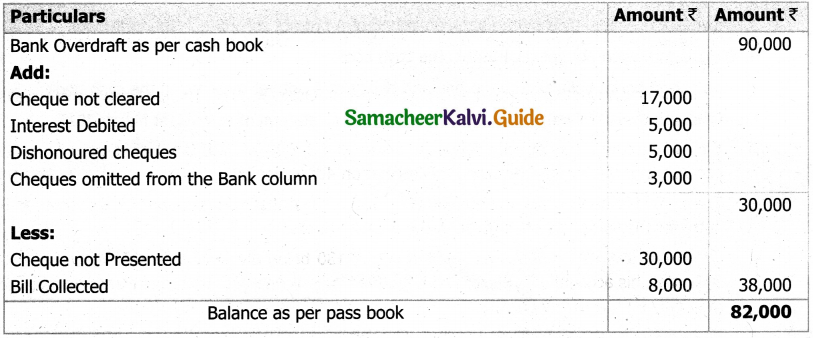
Following is the Receipts and Payments Account of Salem Recreation Club for the year ended 31st March, 2019.
In the books of Salem Recreation Club
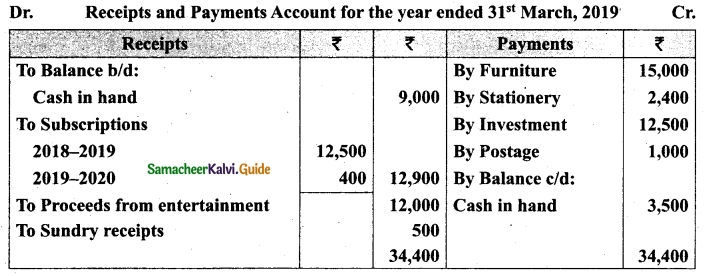
Additional information:
(i) There are 450 members each paying annual subscription of Rs 30.
(ii) Stock of stationery on 31st March, 2018 Rs 300 and on March 31, 2019 Rs 500.
(iii) Capital fund as on 1st April 2018 was Rs 9,300.
Prepare income and expenditure account for the year ended 31st March, 2019 and the balance sheet as on that date.
Answer:
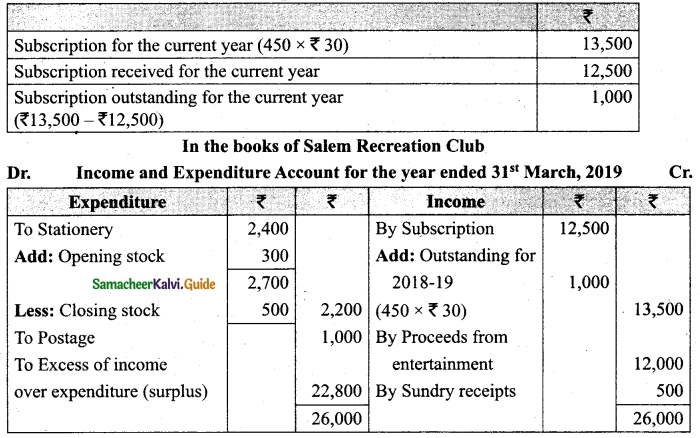
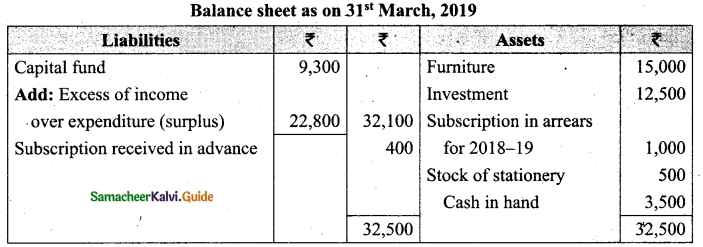
[OR]
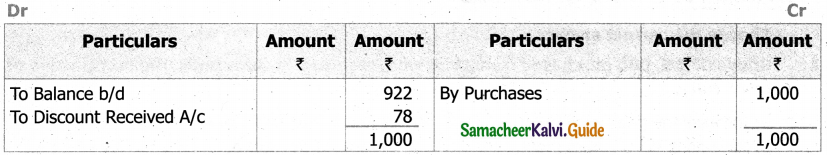
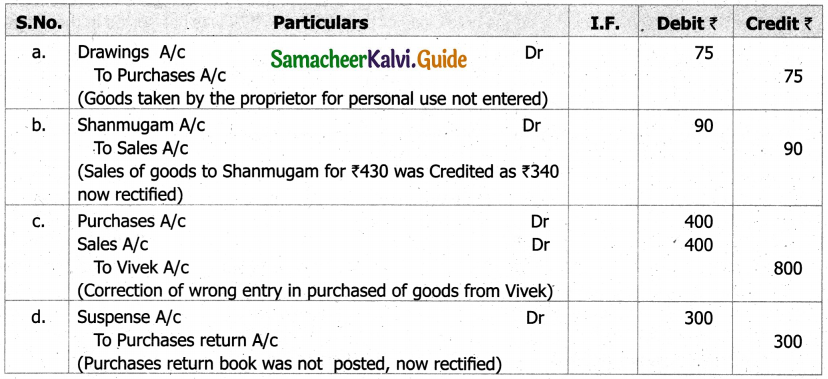
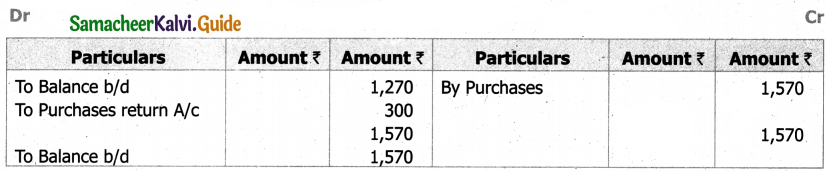
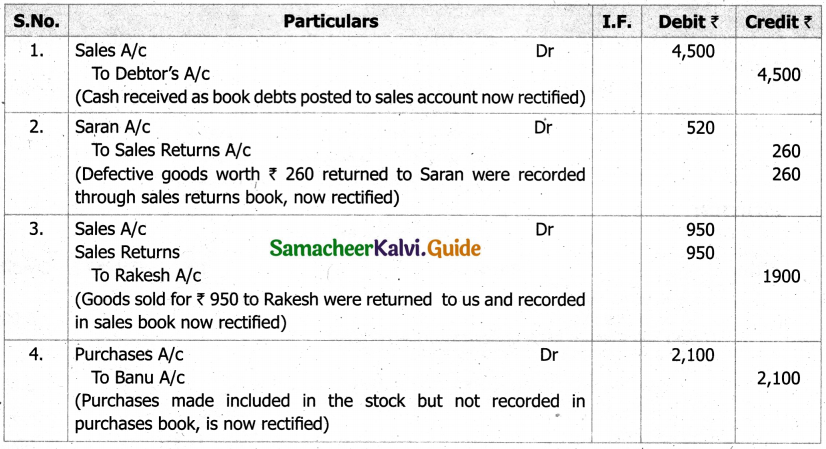
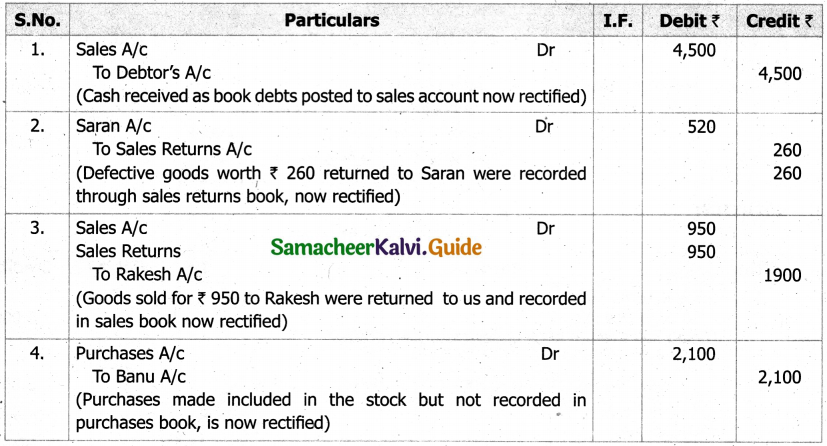
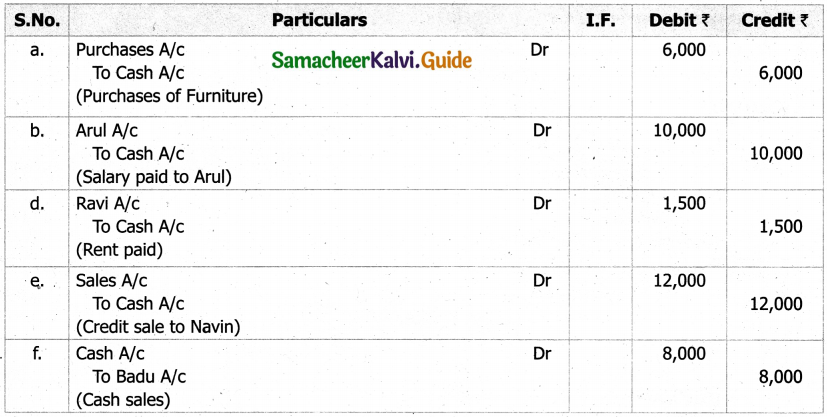
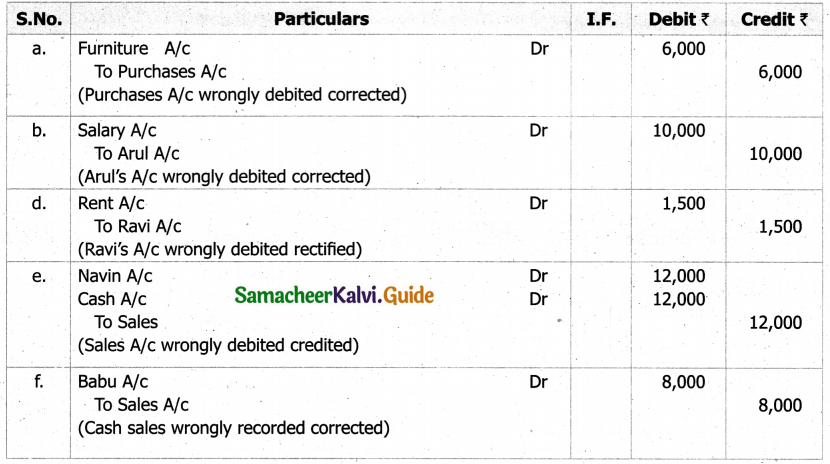
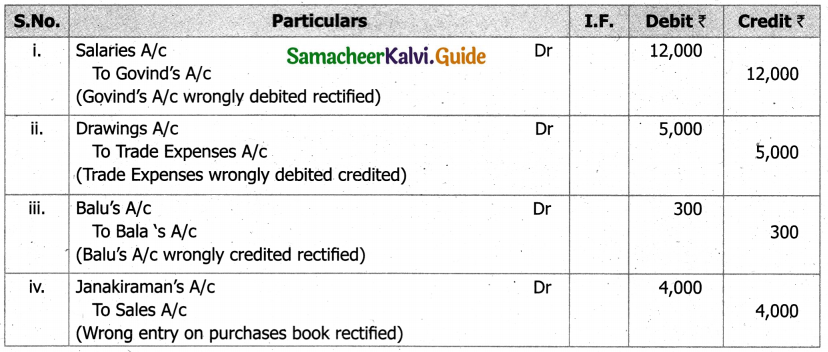
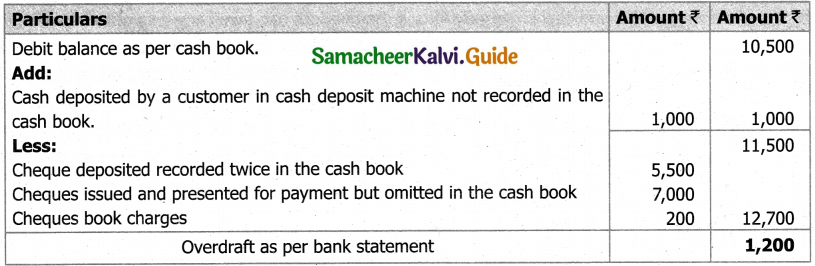
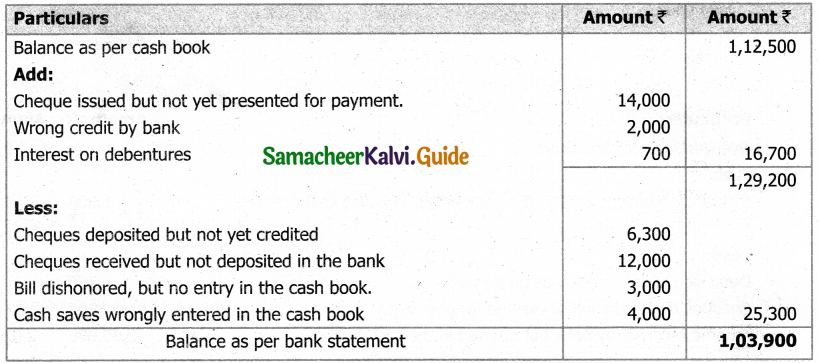
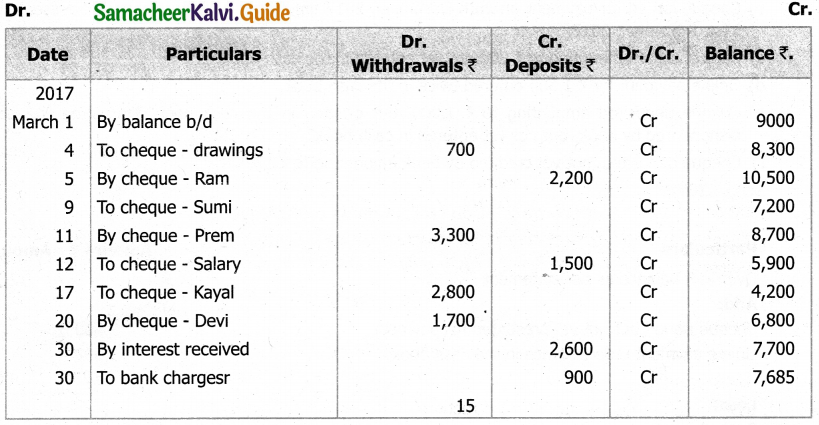
