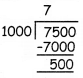
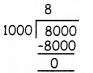
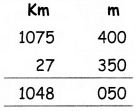
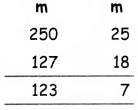
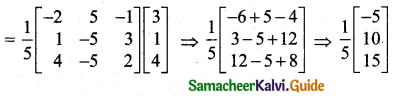
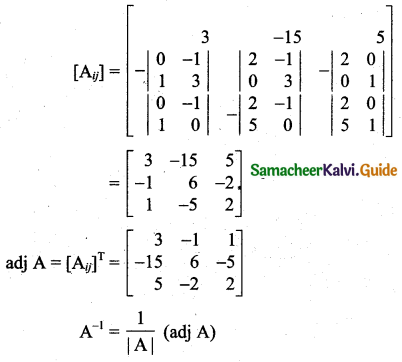
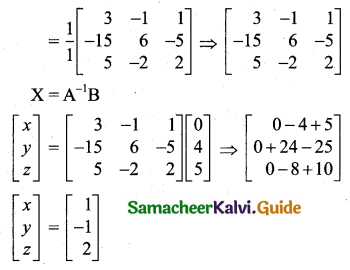
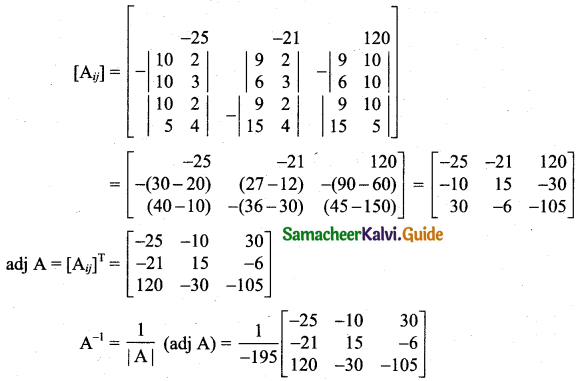
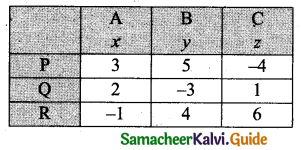
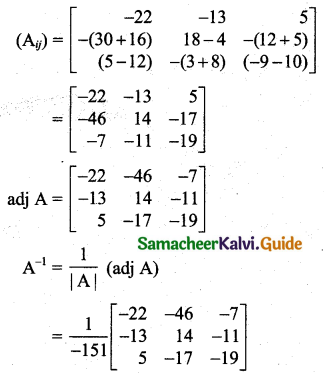
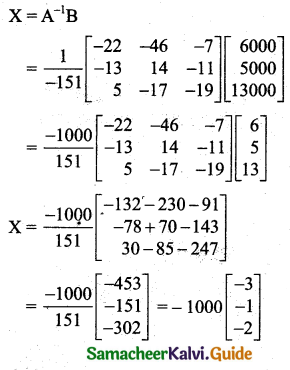
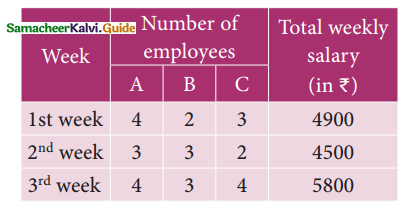
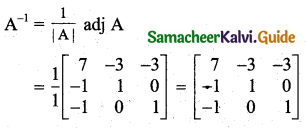
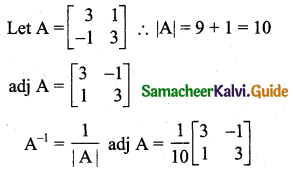
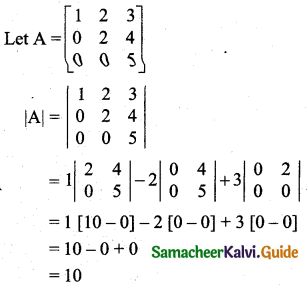
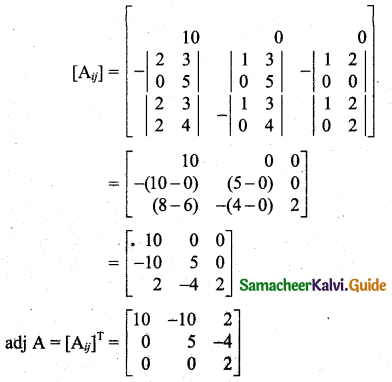
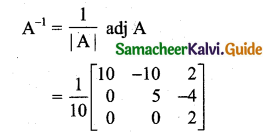
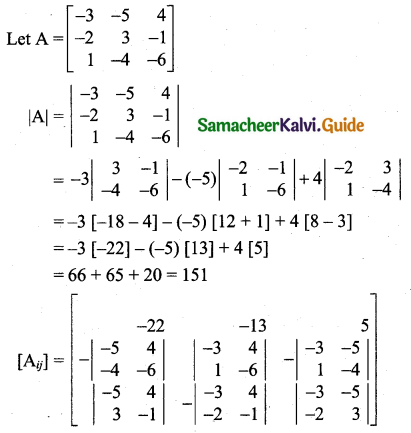
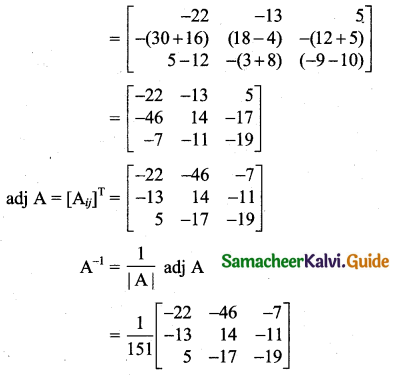
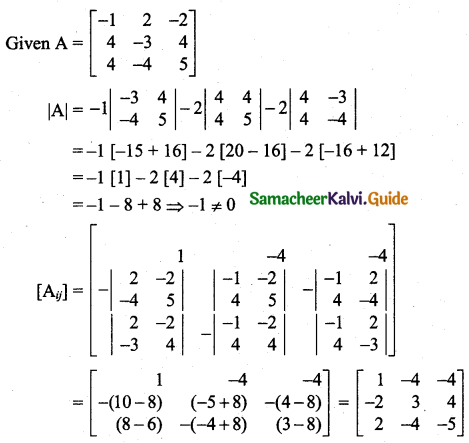
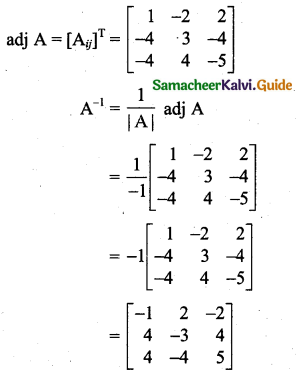
