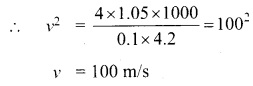Students can download Maths Chapter 8 Statistics and Probability Ex 8.2 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Statistics and Probability Ex 8.2
Question 1.
The standard deviation and mean of a data are 6.5 and 12.5 respectively. Find the coefficient of variation.
Answer:
Standard deviation of a data (σ) = 6.5
Mean of the data (\(\bar{x}\)) = 12.5
Coefficient of variation = \(\frac{\sigma}{\bar{x}} \times 100 \%\)
= \(\frac{6.5}{12.5} \times 100 \%=52 \%\)
Coefficient of variation = 52%
Question 2.
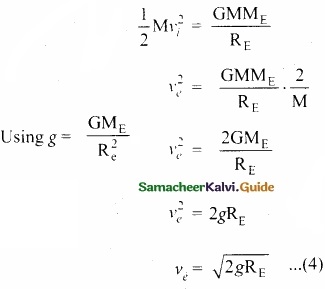
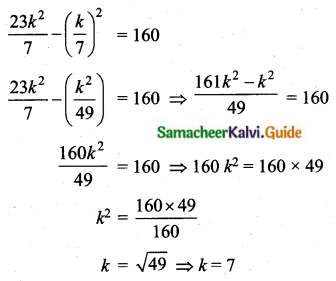
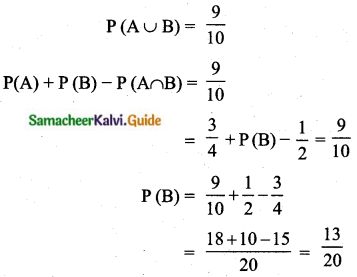
The standard deviation and coefficient of variation of a data are 1.2 and 25.6 respectively. Find the value of mean.
Answer:
Standard deviation (σ) = 1.2
Coefficient of variation = 25.6
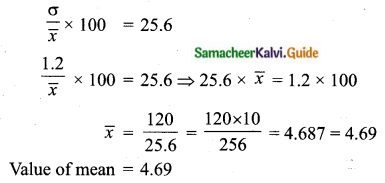
