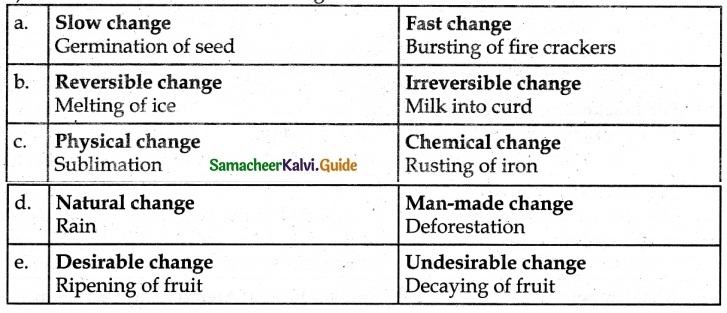
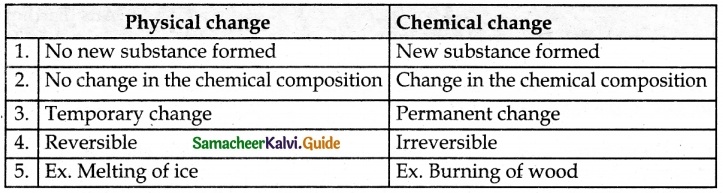
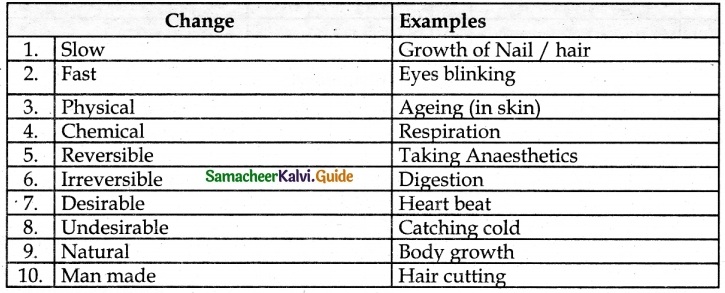
Students can download 6th Science Term 1 Chapter 3 Matter Around Us Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 3 Matter Around Us
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Matter Around Us Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
………. is not made of matter
(a) Gold ring
(b) iron nail
(c) light ray
(d) oil drop
Answer:
(a) light ray
Question 2.
200 ml of water is poured into a bowl of 400ml capacity. The volume of water now will be _____
(a) 400 ml
(b) 600 ml
(c) 200 ml
(d) 800 ml
Answer:
(c) 200 ml
![]()
Question 3.
Seeds from water-melon can be removed by method.
(a) Hand-picking
(b) filtration
(c) magnetic separation
(d) decantation
Answer:
(c) Hand picking
Question 4.
Lighter impurities like dust, when mixed with rice or pulses, can be removed by _____
(a) filtration
(b) sedimentation
(c) decantation
(d) winnowing
Answer:
(d) winnowing
Question 5.
………… of is essential to perform winnowing activity
(a) Rain
(b) Soil
(c) Water
(d) Air
Answer:
(d) Air
Question 6.
Filtration method is effective in separating _____ mixture.
(a) solid – solid
(b) solid – liquid
(c) liquid – liquid
(d) liquid – gas
Answer:
(b) solid – liquid
Question 7.
From the following ………. is not a mixture
(a) Coffee with milk
(b) lemon juice
(c) Water
(d) ice cream embedded with nuts.
Answer:
(c) Water
![]()
II. State whether the following statements are True or False. If false give the correct statement
- Air is not compressible.
- Liquids have no fixed volume but have fixed shape.
- Particles in solids are free to move.
- Then pulses are washed with water before cooking, the water is separated from them by the process of filtration.
- Strainer is a kind of sieve which is used to separate a liquid from solid
- Grain and husk can be separated by winnowing
- Air is a pure substance
- Butter from curds is separated by sedimentation.
Answer:
- False. Air is Compressible.
- False. Liquids have no fixed shape but have fixed volume.
- False Particles in solids are not free to move.
- False. When pulses are washed with water before cooking, the water is separated from them by the process of Decantation.
- False. Strainer is a kind of sieve which is used to separate a solid from liquid.