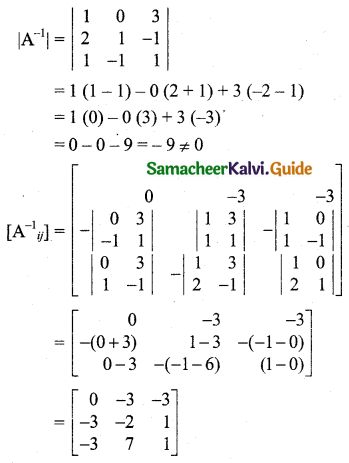
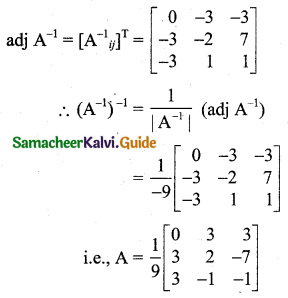
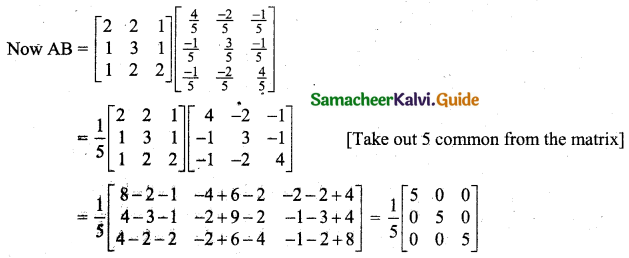
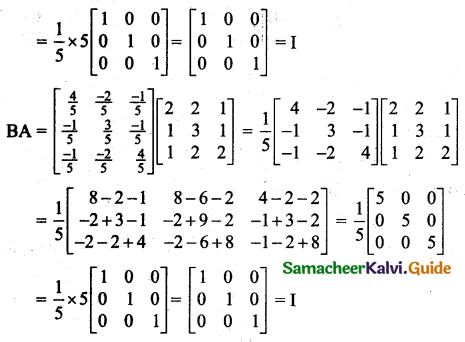
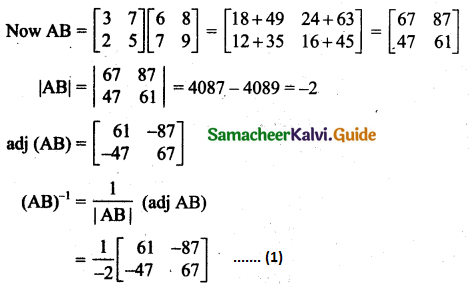
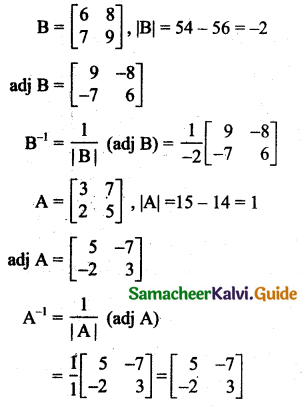
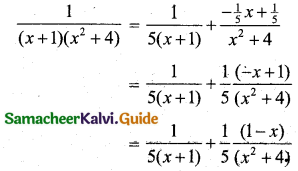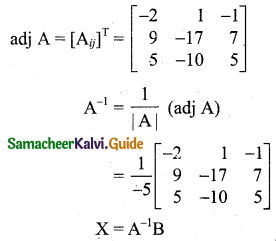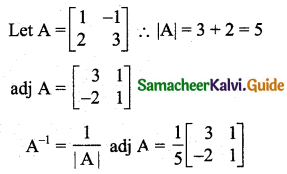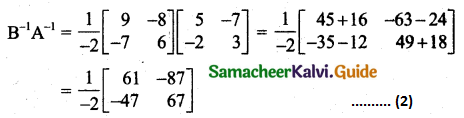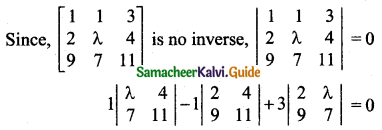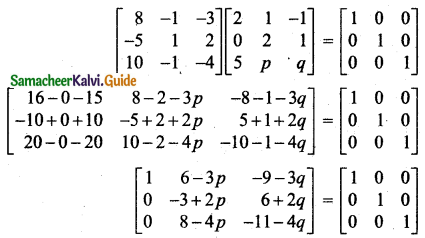Students can download 11th Business Maths Chapter 2 Algebra Ex 2.1 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samcheer Kalvi 11th Business Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Algebra Ex 2.1
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Business Maths Algebra Ex 2.1 Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Resolve into partial fractions for the following:
