Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Guide Pdf Chapter 9 Ratio Analysis Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 9 Ratio Analysis
12th Accountancy Guide Ratio Analysis Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The mathematical expression that provides a measure of the relationship between two figures is called
(a) Conclusion
(b) Ratio
(c) Model
(d) Decision
Answer:
(b) Ratio
Question 2.
Current ratio indicates
(a) Ability to meet short term obligations
(b) Efficiency of management
(c) Profitability
(d) Long term solvency
Answer:
(a) Ability to meet short term obligations
![]()
Question 3.
Current assets excluding inventory and prepaid expenses is called
(a) Reserves
(b) Tangible assets
(c) Funds
(d) Quick assets
Answer:
(d) Quick assets
Question 4.
Debt equity ratio is measure of
(a) Short term solvency
(b) Long term solvency
(c) Profitability
(d) Efficiency
Answer:
(b) Long term solvency
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following is not a tool of financial statement analysis?
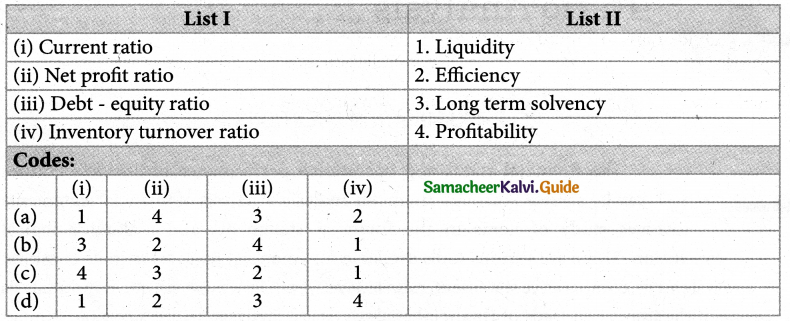
Answer:
(a) (i) – 1,(ii) – 4,(iii) – 3,(iv) – 2
Question 6.
To test the liquidity of a concern, which of the following ratios are useful?
(i) Quick ratio
(ii) Net Profit ratio
(iii) Debt – equity ratio
(d) Current ratio
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and iv)
Answer:
(b) (i) and (iv)
![]()
Question 7.
Proportion of share holders’ funds to total assets is called
(a) Proprietary ratio
(b) Capital gearing ratio
(c) Debt equity ratio
(d) Current ratio
Answer:
(a) Proprietary ratio
Question 8.
Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) Liquid ratio – Proportion
(b) Gross profit ratio – Percentage
(c) Fixed assets turnover ratio – Percentage
(d) Debt – equity ratio – Proportion
Answer:
(c) Fixed assets turnover ratio – Percentage
Question 9.
Current liabilities ₹ 40,000; Current assets ₹ 1,00,000; Inventory ₹ 20,000. Quick ratio is
(a) 1:1
(b) 2,5:1
(c) 2:1
(d) 1:2
Hint:
Quick ratio or Liquid ratio = \(\frac{\text { Liquid Assets }}{\text { Current liabilities }}\)
Liquid assets = Current Assets – Inventory
= 1,00,000 – 20,000
= 80,000
= \(\frac{80,000}{40,000}\)
= 2:1
= 110%
Answer:
(c) 2:1
![]()
Question 10.
Cost of revenue from operation 3,00,000; Inventory at the beginning of the year 60,000; Inventory at the close of the year’ 40,000. Inventory turnover ratio is.
(a) 2 times
(b) 3 times
(c) 6 times
(d) 8 times
Hint:

Answer:
(c) 6 times
II Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by accounting ratios?
Answer:
The ratio is a mathematical expression of the relationship between two related or interdependent items. It is the numerical or quantitative relationship between two items. It is calculated by dividing one item by the other related item. When ratios are calculated on the basis of accounting information, these are called ‘accounting ratios’.
Question 2.
What is the quick ratio?
Answer:
The quick ratio gives the proportion of quick assets to current liabilities. It indicates whether the business concern is in a position to pay its current liabilities and when they become due, out of its quick assets.
Question 3.
What is meant by debt-equity ratio?
Answer:
It is calculated to assess the long-term solvency position of a business concern. The debt equity ratio expresses the relationship between long term debt and shareholder’s funds.
Debt equity ratio = \(\frac{\text { Long term debt }}{\text { Shareholders funds }}\)
Capital employed = Shareholder’s funds + Noncurrent liabilities
Greater the return on investment better is than the profitability of a business and vice versa.
![]()
Question 4.
What does the return on investment ratio indicate?
Answer:
Return on investment shows the proportion of net profit before interest and tax to capital employed (shareholders’ funds and long term debts). This ratio measures how efficiently the capital employed is used in the business. It is an overall measure of the profitability of a business concern.
Question 5.
Statement any two limitations of ratio analysis.
Answer:
Ratios are only means: Ratios are not ended in themselves but they are only means to achieve a particular purpose. Analysis of related items must be done by the management or experts with the help of ratios. Change in price level: Ratio analysis may not reflect price level changes and current values as they are calculated based on historical data given in the financial statement.
![]()
III Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the objectives of ratio analysis.
Answer:
Following are the objectives of ratio analysis:
- To simplify accounting figures
- To facilitate analysis of financial statements
- To analysis the operational efficiency of a business
- To help in budgeting and forecasting
- To facilitate intra firm and inter-firm comparison of performance
Question 2.
What is the inventory conversion period? How is it calculated?
Answer:
The inventory conversion period is the time taken to sell the inventory. A shorter inventory conversion period indicates more efficiency in the management of inventory. It is computed as follows:
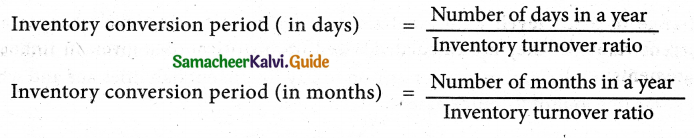
Question 3.