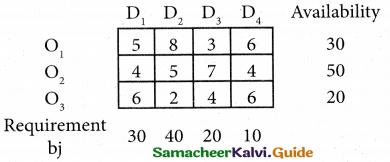
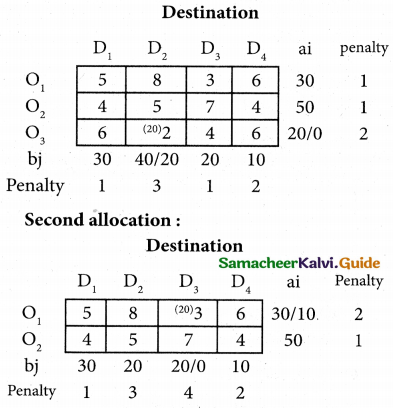
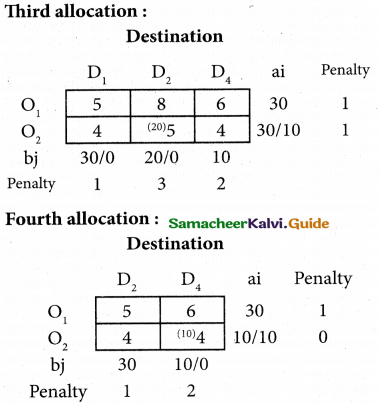
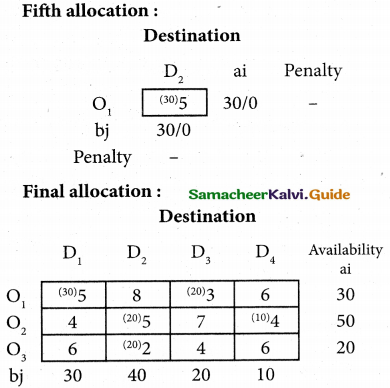
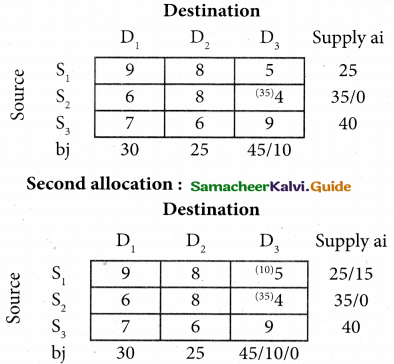
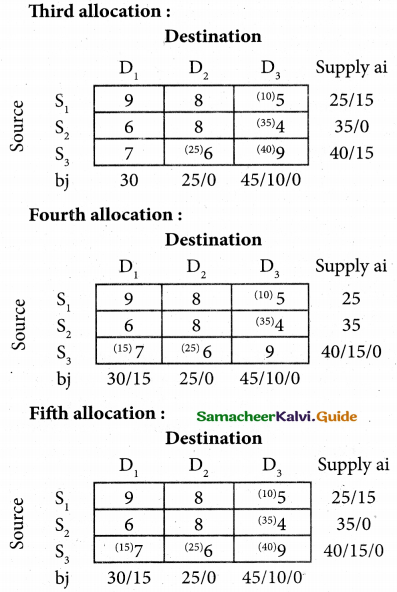
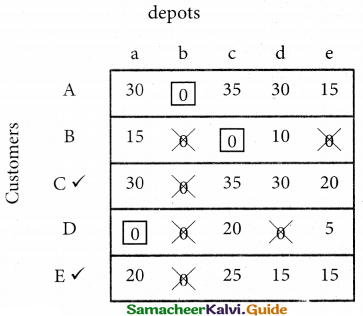
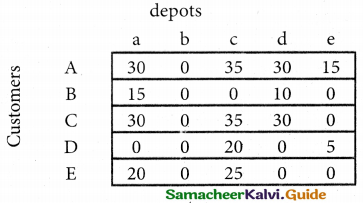
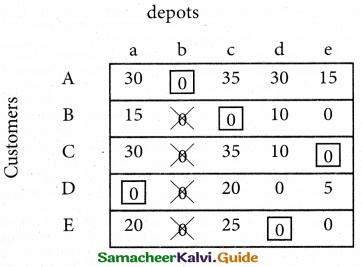
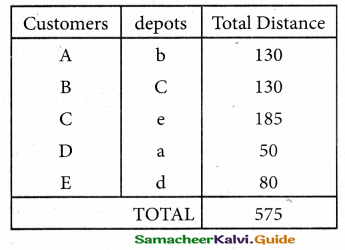
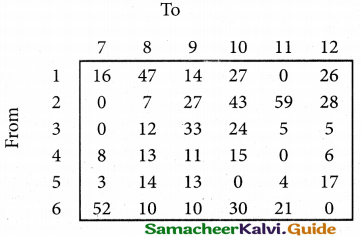
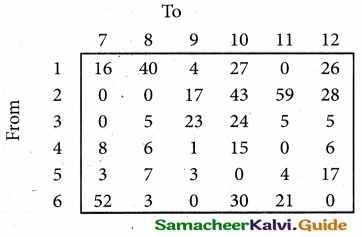
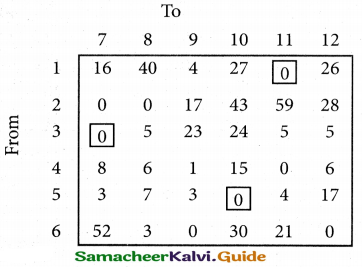
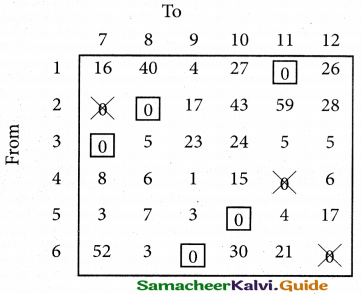
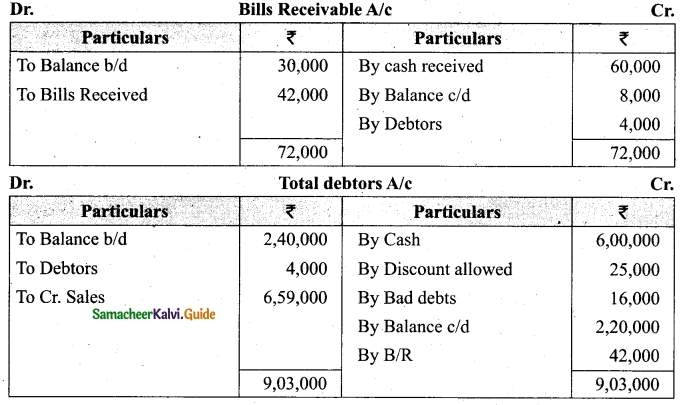
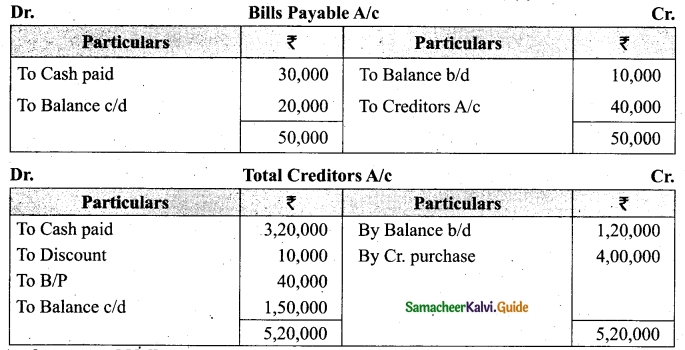
(b) From the following‘details you are required to calculate credit sales and credit purchases by preparing total debtors account, total creditors account, bills receivable account and bills payable account.
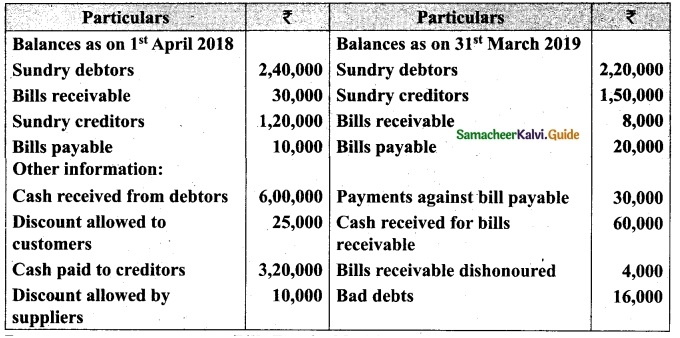
Answer:
![]()
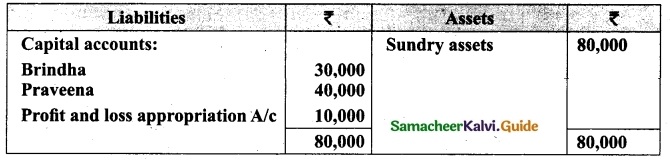
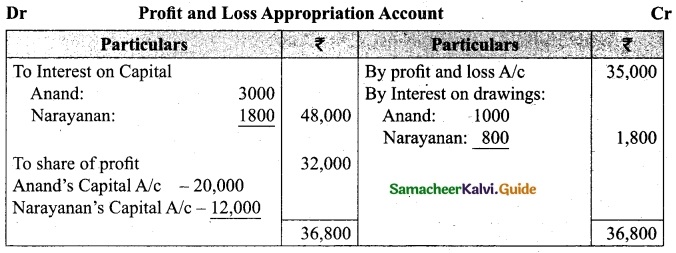
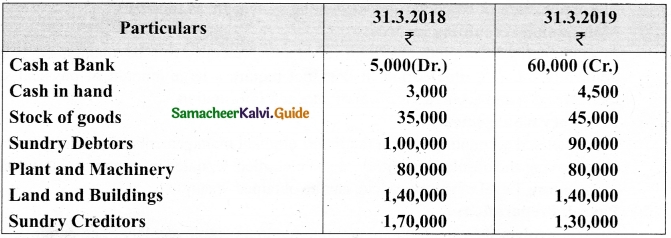
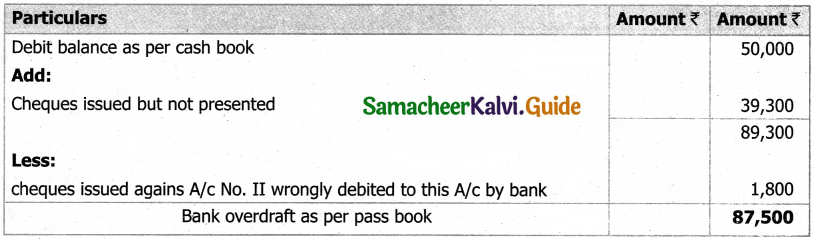
Question 43(a).
