Students can download 6th Social Science Term 3 Civics Chapter 2 Local Bodies: Rural and Urban Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Civics Solutions Term 3 Chapter 2 Local Bodies: Rural and Urban
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Local Bodies: Rural and Urban Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
……………… is set up with several village panchayats
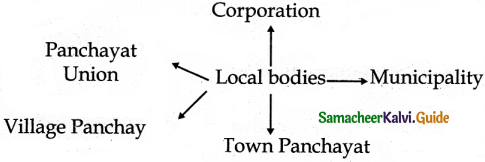
(a) Panchayat Union
(b) District Panchayat
(c) Taluk
(d) Revenue village
Answer:
(a) Panchayat Union
![]()
Question 2.
_______ is National panchayat Raj day
a) January 24
(b) July 24
(c) November 24
(d) April 24
Answer:
(d) April 24
Question 3.
The oldest urban local body in India is ………………
(a) Delhi
(b) Chennai
(c) Kolkata
(d) Mumbai
Answer:
(b) Chennai
![]()
Question 4.
_________ District has the highest number of Panchayat Unions.
(a) Vellore
(b) Thiruvallore
(c) Villupuram
(d) Kanchipuram
Answer:
(c) Villupuram
Question 5.
The head of a corporation is called a ………………
(a) Mayor
(b) Commissioner
(c) Chair Person
(d) President
Answer:
(a) Mayor
II. Fill in the blanks
- ……………… is the first state in India to introduce town Panchayat.
- The Panchayat Raj Act was enacted in the year ………………
- The tenure of the local body representative is ……………… years.
- ……………… is the first municipality in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu
- 1992
- 5
- Walajahphet Municipality
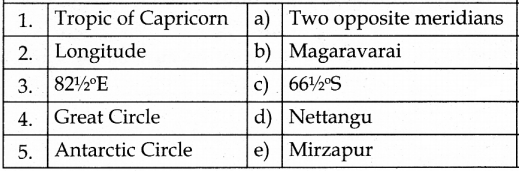
III. Match the following Answer

Answer:
1. – d
2. – c
3. – a
4. – b
IV. Answer the following
Question 1.
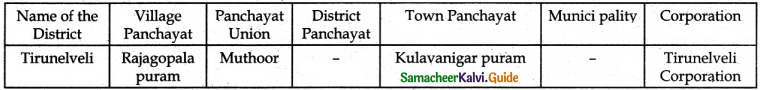
Is there any corporation in your district? Name it.
Answer:
Yes, Tirunelveli Corporation.
Question 2.
What is the need for local bodies?
Answer:
In order to fulfill the requirements of the people and to involve them directly in governance, there is a need for an effective system of local bodies.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the divisions of a rural local body?
Answer:
The rural bodies are categorized into village panchayats, Panchayat Unions, and District panchayats.
Question 4.
What are the divisions of an Urban local body?
Answer:
The Urban local bodies are Categorized into City Municipal Corporations, Municipalities and Town Panchayats.
Question 5.
Who are the representatives elected in a Village Panchayat?
Answer:
The Elected Representatives in a Village Panchayat
- Panchayat president
- Ward members
- Councillor
- District Panchayat Ward Councillor
Question 6.
List out a few functions of corporations.
Answer:
- Drinking-Water Supply
- Street Light
- Maintenance of Clean Environment
- Primary Health facilities
- Corporation Schools
- Birth and Death registration etc.
![]()
Question 7.
List out a few means of revenue of village Panchayats.
Answer:
- House tax
- Professional tax
- Tax on shops
- Water charges
- Specific fees for property tax Funds from Central and State Governments etc.
Question 8.
When are Grama Sabha meetings convened? What are the special on those days?
Answer:
- The Grama Sabha meetings are Convened on January 26, May 1, August 15, and October 2.
- These days are celebrated as National festival days every year.
Question 9.
What are the special features of the Panchayat Raj system?
Answer:
- Special features of Panchayat Raj
- Grama Sabha
- Three-tier local body governance
- Reservations
- Panchayat Elections
- Tenure
- Finance Commission
- Account and Audit etc.
Question 10.
What is the importance of Grama Sabha?
Answer:
- Grama Sabha is essential for the effective functioning of Village Panchayat.
- It enhances public participation in the planning and implementation of schemes for social benefit.
V. HOTS
Question 1.
Local bodies play an important role in the development of villages and cities. How?
Answer:
- India is a vast nation. It is very difficult for a single government to run the entire Country.