- True.
- False. Air is a mixture. (Or) Air is not a pure substance.
- False. Butter from curds is separated by churning.
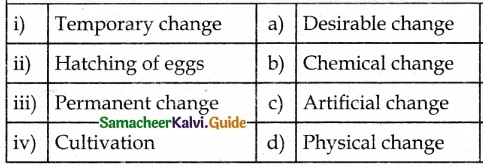
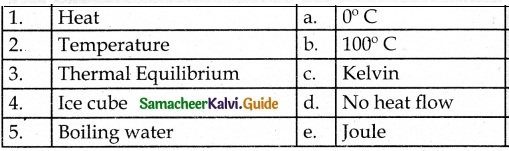
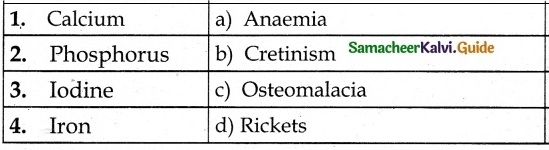
III. Match the following
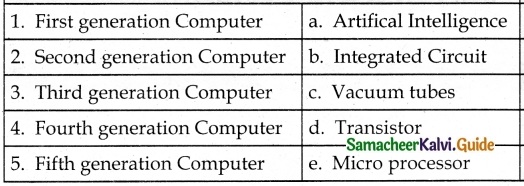
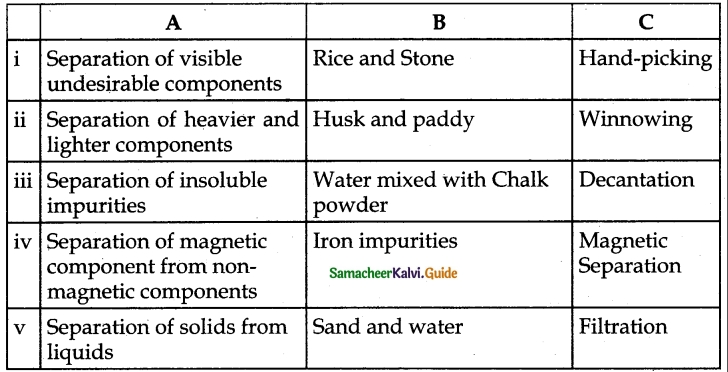
Question 1.
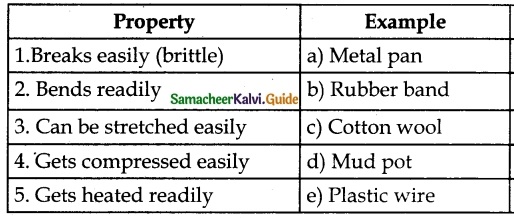
Answer:
1. – d
2. – e
3. – b
4. – c
5. – a
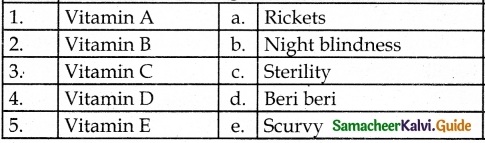
Question 2.
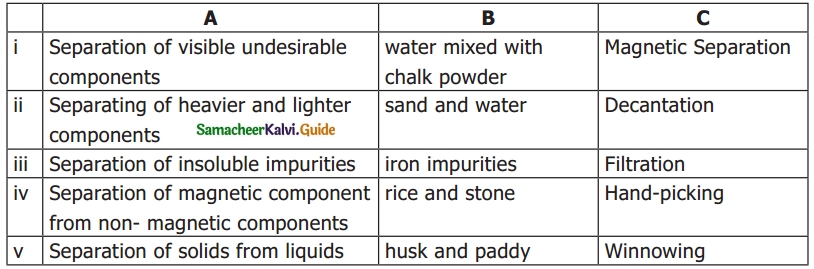
Answer:
IV. Fill in the blanks
- Matter is made up of ………
- In solids, the space between the particles is less than in ……….
- Grains can be separated from their stalks by ……….
- Chillies are removed from ‘upma’ by ……… method.
- The method employed to separate clay particles from water is ……….