Question 1.
\(\frac{3 x+7}{x^{2}-3 x+2}\)
Solution:
Here the denominator x2 – 3x + 2 is not a linear factor.
So if possible we have to factorise it then only we can split up into partial fraction.
x2 – 3x + 2 = (x – 1) (x – 2)
\(\frac{3 x+7}{(x-1)(x-2)}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{x-2}\) …….. (1)
Multiply both side by (x – 1) (x – 2)
3x + 7 = A(x – 2) + B(x – 1) …….. (2)
Put x = 2 in (2) we get
3(2) + 7 = A(2 – 2) + B(2 – 1)
6 + 7 = 0 + B(1)
∴ B = 13
Put x = 1 in (2) we get
3(1) + 7 = A(1 – 2) + B(1 – 1)
3 + 7 = A (-1) + 0
10 = A(-1)
∴ A = -10
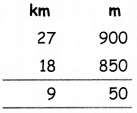
Using A = -10 and B = 13 in (1) we get
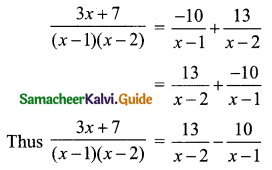
Note: When the denominator is only two linear factors we can adopt the following method.
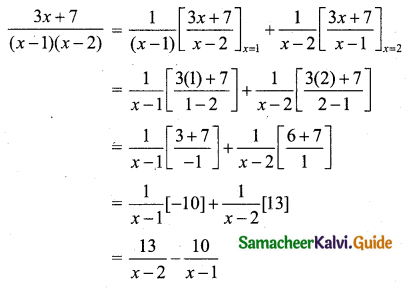
Question 2.