![]()
Question 3.
If the mean and coefficient of variation of a data are 15 and 48 respectively, then find the value of standard deviation.
Answer:
Mean (\(\bar{x}\)) = 15
Co efficient of variation = 48
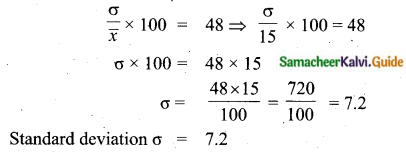
Question 4.
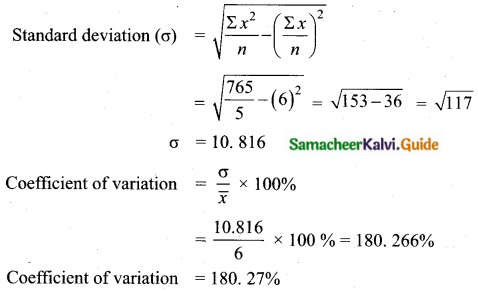
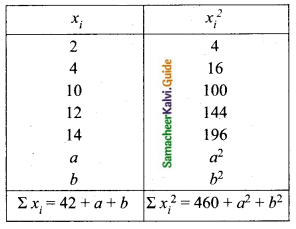
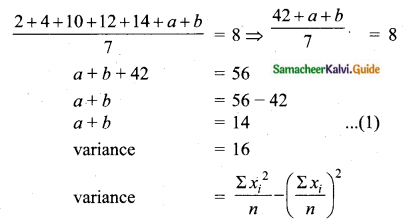
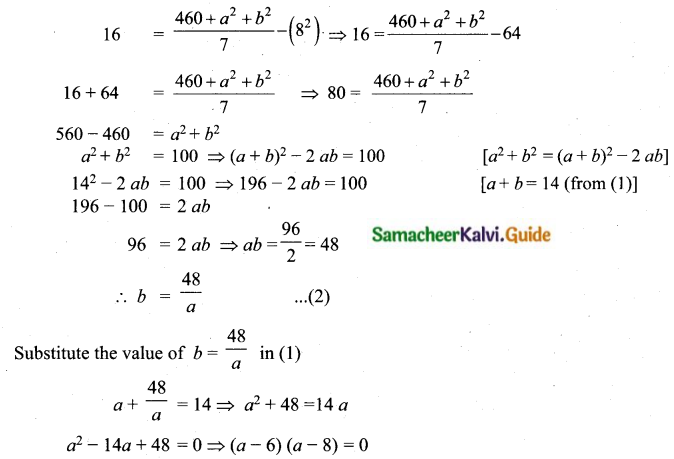
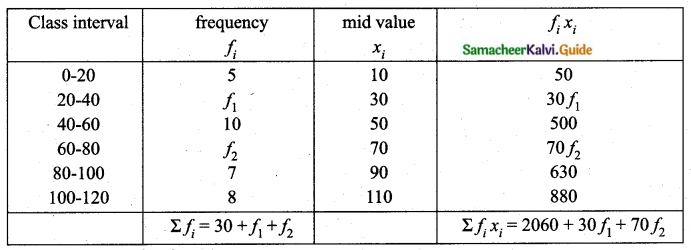
If n = 5, \(\bar{x}\) = 6, Σx2 = 765, then calculate the coefficient of variation.
Answer:
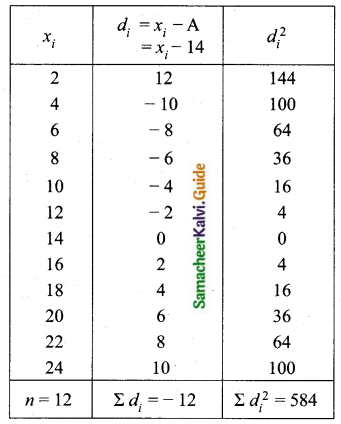
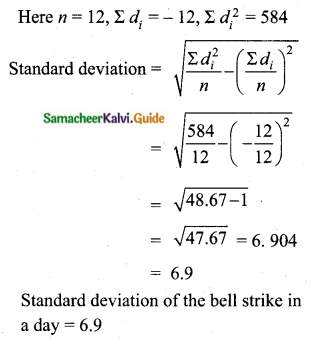
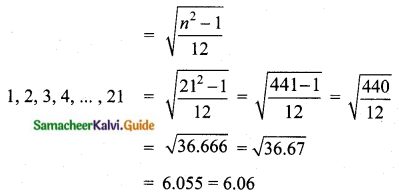
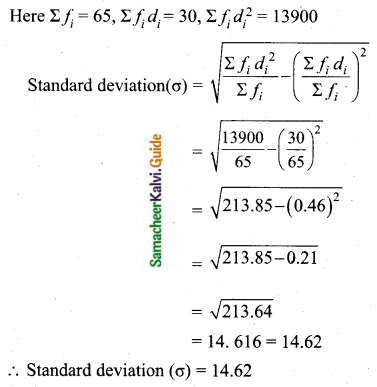
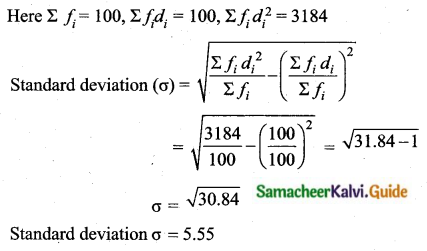
Question 5.
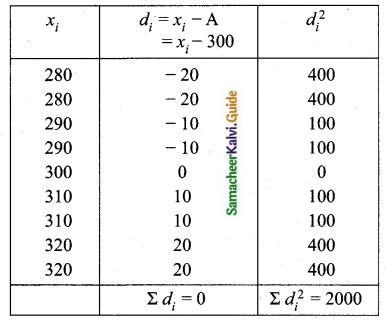
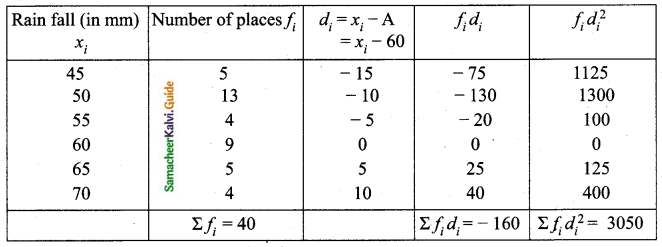
Find the coefficient of variation of 24, 26, 33, 37, 29, 31.
