Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 8 Differentials and Partial Derivatives Ex 8.7 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Differentials and Partial Derivatives Ex 8.7
Question 1.
If each of the following cases, determine whether the following function is homogeneous or not. If it is so, find the degree.
(i) f(x, y) = x²y + 6x³ + 7
(ii) h(x, y) = \(\frac { 6x^2y^3-πy^5+9x^4y }{ 2020x^2+2019y^2 }\)
(iii) g(x, y, z) = \(\frac { \sqrt{3x^2+5y^2+z^2} }{ 4x+7y }\)
(iv) U(x, y, z) = xy + sin(\(\frac { y^2-2z^2 }{ xy }\))
Solution:
(i) f(x, y) = x²y + 6x³ + 7
f(λx, λy) = λ³x²y + 6λ³x³ + 7
There is no common λ in this equation.
∴ It is not homogeneous
![]()
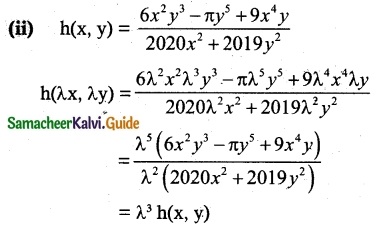
Thus f is homogeneous with degree 3.
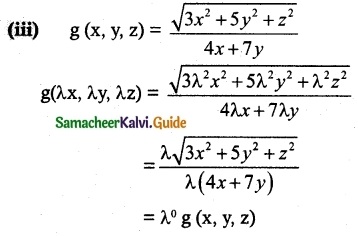
Thus g is homogeneous with degree 0.
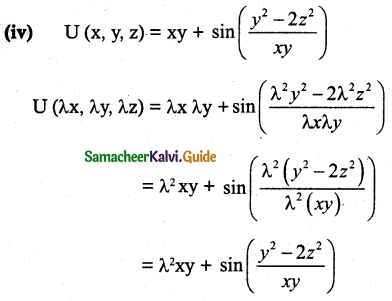
There is no common λ
∴ It is not homogeneous.
![]()
Question 2.
Prove that f(x, y) = x³ – 2x²y + 3xy² + y³ is homogeneous. What is the degree? Verify Euler’s Theorem for f.
Solution:
f(x, y) = x³ – 2x²y + 3xy² + y³
f(λx, λy) = λ³x³ -2λ²x²λy + 3λxλ²y² + λ³y³
= λ³ (x³ – 2x²y + 3xy² + y³)
f is a homogeneous function of degree 3
By Euler’s Theorem,
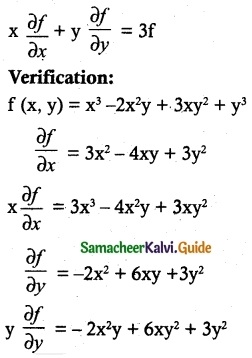
x \(\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}\) + y \(\frac{\partial f}{\partial y}\) = 3x³ – 4x²y + 3xy² – 2x²y + 6xy² + 3y³
= 3x³ – 6x²y + 9xy² + 3y³
= 3(x³ – 2x²y + 3xy² + y³)
x \(\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}\) + y \(\frac{\partial f}{\partial y}\) = 3 f
We verified the Euler’s Theorem.
![]()
Question 3.
Prove that g (x, y) = x log(y/x) is homogeneous What is the degree? Verify Eulers Theorem for g.
Solution:
g (x, y) = x log(y/x)
g (tx, ty) = tx log(\(\frac { ty }{ tx }\))
g is a homogeneous function of degree 1.
∴ By Euler’s Theorem,
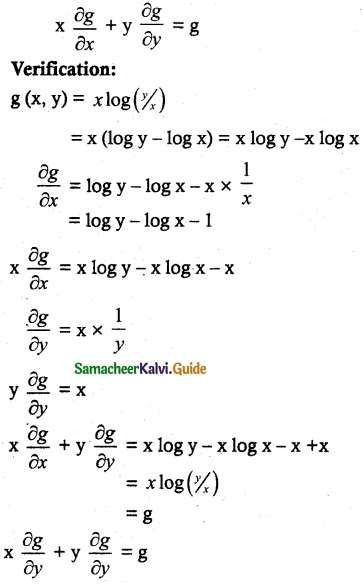
Hence verified
![]()
Question 4.
If u(x, y) = \(\frac { x^2+y^2 }{ \sqrt{x+y} }\), prove that
x \(\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}\) + y\(\frac{\partial u}{\partial y}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)u.
Solution:
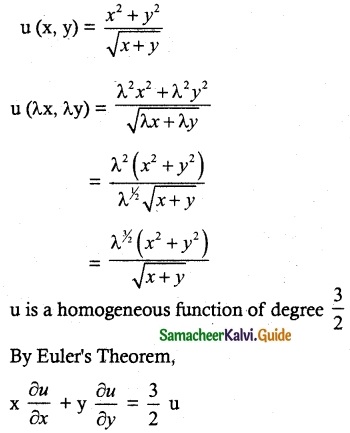
![]()
Question 5.
If v (x, y) = log(\(\frac{x^2+y^2}{x+y}\)) Prove that
x \(\frac{\partial v}{\partial x}\) + y\(\frac{\partial u}{\partial y}\) = 1.
Solution:

Hence Proved
![]()
Question 6.
If w(x, y, z) = log (\(\frac{5x^3y^4+7y^2xz^4-75y^3z^4}{x^2+y^2}\)), find x \(\frac{\partial w}{\partial x}\) + y\(\frac{\partial w}{\partial y}\) + z\(\frac{\partial w}{\partial z}\).
Solution:
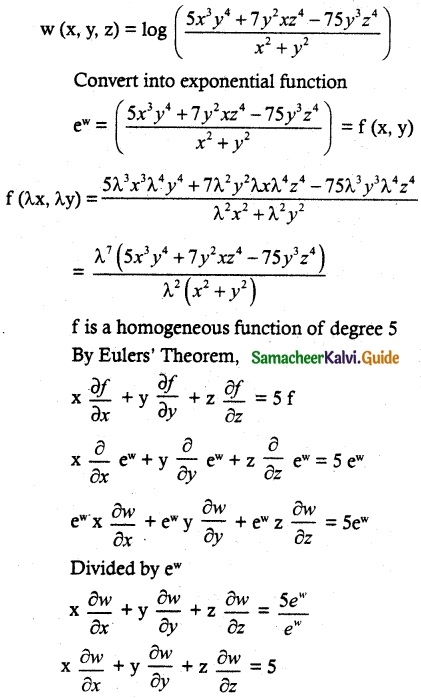
![]()