\(\frac{4 x+1}{(x-2)(x+1)}\)
Solution:
Let \(\frac{4 x+1}{(x-2)(x+1)}=\frac{A}{x-2}+\frac{B}{x+1}\) ……… (1)
Multiply both sides by (x – 2) (x + 1) we get
4x + 1 = A(x + 1) + B(x – 2) ……. (2)
Put x = -1 in (2) we get
4(-1) + 1 = A(-1 + 1) + B(-1 – 2)
-4 + 1 = A(0) + B(-3)
-3 = B(-3)
B = \(\frac{-3}{-3}\) = 1
Put x = 2 in (2) we get
4(2) + 1 = A(2 + 1) + B(2 – 2)
8 + 1 = A(3) + B(0)
9 = 3A
A = 3
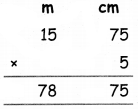
Using A = 3, B = 1 in (1) we get
\(\frac{4 x+1}{(x-2)(x+1)}=\frac{3}{x-2}+\frac{1}{x+1}\)
![]()
Question 3.
\(\frac{1}{(x-1)(x+2)^{2}}\)
Solution:
Here the denominator has repeated factors. So we write
\(\frac{1}{(x-1)(x+2)^{2}}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{(x+2)}+\frac{C}{(x+2)^{2}}\) …… (1)
Multiply both sides by (x – 1) (x + 2)2 we get
1 = A(x + 2)2 + B(x – 1) (x + 2) + C(x – 1) …… (2)
Put x = 1 in (2) we get
1 = A(1 + 2)2 + B(1 – 1) (1 + 2) + C(1 – 1)
1 = A(32) + 0 + 0
1 = 9A
A = \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Put x = -2 in (2) we get
1 = A(-2 + 2)2 + B(-2 – 1) (-2 + 2) + C(-2 – 1)
1 = 0 + 0 + C(-3)
C = \(\frac{-1}{3}\)
From (2) we have
1 = A(x + 2)2 + B(x – 1) (x + 2) + C(x – 1)
0x2 + 1 = A(x2 + 4x + 4) + B(x2 + x – 2) + C(x – 1)
Equating coefficient of x2 on both sides we get
0 = A + B
0 = \(\frac{1}{9}\) (∴ A = \(\frac{1}{9}\))
B = \(-\frac{1}{9}\)
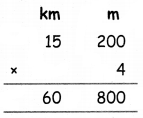
Using A = \(\frac{1}{9}\), B = \(-\frac{1}{9}\), C = \(-\frac{1}{3}\) in (1) we get,
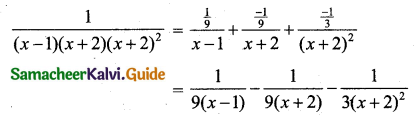
Question 4.
\(\frac{1}{x^{2}-1}\)
Solution:
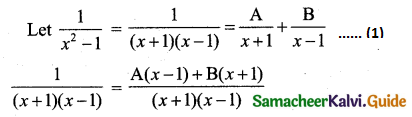
1 = A(x – 1) + B(x + 1) ……. (2)
Put x = 1 in (2) we get
1 = 0 + B(1 + 1)
1 = B(2)
B = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Put x = -1 in (2) we get
1 = A(-1 – 1) + B(-1 + 1)
1 = -2A + 0
A = \(\frac{-1}{2}\)
Using A = \(\frac{-1}{2}\), B = \(\frac{1}{2}\) in (1) we get
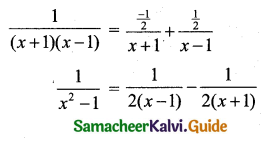
Question 5.
