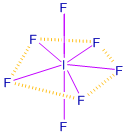
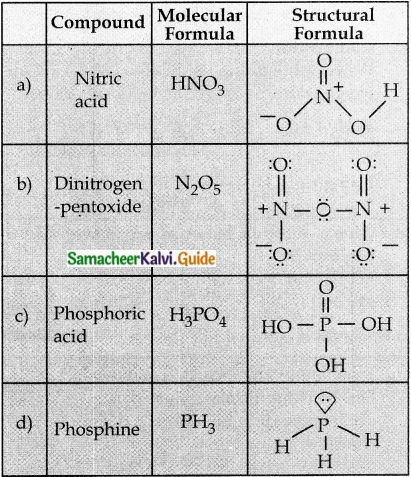
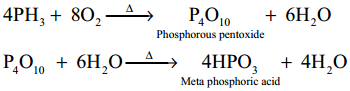
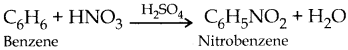
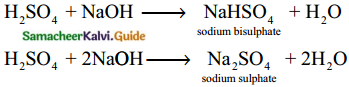
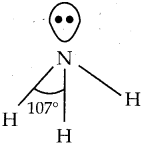
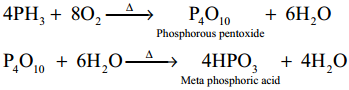
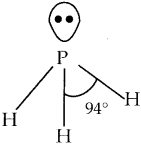
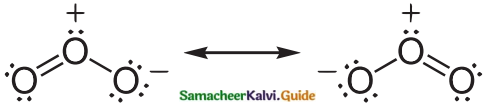
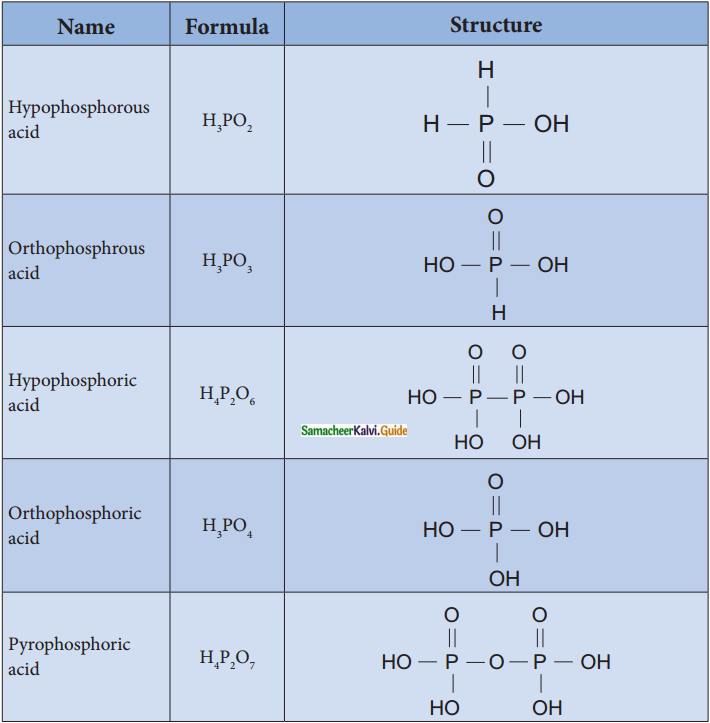
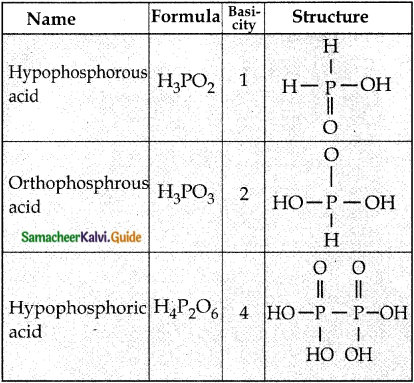
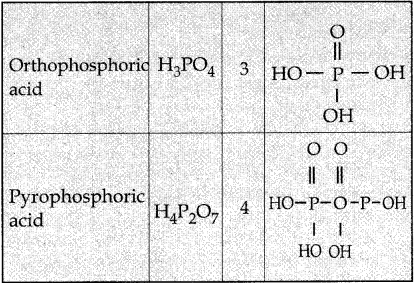
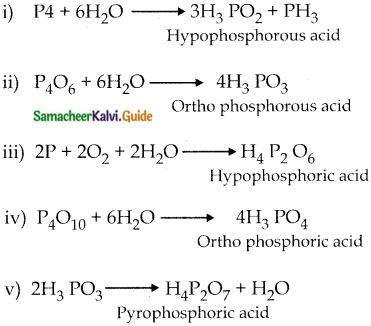
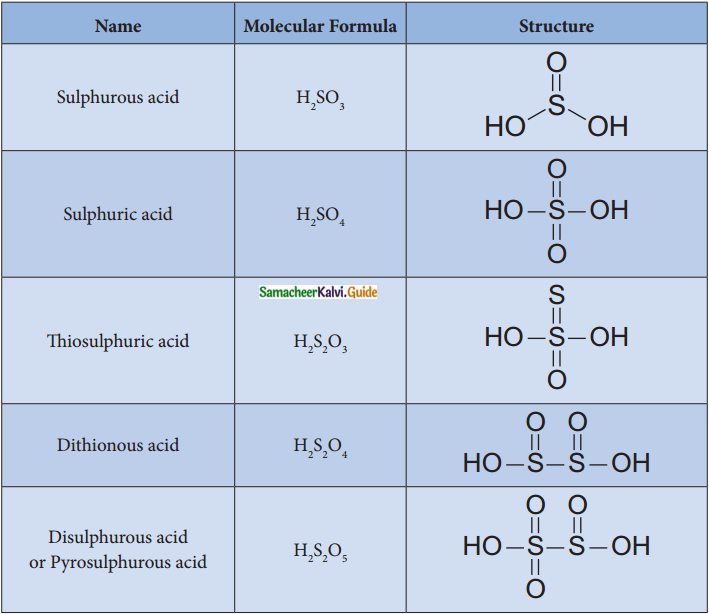
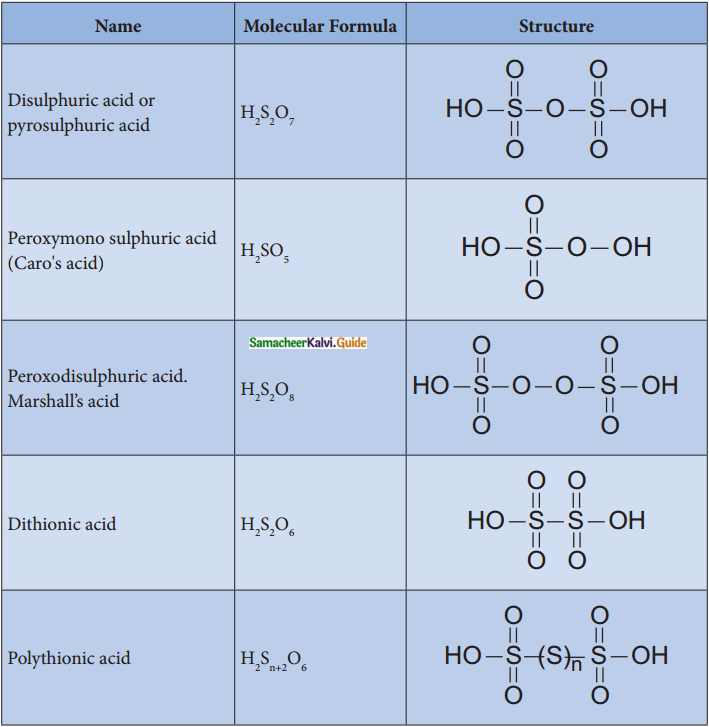
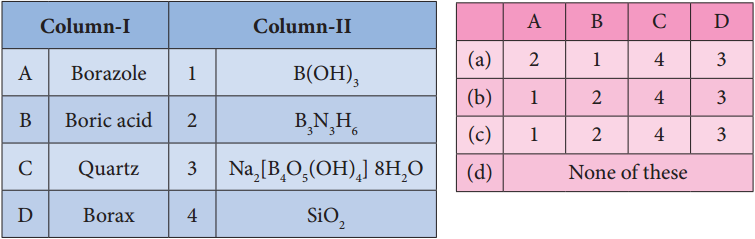
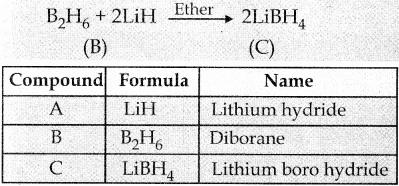
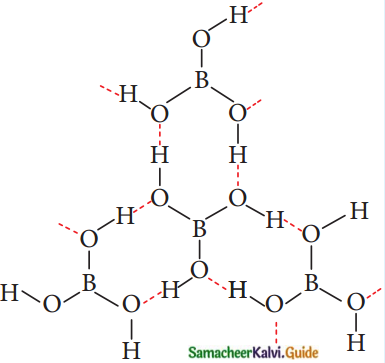
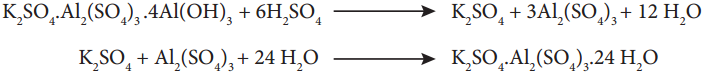
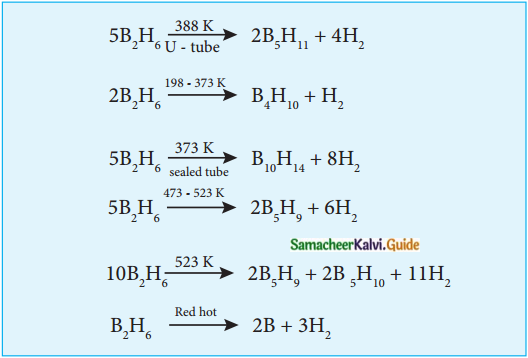
