Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Accounts from Incomplete Records Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 1 Accounts from Incomplete Records
12th Accountancy Guide Accounts from Incomplete Records Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Incomplete records are generally maintained by
(a) A company
(b) Government
(c) Small sized sole trader business
(d) Multinational enterprises
Answer:
(c) Small sized sole trader business
![]()
Question 2.
Statement of affairs is a
(a) Statement of income and expenditure
(b) Statement of assets and liabilities
(c) Summary of cash transactions
(d) Summary of credit transactions
Answer:
(b) Statement of assets and liabilities
Question 3.
Opening statement of affairs is usually prepared to find out the
(a) Capital in the beginning of the year
(b) Capital at the end of the year
(c) Bills payable accepted during the year
(d) Loss occurred during the year
Answer:
(a) Capital in the beginning of the year
Question 4.
The excess of assets over liabilities is
(a) Loss
(b) Cash
(c) Capital
(d) Profit
Answer:
(c) Capital
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following items relating to bills payable is transferred to the total creditors account?
(a) Loss
(b) Cash
(c) Capital
(d) Profit
Answer:
(c) Capital
Question 6.
The amount of credit sales can be computed from
(a) Total debtors account
(b) Total creditors account
(c) Bills receivable account
(d) Bills payable account
Answer:
(a) Total debtors account
Question 7.
Which one of the following statements is not true in relation to incomplete records?
(a) It is an unscientific method of recording transactions
(b) Records are maintained only for cash and personal accounts
(c) It is suitable for all types of organisations
(d) Tax authorities do not accept
Answer:
(c) It is suitable for all types of organisations
Question 8.
What is the amount of capital of the proprietor, if his assets Rs. 85,000 and Liabilities Rs 21,000.
(a) ₹ 85,000
(b) ₹ 1,06,000
(c) ₹ 21,000
(d) ₹ 64,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 64,000
Hint:
Assets = Capital – Liabilities
85,000 = Capital – 21,000
Capital = 85,000 – 21,000
Capital = 64,000
![]()
Question 9.
When capital, in the beginning, is ₹ 10,000, drawings during the year is ₹ 6,000 profit made during the year is ₹ 2,000 and the additional capital introduced is ₹ 3,000, find out the amount of capital at the end.
(a) ₹ 9,000
(b) ₹ 11,000
(c) ₹ 21,000
(d) ₹ 3,000
Answer:
(a) ₹ 9,000
Hint:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Capital at the end | 9,000 |
| Add: Drawings | 6,000 |
| 15,000 | |
| Less: Additional capital | 3,000 |
| 12,000 | |
| Less: Opening Capital | 10,000 |
| Profit | 2,000 |
Question 10.
Opening balance of debtors: ₹ 30,000, cash received: ₹ 1,00,000, credit sales: ₹ 90,000; closing balance of debtors is
(a) ₹ 30,000
(b) ₹ 1,30,000
(c) ₹ 40,000
(d) ₹ 20,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 20,000
Hint:
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by incomplete records?
Answer:
- When accounting records are not strictly maintained according to the double-entry system, these records are called incomplete accounting records.
- Generally, cash accounts and the personal accounts of customers and creditors are maintained fully and other accounts are maintained based on necessity.
![]()
Question 2.
State the accounts generally maintained by the small-sized sole trader when a double-entry accounting system is not followed.
Answer:
Cash account and the personal accounts of customers and creditors are maintained fully and other accounts are maintained based on necessity.
Question 3.
What is a statement of affairs?
Answer:
A statement of affairs is a statement showing the balances of assets and liabilities on a particular date. The balance of assets is shown on the right side and the balance of liabilities on the left side. This statement resembles a balance sheet. The difference between the total of assets and the total of liabilities is taken as capital.
Capital = Assets – Liabilities.
III Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the features of incomplete records?
Answer:
1. Nature:
- It is an unscientific and unsystematic way of recording transactions.
- Accounting principles and accounting standards are not followed properly.
2. Types of accounts maintained – In general only cash and personal accounts are maintained fully. Real accounts and nominal accounts are not maintained properly. Some transactions are correctly omitted.
3. Lack of uniformity – There is no uniformity in recording the transactions among different organizations. Different organizations record their transactions according to their needs and conveniences.
4. Financial statements may not represent true and fair view – Due to the incomplete information and inaccurate records of accounts, the profit or loss calculated from these records cannot be relied upon. It may not represent true profitability. Assets and liabilities may not represent a true and fair view of financial position.
5. Suitability – Only the business concerns which have no legal obligation to maintain books of accounts under the double-entry system may maintain incomplete records. Hence, it may be maintained by small-sized sole traders and partnership firms.
6. Mixing up of personal and business transactions – Generally, personal transactions of the owners are mixed up with the business transactions. For example, the purchase of goods for their own use may be mixed up along with business purchases.
Question 2.
What are the limitations of incomplete records?
Answer:
- Lack of proper maintenance of records: It is an unscientific and unsystematic way of maintaining records. Real and Nominal accounts are not maintained properly.
- Difficulty in preparing trial balance: As accounts are not maintained for all items, the accounting records are incomplete. Hence, it is difficult to prepare a trial balance to check the arithmetical accuracy of the accounts.
- Difficulty in ascertaining true profitability of the business: Profit is found out based on available information and estimates. hence, it is difficult to ascertain true profit as the trading and profit and loss account cannot be prepared with accuracy.
![]()
Question 3.
State the differences between double-entry system and incomplete records.
Answer:
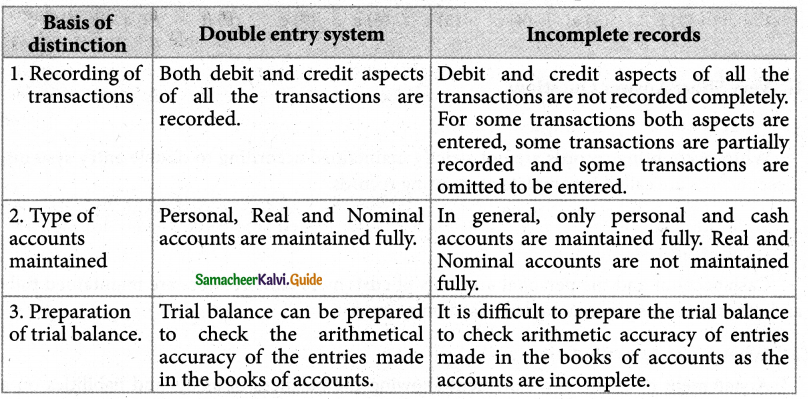
Question 4.
State the procedure for calculating profit or loss through the statement of affairs.
Answer:
The difference between the closing capital and the opening capital is taken as profit or loss of the business. Due adjustments are to be made for any withdrawal of capital from the business and for the additional capital introduced in the business.
Adjusting closing capital = Closing capital + Drawings – Opening capital.
Closing capital + Drawings – Additional capital – Opening capital = Proft/Loss.
![]()
Question 5.
Differentiate between the statement of affairs and the balance sheet.
Answer:
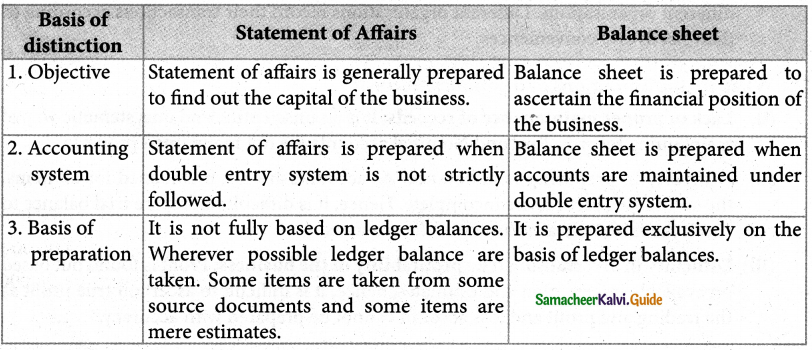

Question 6.
