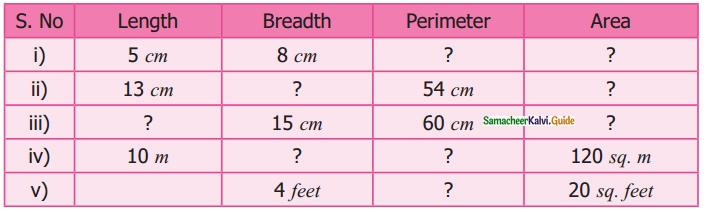
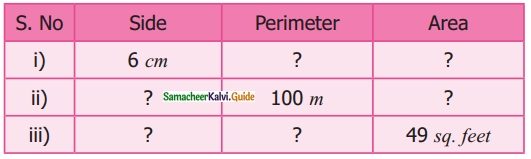
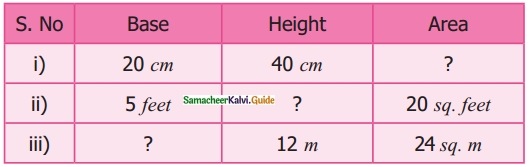
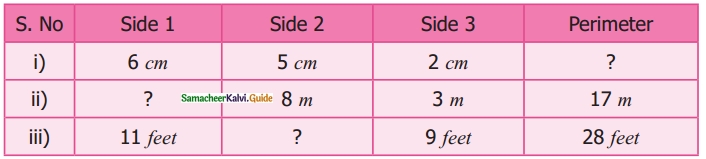
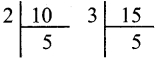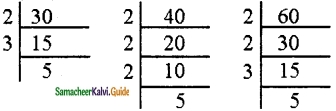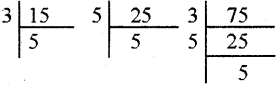Students can download Maths Chapter 3 Perimeter and Area Ex 3.2 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 3 Chapter 3 Perimeter and Area Ex 3.2
Miscellaneous Practice Problems
Question 1.
A piece of wire is 36 cm long. What will be the length of each side if we form
(i) a square
(ii) an equilateral triangle
Solution:
Given the length of the wire = 36 cm
i) When a square is formed out of it
The perimeter of the square = 36 cm
4 × side = 36
side = \(\frac{36}{4}\) = 9 cm
Side of the square
ii) When an equilateral triangle is formed out of it, its perimeter = 36 cm
i.e., side + side + side = 36 cm .
3 × side = 36 cm
side = \(\frac{36}{3}\) = 12 cm
One side of an equilateral triangle = 12 cm
![]()
Question 2.
From one vertex of an equilateral triangle with a side of 40 cm, an equilateral triangle with 6 cm side is removed. What is the perimeter of the remaining portion? The perimeter of the remaining portion
Solution:
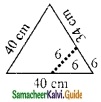
= (40 + 34 + 6 + 34) cm
= 114 cm
Question 3.
Rahim and Peter go for a morning walk, Rahim walks around a. square path of side 50 m and Peter walks around a rectangular path with a length of 40 m and a breadth of 30 m. If both of them walk 2 rounds each, who covers more distance and by how much?
Solution:
Distance covered by Rahim
= 50 × 4 m
= 200 m
If he walks 2 rounds, distance covered = 2 × 200 m
= 400 m
Distance covered by peter
= 2 (40 + 30) m
= 2(70)m
= 140 m
If he walks 2 rounds, distance covered = 2 × 140 m
= 280 m
∴ Rahim covers more distance by (400 – 280) = 120 m
![]()
Question 4.
The length of a rectangular park is 14 m more than its breadth. If the perimeter of the park is 200 m, what is its length? Find the area of the park.
Solution:
Let the length be b + 14 m
breadth = b
perimeter = 200
2 (l + b) = 200
2 (b + 14 + b) = 200
2 (2b + 14) = 200
28 + 4b = 200
4b = 200 – 28
4b = 172 m
b = \(\frac{172}{4}\)
b = 43 m
Length = b + 14
= 43 + 14
Length l = 57 m
Area = l × b units
= 57 × 43 m²
= 2451 m²
![]()
Question 5.
Your garden is in the shape of a square of side 5 m. Each side is to be fenced with 2 rows of wire. Find how much amount is needed to fence the garden at ₹ 10 per metre.
Solution:
a = 5 m
The perimeter of the garden
= 4 a units
= 4 × 5 m
= 20 m
For 1 row
Amount needed to fence l m= Rs 10
Amount needed to fence 20 m
= Rs 10 × 20
= Rs 200
For 2 rows
Total amount needed = 2 × Rs 200 = Rs 400
![]()
Challenge Problems
Question 6.
A closed shape has 20 equal sides and one of its sides is 3 cm. Find its perimeter.
Solution:
Number of equal sides in the shape = 20
One of its side = 3 cm
Perimeter = length of one side × Number of equal sides
∴ Perimeter = (3 × 20) cm = 60 cm
∴ Perimeter = 60 cm
Question 7.
A rectangle has length 40 cm and breadth 20 cm. How many squares with side 10 cm can be formed from it.
