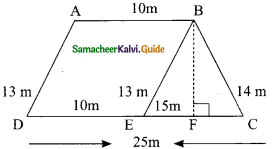
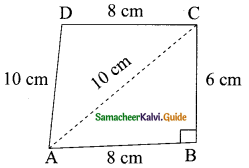
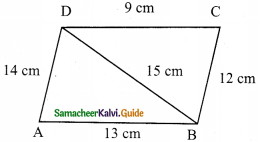
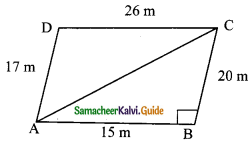
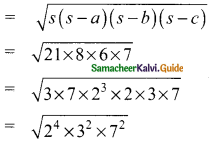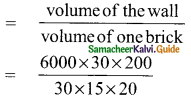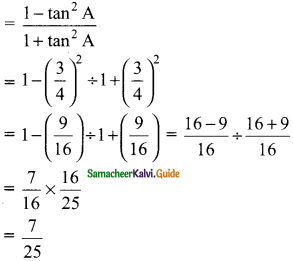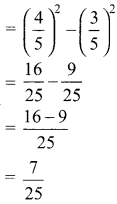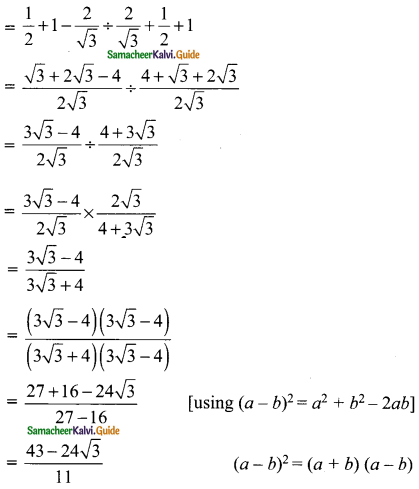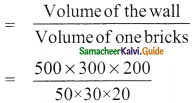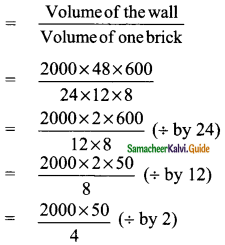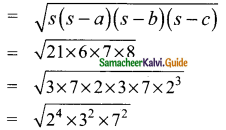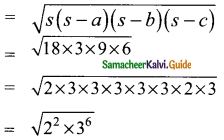Students can download Maths Chapter 8 Statistics Ex 8.1 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Statistics Ex 8.1
Question 1.
In a week, temperature of a certain place is measured during winter are as follows 26°C, 24°C, 28°C, 31°C, 30°C, 26°C, 24°C. Find the mean temperature of the week.
Solution:
Mean temperature of the week

= 27°C
Mean temperature of the week 27° C
![]()
Question 2.
The mean weight of 4 members of a family is 60 kg. Three of them have the weight 56 kg, 68 kg and 72 kg respectively. Find the weight of the fourth member.
Solution:
Weight of 4 members = 4 × 60 kg
= 240 kg
Weight of three members = 56 kg + 68 kg + 72 kg
= 196 kg
Weight of the fourth member = 240 kg – 196 kg
= 44 kg
![]()
Question 3.
In a class test in mathematics, 10 students scored 75 marks, 12 students scored 60 marks, 8 students scored 40 marks and 3 students scored 30 marks. Find the mean of their score.
Solution:
Total marks of 10 students = 10 × 75 = 750
Total marks of 12 students = 12 × 60 = 720
Total marks of 8 students = 8 × 40 = 320
Total marks of 3 students = 3 × 30 = 90
Total marks of (10 + 12 + 8 + 3) 33 students
= 750 + 720 + 320 + 90
= 1880
Mean of marks = \(\frac{1880}{33}\)
= 56.97 (or) 57 approximately
Aliter:
Total number of students = 10+12 + 8 + 3
= 33
Mean of their marks
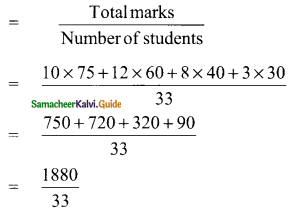
= 56.97 (or) 57 approximately
![]()
Question 4.
In a research laboratory scientists treated 6 mice with lung cancer using natural medicine. Ten days later, they measured the volume of the tumor in each mouse and given the results in the table.