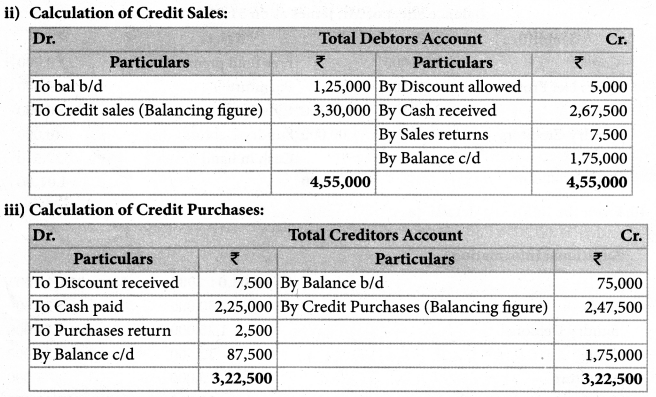
How is the amount of credit sale ascertained from incomplete records?
Answer:
For ascertaining the amount of credit sales, the total debtor’s account should be prepared. The specimen of the total dr’s A/c is given below.
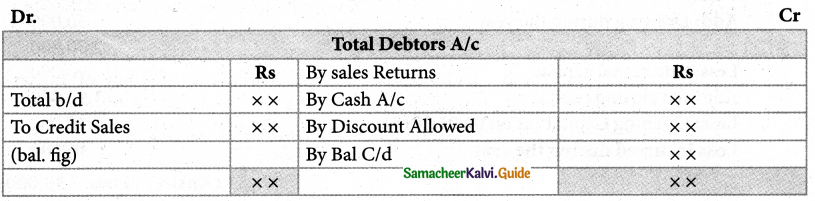
IV Exercise
Question 1.
From the following particulars ascertain profit or loss:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Capital_at the beginning of the year(1st April 2018) | 5,00,000 |
| Capital at the end of the year (31st March 2019) | 8,50,000 |
| Additional capital introduced during the year | 1,20,000 |
| Drawings during the year | 70,000 |
Solution:
Statement of profit or loss for the year ended 31.03.2019
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Closing as on 31.03.2019 | 8,50,000 |
| Add: Drawing during the year | 70,000 |
| 9,20,000 | |
| Less: Additional capital introduced during the year | 1,20,000 |
| Adjusted closing capital | 8,00,000 |
| Less: opening_Capital (as on 01.04.2018) | 5,00,000 |
| Profit ¡nade during the year | 3,00,000 |
Answer:
Profit: ₹ 3,00,000
![]()
Question 2.
From the following particulars ascertain profit or loss :
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Capital as on 1st January 2018 | 2,20,000 |
| Capital as on 31st December 2018 | 1,80,000 |
| Additional capital introduced during the year | 40,000 |
| Drawing made during the year | 50,000 |
Solution:
Statement of profit or loss for the year ended 31.12.2018
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Capital as on 31.12.2018 | 1,80,000 |
| Add: Drawing during the year | 50,000 |
| 2,30,000 | |
| Less: Additional capital | 40,000 |
| Adjusted closing capital | 1,90,000 |
| Less: Opening Capital (as on 01.01.2018) | 2,20,000 |
| Loss incurred during the year | 30,000 |
Answer:
Loss: ₹ 30,000
![]()
Question 3.
From the following details, calculate the missing figure.
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Closing capital as on 31.03.2018 | 80,000 |
| Additional capital introduced during the year | 30,000 |
| Drawings during the year | 15,000 |
| Opening capital on 01.04.2017 | ? |
| Loss for the year ending 31.03.2018 | 25,000 |
Solution:
Calculation \ of opening capital
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Closing Capital as on 31.03.2018 | 80,000 |
| Add: Drawing during the year | 15,000 |
| 95,000 | |
| Less: Additional capital | 30,000 |
| Adjusted closing capital | 65,000 |
| Less: Opening Capital (as on 01.01.2018) | 90,000 |
| Loss incurred during the year | 25,000 |
Answer:
Opening capital: ₹ 90,000
Question 4.
From the following details, calculate the capital as on 31st December 2018.
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Capital as on 1st January 2018 | Particulars 1,00,000 |
| Goods are withdrawn for personal use by the owner | 30,000 |
| Additional capital introduced during the year | 15,000 |
| Profit for the year | 60,000 |
Calculation of closing capital
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Closing Capital as on 31.12.2018 | 1,45,000 |
| Add Drawing (goods are withdrawn for personal use) | 30,000 |
| 1,75,000 | |
| Less Additional capital | 15,000 |
| Adjusted closing capital | 1,60,000 |
| Less opening Capital (as on 01.01.2018) | 1,00,000 |
| Profit for the year | 60,000 |
Answer:
Closing Capital: ₹ 1,45,000
![]()
Question 5.
From the following details, calculate the missing figure:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Capital as on 1st April 2018 | 40,000 |
| Capital as on 31st March 2019 | 50,000 |
| Additional capital introduced during the year | 7,000 |
| Profit for the year | 8,000 |
| Drawing during the year | ? |
Solution:
Calculation of drawings
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Closing Capital as on 31.03.2019 | 50,000 |
| Add: Drawing (bal.fig) | 5,000 |
| 55,000 | |
| Less: Additional capital introduced | 7,000 |
| Adjusted closing capital | 48,000 |
| Less: Opening Capital (as on 01.04.2018) | 1,00,000 |
| Profit made during the year | 8,000 |
Answer:
Drawings: ₹ 5,000
Question 6.
Following are the balance in th books of thomas as on 31st March 2019.
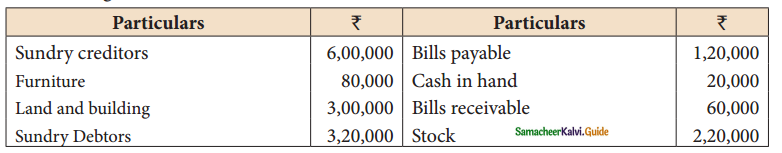
Prepare a statement of affairs as on 31st March 2019 and calculate capitals as at that date.
Solution:
Statement of affairs as on 31.3.2019
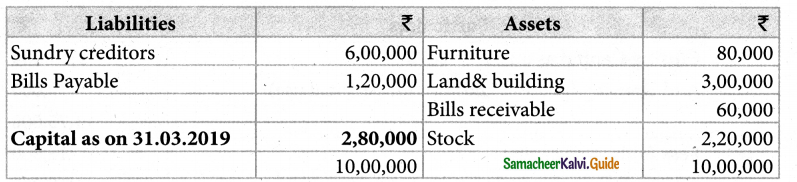
Answer :
Capital: ₹ 2,80,000
![]()
Question 7.
On 1st April 2018 Subha started her business with a capital of ₹ 1,20,000. She did not maintain a proper book of accounts. Following particulars are available from her books as on 31.03.2019.
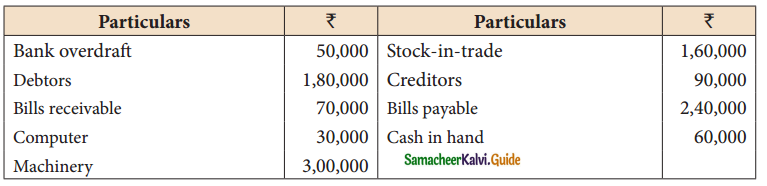
During the year she withdraw ₹ 30,000 for her personal use. She introduced further capital of ₹ 40,000 during the year. Calculate her profile or loss.
Solution:
Statement of affairs as on 31.03.2019
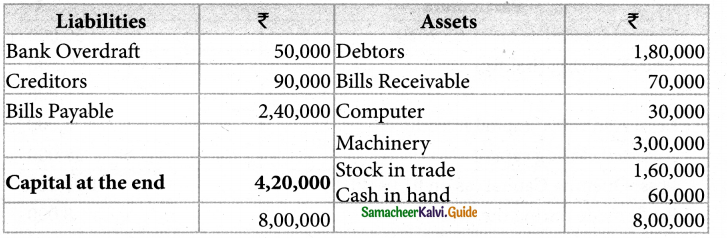
Statement of profit or Loss for year ending 31st March 2019
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Closing capital as on 31.03.2019 | 4,20,000 |
| Add: Drawings | 30,000 |
| 4,50,000 | |
| Less: Additional capital | 40,000 |
| Adjusted closing capital | 4,10,000 |
| Less: opening Capital (as on 01.04.2018) | 1,20,000 |
| Profit made during the year | 2,90,000 |
Answer:
Closing Capital: ₹ 2,80,000; Profit: ₹ 2,90,000
![]()
Question 8.