\(\frac{x-2}{(x+2)(x-1)^{2}}\)
Solution:
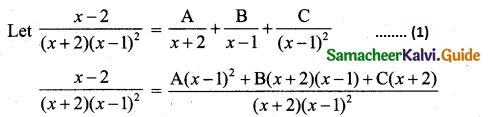
x – 2 = A(x – 1)2 + B(x + 2) (x – 1) + C(x + 2) ……(2)
Put x = 1 in (2) we get
1 – 2 = A(1 – 1)2 + B(1 + 2) (1 – 1) + C(1 + 2)
-1 = 0 + 0 + 3C
C = \(-\frac{1}{3}\)
Put x = -2 in (2) we get
-2 – 2 = A(-2 – 1)2 + B(-2 + 2) (-2 – 1) + C(-2 + 2)
-4 = A(-3)2 + 0 + 0
-4 = 9A
A = \(\frac{-4}{9}\)
From (2) we have,
0x2 + x – 2 = A(x – 1)2 + B(x + 2) (x – 1) + C(x + 2)
Equating coefficients of x2 on both sides we get
0 = A + B
0 = \(\frac{-4}{9}\) + B (∵ A = \(\frac{-4}{9}\))
B = \(\frac{4}{9}\)
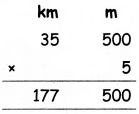
Using A = \(\frac{-4}{9}\), B = \(\frac{4}{9}\), C = \(-\frac{1}{3}\) in (1) we get
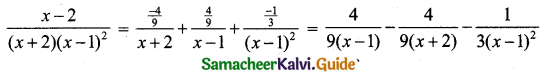
![]()
Question 6.
\(\frac{2 x^{2}-5 x-7}{(x-2)^{3}}\)
Solution:
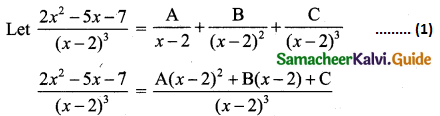
2x2 – 5x – 7 = A(x – 2)2 + B(x – 2) + C
2x2 – 5x – 7 = A(x2 – 4x + 4) + B(x – 2) + C …….. (2)
Put x = 2 in (2) we get
2(22) – 5(2) – 7 = A(0) + B(0) + C
8 – 10 – 7 = 0 + 0 + C
-9 = C
C = -9
Equating coefficient of x2 on both sides of (2) we get
2 = A
A = 2
Equating coefficient of x on both sides of (2) we get
-5 = A(-4) + B(1)
-5 = 2(-4) + B(∵ A = 2)
-5 = -8 + B
B = 8 – 5 = 3
Using A = 2, B = 3, C = -9 in (1) we get
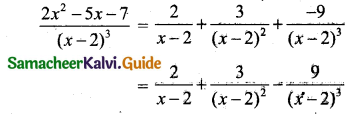
Question 7.
\(\frac{x^{2}-6 x+2}{x^{2}(x+2)}\)
Solution:
Here the denominator has three factors. So given fraction can be expressed as a sum of three simple fractions.
Let \(\frac{x^{2}-6 x+2}{x^{2}(x+2)}=\frac{A}{x}+\frac{B}{x^{2}}+\frac{C}{x+2}\) …… (1)
Multiply both sides by x2 (x + 2) we get
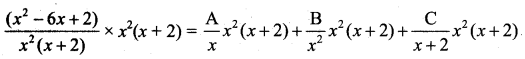
x2 – 6x + 2 = Ax(x + 2) + B(x + 2) + C(x2) ……… (2)
Put x = 0 in (2) we get
0 – 0 + 2 = 0 + B(0 + 2) + 0
2 = B(2)
B = 1
Put x = -2 in (2) we get
(-2)2 – 6(-2) + 2 = 0 + 0 + C(-2)2
4 + 12 + 2 = C(4)
18 = 4C
C = \(\frac{9}{2}\)
Comparing coefficient of x2 on both sides of (2) we get,
1 = A + C
1 = A + \(\frac{9}{2}\)
A = 1 – \(\frac{9}{2}\) = \(\frac{2-9}{2}=\frac{-7}{2}\)
Using A = \(\frac{-7}{2}\), B = 1, C = \(\frac{9}{2}\) in (1) we get,
\(\frac{\left(x^{2}-6 x+2\right)}{x^{2}(x+2)}=\frac{-7}{2 x}+\frac{1}{x^{2}}+\frac{9}{2(x+2)}\)
![]()
Question 8.
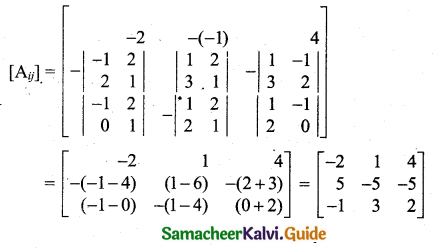
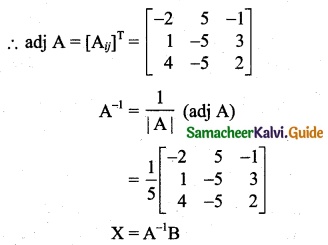
\(\frac{x^{2}-3}{(x+2)\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\)
Solution:
Here the quadratic factor x2 + 1 is not factorisable.