How is operating profit ascertained?
Answer:
Operating profit = Revenue from operations – Operating cost
Cost of revenue from operations = Purchases of stock – in – trade + Change in inventories of stock in trade + Direct expenses.
Operating expenses = Administrative expenses + Selling and distribution expenses.
Operating cost = Cost of revenue from operations + Operating expenses.
![]()
Question 4.
State any three advantages of ratio analysis.
Answer:
Following are the advantage of ratio analysis:
- Measuring operational efficiency: Ratio analysis helps to know the operational efficiency of a business by finding the relationship between operating cost and revenues and also by comparison of present ratios with those of the past ratios.
- Intra firm comparison: Comparison of the efficiency of different divisions of an organization is possible by comparing the relevant ratios.
- Inter-firm comparison: Ratio analysis helps the firm to compare its performance with other firms.
Question 5.
Bring out the limitations of ratio analysis:
Answer:
- Consistency in preparation of financial statements: Inter firm comparisons with the help of ratio analysis will be meaningful only if the firms follow uniform accounting procedures consistently.
- Non-availability of standards or norms: Ratios will be meaningful only if they are compared with accepted standards or norms. Only few financial ratios have universally recognized standards. For other ratios, comparison with standards is not possible.
- Change in price level: Ratio analysis may not reflect price level changes and current values as they are calculated based on historical data given in financial statements.
![]()
IV Exercises
Liquidity ratios
Question 1.
Calculate the current ratio from the following information.
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | ₹ |
| Current investments | 40,000 | Fixed assets | 5,00,000 |
| Inventories | 2,00,000 | Trade creditors | 80,000 |
| Trade debtors | 1,20,000 | Bills Payable | 50,000 |
| Bills receivable | 80,000 | Expenses payable | 20,000 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 10,000 | Non-Current liability | 3,00,000 |
Solution:
Current ratio = \(\frac{\text { Current Assets }}{\text { Current liabilities }}\)
Current Assets = Current Investments + Inventories + Trade Dr’s + B/R+Cash & Cash equivalents
= 40,000 + 2,00,000 + 1,20,000 + 80,000 + 10,000
= Rs. 4,50,000
Current Liabilities
= Trade Cr’s + B/P + Exps. Payable.
= 80,000 + 50,000 + 20,000
= Rs. 1,50,000
Cur. Ratio = \(\frac{4,50,000}{1,50,000}\)
= 3:1
Answer:
Current ratio : 3:1
Question 2.
Calculate quick ratio: Total current liabilities ₹ 2,40,000; total current assets ₹ 4,50,000; Inventories ₹ 70,000; Prepaid Expenses ₹ 20,000
Solution:
Quick Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Quick assets }}{\text { Current liabilities }}\)
Quick assets = Current Assets – Inventories & Prepaid exps.
= 4,50,000 – (70,000 + 2000)
= Rs.3,60,000
Quick Ratio = \(\frac{3,60,000}{2,40,000}\)
=1:5:1
Answer:
Quick ration: 1:5:1
![]()
Question 3.
Following is the balance sheet of Lakshmi Ltd. as of 31st March 2019.
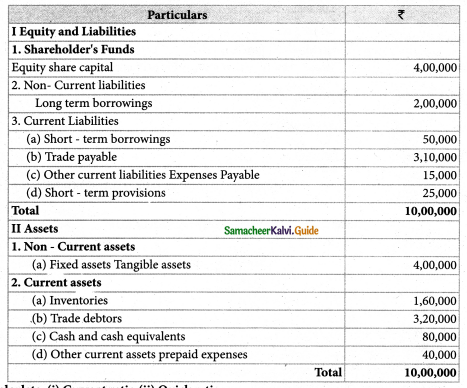
Calculate: (i) Current ratio (ii) Quick ratio
Solution:
Current ratio = \(\frac{\text { Current Assets }}{\text { Current liabilities }}\)
Current Assets = Inventories + Trade Dr’s + Cash & Cash equivalents + Prepaid Exps
= 1,60,000 +3,20,000 + 80,000 + 40,000
= Rs. 6,00,000
Current Liabilities = Short term borrowings + Trade Payable + Expenses payable + Short term provisions.
= 50,000 + 3,10,000 + 15,000 + 25,000
= Rs. 4,00,000
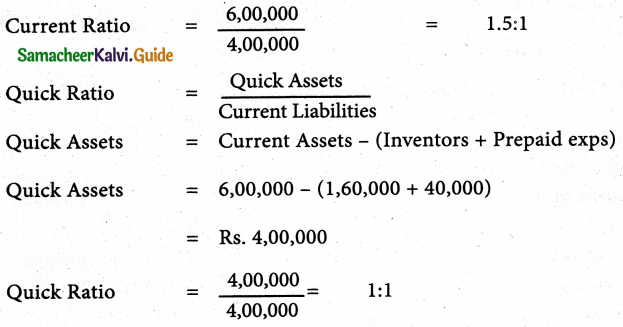
Answer:
(i) Current ratio: 1.5:1;
(ii) Quick ratio: 1:1
![]()
Question 4.
From the following information calculate debt equity ratio.