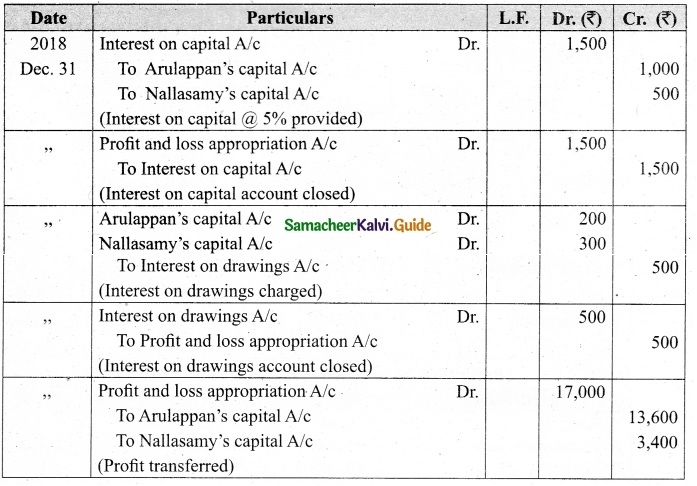
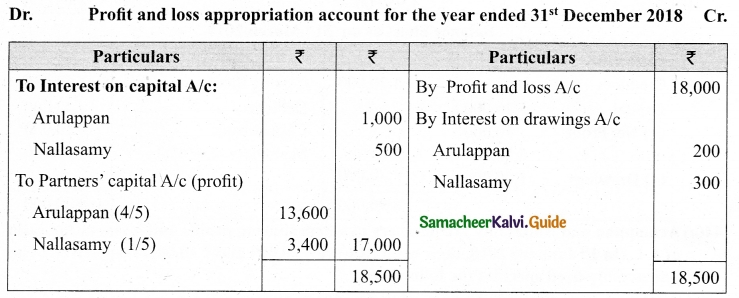
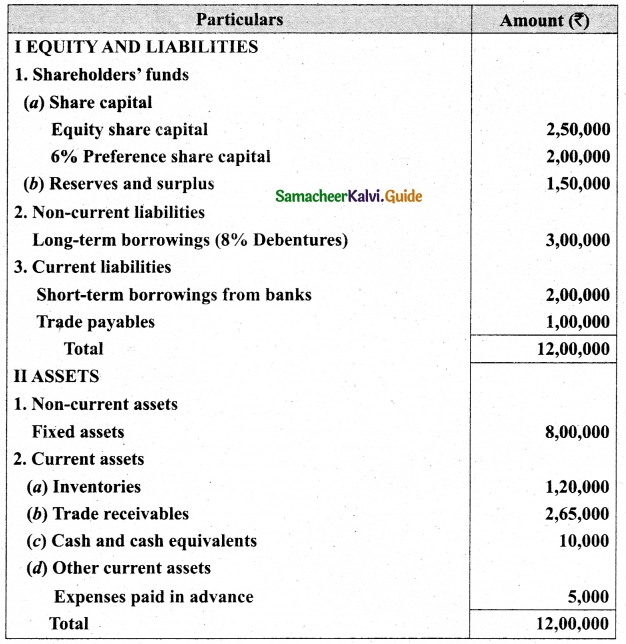
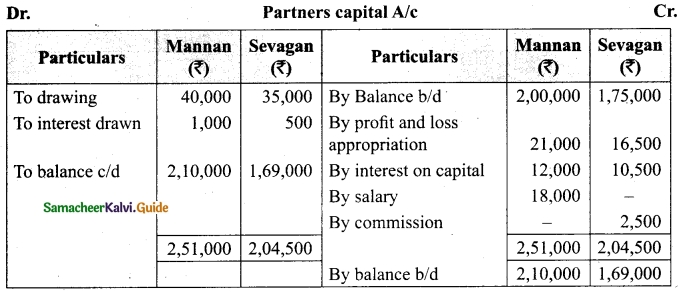
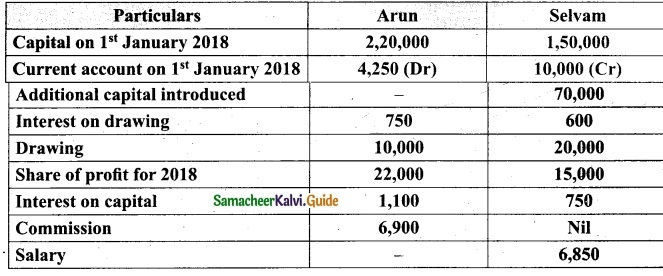
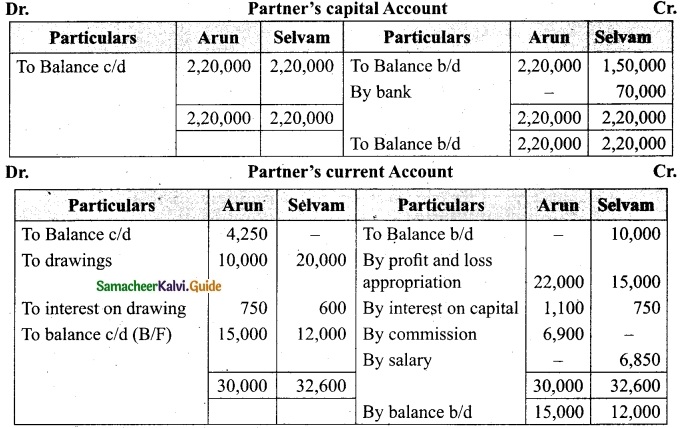
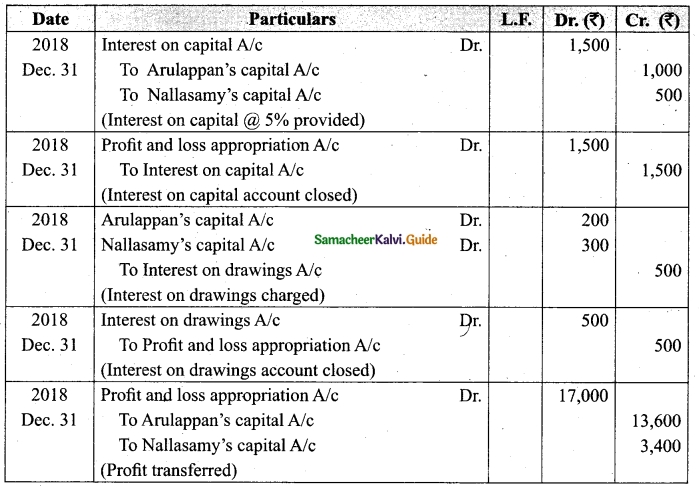
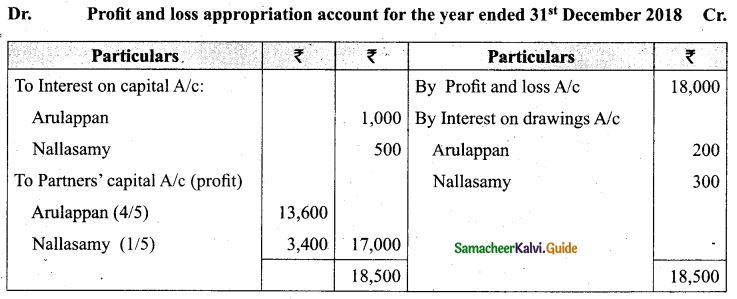
Arulappan and Nallasamy are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 1. On 1st January 2018, their capitals were Rs 20,000 and Rs 10,000, respectively. The partnership deed specifies the following:
(a) Interest on capital is to be allowed at 5% per annum.
(b) Interest on drawings charged to Arulappan and Nallasamy are Rs 200 and Rs 300, respectively.
(c) The net profit of the firm before considering interest on capital and interest on drawings amounted to Rs 18,000.
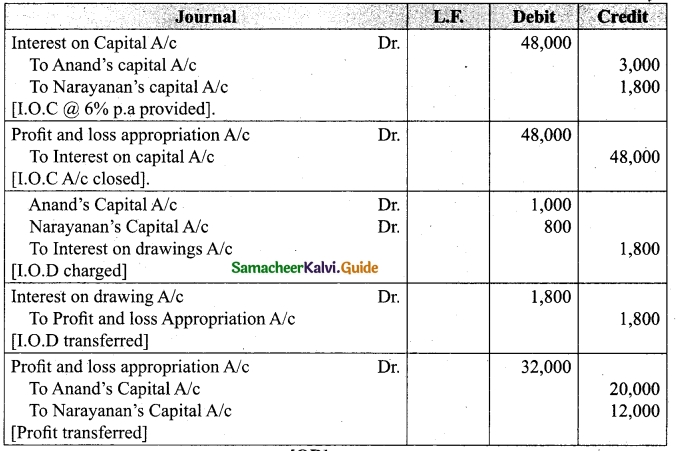
Give necessary journal entries and prepare Profit and loss appropriation account for the year en’ding 31st December 2018. Assume that the capitals are fluctuating.
Answer:
Journal entries
[OR]
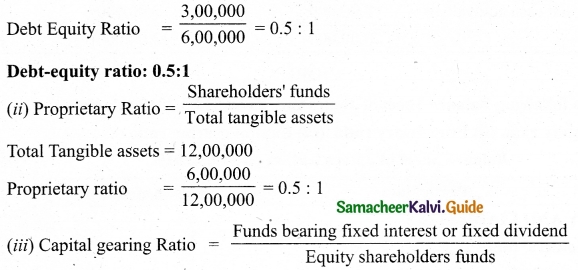
(b) Calculate the value of goodwill at 5 years purchase of super profit from the following information:
(i) Capital employed: Rs 1,20,000
(ii) Normal rate of profit: 20%
(iii) Net profit for 5 years:
2014: Rs 30,000; 2015: Rs 32,000; 2016: Rs 35,000; 2017: Rs 37,000 and 2018: Rs 40,000
(d) Fair remuneration to the partners Rs 2,800 per annum.
Answer:
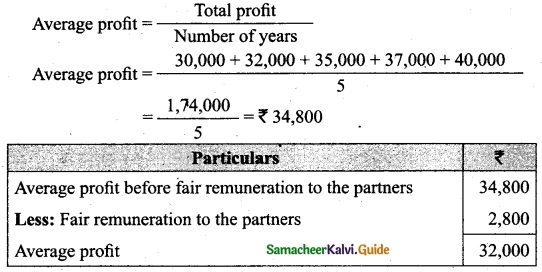
Normal profit = Capital employed × Normal rate of return
= 1,20,000 × 20%
= Rs 24,000
Super profit = Average profit – Normal profit
= 32,000 – 24,000
= 8,000
Goodwill = Super profit × Number of years of purchase
= 8,000 × 5
= Rs 40,000
![]()
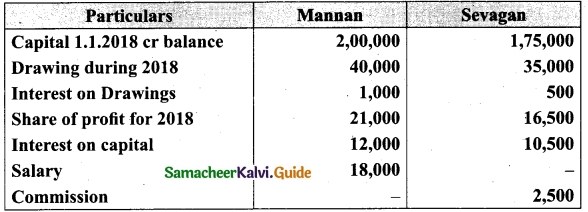
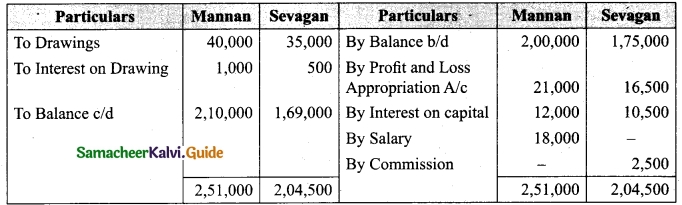
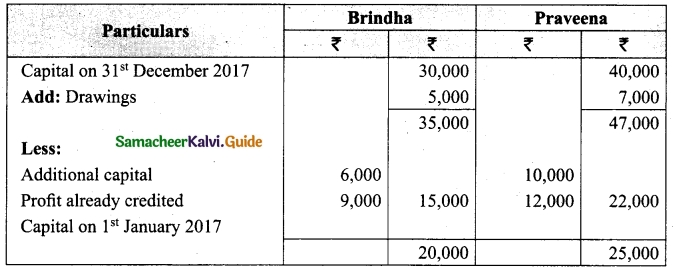
Question 44(a).
Distribution of Profits: Anitha, Ramita were partners sharing profit and losses in the ratio of 7 : 3. Their capitals were Rs. 80,000 and Rs. 60,000, respectively.
(i) Interest on capital @10% p.a
(ii) Interest on drawings @12% p.a
(iii) Both to get a salary of Rs. 10,000 each per annum
(iv) Anitha to get a commission of 10% on the net profit before charging such commission. The profit for the year Rs. 60,000. Drawings were Anitha Rs. 12,000 and Ramita Rs 8,000. Show profit and loss appropriation account and the capital A/c.