Answer:
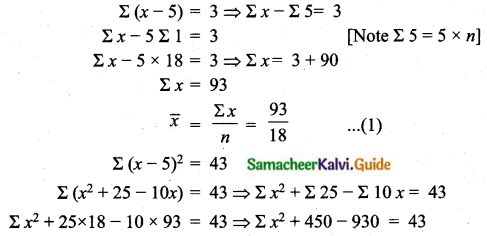
Arrange in ascending order we get 24, 26, 29, 31, 33, 37
Assumed mean = 29
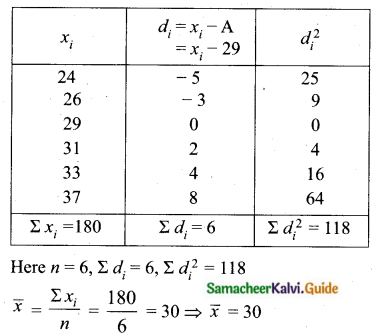
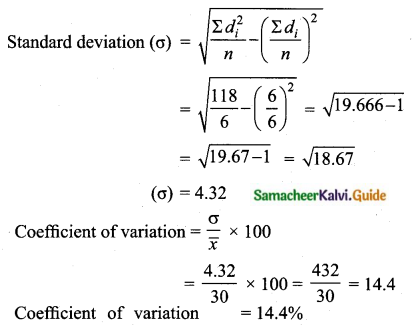
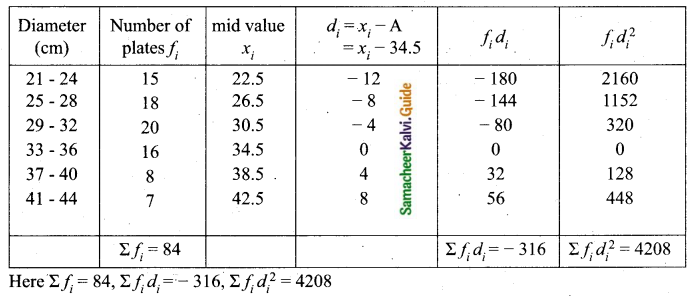
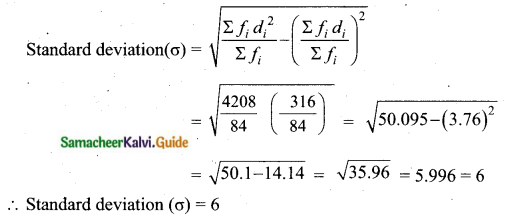
Question 6.
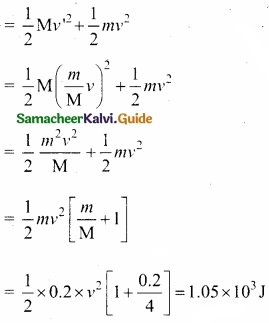
The time taken (in minutes) to complete homework by 8 students in a day are given by 38, 40, 47, 44, 46, 43, 49, 53. Find the coefficient of variation.
Answer:
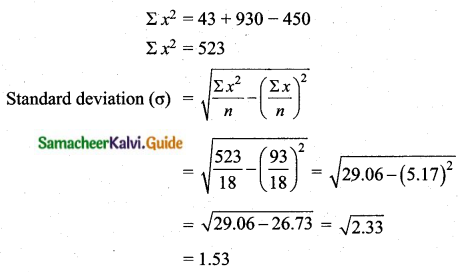
Arrange in ascending order we get, 38, 40, 43, 44, 46, 47, 49, 53.