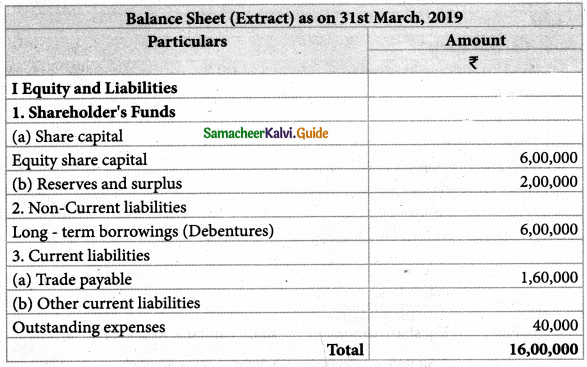
Solution:
Debt Equity Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Long term debt }}{\text { Shareholder’s Funds }}\)
Long term debt = Debenture = Rs. 6,00,000
Shareholder’s Fund = Equity share capital + Reserves & Surplus
= 6,00,000 + 2,00,00 = Rs. 8,00,000
Debt Equity Ratio = \(\frac{6,00,000}{8,00,000}\)
= 0.75:1
Answer:
Debt equity ratio: 0.75:1
Question 5.
From the following Balance Sheet of Sundaram Ltd. Calculate proprietary ratio:
| Balance Sheet of Sundaram Ltd. as on 31.03.2019 | |
| Particulars | Amount ₹ |
| I Equity and Liabilities | |
| 1. Shareholders’ Fund | |
| a) Share capital | |
| (i) Equity share capital | 2,50,000 |
| (ii) Preference share capital | 1,50,000 |
| (b) Reserves and surplus | 50,000 |
| 2. Non – Current Liabilities | |
| Long term borrowings : | |
| 3. Current liabilities | |
| Trade Payable | 1,50,000 |
| Total | 6,00,000 |
| II Assets | |
| 1. Non-Current assets | |
| (a) Fixed Assets | 4,60,000 |
| (b) Non-Current investments | 1 ,00,000 |
| 2. Current assets | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 40,000 |
| Total | 6,00,000 |
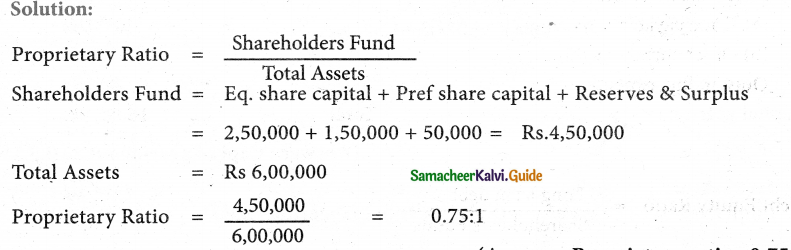
Answer:
Proprietary ratio: 0.75:1
![]()
Question 6.
From the following information calculate the capital gearing ratio:
| Balance Sheet (Extract) as on 31.03.2018 | |
| Particulars | Amount ₹ |
| I Equity and Liabilities | |
| 1. Shareholders Funds | |
| (a) Share capital | |
| Equity share capital | 4,00,000 |
| 5% Preference share capital | 1,00,000 |
| (b) Reserves and surplus | |
| General reserve | 2,50,000 |
| Surplus | 1,50,000 |
| 2. Non-current Liabilities | |
| Long-term borrowings (6% Debentures) | 3,00,000 |
| 3. Current liabilities | |
| Trade payables | 1,20,000 |
| provision for tax | 30,000 |
| Total | 13,50,000 |
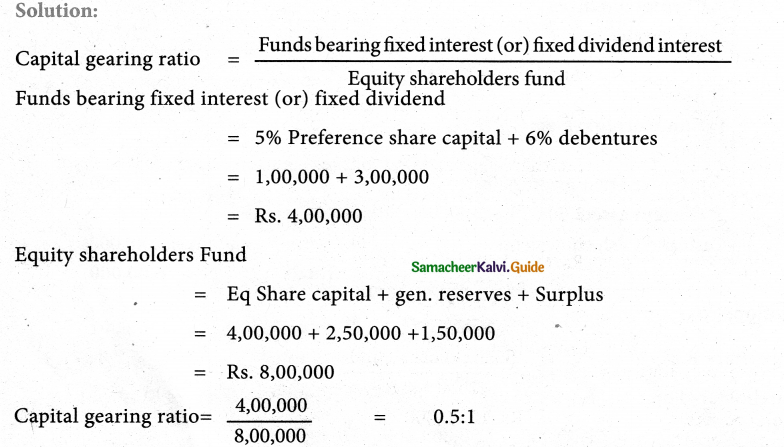
Answer:
Capital gearing ratio: 0.5:1
![]()
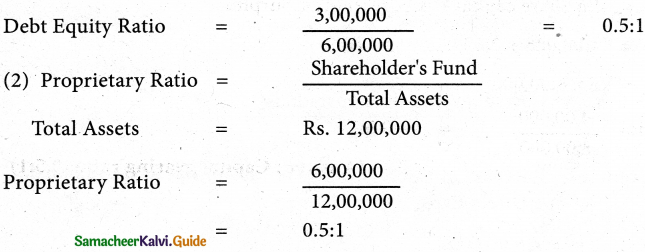
Question 7.
From the following Balance Sheet of James Ltd. as of 31.03.2019 calculate
(i) Debt- Equity ratio
(ii) Proprietary ratio
(iii) Capital gearing ratio
| Balance Sheet (of James Ltd.) as on 31.03.2018 | |
| Particulars | Amount ₹ |
| I Equity and Liabilities | |
| 1. Shareholders Funds | |
| (a) Share capital | |
| Equity share capital | 2,50,000 |
| 6% Preference share capital | 2,00,000 |
| (b) Reserves and surplus | 1,50,000 |
| 2. Current Liabilities | |
| Long –term borrowings(8% Debentures) | 3,00,000 |
| 3. Non-current Liabilities | |
| Short -term borrowings_from banks | 2,00,000 |
| Trade Payables | 1,00,000 |
| Total | 12,00,000 |
Solution:
Debt Equity Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Long Term Debt }}{\text { Shareholder’s Fund }}\)|
Shareholder’s Fund
Long term debt = Debentures = Rs. 3,00,000
Shareholder’s Fund = Eq. share capital +Pref. Shares capital + Reserves & surplus
= 2,50,000 ÷ 2,00,000 + 1,50,000
= Rs. 6,00,000
(3) Capital Gearing ratio
= \(\frac{\text { Funds bearing fixed interest (or) Fixed divided }}{\text { Equity shareholder’s Fund }}\)
Funds bearing fixed interest (or) fixed dividend
= Pref. Share Cap + Debentures
= 2,00,000 + 3,00,000 = Rs. 5,00,000
Equity share holder’s Fund .