Answer:
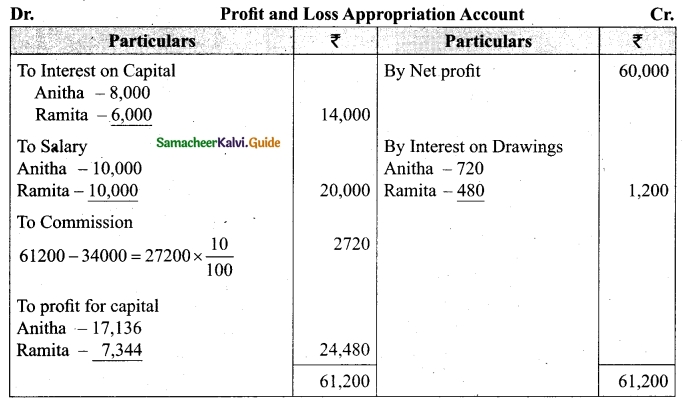
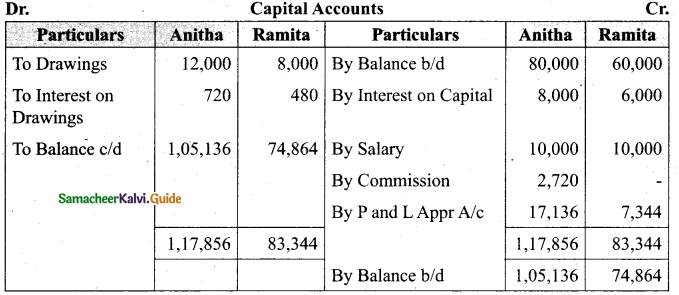
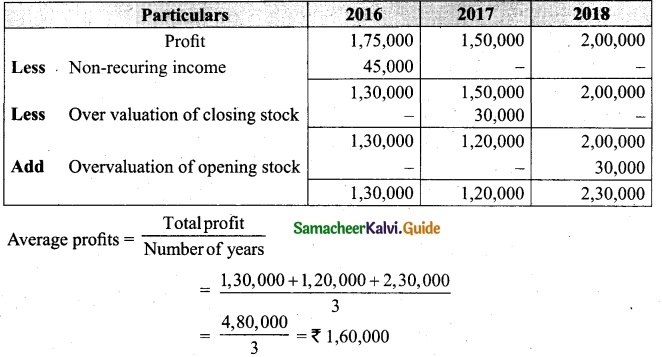
[OR]
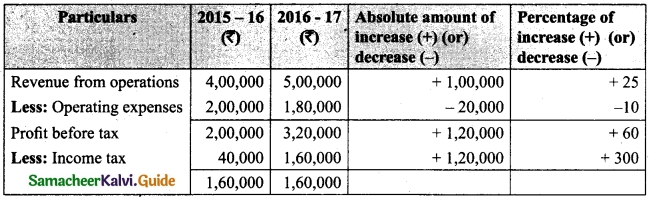
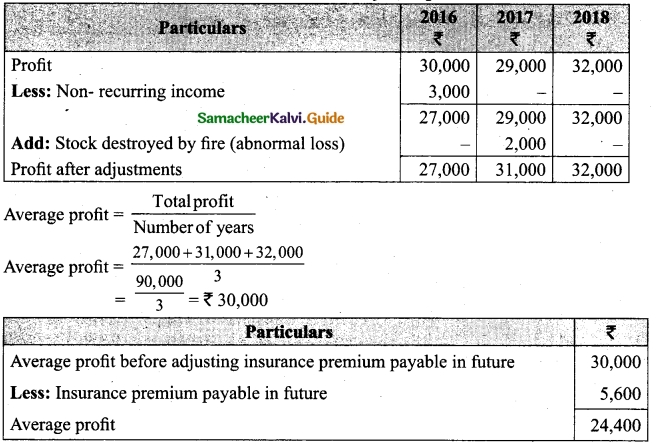
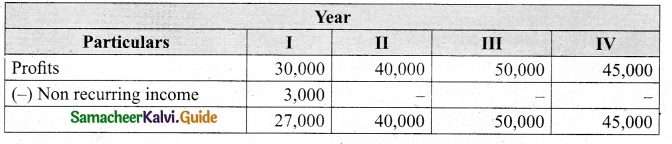
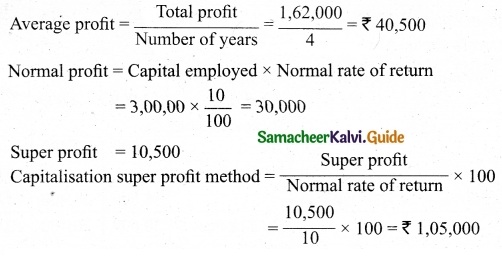
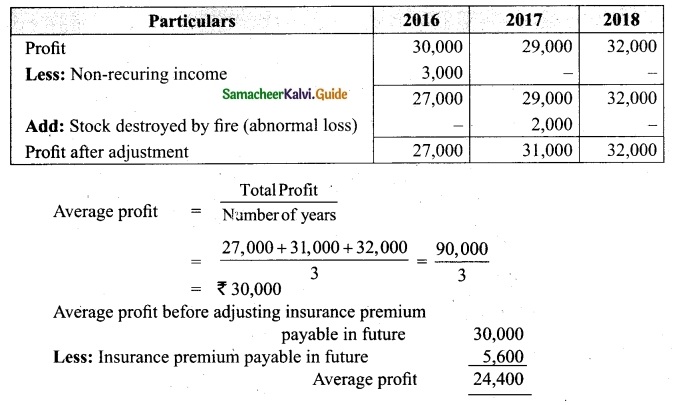
(b) From the following information relating to Sridevi enterprises, calculate the value of goodwill on the basis of 4 years purchase of the average profits of 3 years.
(a) Profits for the years ending 31st December 2016, 2017 and 2018 were Rs 1,75,000, Rs 1,50,000 and Rs 2,00,000, respectively.
(b) A non-recurring income of Rs 45,000 is included in the profits of the year 2016.
(c) The closing stock of the year 2017 was overvalued by Rs 30,000.
Calculation of adjusted profit.
Answer:
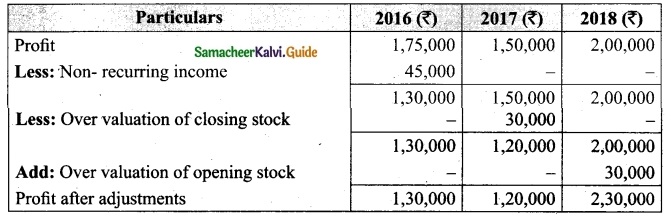
Average profit = \(\frac{Total profit}{Number of years}\)
Total profit 1,60,000 + 1,20,000 + 23,000
= 4,80,000
Average profit = \(\frac{4,80,000}{3}\) = Rs 1,60,000
Goodwill = Average profit × No. of year purchase
= Rs 1,60,000 × 4 = Rs 64,00,000
![]()
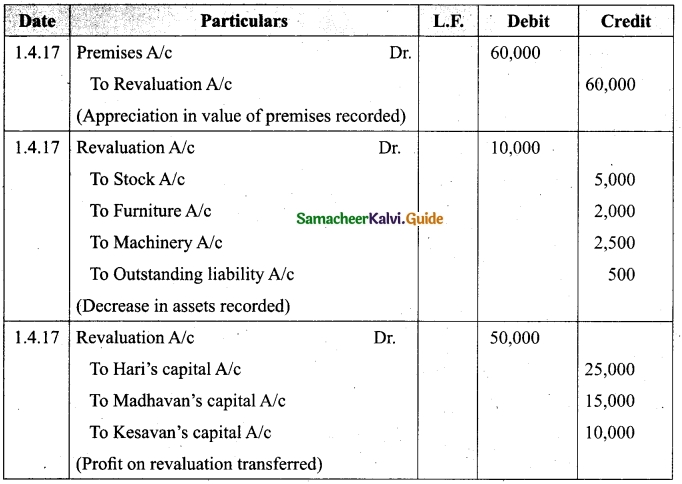
Question 45(a).
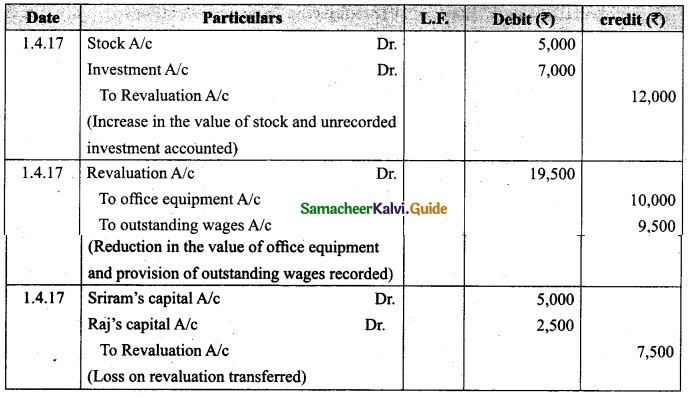
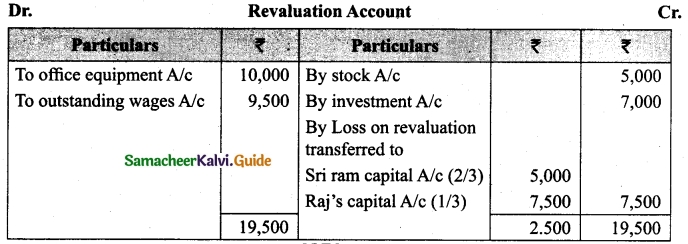
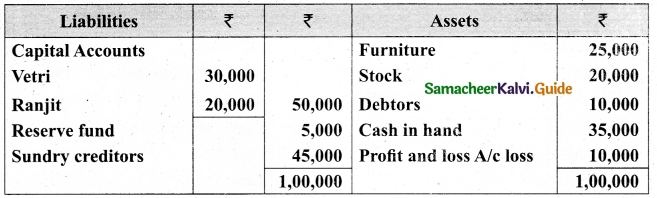
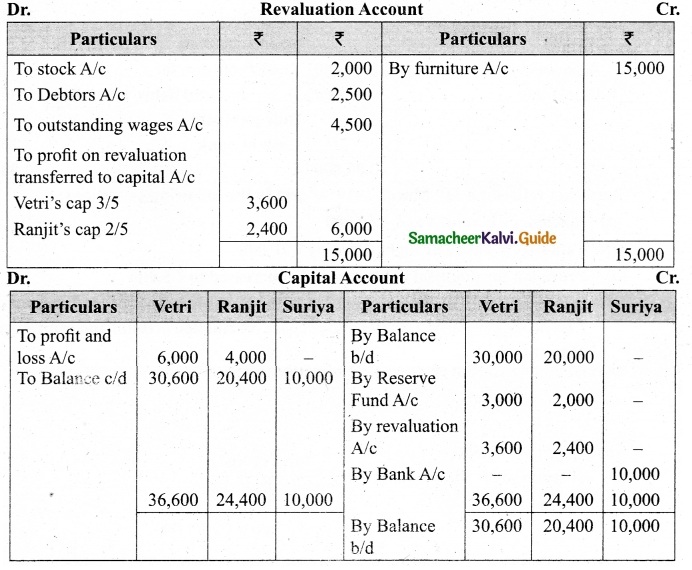
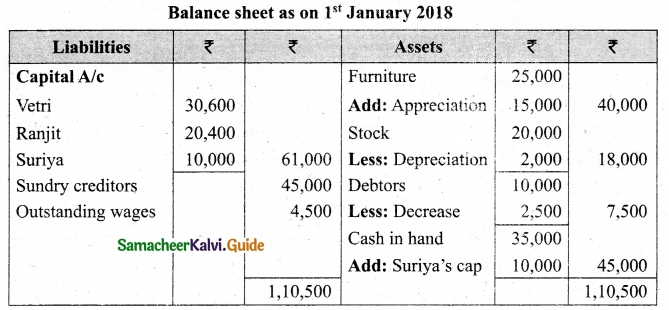
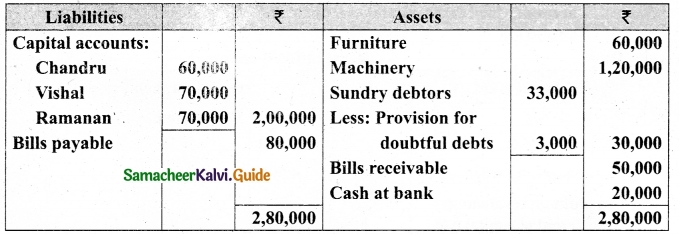
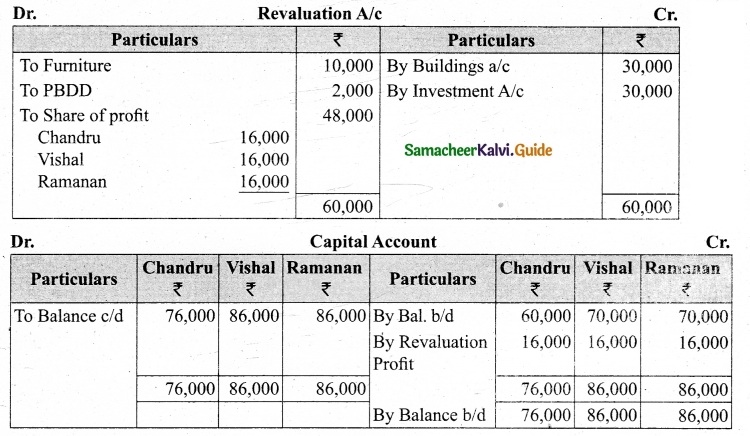
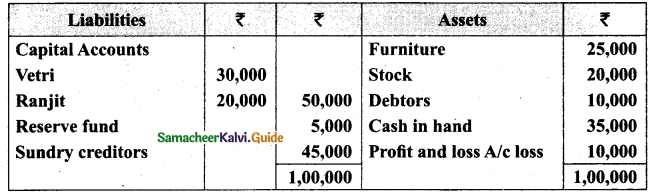
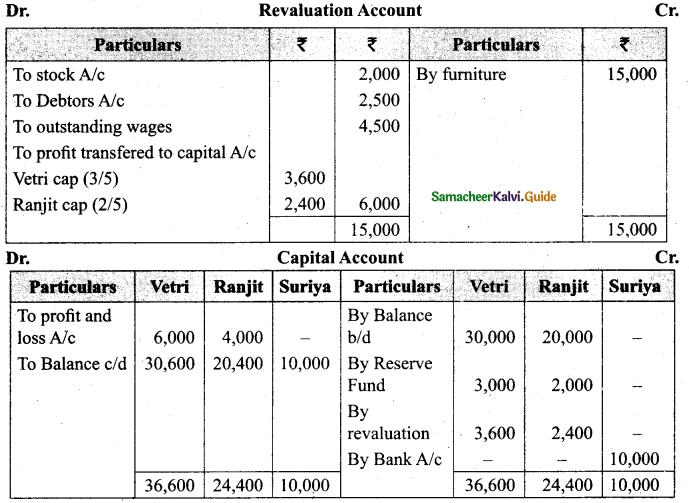
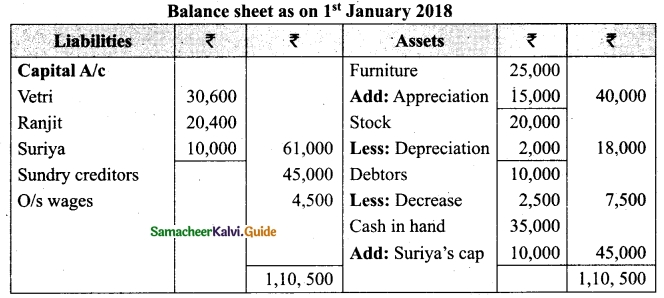
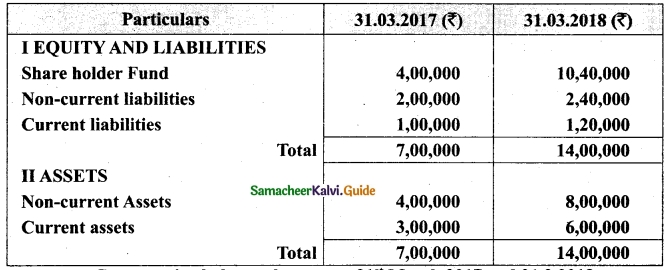
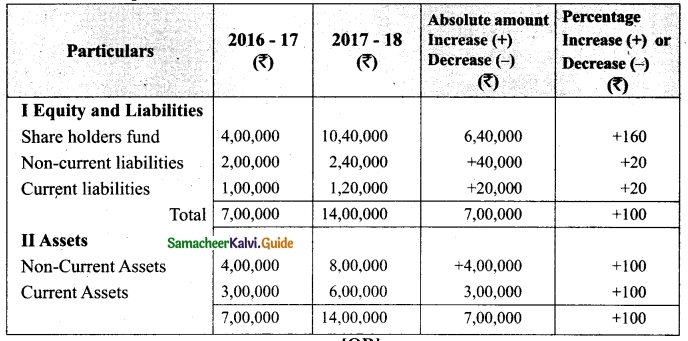
Vetri and Ranjit are partners sharing profit in the ratio 3 : 2. Their balance sheet as on 31st December 2017 is under.