Let \(\frac{x^{2}-3}{(x+2)\left(x^{2}+1\right)}=\frac{A}{x+2}+\frac{(B x+C)}{x^{2}+1}\) ….. (1)
Multiply both sides by (x + 2) (x2 + 1) we get,
x2 – 3 = A(x2 + 1) + (Bx + C) (x + 2)
Put x = -2 we get
(-2)2 – 3 = [A(-2)2 + 1] + 0
4 – 3 = A(4 + 1)
1 = 5A
A = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Equating coefficient of x2 on both sides of (2) we get
1 = A + B
1 = \(\frac{1}{5}\) + B
B = 1 – \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Equating coefficients of x on both sides of (2) we get
0 = 2B + C
0 = 2(\(\frac{4}{5}\)) + C
C = \(\frac{-8}{5}\)
Using A, B, C’s values in (1) we get
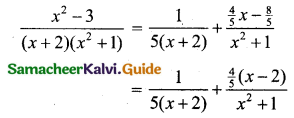
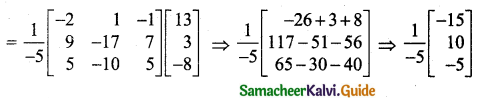
Question 9.
\(\frac{x+2}{(x-1)(x+3)^{2}}\)
Solution:
Here the denominator has three factors. So given fraction can be expressed as a sum of three simple fractions.
Let \(\frac{x+2}{(x-1)(x+3)^{2}}=\frac{A}{x-1}+\frac{B}{x+3}+\frac{C}{(x+3)^{2}}\) ……. (1)
Multiply both sides by (x – 1) (x + 3)2 we get
\(\frac{x+2}{(x-1)(x+3)^{2}}\) (x – 1) (x + 3)2 = \(\frac{A}{x-1}\) (x – 1) (x + 3)2 +
\(\frac{B}{x+3}\) (x – 1) (x + 3)2 + \(\frac{C}{(x+3)^{2}}\) (x – 1) (x + 3)2
x + 2 = A(x + 3)2 + B(x – 1) (x + 3) + C(x – 1) ……. (2)
Put x = 1 in (2) we get
1 + 2 = A(1 + 3)2 + 0 + 0
3 = A(4)2
A = \(\frac{3}{16}\)
Put x = -3 in (2) we get
-3 + 2 = 0 + 0 + C(-3 – 1)
-1 = C(-4)
C = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Comparing coefficient of x2 on both sides of (2) we get,
0 = A + B
0 = \(\frac{3}{16}\) + B
B = \(-\frac{3}{16}\)
Using A = \(\frac{3}{16}\), B = \(-\frac{3}{16}\), C = \(\frac{1}{4}\) in (1) we get,
\(\frac{x+2}{(x-1)(x+3)^{2}}=\frac{3}{16(x-1)}-\frac{3}{16(x+3)}+\frac{1}{4(x+3)^{2}}\)
![]()
Question 10.
\(\frac{1}{\left(x^{2}+4\right)(x+1)}\)
Solution:
Here the quadratic factor x2 + 4 is not factorisable.
Let \(\frac{1}{(x+1)\left(x^{2}+4\right)}=\frac{A}{x+1}+\frac{B x+C}{x^{2}+4}\) ……. (1)
Multiply both sides by (x + 1) (x2 + 4) we get
1 = A(x2 + 4) + (Bx + C) (x + 1) ……. (2)
Put x = -1 in (2) we get
1 = A((-1)2 + 4) + 0
1 = A(1 + 4)
A = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Equating coefficient of x2 on both sides of (2) we get,
0 = A + B
0 = \(\frac{1}{5}\) + B
B = \(\frac{-1}{5}\)
Equating coefficient of x on both sides of (2) we get,
{∵ (Bx + C) (x + 1) = Bx2 + Cx = Bx + C}
0 = B + C
0 = \(\frac{-1}{5}\) + C
C = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Using A = \(\frac{1}{5}\), B = \(\frac{-1}{5}\), C = \(\frac{1}{5}\) we get,