- Among the following items: Safety pins, pencil and rubber band, ………. will get attracted to a magnet.
- Water obtained from tube wells is usually ………. water
Answer:
- Atoms
- An Liquids
- Threshlng
- Hand picking
- Filtration
- Safety pins
- Impure
![]()
V. Complete the given analogy
- Solid: rigidity :: gas: …………
- Large Inter-particle space: gas:: ………. : solid
- Solid : definite shape :: ……… : shape of the vessel.
- Husk-grains: winnowing:: Sawdust-chalk piece: ………..
- Murukku from hot oil: ………. :: coffee powder residue from decoction
- Iron-sulphur mixture: ……….. :: Mustard seeds from Urad-dhal: Rolling
Answer:
- Compressibility
- Little inter-particle space
- Liquids
- Sedimentation and Decantaium
- Hand picking; Filtralion.
- Magnetic Separation.
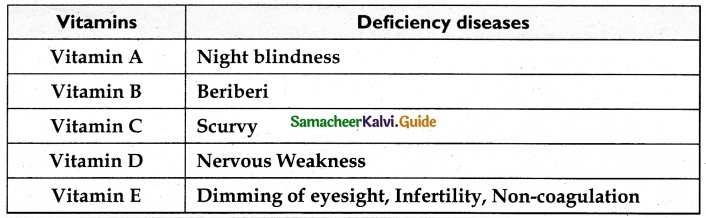
VI. Very short answer
Question 1.
Define the term matter.
Answer:
The matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space. The matter is found in solid, liquid, and gas.
Question 2.
How can husk or fine dust particles be separated from rice before cooking?
Answer:
Before cooking, the husk or fine dust particles in rice are being separated by ‘Sedimentation’. The lighter impurities float while heavier rice grains sink to the bottom.
Question 3.
Why do we separate mixtures?
Answer:
A mixture is an impure substance and contains more than one kind of particles. So, we have to separate mixtures.
![]()
Question 4.
Give an example for mixture and justify your answer with reason.
Answer:
An example of a mixture is 22 Carat Gold. This is composed of Gold and Copper (or) Gold and Cadmium.
Question 5.
Define Sedimentation.
Answer:
Sedimentation is the deposition process of setting down of heavy solids in a mixture of liquid and an insoluble solid.
Question 6.
Give the main difference between a pure substance and an impure substance.
Answer:
Pure Substance :
Made up of only one kind of particles.
Cannot be separated by physical means.
Impure Substance :
Has particles of other Substance mixed in it.
Can be separated by physical means.
VII. Short Answer.
Question 1.
A rubber ball changes its shape on pressing. Can it be called a solid?
Answer:
Yes. A solid has a certain shape and size. The shape of a rubber ball changes only if we squeeze it.
Question 2.
Why do gases not have fixed shape?
Answer:
Gases do not have a fixed shape due to the weak forces of attraction between the gaseous particles. Hence, they can flow and take shape of the container.
Question 3.
What method will you employ to separate cheese (paneer) from milk? Explain.
Answer:
“Churning followed by Coagulation” is employed to separate cheese (Paneer) from milk. There are six important steps in making cheese (Paneer) from milk:
- Acidification
- coagulation
- separating curds and whey
- Salting
- shaping
- ripening
![]()
Question 4.
Look at the picture given below and explain the method of separation illustrated.

Answer:
The given picture shows the ‘Sieving’ method of separation. It is used to separate the solid particles of different sizes. Example: Bran from flour; Sand from gravel.
Question 5.
How can you separate a mixture of a large number of tiny bits of paper mixed with pulses/dal?
Answer:
We can separate the mixture of a large number of tiny bits of paper and pulses/dal by “Winnowing”. The lighter papers will be carried by wind and heavier pulses/dais will fall closer and form a separate heap.
Question 6.
What is meant by food adulteration?
Answer:
The process of mixing harmful and unwanted substances with the foodstuffs that we buy in the market is called food adulteration
Question 7.
Mr. Raghu returns home on a hot summer day and wants to have buttermilk. Mrs. Raghu has only curds. What can she do to get buttermilk? Explain.