Assumed mean = 46
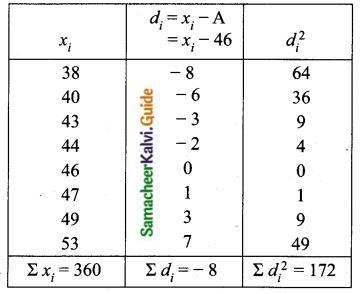
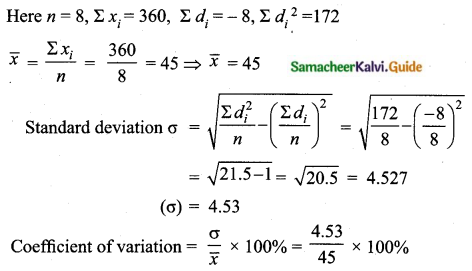
= \(\frac{453}{45}\)%
= 10.066
Coefficient of variation = 10.07%
![]()
Question 7.
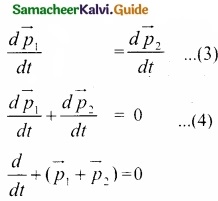
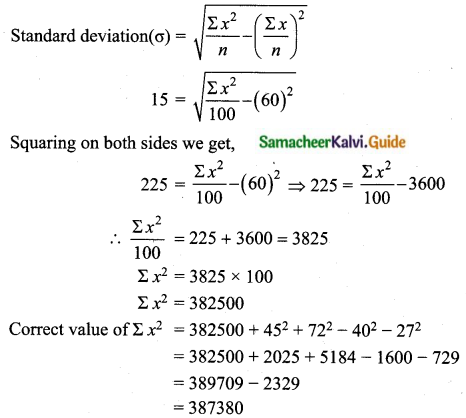
The total marks scored by two students Sathya and Vidhya in 5 subjects are 460 and 480 with standard deviation of 4.6 and 2.4 respectively. Who is more consistent in performance?
Answer:
Total marks scored by sathya = 460
Total marks scored by vidhya = 480
Number of subjects = 5
Mean marks of sathya = \(\frac{460}{5}\)
\(\bar{x}\) = 92%
Given standard deviation, (σ) = 4.6
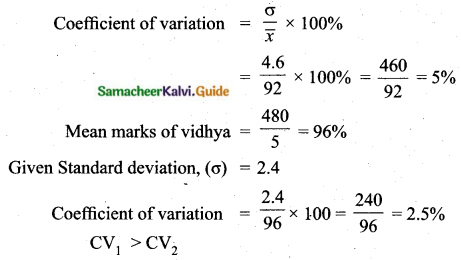
Vidhya coefficient of variation is less than Sathya.
Vidhya is more consistent.
Question 8.
The mean and standard deviation of marks obtained by 40 students of a class in three subjects Mathematics, Science and Social Science are given below.
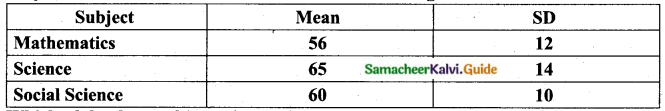
Which of the three subjects shows the highest variation and which shows the lowest variation in marks?