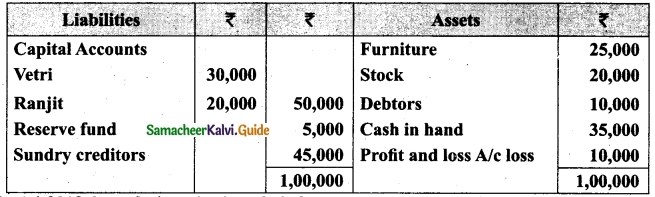
On 1.1.2018 they admit suriya into their firm as a partner on the following arrangements.
(i) Suriya brings Rs 10,000 as capital for 1/4 share of profit
(ii) Stock to be depreciated by 10%
(iii) Debtors to be revalued at Rs 7,500
(iv) Furniture to be revalued at Rs 40,000.
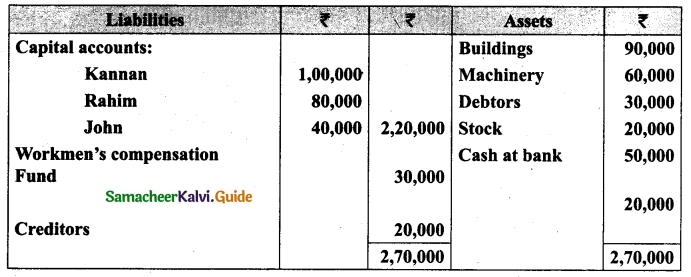
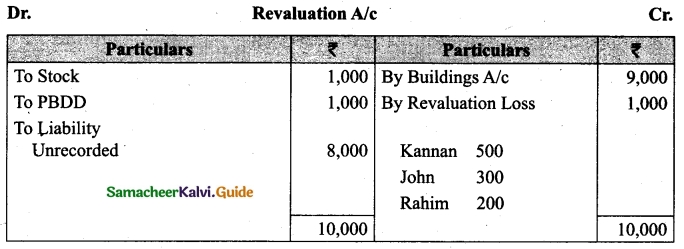
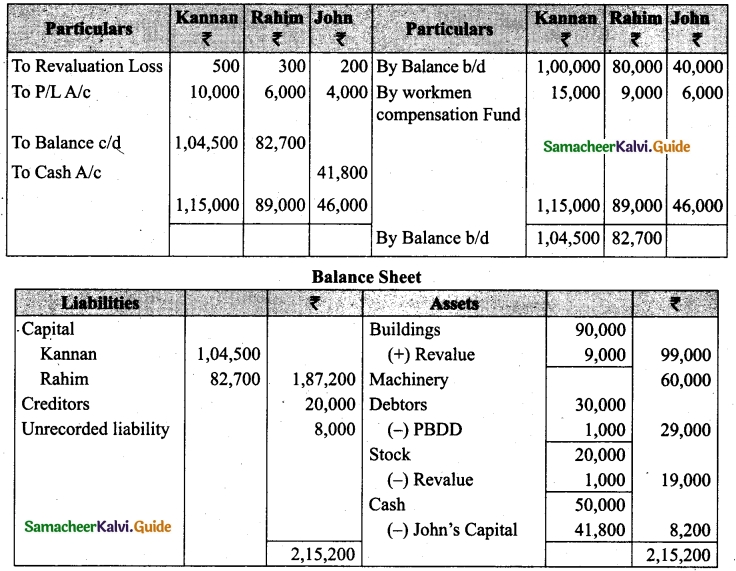
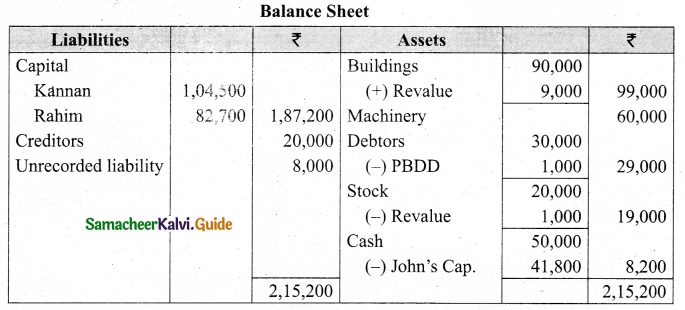
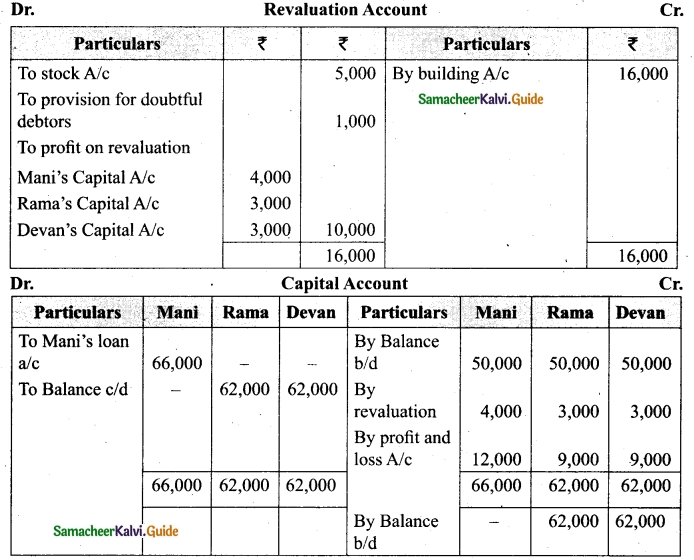
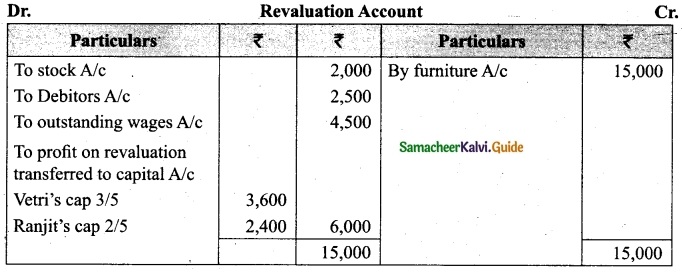
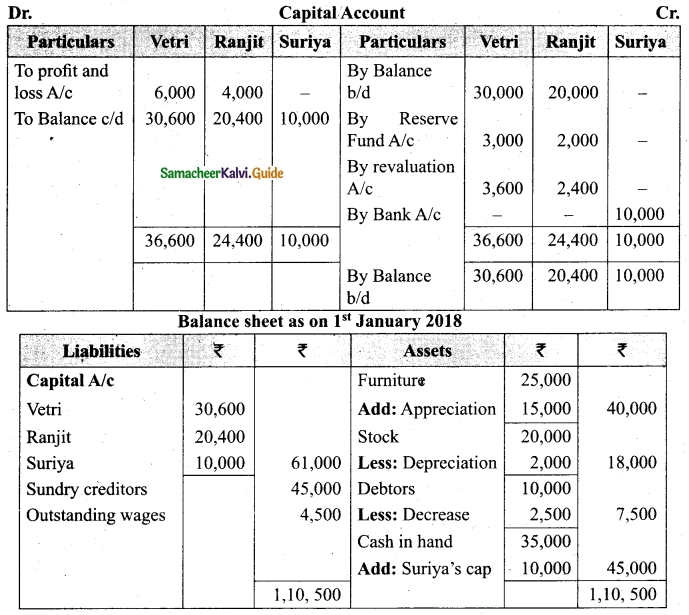
(v) There is an outstanding wages Rs 4,500 not yet recorded. Prepare revaluation account, partners’ capital account and the balance sheet of the firm after admission.
Answer:
[OR]
(b) Sundar and Suresh are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. Their balance sheet as on 1st January, 2017 was as follows:
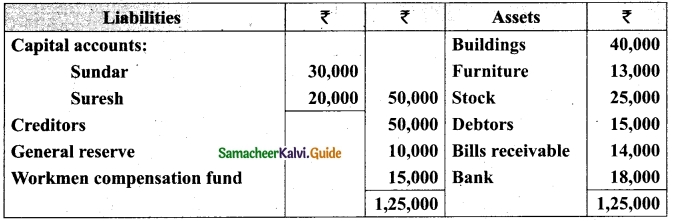
They decided to admit Sugumar into partnership for 1/4 share in the profits on the following terms:
(a) Sugumar has to bring in Rs 30,000 as capital. His share of goodwill is valued at Rs 5,000. He could not bring cash towards goodwill.
(b) That the stock be valued at Rs 20, 000.
(c) That the furniture be depreciated by Rs 2,000.
(d) That the value of building be depreciated by 20%.
Prepare necessary ledger accounts and the balance sheet after admission.
Answer:
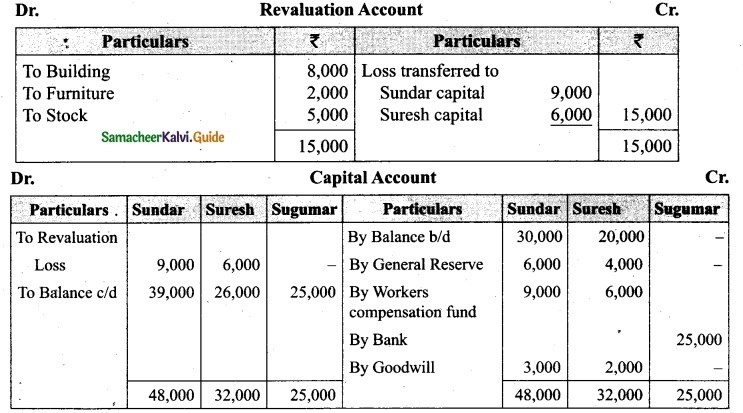
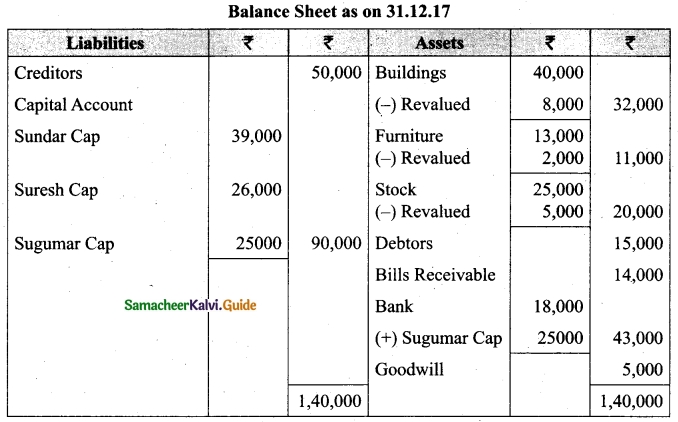
![]()
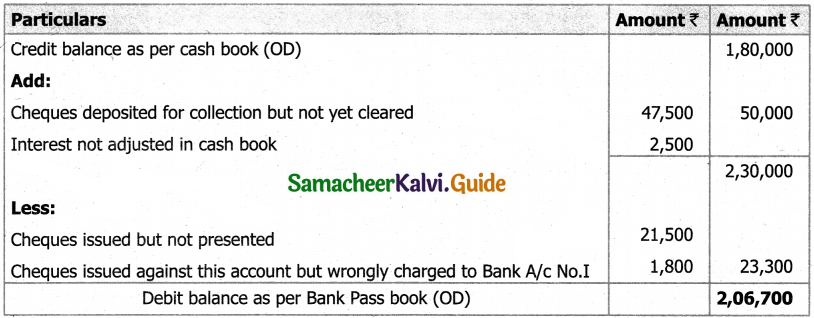
Question 46(a).
