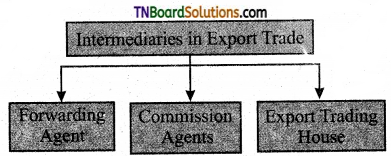
Students get through the TN Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 27 Facilitators of International Business which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 27 Facilitators of International Business
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is SAARC Council?
Answer:
At the top SAARC is represented by the heads of member nations. It meets once in two years. The headquarter is located in Nepal. SAARC secretariat is headed by the Secretary-General appointed by the members.
Question 2.
Write a note on ICSID?
Answer:
ICSID is an autonomous institution set up in order to provide a forum for conciliation and arbitration of the international dispute, It was set up in 1966. It is located in Washington.
![]()
Question 3.
What is a loan for development activities?
Answer:
India got several loan facilities from IMF for its several development projects.
Question 4.
What is export advice?
Answer:
India used to get expert advice from IMF for solving the economic problems. It has given valuable advice to India with regard to financing its 5-year plan.
Question 5.
When WTO established?
Answer:
The world trade organisation was established in 1995. In 1999 there were 135 member countries in the WTO.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Point out the objectives of SAARC.
Answer:
The objectives of SAARC include:
- Promoting the welfare of the people of Asia
- Achieving economic growth, social programme and cultural development in member countries.
- Strengthening self-reliance among the members.
- Strengthening co-operation among the members as well as with other developing countries and international and regional organization.
- Maintaining peace among the member nations in the region.
![]()
Question 2.
Point out the objectives of IMF.
Answer:
” The objective of IMF are:
- Promoting international monetary cooperation.
- Ensuring balanced international trade
- Ensuring exchange rate stability
- Eliminating or minimizing exchange restrictions by promoting multilateral payments.
- Providing economic assistance to member countries for correcting the imbalance in the balance of payments of countries
- Minimizing imbalance in quantum and duration of the balance of payment.
Question 3.
What are the IDA?
Answer:
It was set up in 1960. It provides term loans to member countries at concessional terms and conditions for their economic development. It creates supplementary sources of credit for member countries. It assists in the poverty alleviation programme of least developed countries. It provides support for health, education, infrastructure agriculture, human resources development of developing and least developed countries.
Question 4.
What is the meaning of IMF?
Answer:
International Monetary fund (IMF) is an international organization headquartered in Washington DC. It has a membership of 189 countries. It was established on 27th December 1945 on the recommendation of the Bretton Wood Conference. It provides shorter loan to member countries to their correct balance of payments disequilibrium.
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What is a world trade organisation? Explain functions and merits.
Answer:
Meaning: The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations. The goal is to help producers of goods and services, exporters, and importers in the conduct of international trade. Its main aim is to ensure the smooth flow of trade. The World Trade Organization (WTO) was established in 1995. In 1999, there were 135 member countries in the WTO.
Functions: The following are the functions of WTO:
- It facilitates the operations, implementations and administration of the objectives of Trade agreements.
- It provides negotiation facilities among member countries for smooth world trades.
- It helps for the settlement Of disputes between the member countries.
- It cooperates with International Monetary Fund and the World Bank to get greater coherence in global economic policymaking.
Merits:
- The system helps to promote peace.
- Disputes are handled constructively.
- Rules make life easier for all.
- Free trade cuts the costs of living.
- It provides more choice of products and qualities.
For Own Thinking
1. A vital role played in international business by WTO.
Answer:
World Trade Organisation (WTO) is the only global international organisation dealing with the rules of trade between nations.
2. Necessity for the world as a global village through IMF IBRD and SAARC.
Answer:
- It acts as short term credit institution at the international level.
- Promoting the welfare of the people of Asia.
![]()
For Future Learning
1. WTO- new agreements.
Answer:
Its main aim is to ensure smooth flow of goods trade. World organisation was established on 1st January 1993. The GATT was renamed as WTO with some changes WTO has 164 member countries as of 29th July 2016.
2. IMF World Bank and SAARC major role in international business.
Answer:
- Monitoring and coordinating the development programme.
- Dealing with modalities of financing.
- World Bank: Providing long term loans to developing countries.
- IMF: It works for faster global growth.
Multiple-choice questions
1. WTO is promoting international peace and creating a conducive environment for conducting:
(a) home trade
(b) itinerant trade
(c) small scale fixed retailers trade
(d) International trade
Answer:
(d) International trade
2. WTO meets almost once every years:
(a) three
(b) two
(c) one
(d) five
Answer:
(a) three
3. WTO has ………… member countries as of 29th July 2016.
(a) 184
(b) 172
(c) 164
(d) 192
Answer:
(c) 164
![]()
4. The WTO trade organisation WTO was established on:
(a) 1.1.1996
(b) 1.7.1998
(c) 1.8.1995
(d) 1.1.1995
Answer:
(d) 1.1.1995
5. World bank it was set up in ……….. order to reconstruct and rehabilitate the first world was affected countries of Europe and assist in the development of developing countries.
(a) 1955
(b) 1944
(c) 1996
(d) 2000
Answer:
(b) 1944
6. IMF has a membership of ……… countries.
(a) 189
(b) 190
(c) 119
(d) 168
Answer:
(a) 189
7. IMF was established on 27th December …………… on the recommendation of the Bretton wood conference.
(a) 1984
(b) 1945
(c) 1845
(d) 1996
Answer:
(b) 1945
8. SAARC number of member countries include:
(a) 12
(b) 10
(c) 8
(d) 9
Answer:
(c) 8
![]()
9. SAARC was established on:
(a) 8.12.1985
(b) 8.12.1986
(c) 8.12.1987
(d) 8.12.1988
Answer:
(a) 8.12.1985
10. SAARC the headquarter is located in:
(a) Nepal
(b) Asia
(c) Bengal
(d) London
Answer:
(a) Nepal
11. SAARC it meets once in ………. years.
(a) Five
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) One
Answer:
(b) Two