Answer:
(i) Mathematics:
Mean (\(\bar{x}\)) = 56
Standard deviation (σ) = 12
Coefficient variation (CV1) = \(\frac{\sigma}{\bar{x}} \times 100=\frac{12}{56} \times 100\)
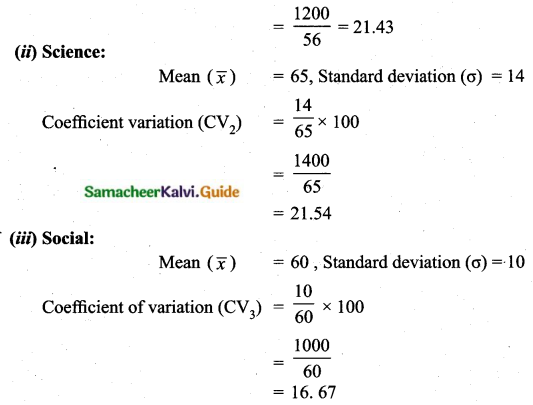
Science shows the highest variation
Social science shows the lowest variation
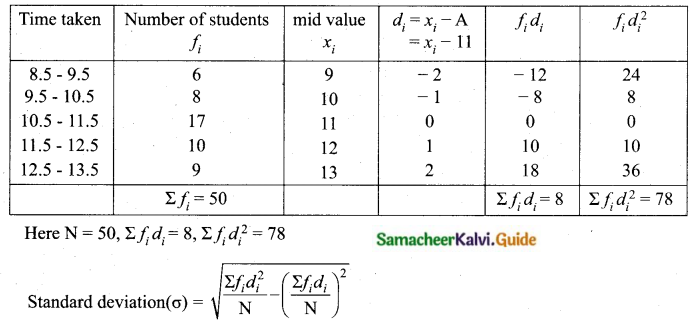
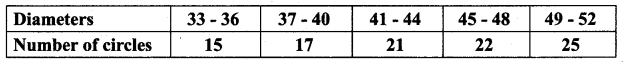
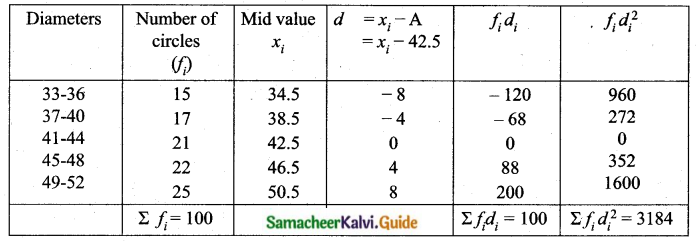
Question 9.
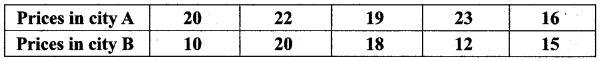
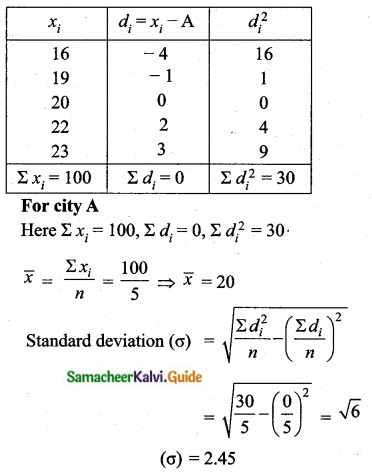
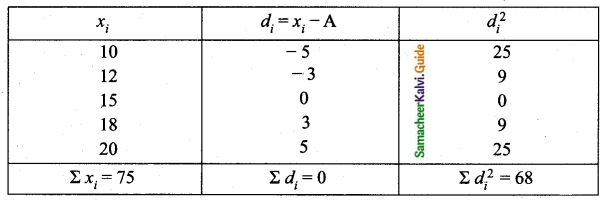
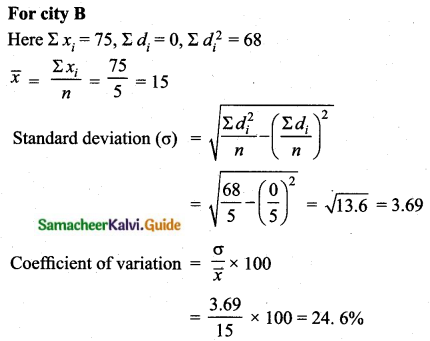
The temperature of two cities A and B in the winter season are given below.

Find which city is more consistent in temperature changes?