Answer:
Mrs. Raghu has to take half a cup of curd, add half a cup of water to it, and mix well. Now, she can serve buttermilk.
VIII. Answer In Detail.
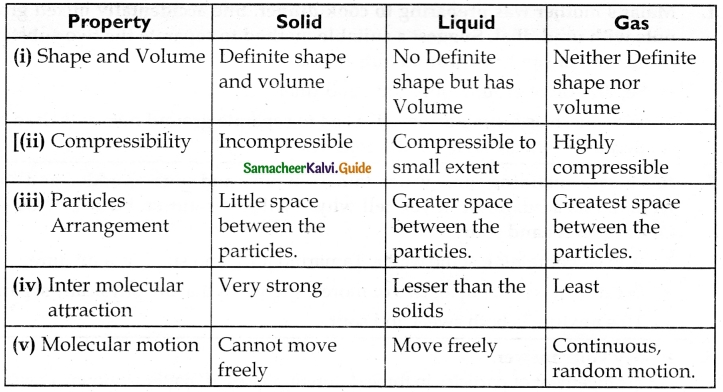
Question 1.
Distinguish between properties of solid, liquid, gas. Draw a suitable diagram.
Answer:
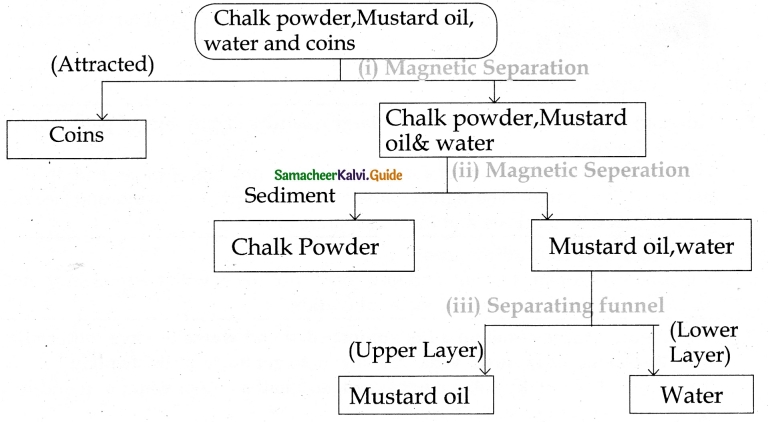
Question 2.
Using a suitable apparatus from your laboratory, separate the mixture of chalk powder, mustard oil, water, and coins. Draw a flow chart to show the separation process.
Answer:
![]()
HOTS
Question 1.
Malar’s mother was preparing to cook dinner. She accidentally mixed ground nuts with urad-dhal. Suggest a suitable method to separate the two substances so that Malar can have ground nuts to eat.
Answer:
The groundnuts shall be separated by hand-picking method because they are in a different size When compared with urad-dhal.
Question 2.
In a glass containing some water, tamarind juice and sugar is added and stirred well. Is this a mixture-can you tell why? Will this solution be sweet? Or sour? Or both sweet and sour?
Answer:
- A glass containing some water, Tamarind juice, and sugar is a mixture.
- Because it is made up of two or more ingredients that are physically separable.
- This mixture is both sweet and sour.
Question 3.
Justify your answer.
An arrangement of particles in three different phases of matter is shown above.
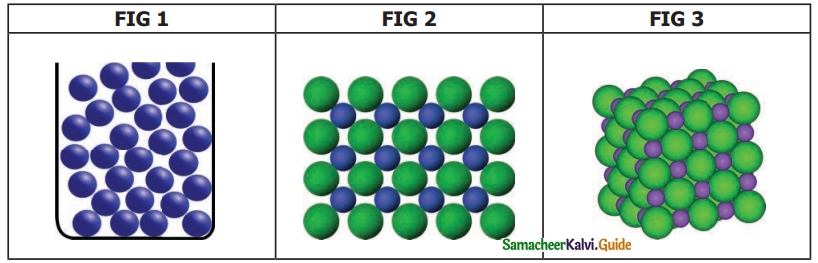
(a) Which state is represented by fig. I?
Answer:
Figure 1 represents a gas.