= Equity Share cap + Reserves & Surplus
= 2,50,000 + 1,50,000
= Rs. 4,00,000
Capital gearing ratio = \(\frac{5,00,000}{4,00,000}\)
= 1.25:1
Answer:
- Debt-equity ration; 0.5:1;
- Proprietary ration; 0.5:1;
- Capital gearing ratio:1.25:1
![]()
Question 8.
From the given information calculate the inventory turnover ratio and inventory conversion period (in months) of Devi Ltd.
| Particulars | Rs. |
| Revenue from operations | 12,00,000 |
| Inventory at the beginning of the year | 1,70,000 |
| Inventory at the end of the year | 1,30,000 |
| Purchase made during the year | 6,90,000 |
| Carriage inwards | 20,000 |
Solution:
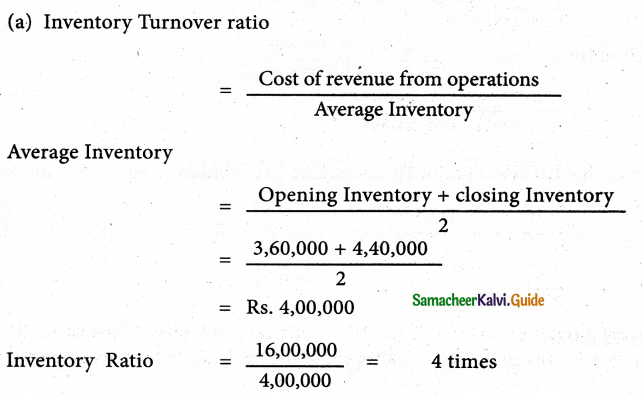
Inventory Turnover Ratio = \(\frac{\text { cost of revenue from operations }}{\text { Average Inventory }}\)
Cost of revenue from operations = Purchase of stock + change in inventories of finished goods operations + Direct Exps.
= Rs. 6,90,000
AverageInventory = \(\frac{\text { Opening Inventory + Closing inventory }}{2}\)
= \(\frac{1,70,000+1,30,000}{2}\)
= Rs. 1,50,000
Change in inventory = Opening inventory – Closing inventory
= 1,70,000 – 1,30,000
= Rs. 40,000
Cost of revenue from operation
= 6,90,000 + 40,000 + 20,000
= Rs. 7,50,000
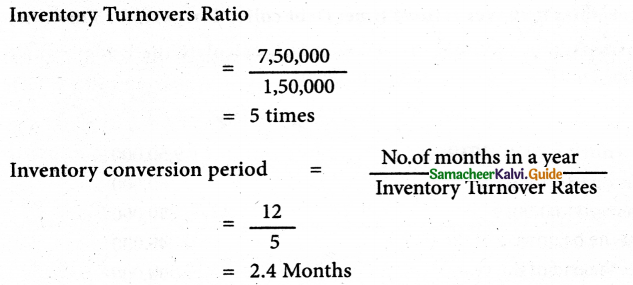
Answer:
Inventory turnover ratio 5times; Inventory conversion period 2.4 months
Question 9.
The credit revenue from operations of Velavan Ltd, amounted to ₹ 10,00,000. Its debtors and bills receivables at the end of the accounting period amounted to ₹ 1,10,000 and ₹ 1,40,000 respectively. Calculate trade receivables turnover ratio and also.collection period in months.
Solution:
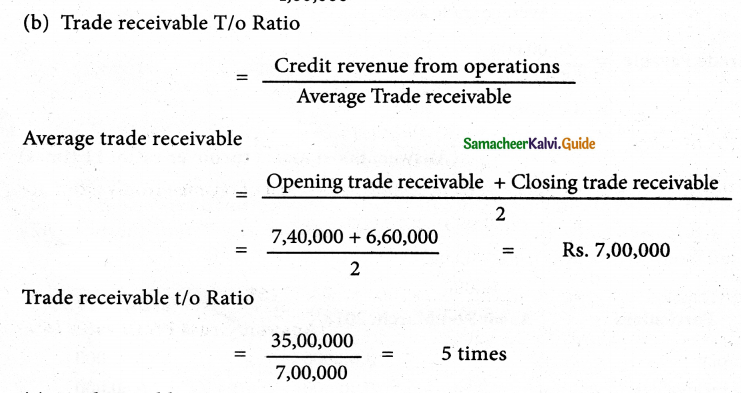
Trade receivable Turnover ratio = \(\frac{\text { Credit revenue from Operations }}{\text { Average trade receivables }}\)
Average trade receivables = \(\frac{\text { Opening trade receivables + Closing trade receivables }}{2}\)
Trade receivable = Trade Drs + B/R
Inventory Turnovers Ratio = \(\frac{10,00,000}{2,50,000}\)
= 4 times
Average Trade receivable
= 1,10,000 + 1,40,000
= Rs. 2,50,000
Debt collection period = \(\frac{\text { Number of months in a year }}{\text { Trade receivable turnover ratio }}\)
= \(\frac{12}{4}\)
= 3 months
Answer:
Trade receivables turnover ratio: 4 time; Debt collection period: 3 months
![]()
Question 10.