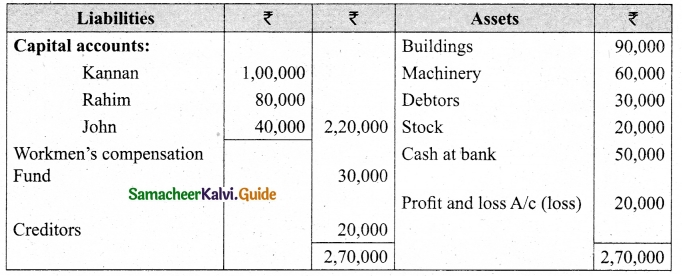
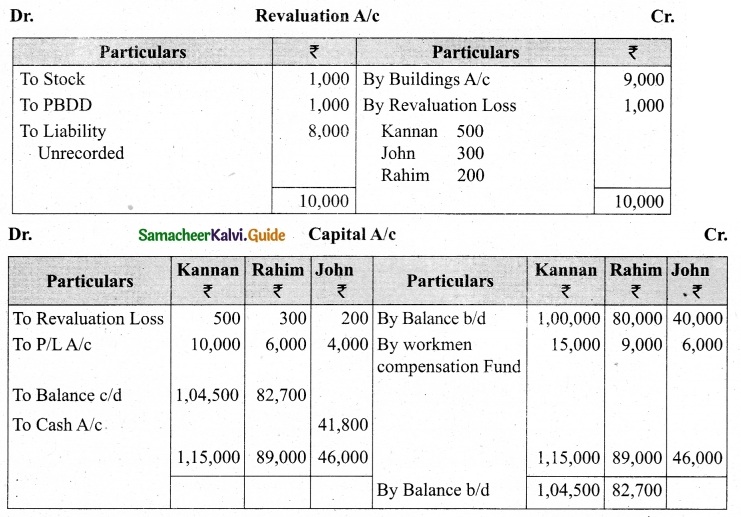
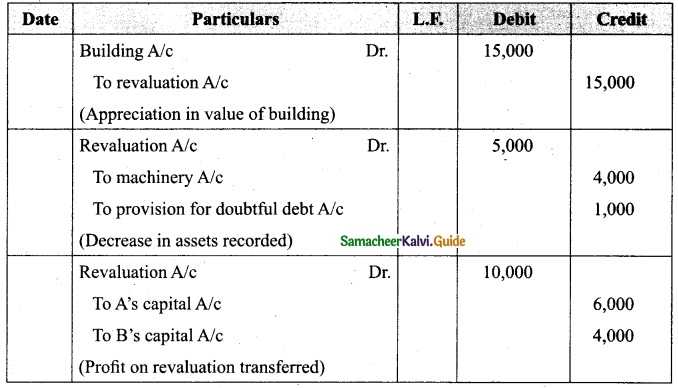
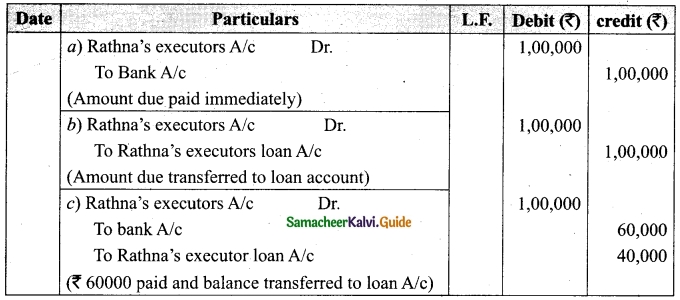
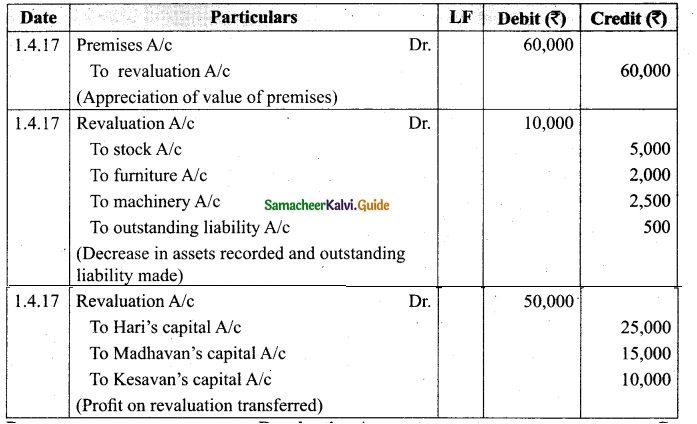
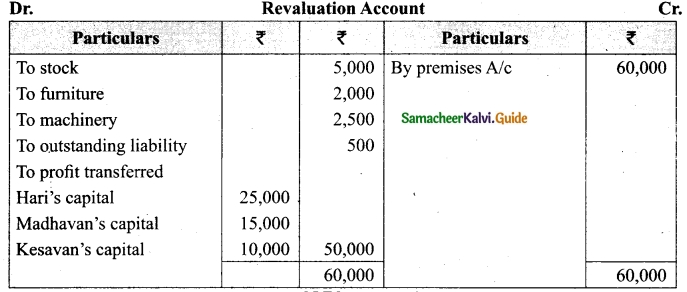
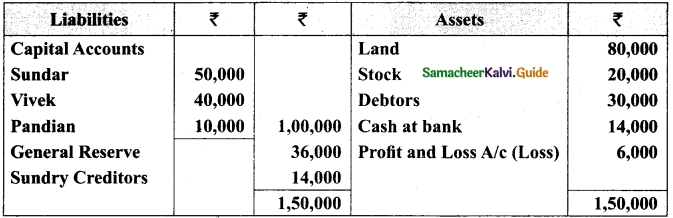
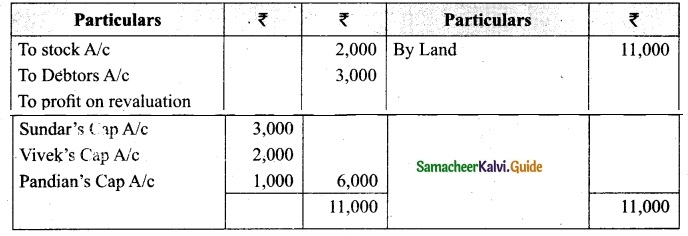
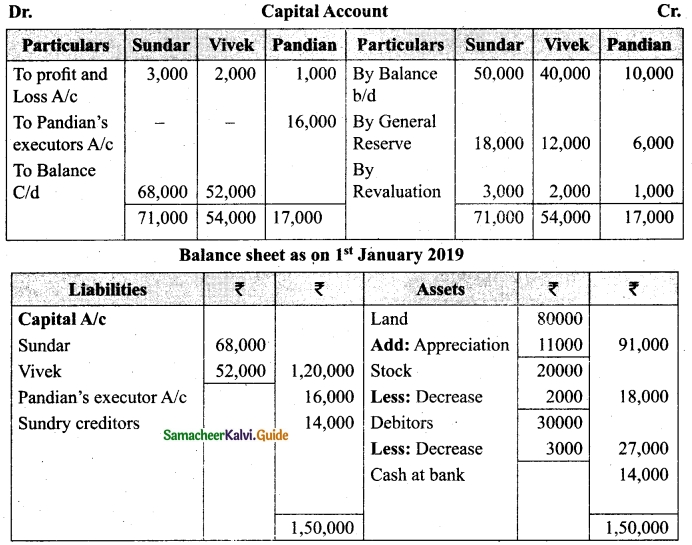
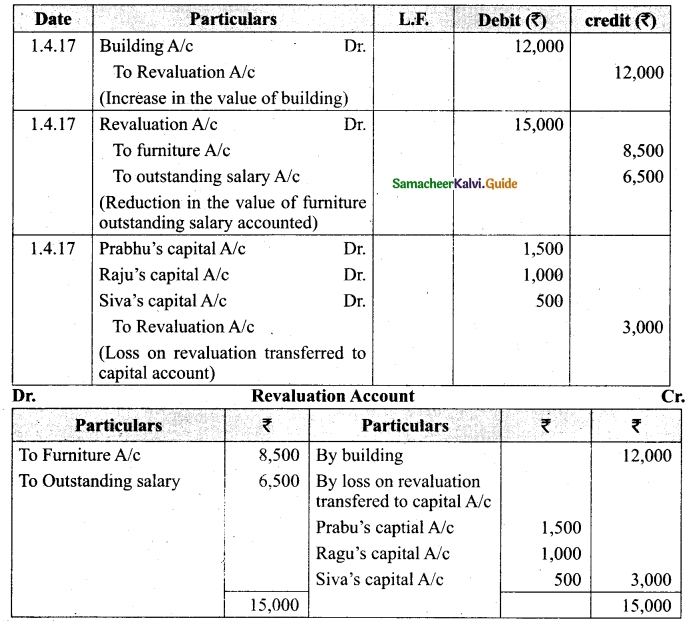
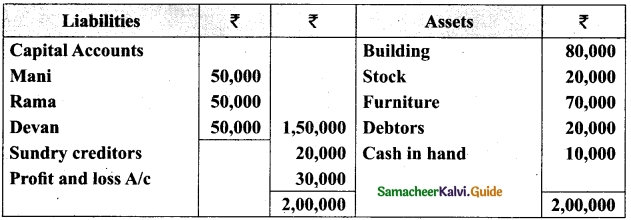
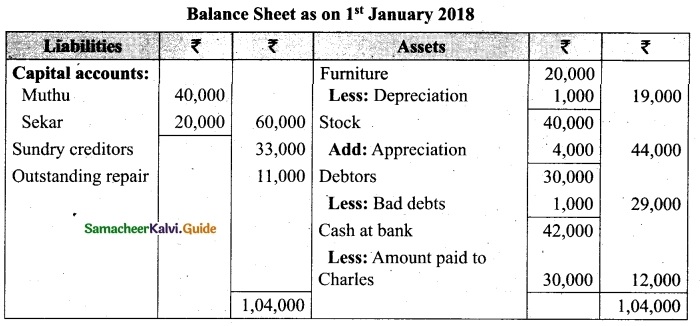
Charles, Muthu and Sekar are partners, sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 4 : 2. Their balance sheet as on 31st December 2018 is as under:
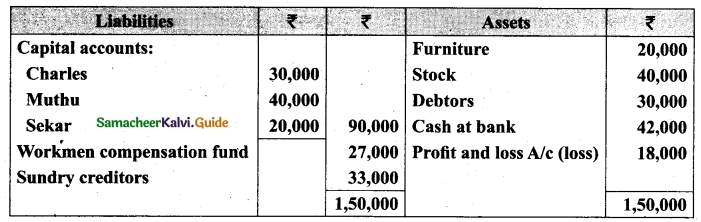
On 1,1.2019, Charles retired from the partnership firm on the following arrangements:
(i) Stock to be appreciated by 10%
(ii) Furniture to be depreciated by 5%
(iii) To provide Rs 1,000 for bad debts
(iv) There is an outstanding repair of Rs 11,000 not yet recorded
(v) The final amount due to Charles was paid
Prepare revaluation account, partners capital account and the balance sheet of the firm after retirement.