Raju does not keep proper books of accounts. The following details are taken from his records.
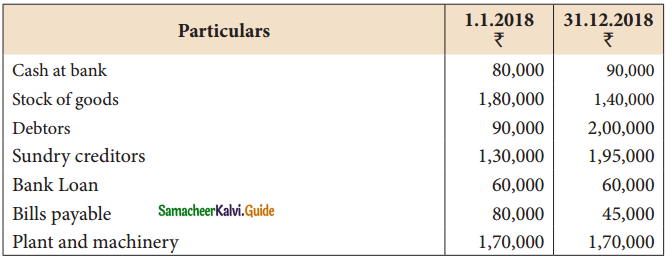
During the year he introduced further capital of ₹ 50,000 and withdraw ₹ 2,500 per month from the business for his personal use. Prepare a statement of profit or loss with the above information.
Solution:
Statement of affairs as on 1.1.2018
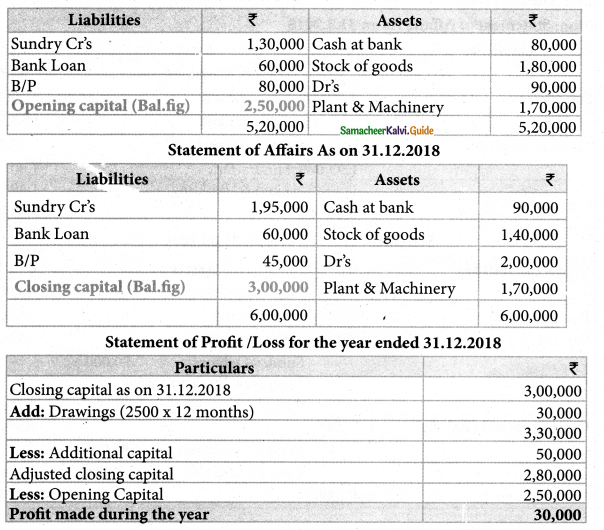
Answer:
Opening Capital: ₹ 2,50,000; Closing capital: ₹ 3,00,000; Profit: ₹ 30,000
![]()
Question 9.
Ananth does not keep his books under the double-entry system. Find the profit or loss made by him for the year ending 31st March 2019.
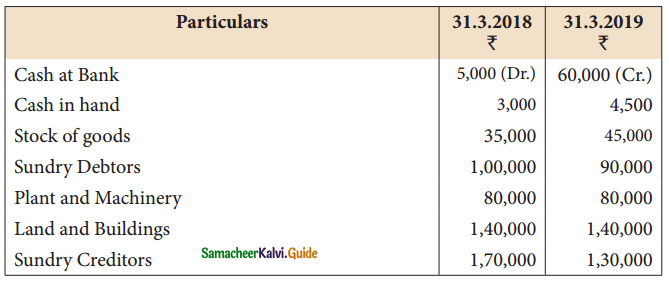
Ananth had withdrawn ₹ 60,000 for his personal use. He had introduced ₹ 17,000 as capital for expansion of his business. Create a provision of 5% on debtors. Plant and machinery is to be depreciated at 10%.
Solution:
Statement of Affairs As on 31.3.2018
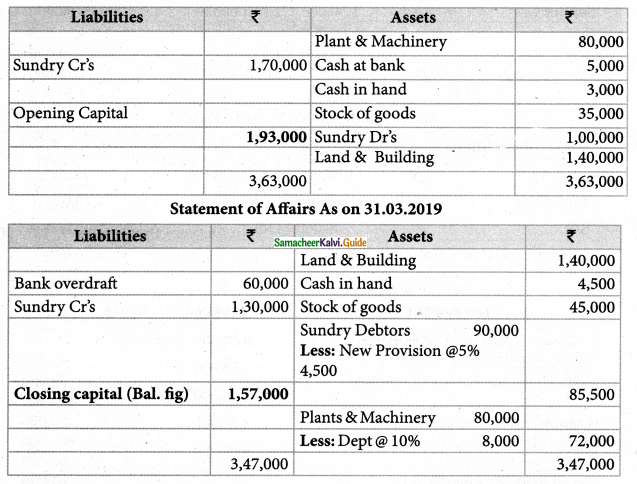
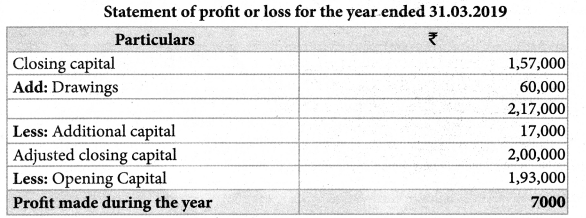
Answer:
Opening Capital: ₹ 1,93,000; Closing capital: ₹ 1,57,000; Profit: ₹ 7,000
Question 10.
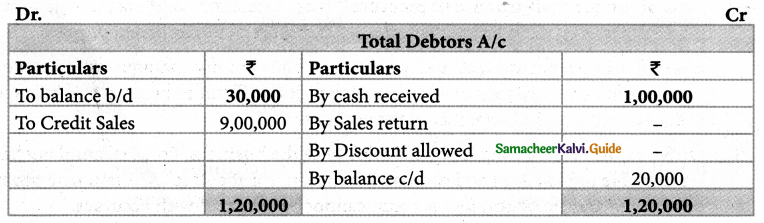
Find out credit sales from the following information.
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Debtors on 1st April, 2018 | 1,00,000 |
| Cash received from debtors | 2,30,000 |
| Discount allowed | 5,000 |
| Returns inward | 25,000 |
| Debtors on 31st March 2019 | 1,20,000 |
Solution:
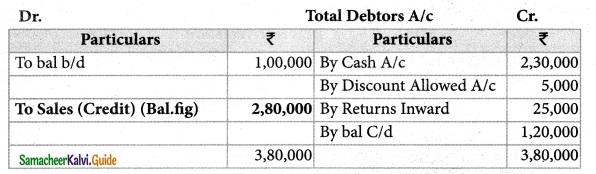
![]()
Question 11.
From the following details find out total sales made during the year.
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Debtors on 1st January, 2018 | 1,30,000 |
| Cash received from debtors during the year | 35,000 |
| Sales returns | 4,20,000 |
| Bad debts | 15,000 |
| Debtors on 31st December 2018 | 2,00,000 |
| Cash Sales | 4,60,000 |
Solution:
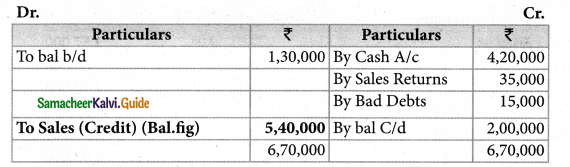
Total sales = Credit Sales + Cash Sales
= 5,40,000 + 4,60,000
Total Sales = Rs. 10,00,000
Answer :
Credit sales : ₹ 5,40,000; Total Sales : ₹ 10,00,000
Question 12.
From the following particulars, prepare bills receivable amount and compute the bills received from the debtors.
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Bills receivable at the beginning of the year | 1,40,000 |
| Bills receivable at the end of the year | 2,00,000 |
| Bills receivable at the end of the year | 3,90,000 |
| Bills received dishonoured | 30,000 |
Solution:
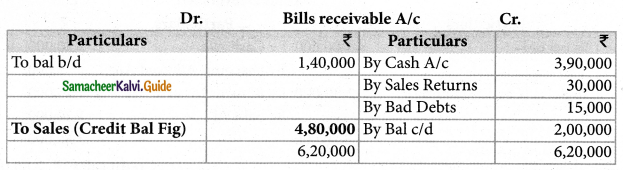
Answer:
B/R received: ₹ 4,80,000;
Question 13.
From the following particulars, calculate total sales.