find the mean.
Solution:
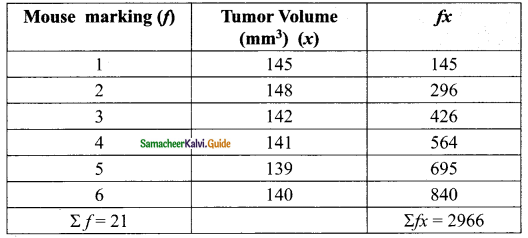
\(\bar { x }\) = \(\frac{Σfx}{Σf}\)
= \(\frac{2966}{21}\)
= 141.238
= 141.24
The Arithmetic mean = 141.24 mm³
![]()
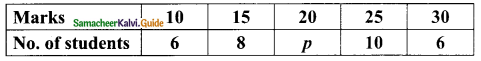
Question 5.
If the mean of the following data is 20.2, then find the value of p.
Solution:
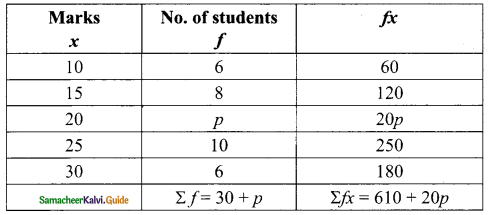
\(\bar { x }\) = \(\frac{Σfx}{Σf}\)
20.2 = \(\frac{610+20p}{30+p}\)
610 + 20 p = 20.2 (30 + p)
610 + 20 p = 606 + 20.2 p
610 – 606 = 20.2 p – 20 p
4 = 0.2 p
p = \(\frac{4}{0.2}\)
= \(\frac{4×10}{2}\)
= 20
The value of p = 20
Question 6.
In the class, weight of students is measured for the class records. Calculate mean weight of the class students using direct method.

Solution:
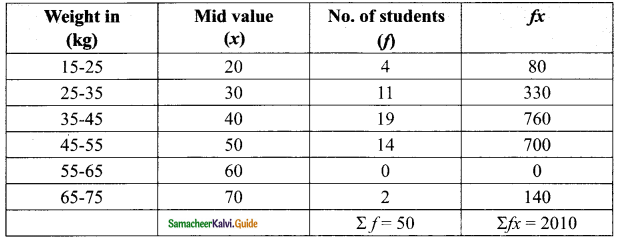
Arithmetic mean \(\bar { x }\) = \(\frac{Σfx}{Σf}\)
= \(\frac{2010}{50}\)
= 40.2
Arithmetic mean = 40.2
![]()
Question 7.
Calculate the mean of the following distribution using Assumed Mean Method.

Solution:
Assumed Mean (A) = 25
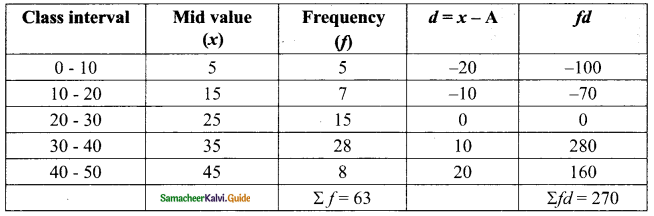
Arithmetic mean (\(\bar { x }\)) = A+\(\frac{Σfd}{Σf}\)
= 25 + \(\frac{270}{63}\)
= 25 + 4. 29
Assumed Mean = 29.29
![]()
Question 8.
Find the Arithmetic Mean of the following data using Step Deviation Method:

Solution:
Assumed Mean (A) = 32
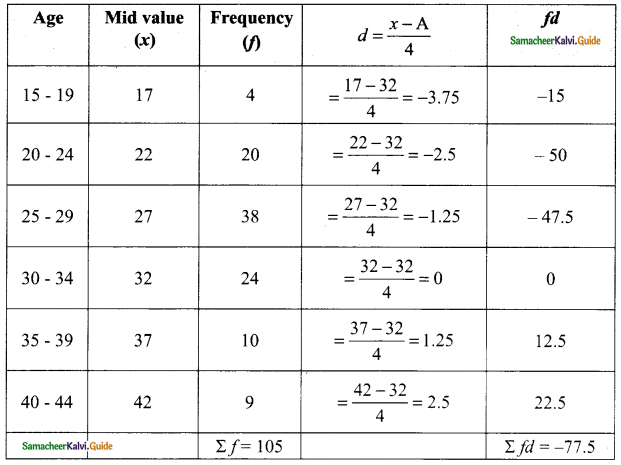
Arithmetic mean = A+\(\frac{Σfd}{Σf}\) × c
= 32 + (\(\frac{-77.5}{105}\)×4)
= 32 – 2.95
= 29.05
Arithmetic mean = 29.05