Answer:
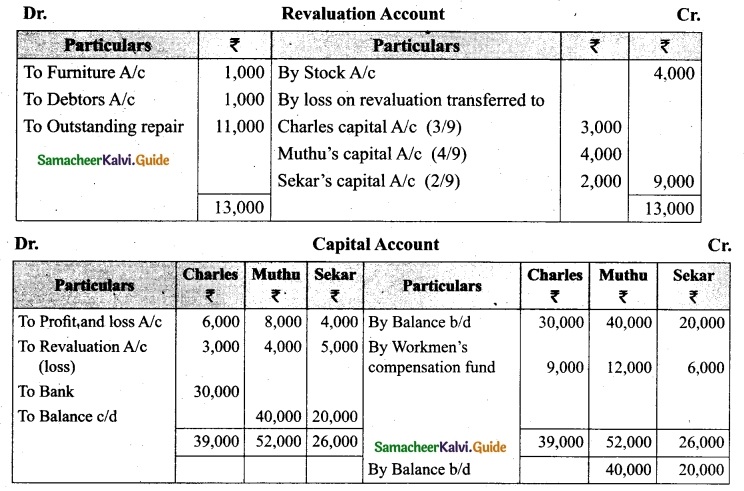
![]()
[OR]
(b) Varsha, Shanthi and Madhuri are partners, sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 4 : 3. Their balance sheet as on 31st December 2017 is as under:
Balance Sheet as on 31st December 2017
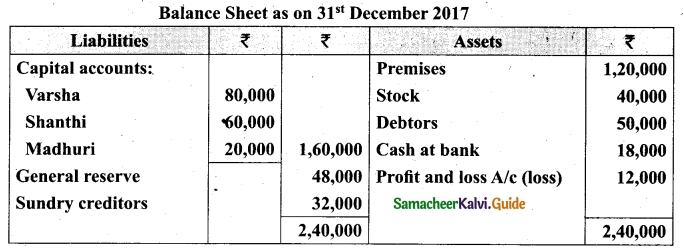
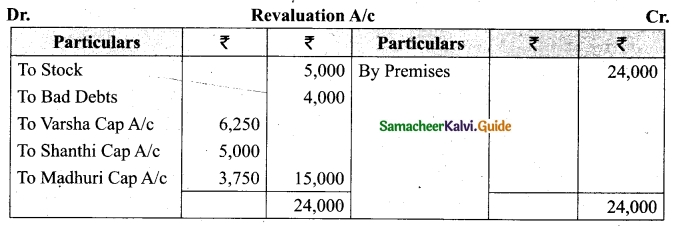
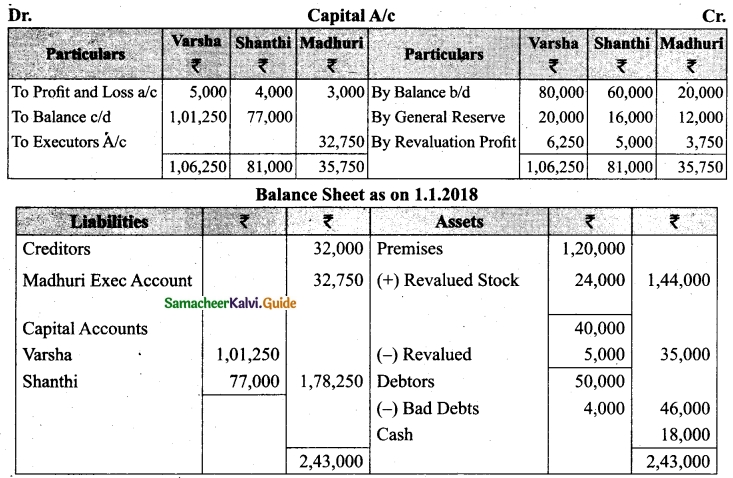
On 1.1.2018, Madhuri died and on her death the following arrangements are made:
(i) Stock to be depreciated by Rs 5,000
(if) Premises is to be appreciated by 20%
(iii) To provide Rs 4,000 for bad debts
(iv) The final amount due to Madhuri was not paid
Prepare revaluation account, partners capital account and the balance sheet of the firm after death.
Answer:
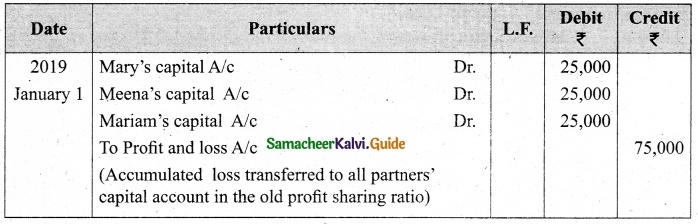
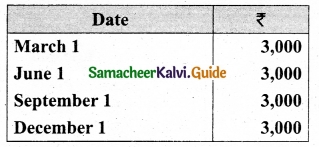
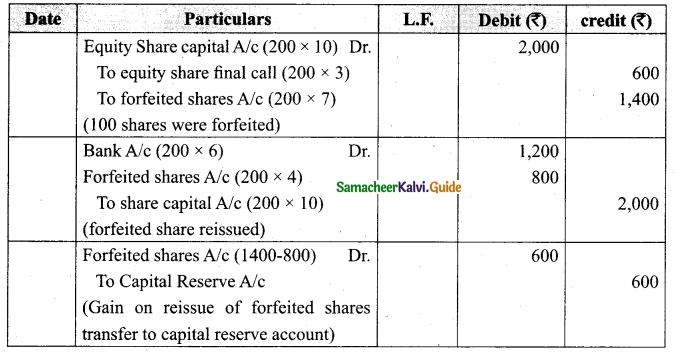
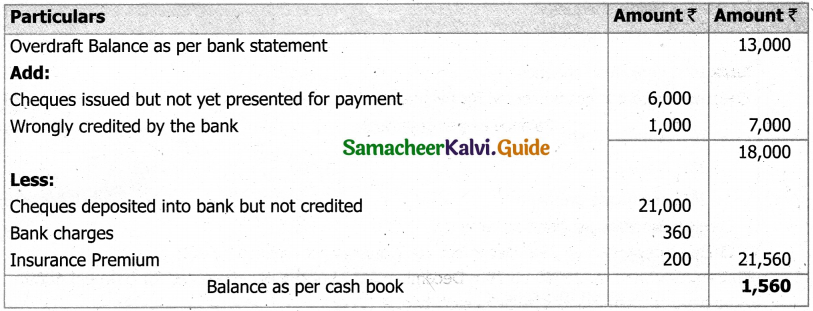
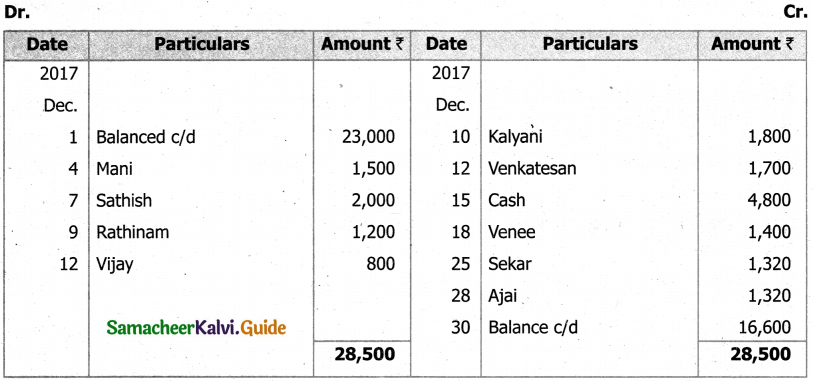
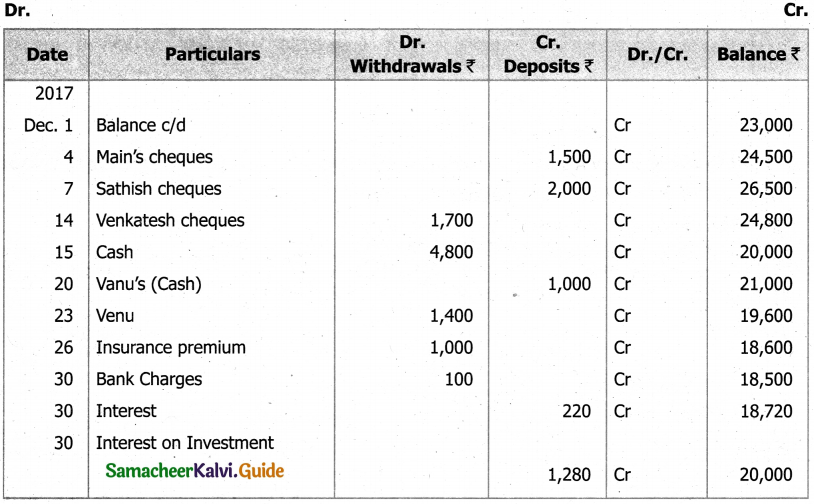
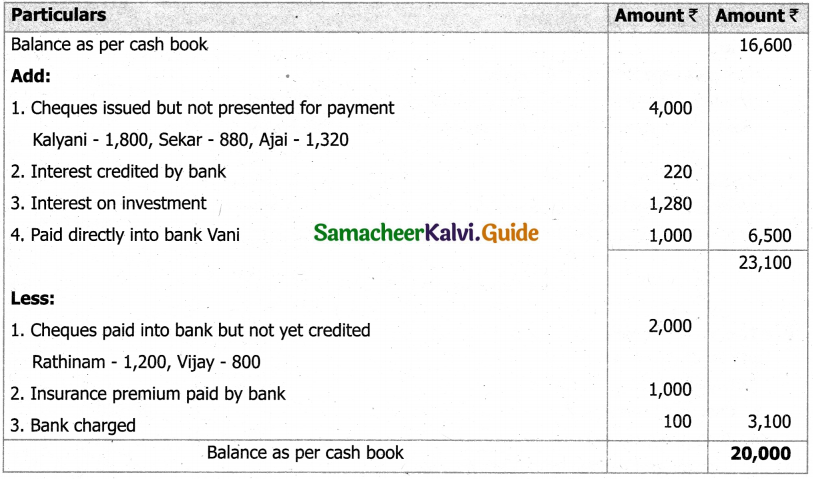
Question 47 (a).
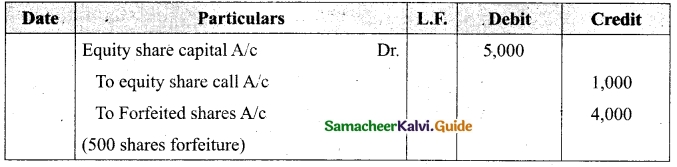
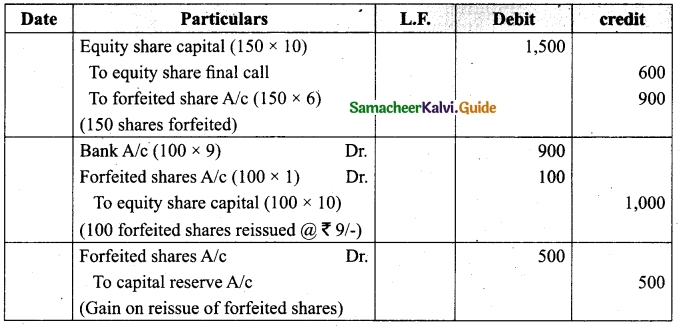
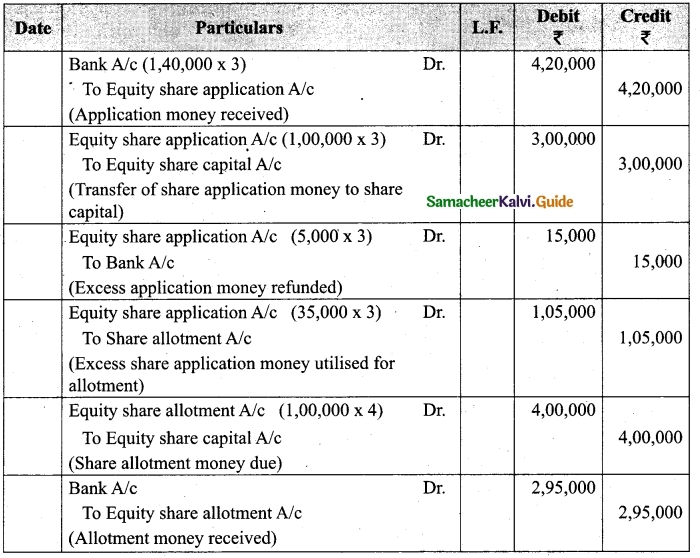
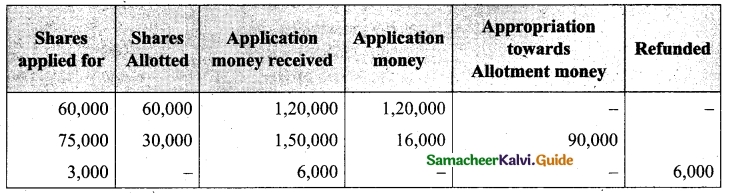
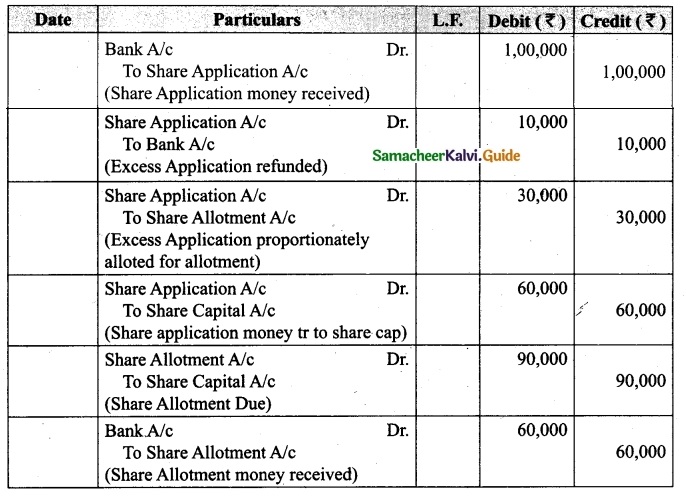
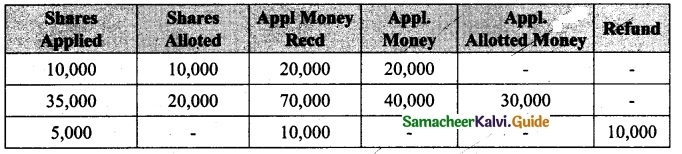