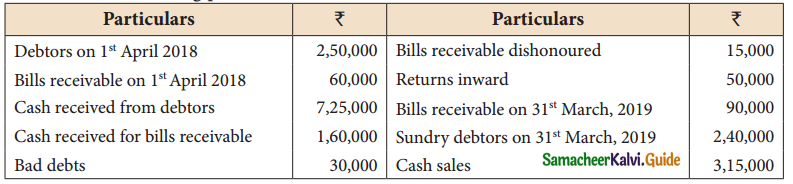
Prepare a statement of affairs as on 31st March 2019 and calculate capitals as at that date.
Solution:
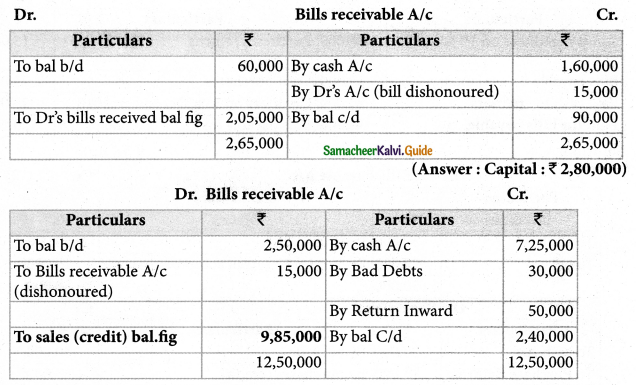
Total sales = Credit Sales + Cash Sales
= 9,85,000 + 3,15,000
Total Sales = Rs. 13,00,000
Answer:
B/R received : ₹ 2,05,000; Credit sales: ₹ 9,85,000; Total sales: ₹ 13,00,000
![]()
Question 14.
From the following details, calculate credit puchases
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Opening creditors | 1, 70,000 |
| Purchase returns | 20,000 |
| Cash paid to creditors | 4,50,000 |
| Closing creditors | 1,90,000 |
Solution:
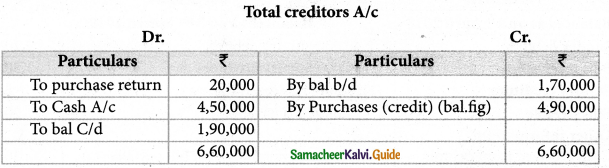
Answer:
Credit sales : ₹ 2,80,000
Question 15.
From the following particulars calculate total purchases.
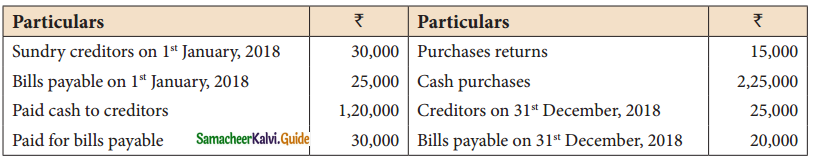
Solution:
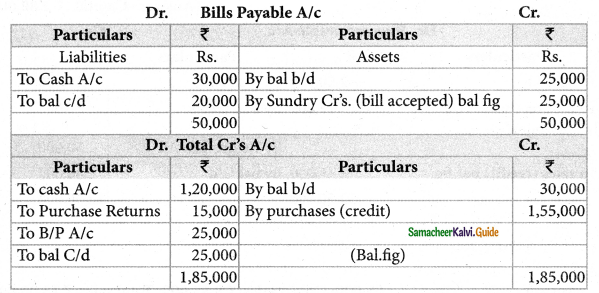
Total Purchase = Cr Purchase + Cash Purchase
= 1,55,000 + 2,25,000
Total Purchase = Rs. 3,80,000
Answer:
B/P accepted: ₹ 25,000; Credit purchases: ₹ 1,55,000; Total Purchases: ₹ 3,80,000
Question 16.
From the following details you are required to calculate credit sales and credit purchases by preparing total debtors account, total creditors account, bills receivable account and bills payable account.
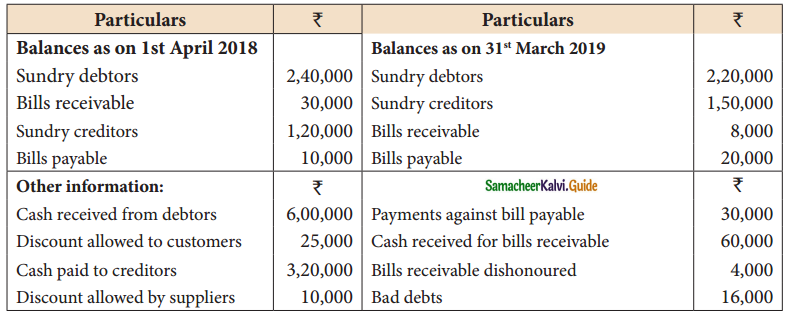
Solution:
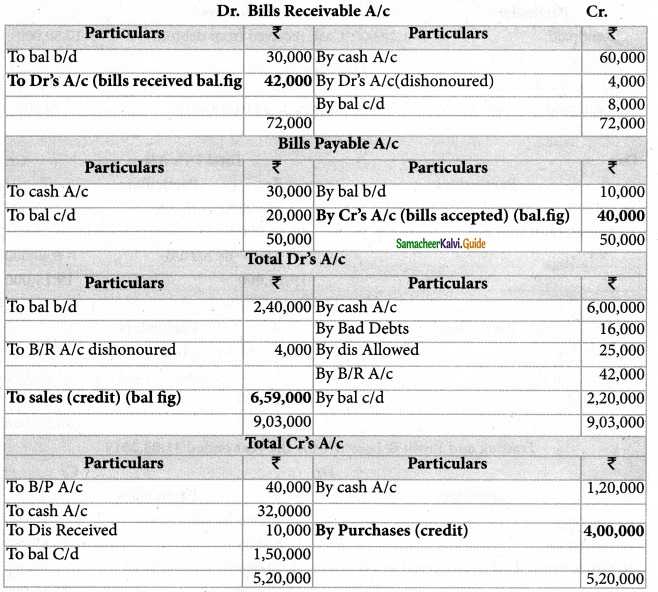
Answers:
B/R received: ₹ 42,000; Credit sales : ₹ 6,59,000; B/P accepted : ₹ 40,000; Credit Purchases: ₹ 4,00,000
![]()
Question 17.
From the following details of Rakesh, prepare Trading and Profit and Loss account for the year ended 31st March, 2019 and a Balance Sheet as on that date.
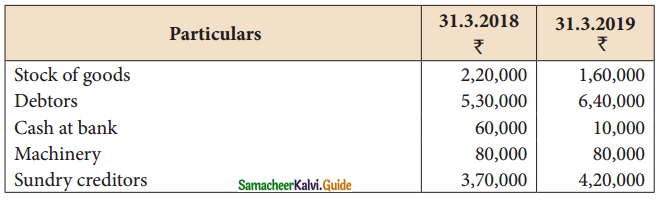
Other details
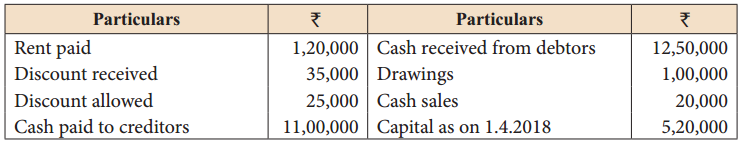
Solution:
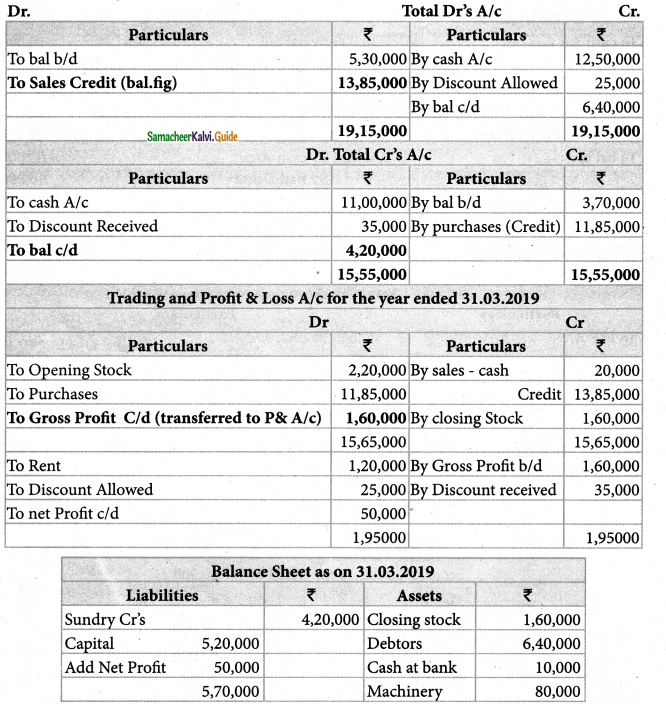
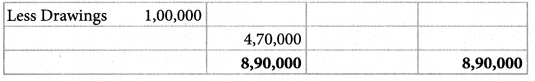
Answer:
Credit Sales: ₹ 13,85,000; Credit purchases: ₹ 11,85,000; Gross profit: ₹ 1,60,000; Net profit: ₹ 50,000, Balance Sheet Total: 8,90,000
Question 18.
