Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 6 Applications of Vector Algebra Ex 6.8 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Applications of Vector Algebra Ex 6.8
Question 1.
Show that the straight lines
\(\overline { r }\) = (5\(\hat { i }\) + 7\(\hat { j }\) – 3\(\hat { k }\)) + s(4\(\hat { i }\) + 4\(\hat { j }\) – 5\(\hat { k }\)) and
\(\overline { r }\) = (8\(\hat { i }\) + 4\(\hat { j }\) + 5\(\hat { k }\)) + t(7\(\hat { i }\) + \(\hat { j }\) + 3\(\hat { k }\)) are coplanar. Find the vector equation of the, plane in which they lie.
Solution:
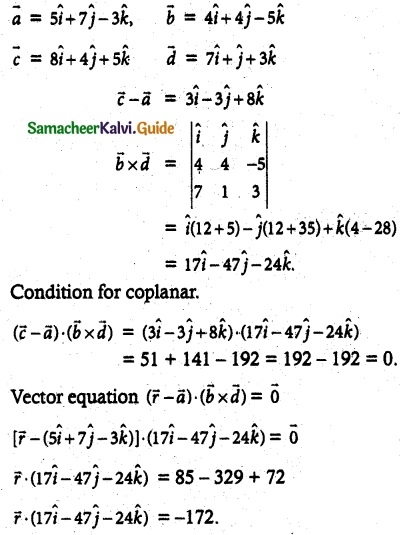
![]()
Question 2.
Show that the lines \(\frac { x-2 }{ 1 }\) = \(\frac { y-3 }{ 1 }\) = \(\frac { z -4}{ 3 }\) and \(\frac { x-1 }{ -3 }\) = \(\frac { y-4 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { z-5 }{ 1 }\) are coplanar. Also, find the plane containing these lines.
Solution:

Cartesian equation
x + 2y – 2z = 4
x + 2y – 2z – 4 = 0
Question 3.
If the straight lines \(\frac { x-1 }{ 1 }\) = \(\frac { y-2 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { z-3}{ m^2 }\) and \(\frac { x-3 }{ 1 }\) = \(\frac { y-2 }{ m^2 }\) = \(\frac { z-1 }{ 2 }\) are coplanar, find the distinct real values of m
Solution:
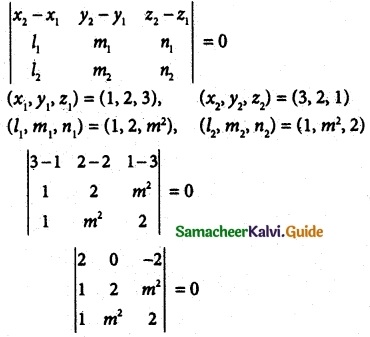
2(4 – m4) – 2(m² – 2) = 0
8 – 2m4 – 2m² + 4 = 0
12 – 2m4 – 2m² = 0
(÷ -2) -6 + m4 + m² = 0
m4 + m² – 6 = 0
(m² – 2)(m² + 3) = 0
m² – 2 = 2; m² = -3 (not possible)
m² = 2
m = ±√2
![]()
Question 4.
If the straight lines \(\frac { x-1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { y+1 }{ λ }\) = \(\frac { z }{ 2 }\) and \(\frac { x+1 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac { y+1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { z }{ λ }\) are coplanar, find λ and equations of the planes containing these two lines.
Solution:
If the two lines are coplanar
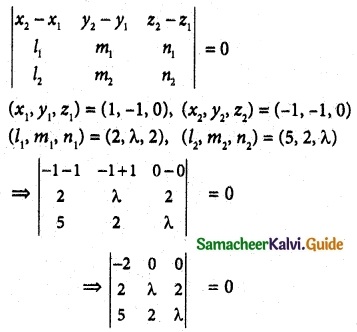
When λ = 2
(x1, y1, z1) = (1, -1, 0)
(b1, b2, b3) = (2, 2, 2)
(d1, d2, d3) = (5, 2, 2)
\(\left|\begin{array}{ccc}
x-x_{1} & y-y_{1} & z-z_{1} \\
b_{1} & b_{2} & b_{3} \\
d_{1} & d_{2} & d_{3}
\end{array}\right|\) = 0
⇒ \(\left|\begin{array}{ccc}
x-1 & y+1 & z-0 \\
2 & 2 & 2 \\
5 & 2 & 2
\end{array}\right|\) = 0
⇒ (x – 1)(0) – (y + 1)(-6) + z(6) = 0
⇒6(y + 1) – 6z = 0
⇒ 6y + 6 – 6z = 0
⇒ y – z + 1 = 0
When λ = 2
(b1, b2, b3) = (2, -2, 2)
(d1, d2, d3) = (5, 2, -2)
⇒ \(\left|\begin{array}{ccc}
x-1 & y+1 & z-0 \\
2 & -2 & 2 \\
5 & 2 & -2
\end{array}\right|\) = 0
⇒ (x – 1)(0) – (y + 1)(-14) + z(4 + 10) = 0
⇒ 14(y + 1) + 14z = 0
⇒ 14y + 14 + 14z = 0
⇒ y + z + 1 = 0
![]()