(b) In which will be the interparticle attraction maximum?
Answer:
Inter Particle attraction is maximum in solids (fig. 3)
(c) Which one of them cannot be contained in an open vessel?
Answer:
A gas (fig. 1) cannot be contained in an open vessel.
(d) Which one can take the shape of its container?
Answer:
Liquid (fig.2) can take the shape of its container.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Matter Around Us Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which of the following are homogeneous in nature?
(i) ice
(ii) wood
(iii) soil
(iv) Air
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iv)
Question 2.
A standard sheet of paper is about atoms thick.
(a) Thousands
(b) Crores
(c) Lakhs
(d) Million
Answer:
(d) Million
Question 3.
Which among the following is not a matter?
(a) Electron
(b) Blood
(c) Moonrock
(d) Humidity
Answer:
(a) Electron
Question 4.
One dot that you make with your pen has more than ______ lakh molecules.
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Four
(d) Three
Answer:
(b) Two
Question 5.
Pure rava, when adultered with wheat flour, is separated by
(a) Sieving
(b) Filtration
(c) Winnowing
(d) Threshing
Answer:
(a) Sieving
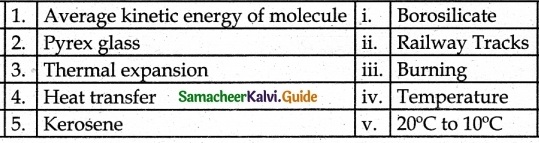
II. Match the following
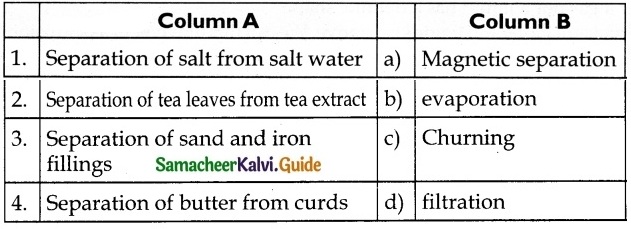
Answer:
1. – b
2. – d
3. – a
4. – c
![]()
III. Fill in the blanks
- ……… particles are tightly packed into a definite shape.
- The tendency of particles to spread out in order to occupy the available space is ………..
- The purest form of gold is denoted by ………..
- Milk is a ………..
- The principle of ………. is used in washing machines.
Answer:
- Solid
- diffusion
- 24 carat
- mixture
- centrifugation
IV. Very short answer.
Question 1.
Name the two microscopes which are used to identify the structure of the atom.
Answer:
- SEM – Scanning Electron Microscope
- TEM – Tunnelling Electron Microscope
Question 2.
What type of matter glass is?
Answer:
Glass is looking like a solid, but not. It is actually a very slow-moving liquid.
Question 3.
Give two examples of diffusion.
Answer:
- Spread of a drop of ink in a glass of water.
- Spread of the smell of an incense stick.
Question 4.
Mention the method of separation of Bran from flour. Explain.
Answer:
Bran from flour is separated by ‘sieving’.
Solid particles of different sizes can be separated by sieving.
![]()
Question 5.
Define the term ‘Liquefaction of gases’.
Answer:
The process by which substances in their gaseous state are converted to the liquid state is called Liquefaction of gases.
V. Answer in detail
Question 1.
What are the similarities between a gas and a liquid?
Answer:
- Neither gas nor a liquid has a definite shape.
- The particles of gases and liquids can move. We call this movement diffusion.
- Liquids can evaporate into gases and the gases can condense into liquids.
- They can have the property of compressibility to some extent.
Question 2.
How do decantation and filtration differ and which is faster?
Answer:
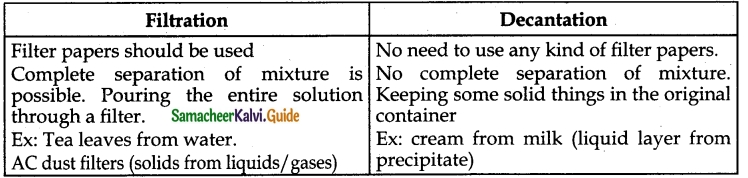
Note: Normally filtration will give a better separation than decantation.