Answer:
(i) city A:
Assumed mean = 22
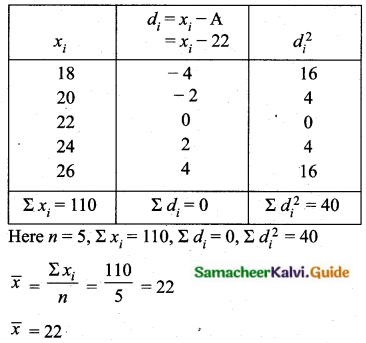
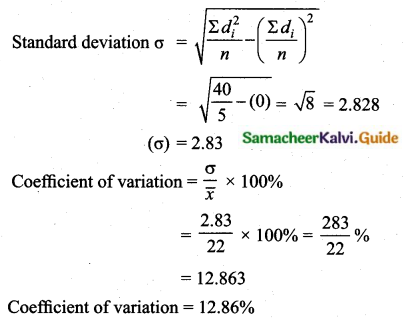
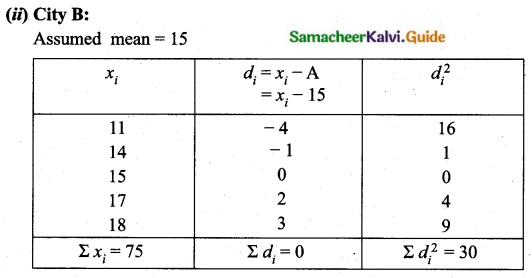
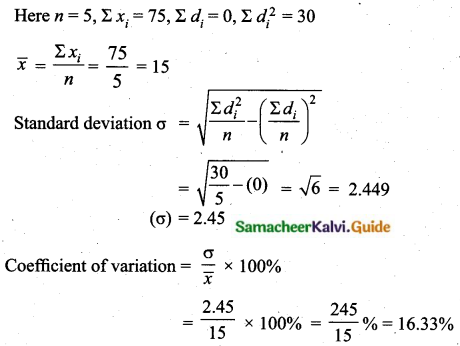
C.V of city A < C.V of city B
City A is more consistent in temperature change.
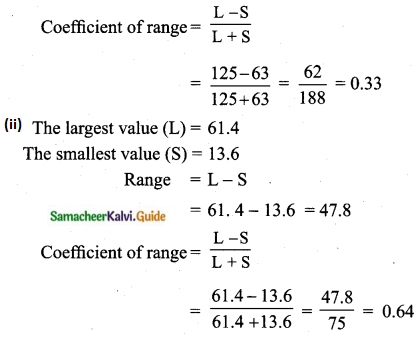

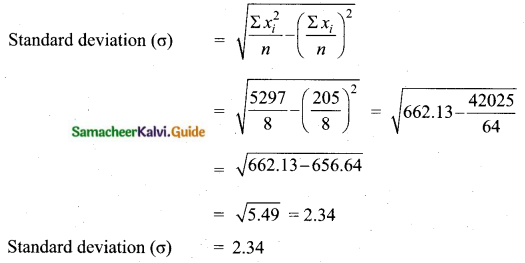
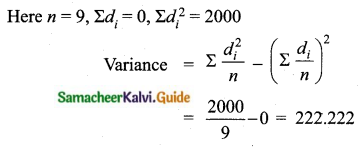
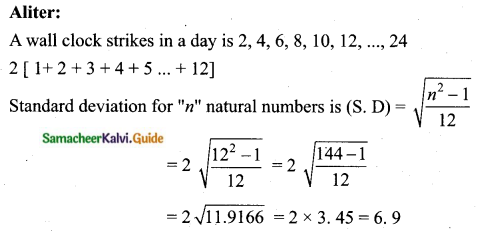



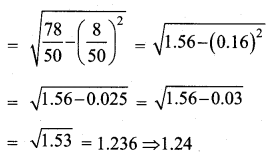
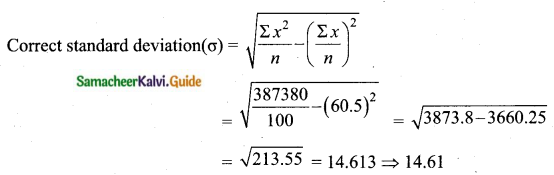



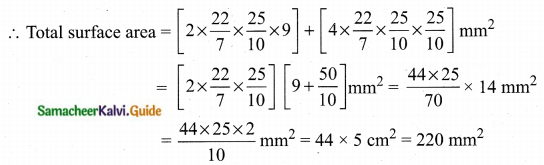
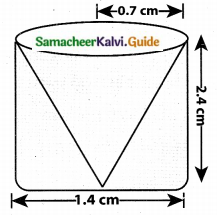