From the following figures obtained from Arjun Ltd, calculate the trade payable turnover ratio and credit payment period (in days)
| Particulars | Rs. |
| Credit purchases during 2018 -2019 | 9,50,000 |
| Trade creditors as on 01.04.2018 | 60,000 |
| Trade creditors as on 3 1.03.2019 | 50,000 |
| Bills payable as on 0L04.2018 | 45,000 |
| BillS payable as on 3 1.03.2019 | 35000 |
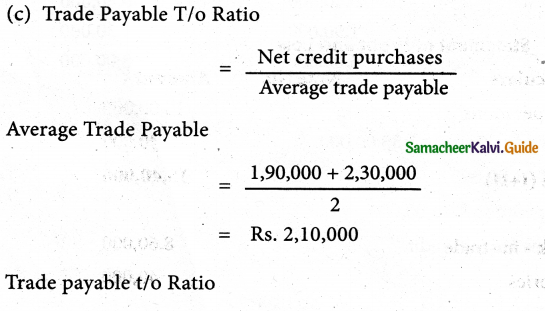
Solution:
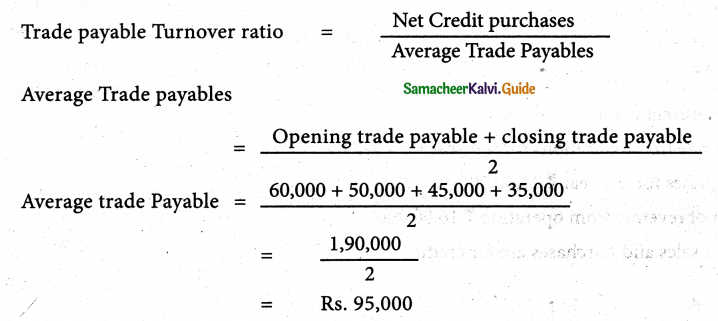
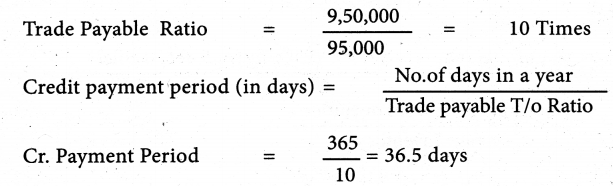
Answer:
Trade payable turnover ratio: 10 times; Credit payment period: 36.5 days
![]()
Question 11.
From the following information of Geetha Ltd., Calculate fixed assets turnover ratio
(i) Revenue from operations during the year was ₹ 55,00,000.
(ii) Fixed assets at the end of the year ₹ 5,00,000
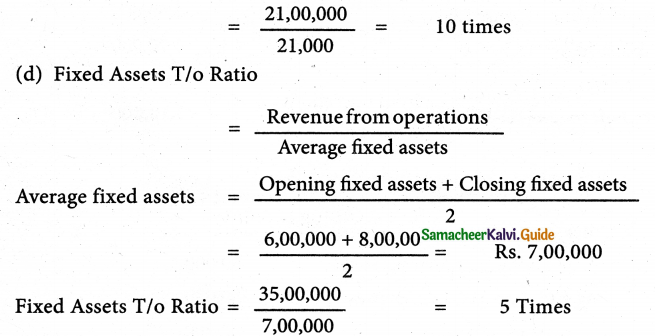
Solution:
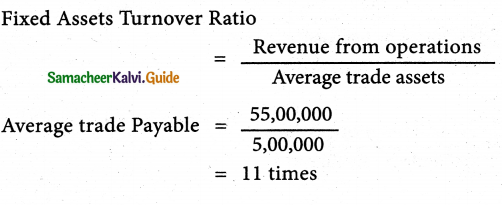
Answer:
Fixed assets turnover ratio: 11 times
Question 12.
Calculate
- Inventory turnover ratio
- Trade receivable turnover ratio
- Trade payables turnover ratio and
- Fixed assets turnover ratio from the following obtained from Aruna Ltd.
Particulars As of 31st March 2018 ₹ As of 31st March 2019 ₹ Inventory 3,60,000 4,40,000 Trade receivables 7,40,000 6,60,000 Trade Payable 1,90,000 2,30,000 Fixed assets 6,00,000 8,00,000
Additional information:
- Revenue from operations for the year ₹ 35,00,000
- Purchases for the year ₹ 21,00,000
- Cost of revenue from operation ₹ 16,00,000
Assume that sales and purchases are for credit.
Solution
Answer:
- Inventory turnover ratio; 4 times;
- Trade receivable turnover ratio; 5 times;
- Trade payables turnover ratio: 10 times;
- Fixed assets turnover ratio: 5 times
![]()
Question 13.
Calculate gross profit ratio form the following: Revenue from operations ₹ 2,50,000, Cost of revenue from operation ₹ 2,10,000 and Purchases ₹ 1,80,000.
Solution:
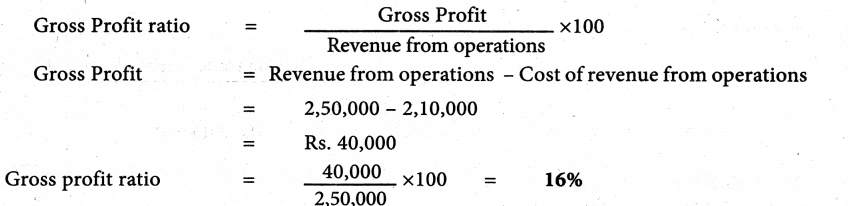
Answer:
Gross Profit ratio 16%
Question 14.
Following is the statement of profit and loss of Padma Ltd. for the year ended 31st March, 2018. Calculate the operating cost ratio.