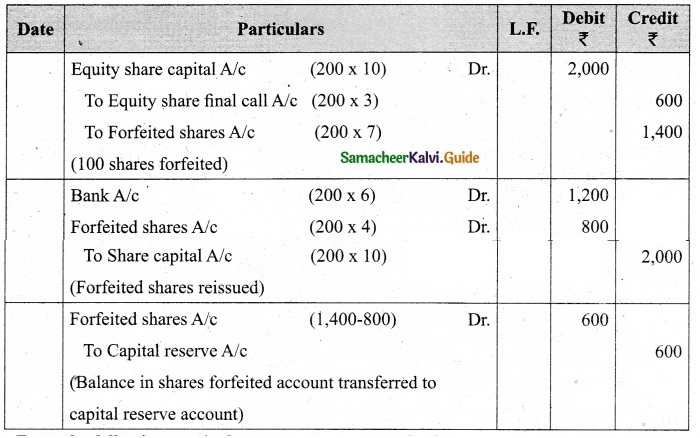
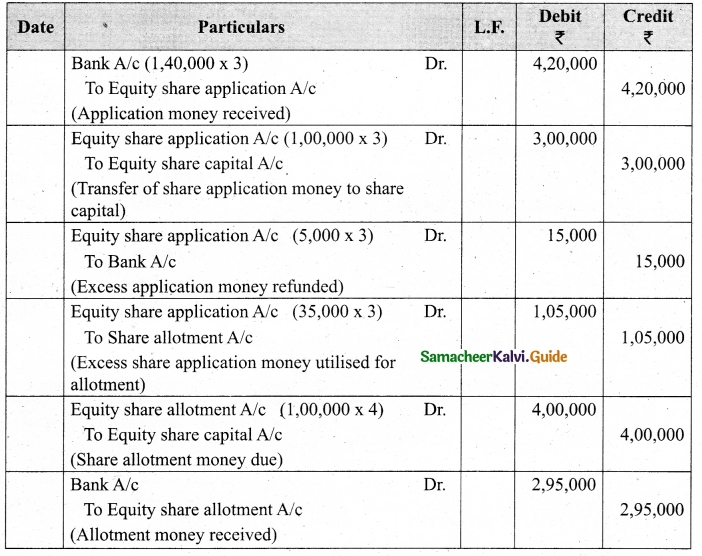
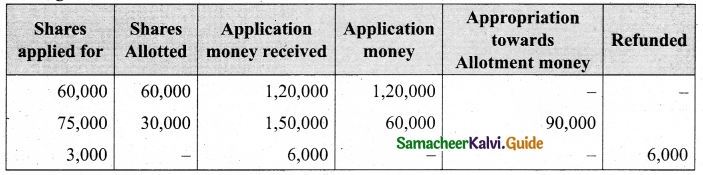
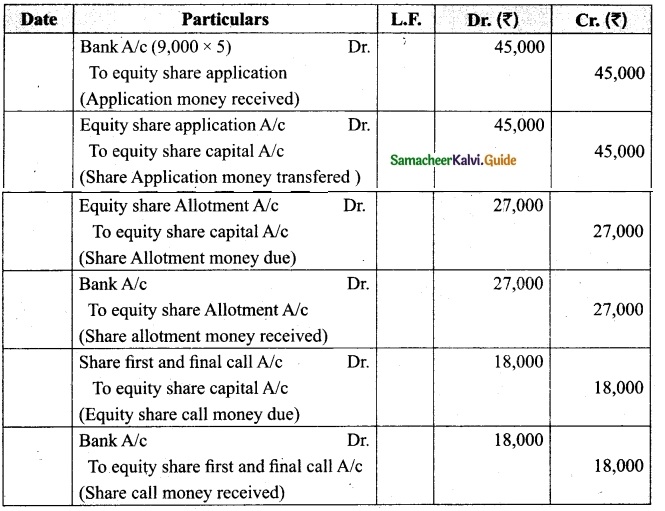
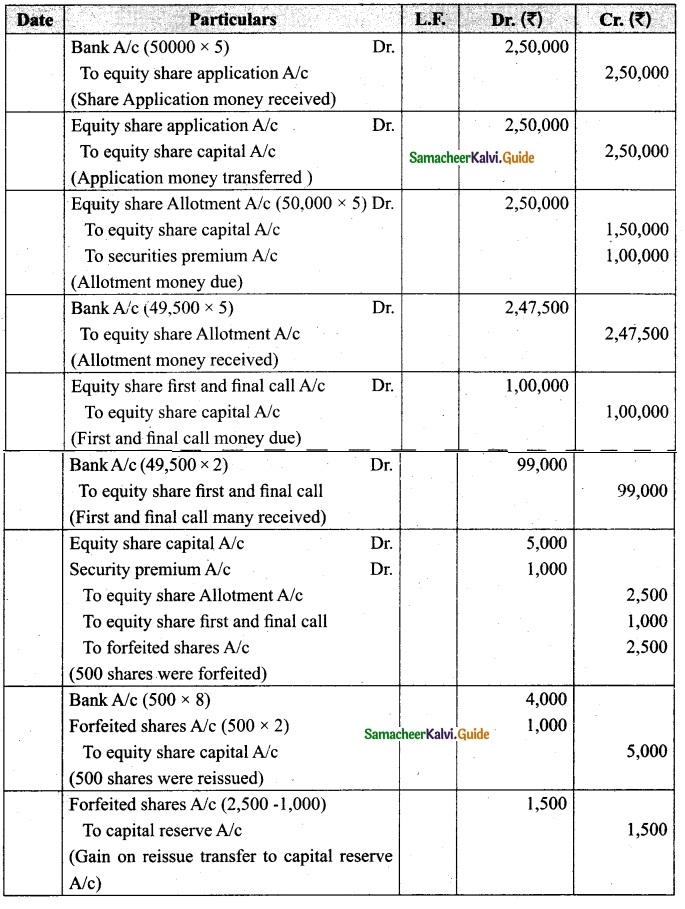
Lalitha Ltd. offered Rs 30,000 equity shares of ? 10 each to the public payable Rs 2 per share on application, Rs 3 on share allotment and the balance when required. Applications for 50,000 shares were received on which the directors allotted as:
Applicants for 10,000 shares – Full
Applicants for 35,000 shares – 20,000 shares (excess money will be utilised for allotment)
Applicants for 5,000 shares – Nil
All the money due was received. Pass journal entries upto the receipt of allotment.
Answer:
Journal Entries
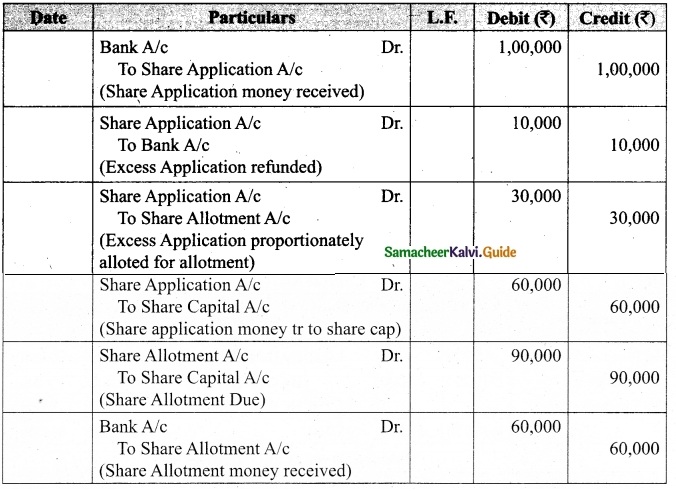
Working notes
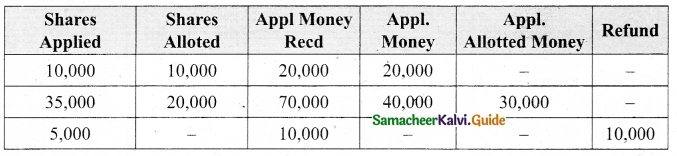
![]()
[OR]
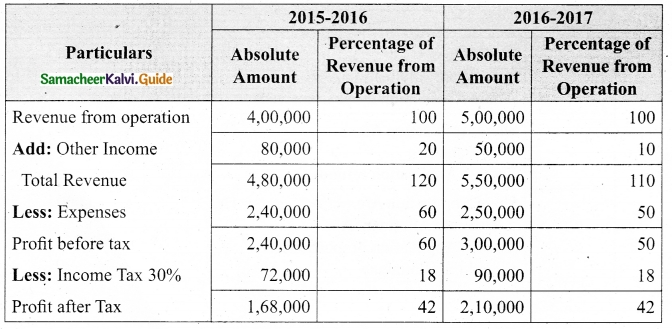
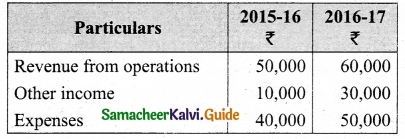
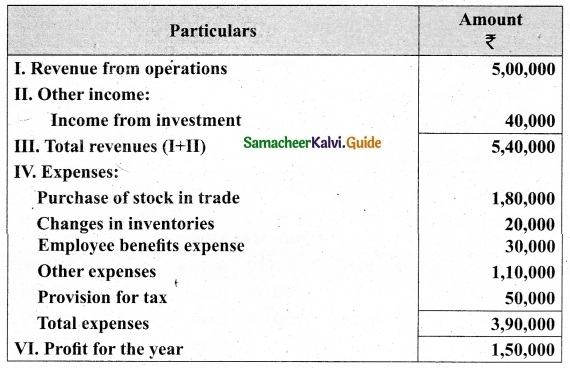
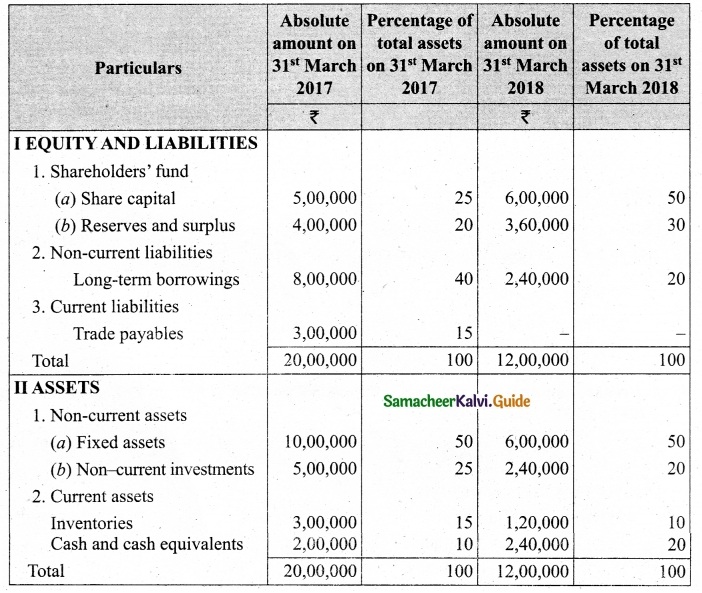
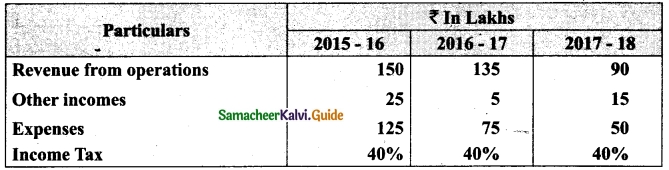
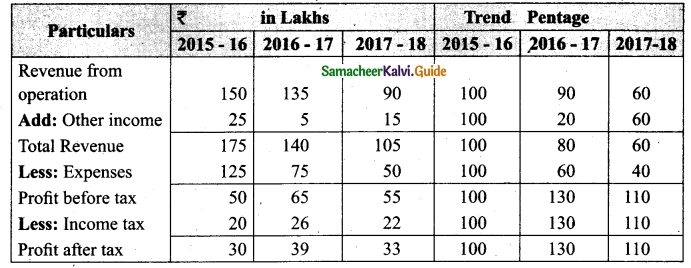
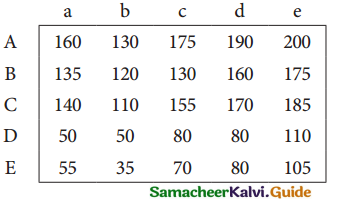
(b) Prepare common-size income statement for the following particulars of Sam Ltd.
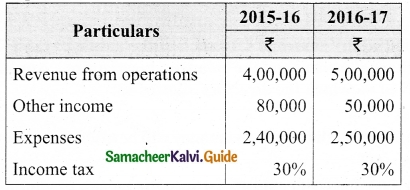
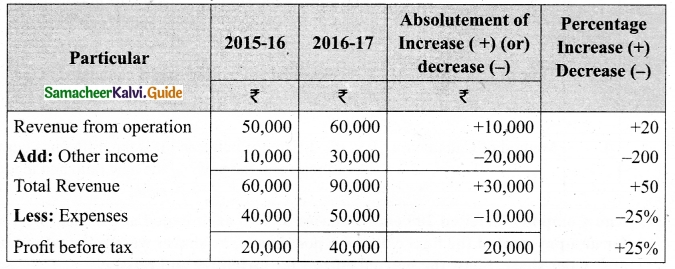
Answer:
Common Size Income statement of Sam Ltd.