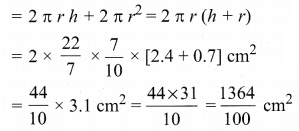
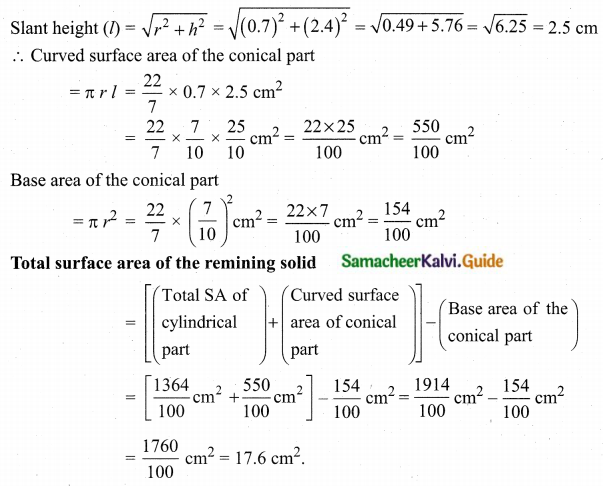


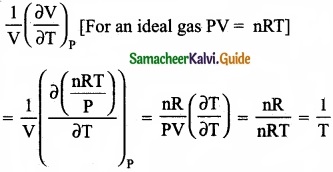
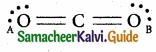

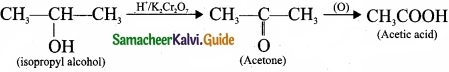
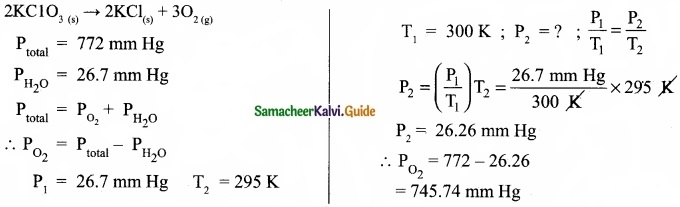

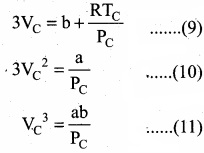

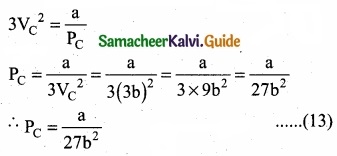
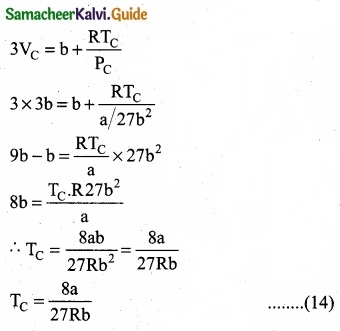

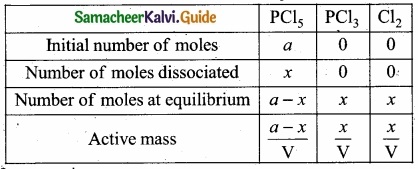
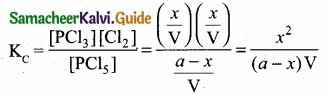
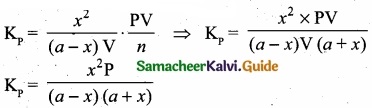
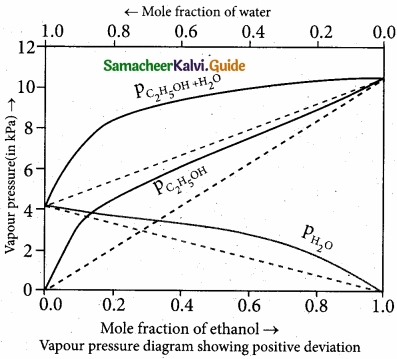
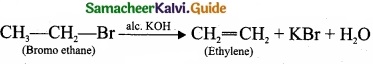



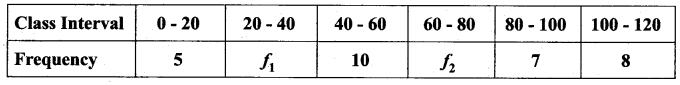