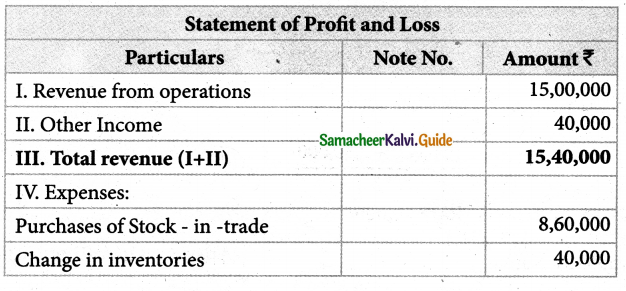
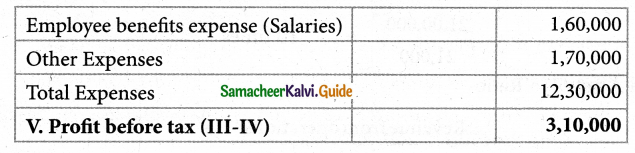
Notes to Accounts
| Particulars | Rs. |
| I. Other expenses | |
| Office and administrative expenses | 50,000 |
| Selling and distribution expenses | 90,000 |
| Loss on sale of furniture | 30,000 |
| 1,70,000 |
Solution:
Operating cost Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Operating cost }}{\text { Revenue from operation }}\) × 100
Operating cost = Cost of revenue from operations + Operating expenses.
Cost of revenue from operations = Purchase + Change in inventory + Direct Expenses
= 8,60,000 + 40,000 + Nil
= Rs. 9,00,000
Operating Exps = Salaries + Office & Administration Exps + Selling+Distribution Exps
= 1,60,000 + 50,000 + 90,000
= Rs. 3,00,000
Operating cost = 9,00,000 + 3,00,000
= Rs, 12,00,000
Operating cost Ratio = \(\frac {12,00000}{15,00000}\) × 100
= 80%
Answer:
Operating cost ratio 80%
![]()
Question 15.
Calculate operating profit ratio under the following cases.
Case 1 : Revenue from operations ₹ 8,00,000 Operating Profit ₹ 2,00,000.
Case 2 : Revenue from operations ₹ 20,00,000 Operating Cost ₹ 14,00,000.
Case 3 : Revenue from operations ₹ 10,00,000 Gross profit 25% on revenue from operations, operating expenses ₹ 1,00,000.
Solution:
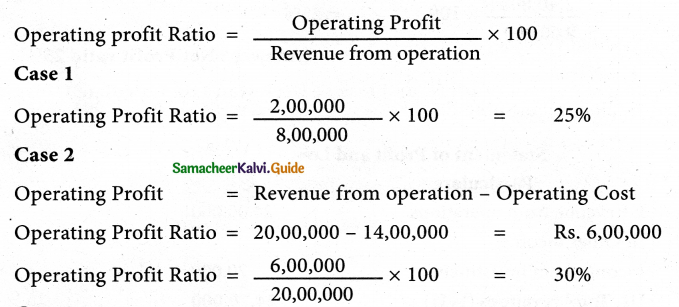
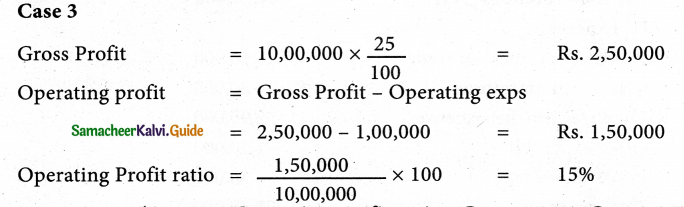
Answer:
Operating profit ratio – Case 1: 25%; Case 2:30%; Case 3:15%
Question 16.
From the following details of a business, concern calculates net profit ratio.
| Particulars | Amount Rs. |
| Revenue from operations | 9,60,000 |
| Cost of revenue from operations | 5,50,000 |
| Office and administrationexpenses | 1,45,000 |
| Selling and distribution expenses | 25,000 |
Solution
Net Profit Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Net Profit }}{\text { Revenue from operations }}\)× 100
Gross profit = Revenue from operations – Cost of revenue from operation
= 9,60,000-5,50,000 Rs. 4,10,000
Operating Profit = Gross Profit – Operating Exps
Operating Exps = Office & Administrative Exps + Selling & Distribution Exps
= 1,45,000 + 25,000 = Rs. 1,70,000
Operating Profit = 4,10,000 – 1,70,000
Operating Profit = Rs. 2,40,000
Net Profit ratio = \(\frac{2,40,000}{9,60,000}\)× 100 = 25%
Answer :
Net Profit ratio 25%
![]()
Question 17.
From the following statement of profit. and loss of Dericston Ltd. Calculate
(i) Gross Profit ratio
(ii) Net Profit ratio.
| Statement of Profit and Loss | ₹ |
| Particulars | |
| I. Revenue from operations | 24,00,000 |
| II. Other income: | |
| Income from investment | 70,000 |
| III. Total revenues (I+II) | 24,70,000 |
| IV. Expenses: | |
| Purchases of stock-in-trade | 18,80,000 |
| Changes in inventories | -80,000 |
| Employee benefits expense | 2,90,000 |
| Other expenses | 1,10,000 |
| Provision for tax | 30,000 |
| Total expenses | 22,30,000 |
| V. Profit for year | 2,40,000 |
Solution
Gross Profit Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Gross Profit }}{\text { Revenue from operations }}\)×100
Gross profit = Revenue from operations – Cost of revenue from operation
Cost of revenue from operations = Purchase + Change in inventories
= 18,80,000 – 80,000 = Rs. 18,00,000
Gross Profit = 24,00,000 – 18,00, 000 = Rs. 6,00,000

Answer :
- Gross profit ratio of 25%
- net Profit ratio 10%
![]()
Question 18.