Solution:
Area of rectangle = (length × breadth) units2
Length = 40 cm
Breadth = 20 cm
∴ Area = (40 × 20) cm2 = 800 cm2
Area of rectangle = 800 cm2
Area of square = (side × side) units2
side = 10 cm
∴ Area of square = (10 × 10) cm2 = 100 cm2
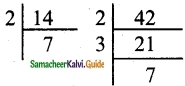
Required number of squares = \(\frac{\text { Area of Rectangle }}{\text { Area of } 1 \text { square }}=\frac{800 \mathrm{cm}^{2}}{100 \mathrm{cm}^{2}}\) = 8
8 squares can be formed.
![]()
Question 8.
The length of a rectangle is three times its breadth. If its perimeter is 64 cm, find the sides of the rectangle.
Solution:
Given perimeter of a rectangle = 64 cm
Also given length is three times its breadth.
Let the breadth of the rectangle = b cm
∴ Length = 3 × b cm
Perimeter = 64 m
i.e., 2 × (l + b) = 64 m
2 × (3b + b) = 64 m
2 × 4b = 64m
4b = \(\frac{64}{2}\) = 32 m
b = \(\frac{32}{4}\) = 8 m
l = 3 × b = 3 × 8 = 24 m
∴ Breadth of the rectangle = 8 m
Length of the rectangle = 24 m
Question 9.
How many different rectangles can be made with a 48 cm long string? Find the possible pairs of length and breadth of the rectangles.
Solution:
Length of the string to be made into rectangle = 48 cm
∴ Perimeter of the rectangle = 48 cm
2 × (l + b) = 48 cm
l + b = \(\frac{48}{2}\)
l + b = 24 cm
Possible pairs of length and breadth are (1, 23), (2, 22) (3, 21), (4, 20), (5, 19),
(6, 18), (7, 17), (8, 16), (9, 15), (10, 14), (11, 13), (12, 12)
Number of different rectangles = 12.
![]()
Question 10.
Draw a square B whose side is twice of the square A. Calculate the perimeters of the squares A and B.
Solution:
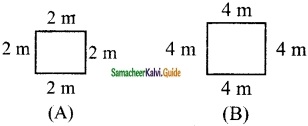
Perimeter of A = s + s + s + s units = 4 s units
Perimeter of B = (2s + 2s + 2s + 2s) units
= 8s units = 2 (4s) units.
∴ The perimeter of B is twice the perimeter of A
Question 11.
What will be the area of a new square formed if the side of a square is made one – fourth?
Solution:
Let the side of square is s units then area = (s × s) units2
If the side of the new square is made one fourth then side = \(\left(\frac{1 \times s}{4}\right)\) units
Then area = \(\left(\frac{1 \times s}{4} \times \frac{1 \times s}{4}\right)\) units2 = \(\frac{s \times s}{16}=\frac{1}{16}\) (s × s) units2
Area of the new square is reduced to \(\frac{1}{16}\) times to that of original area.
Question 12.
Two plots have the same perimeter. One . is a square of side 10 m and another is a rectangle of breadth 8 m. Which plot has the greater area and by how much?
Solution:
a = 10 m, b = 8 m
Perimeter of the square plot
= 4 a units
= 4 × 10 m
= 40 m
Perimeter of the rectangular plot
40 = 2 (l + b) units
40 = 2 (l + 8) m
40 = 2 l + 16
2 l = 40 – 16
2 l = 24
l = \(\frac{24}{2}\)
l = 12 m
Area of the square plot
= a × a sq units
= 10 × 10 m²
= 100 m²
Area of the rectangular plot
= l × b sq units
= 8 × 12 m²
= 96 m²
Square plot has the greater area by 100 m² – 96 m² – 4 m²
![]()
Question 13.
Look at the picture of the house given and find the total area of the shaded portion.
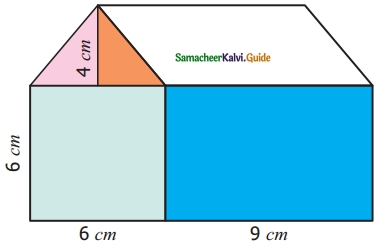
Solution:
Total area of the shaded region = Area of a right triangle + Area of a rectangle
= (\(\frac{1}{2}\) × b × h) + (l × b) cm2
= [(\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 3 × 4) + (9 × 6)] cm2
= (6 + 54) cm2 = 60 cm2
![]()
Question 14.
Find the approximate area of the flower in the given square grid.
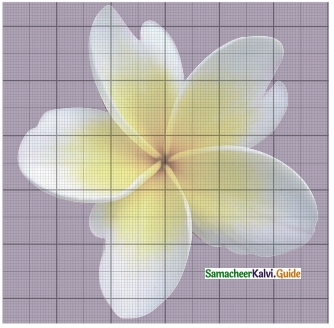
Solution:
No of full squares = 11
No of half squares = 9
Area of 11 full squares
= 11 x 1 cm²
= 11 cm²
Area of 9 half squares
= 9 × \(\frac{1}{2}\) cm²
= 4.5 cm²
Area of the flower = (11 + 4.5) cm²
= 15.5 cm²