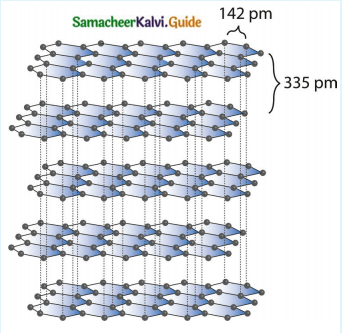
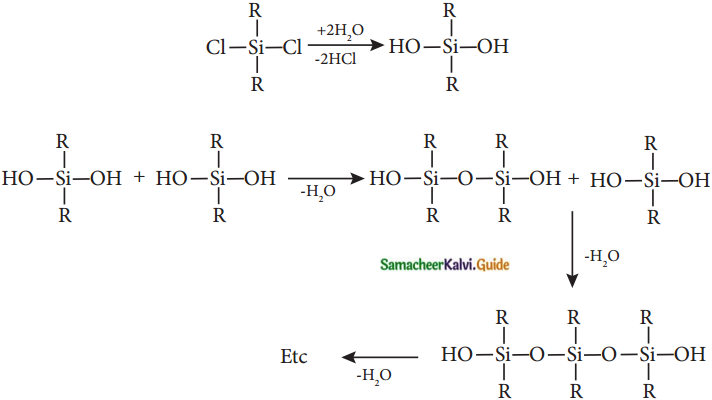
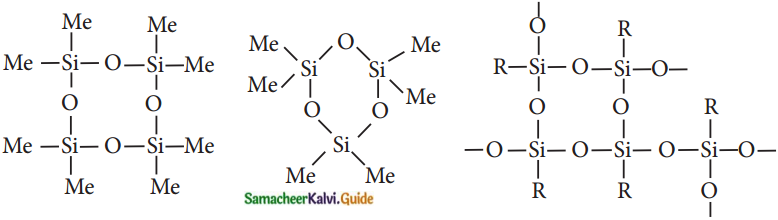
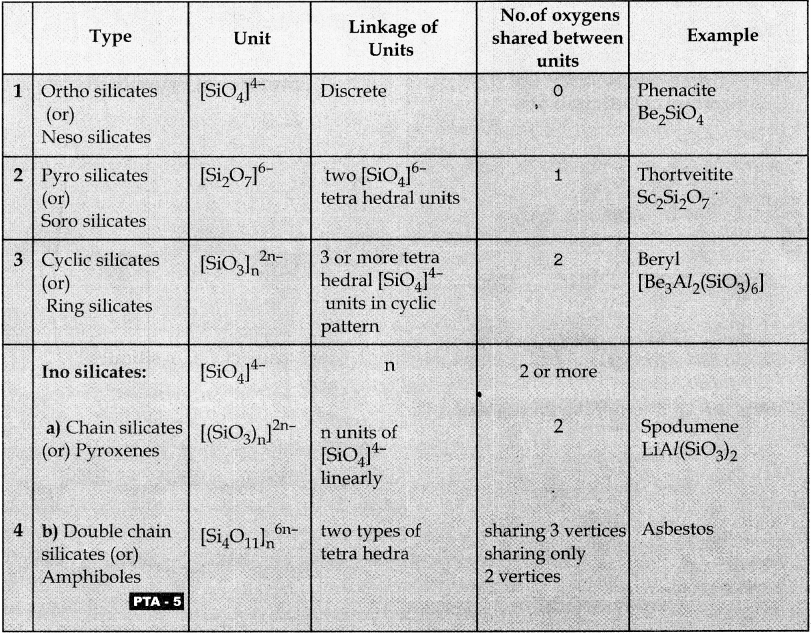
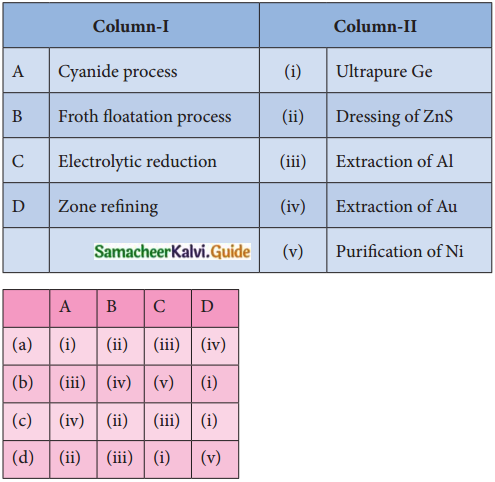
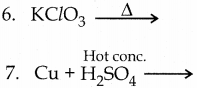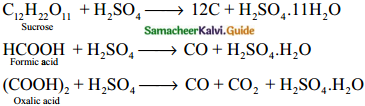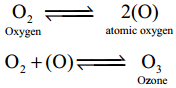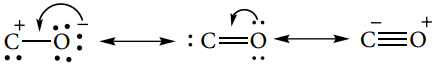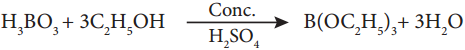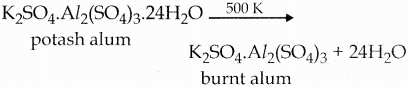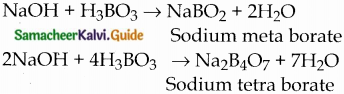Subject Matter Experts at SamacheerKalvi.Guide have created Tamilnadu State Board Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Answers Solutions Guide Pdf Free Download in English Medium and Tamil Medium are part of Samacheer Kalvi 12th Books Solutions.