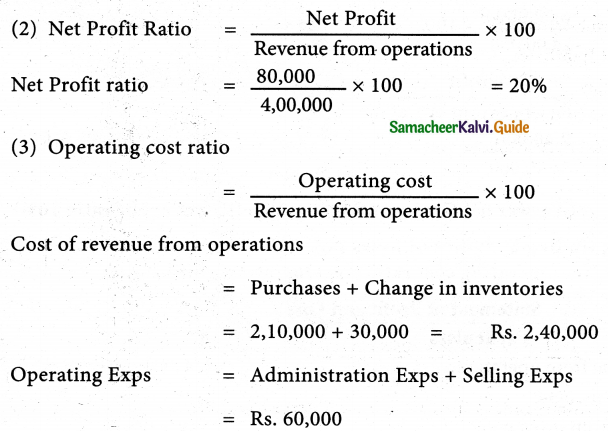
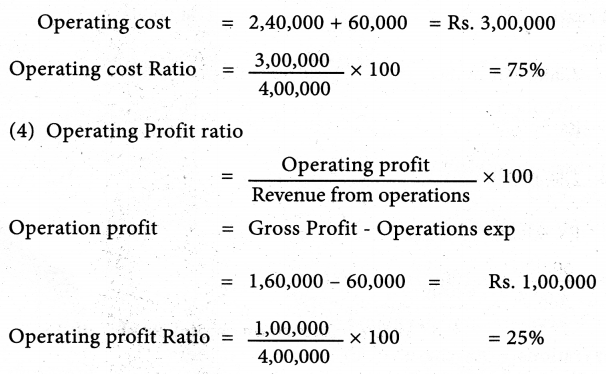
From the following trading activities of Jones Ltd. Calculate
- Gross profit ratio
- Net Profit ratio
- Operating cost ratio
- Operating profit ratio
| Statement of Profit and Loss | |
| Particulars | Rs. |
| I Revenue from operations | 4,00,000 |
| II. Other income: | |
| Income from investment | 4,000 |
| III. Total revenues (I+II) | 4,04,000 |
| IV. Expenses: | |
| Purchases of stock-in-trade | 2,10,000 |
| Changes in inventories | 30,000 |
| Employee benefits expense | 24,000 |
| Other expenses (Administration and selling) | 60,000 |
| Total expenses | 3,24,000 |
| V. Profit for year | 80,000 |
Solution
(1) Gross Profit Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Gross Profit }}{\text { Revenue from operations }}\)× 100
cost of Revenue from operations = Purchase + Change in inventories
= 2,10,000 + 30,000
= Rs. 2,40,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operations – cost of revenue from operations
= 4,00,000 – 2,40,000
= Rs. 1,60,000
Gross Profit ratio = \(\frac{1,60,000}{4,00,000}\)× 100 = 40%
Answer :
- Gross profit ratio 40%
- Net Profit ratio 20%
- Operating cost ratio 75%
- Operating profit ratio 25%
![]()
Question 19.
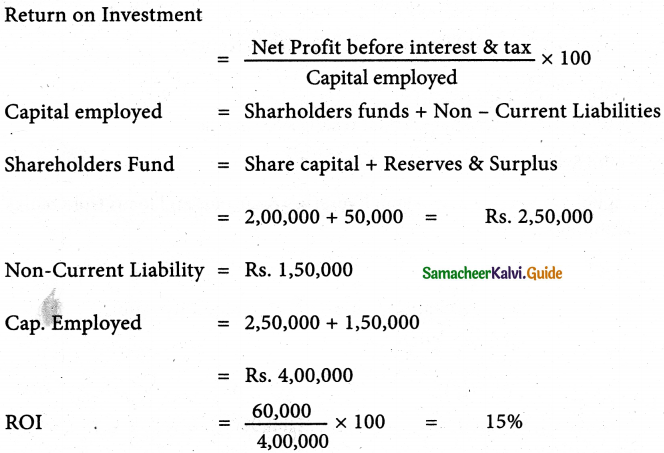
Following is the extract of the balance sheet of Abdul Ltd., as of 31st March 2019
| Particulars | Rs. |
| I. Equity and Liabilities | |
| 1. Shareholders’ Funds | |
| a) Share capital | 2,00,000 |
| b) Reserves and surplus | 50,000 |
| 2. Non-Current liabilities | |
| Long-term borrowings | 1,50,000 |
| 3. Current liabilities | |
| (a) Trade Payable | 1,30,000 |
| (b) Reserves and surplus | 5,000 |
| (c) Short – term provisions | 20,000 |
| Total | 5,55,000 |
Net Profit before interest and tax for the year was ₹ 60,000. Calculate the return on capital employed for the year.
Solution:
Answer :
Return on capital employed: 15%
![]()
12th Accountancy Guide Ratio Analysis Additional Important Questions and Answers
Other Important question & Answers
Question 1.
All solvency ratios are express in terms of
(a) Proportion
(b) Times
(c) Percentage
Answer:
(b) Times
Question 2.
All activity ratios, (or) Turnover ratios in terms of
(a) Proportion
(b) Times
(c) Percentage
Answer:
(b) Times
Question 3.
All profitability ratios are expressed in terms of ………………
(a) Proportion
(b) Times
(c) Percentage
Answer:
(c) Percentage
![]()
Question 4.
Shareholders funds include
(a) Equity share capital, preference share capital reserves & Surplus
(b) Loans from banks & financial institutions.
(c) Equity share capital, preference share capital, reserves & surplus, and loans from banks & financial institutions.
Answer:
(a) Equity share capital, preference share capital reserves & Surplus
Question 5.
The current ratio is a
(a) Solvency ratio
(b) Profitability ratio
(c) Liquidity ratio
Answer:
(a) Solvency ratio
Question 6.
The ratio is expressed in ……………… way
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 3
Answer:
(c) 3
![]()
Question 7.
The cost of revenue from the operation is Rs. 4,00,000. Average inventories Rs. 8,00,000 Inventory turnover ratio is
(a) 5 times
(b) 4 times
(c) 7 times
Answer:
(a) 5 times
Question 8.