Mary does not keep her books under double entry system. From the following details prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ending 31st March, 2019 and a balance sheet as on that date.
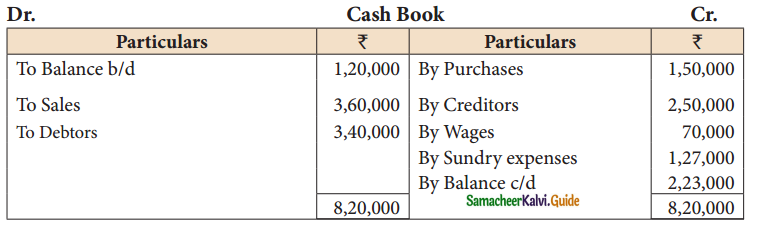
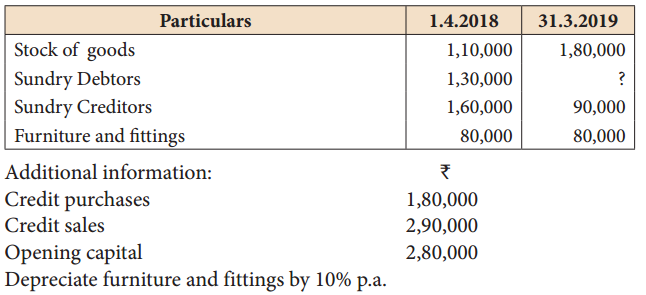
Solution:
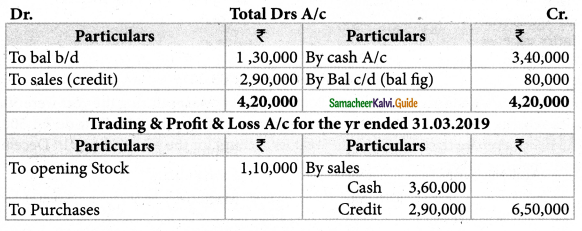
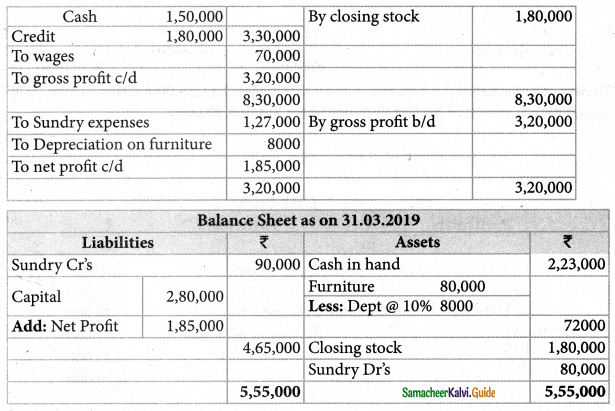
![]()
Question 19.
Arun carries on hardware business and does not keep his books on double entry basis The following particulars have been extracted from his books.
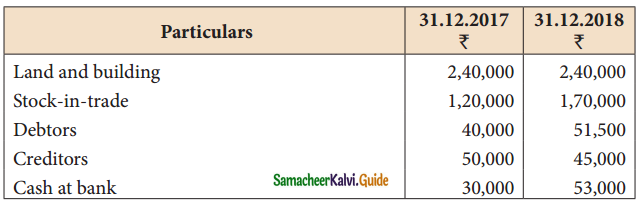
Other information for the year ending 31.12.2018 showed the following:

Total sales during the year were ₹ 7,70,000. Purchases returns during the year were 30,000 and sales returns were ₹ 25,000. Depreciate land and building by 5%. Provide ₹ 1,500 for doubtful debts. Prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ending 31st December, 2018 and a balance sheet as on that date.
Solution:
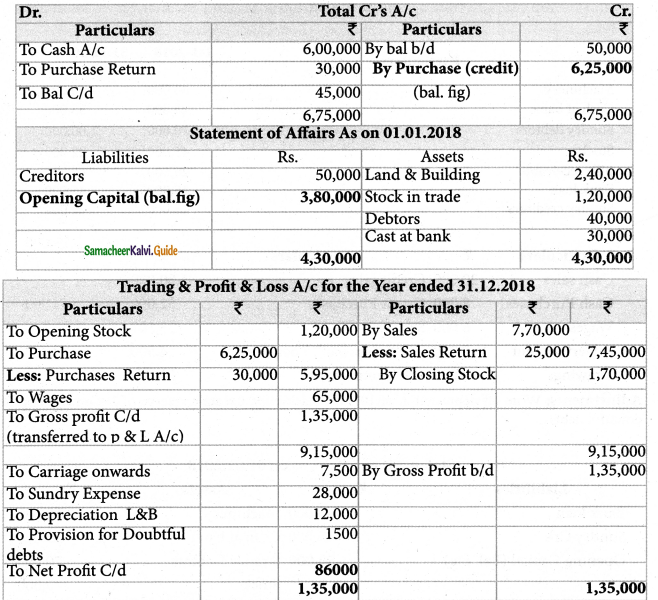
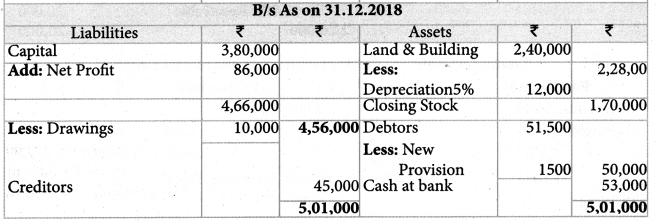
Answer:
Opening capital: ₹ 3,80,000; Credit purchases: ₹ 6,25,000; Gross profit: ₹ 1,35,000; Net profit:: ₹ 86,000, Balance Sheet Total: ₹ 5,01,000
Question 20.
Selvam does not keep ; books under double entry system. From the following information prepare trading and Profit and loss A/c and Balance Sheet as on 31-12-2018
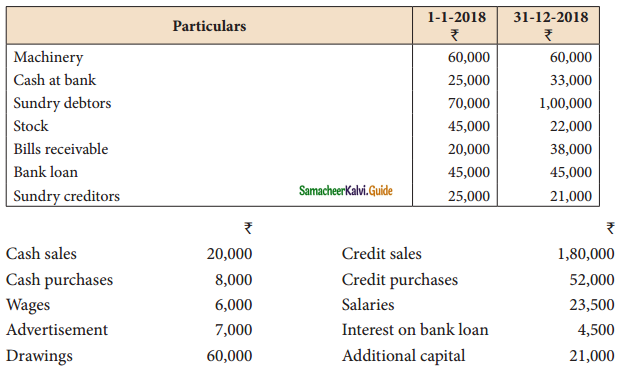
Adjustments: Write off depreciation of 10% on machinery Create a reserve of 1% on debtors for doubtful debts.