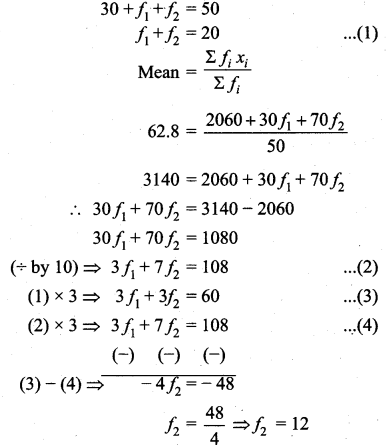
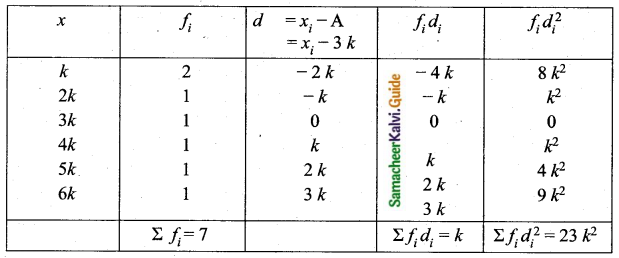
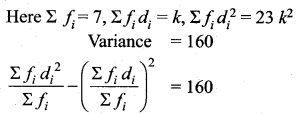

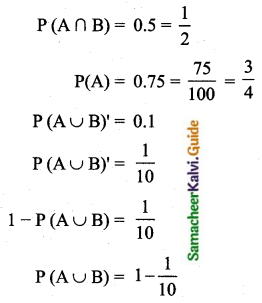
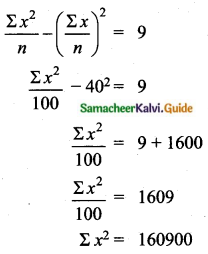
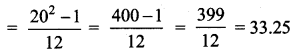
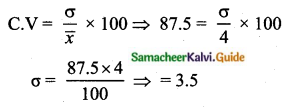

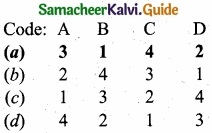
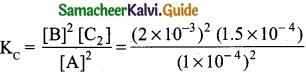



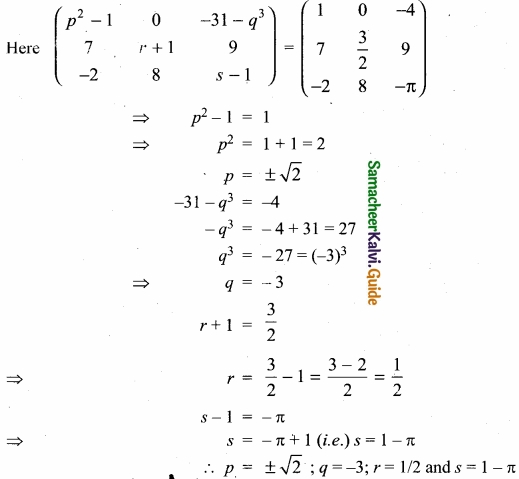
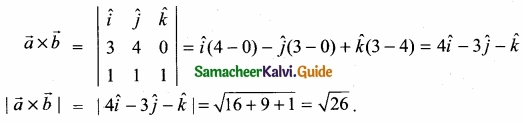
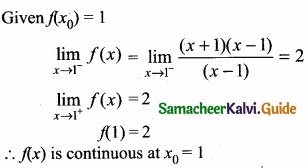

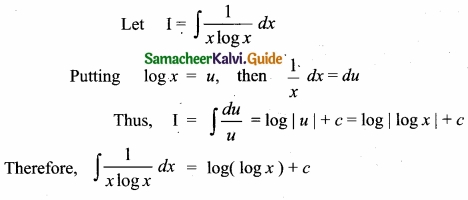
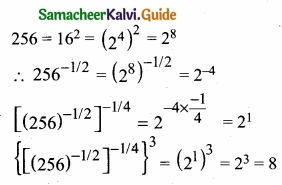
 = \(\frac{80}{40}\)
= \(\frac{80}{40}\)