The operating ratio is equal to
(a) 100-operating profit ratio
(b) 100 +operating profit ratio
(c) Operating profit ratio
Answer:
(a) 100-operating profit ratio
Question 9.
Operating expenses include
(a) Selling & administration expenses
(b) Selling & administration expens
(c) a & b
Answer:
(c) a & b
![]()
Question 10.
Equity share capital Rs. 2,00,000 Reserves & Surplus Rs. 30,000 Debenture Rs. 40,000 and shareholders fund will be.
(a) Rs. 200,000
(b) 2,70,000
(c) Rs. 2,30,000
Hint:
Share holder fund = Equity share capital + Reserve and surplus
= 2,00,000 + 30,000
= ₹ 2,30,000
Answer:
(c) Rs. 2,30,000
![]()
III Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Ratio Analysis
Answer:
According to Myers, “Ratio analysis is a study of the relationship among various financial factors in a business”.
Question 2.
What do you mean by ratio Analysis?
Answer:
Ratio analysis is a tool which involves analyzing the financial statements by calculating various. It is a tool of financial statement analysis, in which, inferences are drawn based on the computation and analysis of different ratios.
Question 3.
What are the two ways of classifying the ratios?
Answer:
Ratios may be classified in the following two ways:
- Traditional classification
- Functional classification
![]()
Question 4.
What do you mean by the traditional classification of ratio? Explain
Answer:
The traditional classification of ratios is done on the basis of the financial statements from which the ratios are calculated. Under the traditional classification, the ratio is classified as:
- Balance sheet ratio: If both items in a ratio are from the balance sheet, it is classified as a balance sheet ratio.
- Income statement ratio: If the two items in a ratio are from the income statement, it is classified as an income statement ratio.
- Inter – Statements ratio: If a ratio is computed with a tone item from the income statement and another item from the balance sheet, it is called an inter-statement ratio.
Question 5.
What is the functional classification of ratios?
Answer:
Under the functional classification, the rations are classified as follows:
- Liquidity ratios
- Long term solvency ratios
- Turnover ratios.
- Profitability ratios.
![]()
Question 6.
What do you mean by Liquidity ratios?
Answer:
Liquidity means the capability of being converted into cash with ease. Liquidity ratios help to assess the ability of a business concern to meet its short term financial obligations. Short term assets (current assets) are more liquid as compared to long term assets (fixed assets). Liquidity ratios are also called as short term solvency ratios.
Question 7.
What do you mean by the current ratio?
Answer:
Current ratio gives the proportion of current assets to current liabilities of a business concern. It is computed by dividing current assets by current liabilities. The current ratio indicates the ability of an entity to meet its current liabilities as and when they are due for payment.
Question 8.
What do you mean by Long-term solves ratios? what are its types?
Answer:
Long term solvency means the firm’s ability to meet its liabilities in the long run. Long term solvency ratios help to determine the ability of the business to repay its debts in the long run. The following ratios are normally computed for evaluating long term solvency of the business:
- Debt equity ratio
- proprietary ratio
- Capital gearing ratio
![]()
Question 9.
What do you mean by Turnover Ratios? What are its types?
Answer:
Turnover ratios show how efficiently assets or other items have been used to generate revenue from operations. They are also called as activity ratios or efficiency ratios. They how the speed of movement of various items. They are expressed as number of times in relation to the item compared.
The important turnover ratios are:
- Inventory turnover ratio
- Trade receivable turnover ratio
- Trade payable turnover ratio
- Fixed assets turnover ratio.
Question 10.
What do you mean by Trade Receivable Turnover ratio?
Answer:
Trade receivable turnover ratio is the comparison of credit revenue from operations with average trade receivables during an accounting period. It gives the velocity of the collection of cash from trade receivables.
Question 11.
What do you mean by Debt collection Period?
Answer:
Debt collection period is the average time taken to collect the amount due from trade receivables. Lesser the debt collection period, grater is the efficiency of management in the collection of cash from trade receivables. It is calculated as follows.
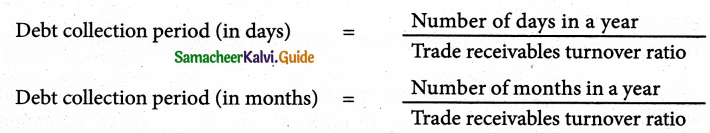
What do you mean by Trade payable Turnover ratio?
Trade payable turnover ratio is the comparison of net credit purchases with average trade payables during an accounting period. It gives the velocity to payment of cash towards trade payables.
![]()
Question 12.
What do you mean by credit payment period?
Answer:
It is the average time taken by the business for payment of accounts payable. Lesser the credit payment period, greater is the efficiency of the management in managing accounts payable as it indicated quicker settlement of trade payables. It is calculated as follows:
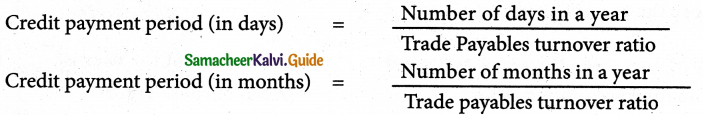
Question 13.
What do you mean by Fixed Assets Turnover
Answer:
The fixed assets turnover ratio gives the number of times the fixed assets are turned over during the year in relation to the revenue from operations. This ratio indicates the efficiency of utilization of fixed assets.
Question 14.
What do you mean by profitability ratios? What are its types?
Answer:
Profitability ratios help to assess the profitability of a business concern. These rations also help to analyze the earning capacity of the business in terms of utilization of resources employed in the business. Generally, these rations are expressed as a percentage.
The profitability ratios commonly used are:
- Gross profit ratio
- Operating cost ratio
- Operating profit ratio
- Net profit ratio
- Return on investment.