Solution:
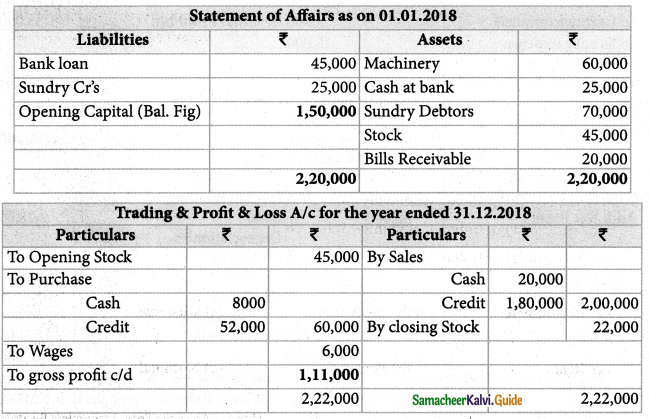
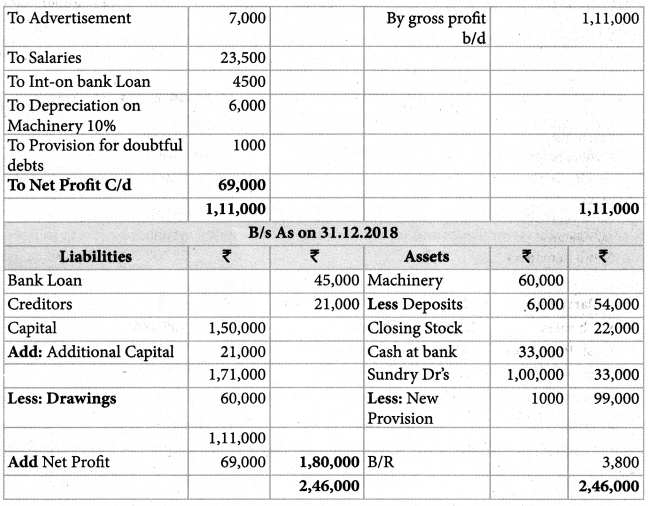
Answer:
Opening capital: ₹ 1,50,000; Gross Profit: ₹ 1,11,000; Net profit:: ₹ 69,000, Balance Sheet Total: ₹ 2,46,000
![]()
12th Accountancy Guide Accounts from Incomplete Records Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer
Question 1.
Companies must maintain accounting records under double entry system as per
(a) Sec. 128 (1) of Indian Companies Act, 1956
(b) Sec. 128 (1) of Indian Companies Act, 2000
(c) Sec. 128 (1) of Indian Companies Act, 2013
Answer:
(b) Sec. 128 (1) of Indian Companies Act, 2000
Question 2.
Single entry system is an ………………….system of bookkeeping.
(a) incomplete
(b) inefficient
(c) adequate
Answer:
(a) incomplete
Question 3.
Single entry system maintains only ……………. and cash accounts
(a) Real
(b) Personal
(c) Nominal
Answer:
(b) Personal
Question 4.
Single entry system does maintain ………………… and ………………… accounts
(a) Assets & liabilities
(b) Debtors, Creditors
(c) Read, Nominal
Answer:
(c) Read, Nominal
![]()
Question 5.
Single entry system is not based on …………….. as pect concept
(a) Double Entry
(b) Dual
(c) Single
Answer:
(b) Dual
Question 6.
Incomplete records are those records which are not kept under……………………….
(a) Single Entry
(b) Double Entry
(c) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Double Entry
Question 7.
Credit purchases can be ascertained as a balancing figure in the ……………………
(a) Total Creditors A/c
(b) Debtors A/c
(c) Capital A/c
Answer:
(a) Total Creditors A/c
Question 8.
To know total purchases and total sales under single entry system, one has to depend on
(a) Trading A/c
(b) Copies of invoice and Vouchers
(c) Profit 8c Loss A/c
Answer:
(b) Copies of invoice and Vouchers
Question 9.
Under single entry system, the arithmetical accuracy of………………. cannot be checked.
(a) Trial Balance
(b) Trading A/c
(c) Balance Sheet
Answer:
(a) Trial Balance
![]()
Question 10.
If the adjusted closing capital is more than the opening capital, it is …………………
(a) Loss
(b) Profit
(c) Asset
Answer:
(b) Profit
Question 11.
If the adjusted closing capital is less than the opening capital, it is…………….
(a) Loss
(b) Profit
(c) Asset
Answer:
(a) Loss
Question 12.
Statement of Affairs resembles a…………………
(a) Balance Sheet
(b) Trading A/c
(c) Profit A/c Loss A/c
Answer:
(a) Balance Sheet
Question 13.
Profit under ……………… Entry system is only an estimate
(a) Double
(b) Single
(c) Income
Answer:
(b) Single
Question 14.
The total assets of a proprietor is Rs. 5,00,000. His liabilities are Rs.3,50,000 His capital in the business is
(a) Rs. 1,50,000
(b) Rs. 8,50,000
(c) Rs. 3,50,000
Hint:
Assets = Capital – Liabilities
5,00,000 = ? – 3,50,000
Capital = 5,00,000 – 3,50,000
= 1,50,000
Answer:
(a) Rs. 1,50,000
![]()
Question 15.
Statement of affairs method is also called
(a) Conversion method
(b) Net worth method
(c) Adjusted closing capital method
Answer:
(b) Net worth method
II Short Answer Questions
Question 16.
Define single Entry System
Answer:
According to Kohler, Single Entry System is a system of book keeping in which as a rule only records of cash and personal accounts are maintained. It is always incomplete double entry varying with circumstances.
Question 17.
What is conversion method?
Answer:
If it is desired to calculated profit by preparing trading and profit & loss Account under single entry system then it is called conversion method.
Question 18.
State the steps to be followed to prepare final accounts from incomplete records
Answer:
Following are the steps to be followed to prepare final accounts from incomplete records.
1. Opening statement of affairs is to be prepared, to ascertain the opening capital.
2. Missing figures must be found out with the available data.
This can be done by preparing memorandum accounts or by making necessary adjustments to the existing figures. For example,
- It may become necessary to prepare a cash book to find out the missing items such as cash purchases, cash sales, etc.
- By preparing total debtors account and total creditors account, credit sales and credit purchases can be ascertained respectively.
- Bills receivable account and bills payable account are to be prepared to find out the balances of bills receivable received and bills payable accepted respectively.
3. The final step is to prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet.
![]()
III Exercises
Question 1.
Find out profit or loss from the following information
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Opening Capital | 4,00,000 |
| Drawings | 90,000 |
| Closing Capital | 5,00,000 |
| Additional Capital during the year | 30,000 |
Solution:
| Statement of profit or loss | |
| Rs. ₹ | |
| Closing Capital | 5,00,000 |
| Add: Drawings | 90,000 |
| 5,90,000 | |
| Less: Additional Capital | 30,000 |
| Adjusted closing capital | 5,60,000 |
| Less: Opening capital | 4,00,000 |
| Profit for the year | 1,60,00 |
Question 2.
Calculate the missing information from the following.
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Profit made during the year | 4,800 |
| Capital at the end | ? |
| Additional Capital introduced during the year | 4,000 |
| Drawings | 2,400 |
| Capital in the beginning | 9,600 |
Solution:
Calculation of Closing Capital
| ₹ | |
| Closing capital (Bal. Fig) | 16,000 |
| Add: Drawings | 2,400 |
| 18,400 | |
| Less: Additional Capital | 4,000 |
| Adjusted closing capital | 14,400 |
| Less: Opening capital | 9,600 |
| Profit made during the year | 4,800 |
Answer:
Capital at the end Rs. 16,000
![]()
Note:
Step1: Add Profit of Rs. 4,800 with opening capital Rs. 9,600 = Adjusted closing capital Rs. 14,400
Step2: Add Additional capital of Rs. 4,000 with Adjusted closing capital Rs. 14,400 = Rs. 18,400
Step3: Deduct drawing Rs.2,400 from the total amount arrived (Step 2) Rs. 18,400 = Clsoing Capital Rs. 16,000.
Question 3.
