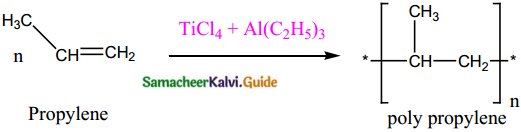
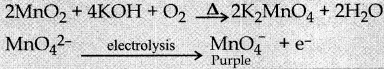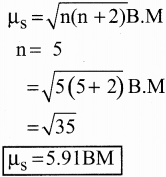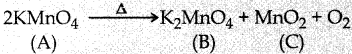Subject Matter Experts at SamacheerKalvi.Guide have created Samacheer Kalvi Tamil Nadu State Board Syllabus New Paper Pattern 11th Physics Model Question Papers 2020-2021 with Answers Pdf Free Download in English Medium and Tamil Medium of TN 11th Standard Physics Public Exam Question Papers Answer Key, New Paper Pattern of HSC 11th Class Physics Previous Year Question Papers, Plus One +1 Physics Model Sample Papers are part of Tamil Nadu 11th Model Question Papers.
Let us look at these Government of Tamil Nadu State Board 11th Physics Model Question Papers Tamil Medium with Answers 2020-21 Pdf. Students can view or download the Class 11th Physics New Model Question Papers 2021 Tamil Nadu English Medium Pdf for their upcoming Tamil Nadu HSC Board Exams. Students can also read Tamilnadu Samcheer Kalvi 11th Physics Guide.
TN State Board 11th Physics Model Question Papers 2020 2021 English Tamil Medium
Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Papers English Medium 2020-2021
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 2 English Medium
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Papers Tamil Medium 2020-2021
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 1 Tamil Medium
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 2 Tamil Medium
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 3 Tamil Medium
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 4 Tamil Medium
- Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 5 Tamil Medium
11th Physics Model Question Paper Design 2020-2021 Tamil Nadu
| Types of Questions | Marks | No. of Questions to be Answered | Total Marks |
| Part-I Objective Type | 1 | 15 | 15 |
| Part-II Very Short Answers (Totally 9 questions will be given. Answer any Six. Any one question should be answered compulsorily) |
2 | 6 | 12 |
| Part-Ill Short Answers (Totally 9 questions will be given. Answer any Six. Any one question should be answered compulsorily) |
3 | 6 | 18 |
| Part-IV Essay Type | 5 | 5 | 25 |
| Total | 70 | ||
| Practical Marks + Internal Assessment (20+10) | 30 | ||
| Total Marks | 100 | ||
Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper Weightage of Marks
| Purpose | Weightage |
| 1. Knowledge | 30% |
| 2. Understanding | 40% |
| 3. Application | 20% |
| 4. Skill/Creativity | 10% |
It is necessary that students will understand the new pattern and style of Model Question Papers of 11th Standard Physics Tamilnadu State Board Syllabus according to the latest exam pattern. These Tamil Nadu Plus One 11th Physics Model Question Papers State Board Tamil Medium and English Medium are useful to understand the pattern of questions asked in the board exam. Know about the important concepts to be prepared for TN HSLC Board Exams and Score More marks.
We hope the given Samacheer Kalvi Tamil Nadu State Board Syllabus New Paper Pattern Class 11th Physics Model Question Papers 2020 2021 with Answers Pdf Free Download in English Medium and Tamil Medium will help you get through your subjective questions in the exam.
Let us know if you have any concerns regarding the Tamil Nadu Government 11th Physics State Board Model Question Papers with Answers 2020 21, TN 11th Std Physics Public Exam Question Papers with Answer Key, New Paper Pattern of HSC Class 11th Physics Previous Year Question Papers, Plus One +1 Physics Model Sample Papers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.