Let us look at these TN Board Samacheer Kalvi 12th Std Accountancy Guide Pdf of Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes, Chapter Wise Important Questions, Model Question Papers with Answers, Study Material, Question Bank, Formulas and revise our understanding of the subject.
Students can also read Tamil Nadu 12th Accountancy Model Question Papers 2020-2021 English & Tamil Medium.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Book Solutions Answers Guide
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Back Answers
Tamilnadu State Board Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Book Back Answers Solutions Guide.
- Chapter 1 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- Chapter 2 Accounts of Not-For-Profit Organisation
- Chapter 3 Accounts of Partnership Firms-Fundamentals
- Chapter 4 Goodwill in Partnership Accounts
- Chapter 5 Admission of a Partner
- Chapter 6 Retirement and Death of a Partner
- Chapter 7 Company Accounts
- Chapter 8 Financial Statement Analysis
- Chapter 9 Ratio Analysis
- Chapter 10 Computerised Accounting System-Tally
We hope these Tamilnadu State Board Class 12th Accountancy Book Solutions Answers Guide Pdf Free Download in English Medium and Tamil Medium will help you get through your subjective questions in the exam.
Let us know if you have any concerns regarding TN State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Standard Accountancy Guide Pdf Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes, Chapter Wise Important Questions, Model Question Papers with Answers, Study Material, Question Bank, Formulas, drop a comment below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.