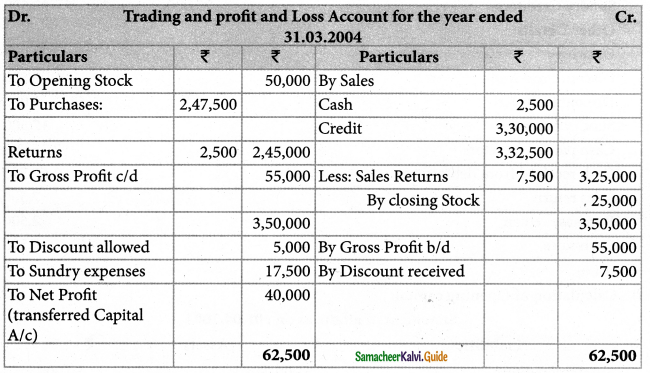
Mr. Suresh Strated business with Rs. 2,00,000 on 1st April 2003. His books are kept under single entry. On 31st March, 2004 his position was as under:
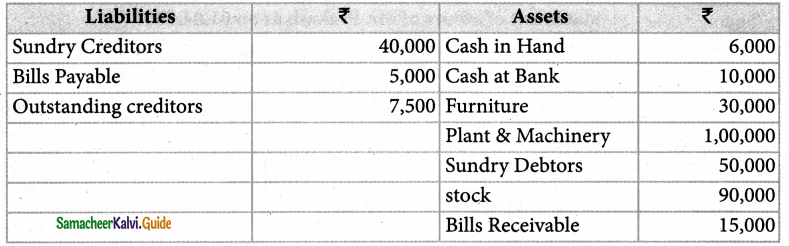
Ascertain the profit or loss made by Mr.Suresh for the year ended 31st March 2004.
Solution:
Statement of affairs of Mr. Suresh as on 31.03.2004
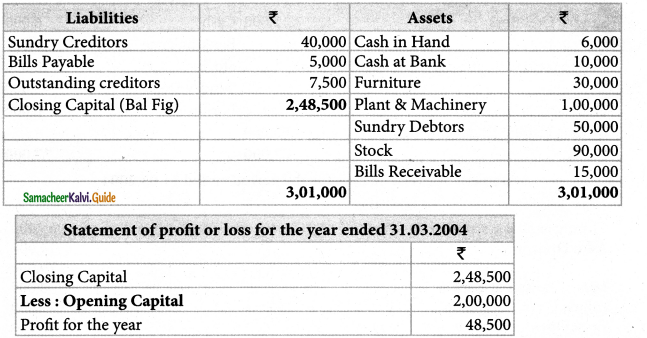
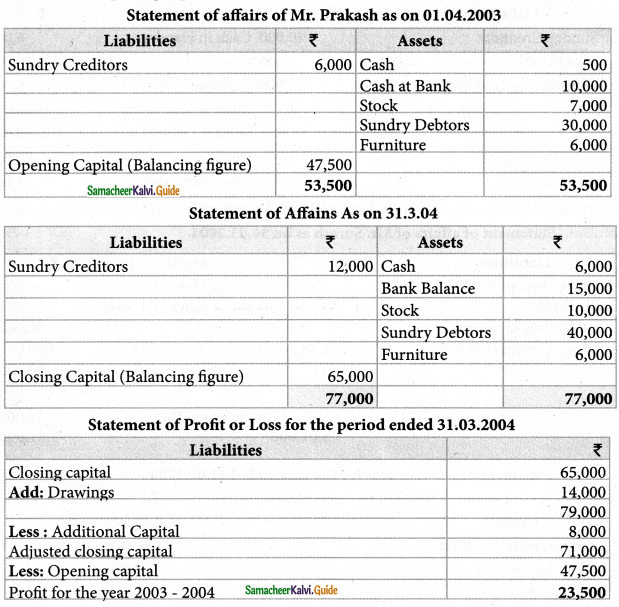
Question 4.
Prakash keeps his books by ‘Single Entry System His position on 01.04.2003 and
3 1.03.2004 was as follows.

He introduced an additional capital of Rs. 8,000 during the financial year. He withdraw Rs.= 14,000 for domestic purpose. Find out the profit for the year ended 3 1.03.2004.
Solution:
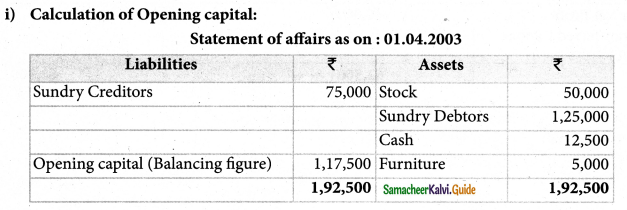
i) Calculation of opening capital:
Question 5.
Mrs. Vanitha keeps her books on singly entry basis. Find out the profit or loss made for the period ending 31. 03. 2004.
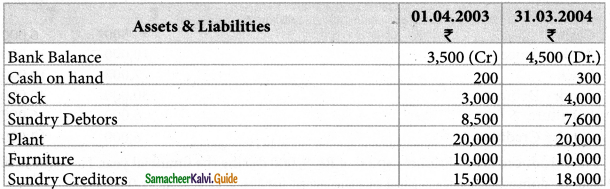
Mrs. Vanitha had withdrawn Rs. 10,000 for her personal use and had intrdocued fresh capital of Rs.4,000. A provision of 5% on debtors is necessary. Write off depreciation of plant at 10% and furniture at 15%.
Solution:
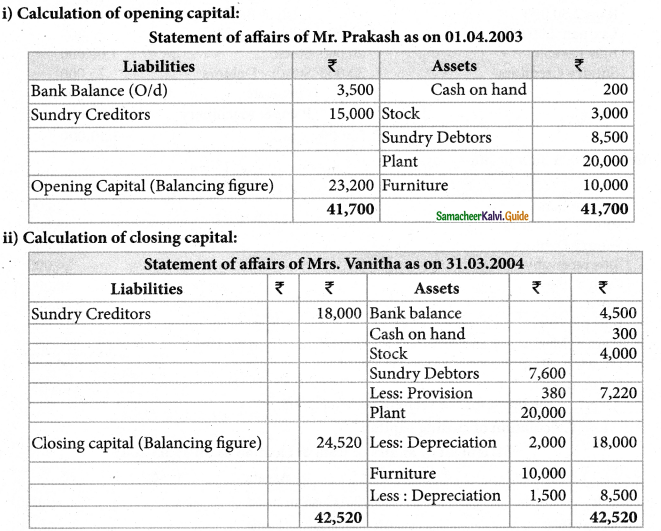

![]()
Question 6.
Ram and Laxman are equal partners in a business in which the books are kept by single entry. On 01.04.2004 their position was as under:
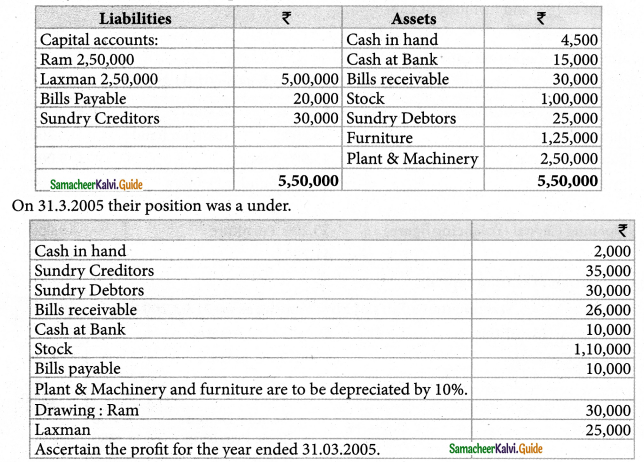
Solution:
Calculation of closing capital:
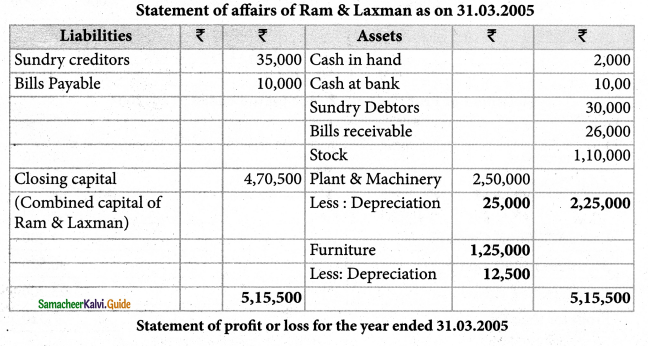
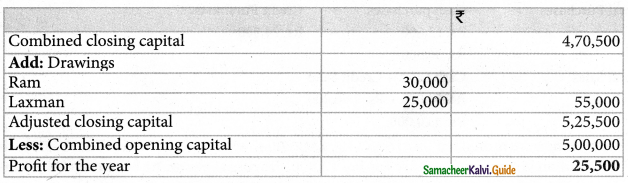
Question 7.