- Our Constitution has provided for three separate levels of government.
- Union government
- State government
- Local government
- The Local government takes care of the local administration of cities and villages.
- The main jobs of these bodies are
- Keeping an area clean
- Construction of roads and schools
- arrangements for water and electricity etc.
VI. Activities
- Prepare a questionnaire to interview a local body representative.
- Discuss; If there is a contribution to the improvement of your school by local body representatives.
- If I were a local body representative, I would
- Find out the number of local bodies in your district and list them.
Question 1.
Prepare …………… representative
1. What is your plan to bring in a good drainage system?
2. When will the bridgework Connecting Maharaja Nagar and Thyagaraja Nagar be completed?
3. How many months it will take to bring street lights in our area?
![]()
Question 2.
Discuss: If there representatives:
1. Local body members of our area have Contributed much to the upliftment of our school.
2. They met the VIPS, the Common public, and the old Students to meet out the needs of the school.
3. From the Sponsorship they supplied things like Computer Laboratory equipment and books for the library.
Question 3.
If I were …………… them.
1. I would take steps to eradicate Dengu and all sorts of infectious diseases.
2. I would try to maintain a proper drainage system.
3. I would bring in proper roads and lightings etc.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Local Bodies: Rural and Urban Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Fill in the blanks Answer
- There are ………………. Corporations in Tamil Nadu.
- The Chennai Corporation was founded in ……………….
- ………………. District has the most number of municipalities
- A ………………. Panchayat is between a Village and a city
- The ………………. Panchayats are the local bodies of Villages.
- The ………………. and ………………. Districts have the lowest number of Panchayat Unions.
- The Constituencies are also called……………….
Answer:
- Twelve
- 1688
- Kanchipuram
- Town
- Village
- Nilgris and Perambalur
- Wards
II. Choose the Correct answer
Question 1.
advocated Panchayat Raj as the foundation of India’s Political System ……………….
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) Rajendra Prasad
Answer:
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
Question 2.
A Bio element Officer (BDQ) is the administrative head of a __________
(a) Village Panchayat
(b) District Panchayat
(c) Panchayat Union
(d) Town Panchayat
Answer:
(c) Panchayat Union
Question 3.
In the 2011 Local Bodies election, percent Seats were won by women ……………….
(a) 38
(b) 28
(c) 48
Answer:
(a) 38
![]()
Question 4.
Discretionary function of a Village Panchayat __________
(a) Cleaning roads
(b) Libraries
(c) Water supply
(d) Street lighting
Answer:
(b) Libraries
Question 5.
The Tamil Nadu State Election Commission is situated in ……………….
(a) Chennai
(b) Coimbatore
(c) Trichy
Answer:
(a) Chennai
III. Answer the following briefly
Question 1.
Write about the officials of Municipal Corporation.
Answer:
- A City Municipal Corporation has a Commissioner, who is an IAS Officer.
- Government Officials are deputed as Commissioners for municipalities.
- The administrative officer of a Municipality is an Executive officer (EO)
Question 2.
Explain briefly about Panchayat Union.
Answer:
- Many Village Panchayats join to form a Panchayat Union.
- A Councillor is elected from each Panchayat.
- The Councillors will elect a Panchayat union Chairperson among themselves.
- A Vice-Chairperson is also elected.
- A Block Development Officer (BDO) is the administrative head, of a Panchayat Union.
- The Services are provided on the Panchayat Union level.
![]()
Question 3.
List out the Strength of local bodies in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Tamil Nadu:
- Village Panchayats – 12, 524
- Panchayat Unions – 385
- District Panchayats – 31
- Town Panchayats – 561
- Municipalities – 125
- City Municipal Corporation – 12
IV. Answer the following in detail
Question 1.
Discuss the District Panchayat
Answer:
- A District Panchayat is formed in every district.
- A district is divided into wards on the basis of a 50,000 population.
- The ward members are elected by the village panchayats.
- The members of the District Panchayat elect the District Panchayat Committee Chairperson.
- They provide essential services and facilities to the rural population.
- They also provide planning and execution of development programmes for the district.
Question 2.
List out the Works carried out by local bodies during natural disasters and outbreaks of diseases.
Answer:
- Rescuing the public and settle them in a safer places.
- Arranging food packets and pure drinking water.
- Assisting them with medical Aids.
- Creating awareness about the clean environment to the public.
- Keeping the medicines in the upto date conditions.
- Preventing them from getting panic against the diseases and make the situation, calm.
V. Mind map