Find out total purchases and total sales from the following details by making necessary accounts:
| ₹ | |
| Opening balance of Sundry debtors | 50,000 |
| Opening balance of Sundry creditors | 30,000 |
| Cash collected from Sundry debtors | 3,00,000 |
| Discount received | 1,500 |
| Cash Paid to Sundry creditors | 20,000 |
| Discount allowed | 5,000 |
| Return inwards | 6,000 |
| Return in outwards | 8,000 |
| Closing balance of Sundry debtors | 35,000 |
| ciosi balance of Sundry creditors | 25,000 |
| Cash Purchases | 12,000 |
| Cish SaIes | 24,000 |
Solution:
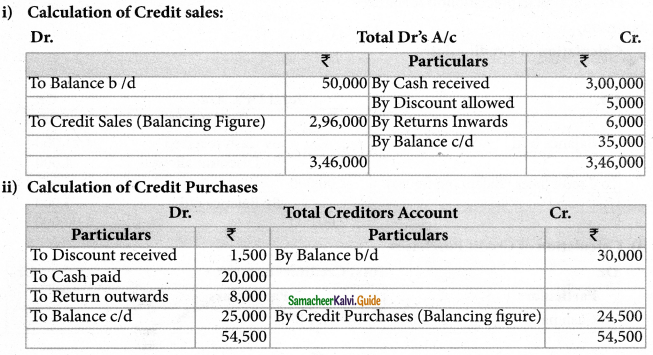
Total Purchases = Cash Purchases + Credit Purchases
= Rs. 12,000 + Rs. 24,500
= Rs. 36,500
Total Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales
= Rs. 24,000 + Rs. 2,96,000
= Rs. 3,20,000
![]()
Question 8.
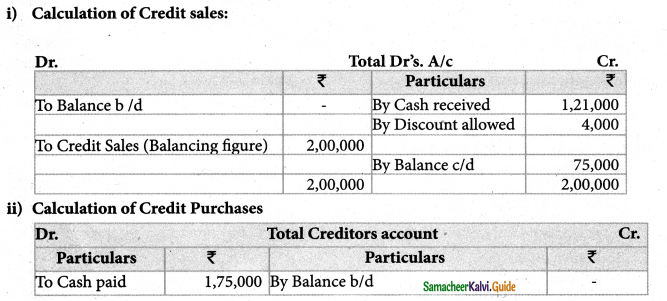
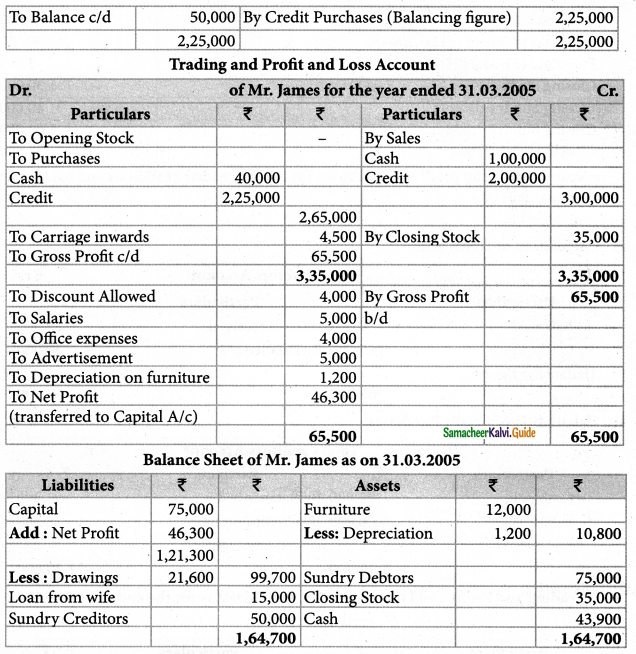
Mr. James commenced business on 1.04.2004 with a Capital of Rs. 75,000. he immediately bought furniture for Rs. 12,000. During the year, he borrowed Rs. 15,000 from his wife as loan. He has withdrawn Rs. 21,600 for his family expenses. From the following particulars you are required to prepare Trading and Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet as on 31.03.2005.
| Rs. | |
| Cash received from Sundry debtors | 1,21,000 |
| Cash paid to Sundry creditors | 1,75,000 |
| Cash Purchases | 1,00,000 |
| Cash Sales | 40,000 |
| Carriage inwards | 4,500 |
| Discount allowed to Sundry debtors | 4,000 |
| Salaries | 5,000 |
| Office Expenses | 4,000 |
| Advertisement | 5,000 |
| Closing balance of Sundry debtors | 75,000 |
| Closing balance of Sundry creditors | 50,000 |
| Closing Stock | 35,000 |
| Closing cash balance | 43,900 |
Provide 10% depreciationon furnitures
Solution:
Question 9.
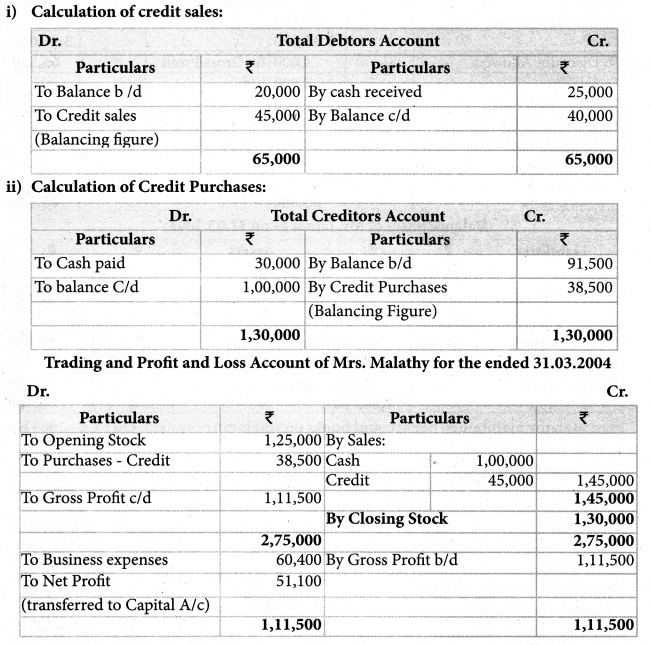
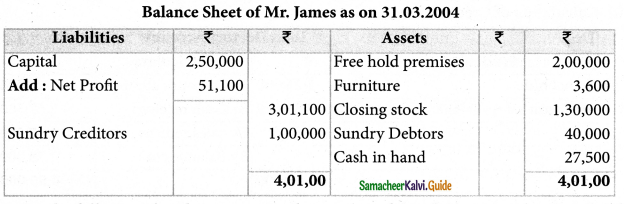
Mrs. Malathy maintained her account books on single entry system. On 01.04.2003 her Capital was Rs. 2,50,000.
Additional Information:
| Opening Stock | 1,25,000 |
| Cash received from Sundry debtors | 25,000 |
| Cash Sales | 1,00,000 |
| Cash Paid to Sundry creditors | 30,000 |
| Opening Sundry debtors | 20,000 |
| Opening Sundry creditors | 91,500 |
| Business expenses | 60,400 |
| Free hold premises (3 1.03.2004) | 2,00,000 |
| Furniture (31.03.2004) | 3,600 |
| Closing Stock | 1,30,000 |
| Closing Sundry debtors | 40,000 |
| Closing Sundry creditors | 1,00,000 |
| Closing cash balance | 27,500 |
Prepare trading and profit & loss account for the year ended 31.03.2004 and balance sheet
as on that date.
Solution:
![]()
Question 10.
From the following details, prepare Trading and Profit & Loss account for the period ended 31.03.2004 and a Balance sheet on that date.
Additional Information:
Solution: