Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 10 Organisms and Population which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 10 Organisms and Population
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Define Ecosphere.
Answer:
Ecosphere is defined as the largest and nearly self-sufficient biological system which includes all the living organisms of the Earth. They interact with the physical environment to regulate their distribution abundance, production, and evolution.
Question 2.
Name the abiotic factors of an environment.
Answer:
The abiotic factors of an environment include light, temperature, pressure, water, and salinity.
![]()
Question 3.
Define the niche of an organism.
Answer:
The niche of an organism is defined as the total position and function of an individual in its environment.
Question 4.
What is Van’t Hoff’s rule?
Answer:
Van’t Hoffs’s rule is that with the increase of every 10°C, the rate of metabolic activity doubles, or with the decrease of every 10°C, the metabolic rate is halved.
Question 5.
Define Phototaxis.
Answer:
Phototaxis is defined as the movement of an organism in response to light.
Eg: Moth (Positive Phototaxis), Earthworm (Negative Phototaxis).
Question 6.
Define porosity of soil.
Answer:
The porosity of the soil is defined as the percentage of soil volume occupied by pore space or by interstitial space.
Question 7.
Name any two plants present in hot deserts.
Answer:
- Agave
- Euphorbia
![]()
Question 8.
What is meant by cold deserts?
Answer:
Cold deserts are referred to as places where cold with snowfall and high overall rainfall throughout the winter and occasionally during summer.
Question 9.
Define population.
Answer:
The population is defined as any group of organisms of the same species, which can interbreed among themselves.
Question 10.
Explain population dispersion.
Answer:
Population dispersion is the tendency of the population to disperse or spread out in all directions until some barriers are reached.
Question 11.
What is meant by relative abundance?
Answer:
Relative abundance is a time-related index, which can show the changes in number in a population with respect to time. Eg: The number of birds of a particular species spotted in a unit area over a period of time.
![]()
Question 12.
Mention the factors, that regulate a population.
Answer:
- Extrinsic factors. Density independent.
- Intrinsic factors. Density-dependent.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between anadromous migration and catadromous migration.
Answer:
| Anadromous Migration | Catadromous Migration |
| Anadromous migration is the migration of organisms from sea to freshwater. Eg: Salmon fish. |
Catadromous migration is the migration of organisms from freshwater to sea. Eg: Eel. |
Question 2.
What is structure adaptation? Give one example.
Answer:
Structural adaptation is the modification of the external and internal structures of an organism to suit them to adapt better to their environment.
Eg: Growing thicker fur in mammals to withstand the freezing climate in Arctic regions.
Question 3.
List out the adaptations of desert animals.
Answer:
The desert animals possess special adaptations to cope up with the desert environment. They are:
- The animals living in the desert are capable of taping available water and storing sufficiently to withstand the heat.
- Small nocturnal carnivores are predominant animals in the desert.
- They are burrowers having cursorial, fossorial, and saltatorial adaptations.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain briefly about relative humidity.
Answer:
The amount of water vapor present in the air is known as relative humidity. It is expressed as a percentage of the amount needed for saturation at the same temperature. At a given temperature, a high percentage of humidity means that the air mixture is more humid. Humidity can be measured using an instrument called a Hygrometer.
Question 5.
Mention any three functions of soil.
Answer:
The functions of soil include:
- The soil forms a medium for plant growth.
- Soil is meant for water storage and purification.
- Soil is the habitat for many organisms, which in turn modify and enrich the soil.
Question 6.
Explain the term “Photokinesis”.
Answer:
Photokinesis is a change in the speed of locomotion in the motile organisms or cells in response to a change in light intensity. This change of movement (or frequency of turning) is brought out by the change in the intensity of light. The movement may be undirected random movement of an organism in response to light.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Give an account of adaptations of animals in response to temperature.
Answer:
- Temperature is one of the major abiotic factors of the environment, which decide the survival of an animal in a particular environment.
- The survival of an organism in an environment depends on its adaptation to temperature. Eurytherms are organisms, which can survive a wide range of temperatures.
Eg: Cat, dog, tiger, and human. - Eurythmy is an aspect of thermoregulation in animals. Cold erythema is the adaptation of animals for the survival of the species during the ice ages. The ability of animals to survive in a wide range of temperatures increases a species ability to inhabit other areas – an advantage for natural selection.
- Stenotherms are animals that can tolerate a narrow range of temperatures. Eg: Fish, frogs, lizards, and snakes.
The adaptation includes:
- In the case of extreme temperatures, organisms have adapted by forming heat-resistant spores, cysts. Eg: Entamoeba
- They form antifreeze protein to withstand severe cold.
Eg: Arctic fishes. - They adapt to hibernation (Winter sleep) and aestivation (Summer sleep).
- In certain conditions, migration is an appropriate adaptation to overcome extreme temperatures.
![]()
Question 2.
Draw and label the graphical representation of types of organisms based on temperature tolerance.
Answer:
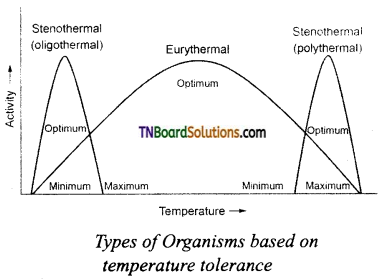
Question 3.
List out any five adaptations of aquatic animals.
Answer:
The adaptations of aquatic animals include the following:
- In fish, the pectoral fins and dorsal fins act as balancers and the caudal fin helps in changing direction as a rudder.
- Streamlined body structure helps in the swift movement of animals in the water.
- The presence of an air bladder filled with air helps for buoyancy.
- Integument rich in mucous glands is protected by scales.
- With well-developed excretory organs, they maintain water and ionic balance in their body.
Question 4.
Give an account of the role of migration in a population.
Answer:
Migration is the mass movement of a population from one place to another and back.
Migration is a peculiar and unique kind of mass movement to avoid extreme conditions of weather. The Siberian cranes migrate from Siberia to Vedanthangal in TamilNadu, in order to avoid severe winter cold in Siberia. Likewise, some fishes migrate from sea to freshwater (anadromous migration Eg: salmon) and some fresh water to sea (catadromous migration Eg: Eel).
Migration is of two types Emigration and Immigration.
Emigration: It is the type of migration outside the habitat, due to overcrowding of the population. This helps to prevent over-exploitation of habitat. It leads to the establishment of new habitat.
Immigration: It refers to the movement of population into the habitat from outside. It results in population levels. If the population increases beyond the carrying capacity of the habitat, it can result in increased mortality of immigrants or decrease the reproductive capability of individuals.
![]()
Choose the correct answers:
1. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
2. Match the following:
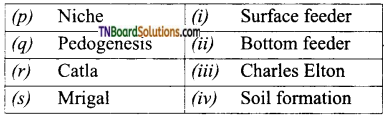
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
3. Match the following:
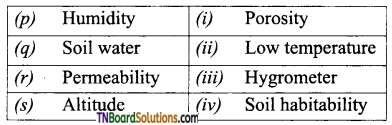
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii);'(s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
4. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
5. Ethology is the scientific study of:
(a) animal reproduction
(b) plant reproduction
(c) animal behaviour
(d) plant response to light
Answer:
(c) animal behavior
6. Arrangement of body muscles in the form of bundles help in:
(a) metabolism
(b) locomotion
(c) hunting
(d) predation
Answer:
(b) locomotion
7. In the pond ecosystem, the column feeder is:
(a) catla
(b) mrigal
(c) common carp
(d) rohu
Answer:
(d) rohu
![]()
8. Tundra herbivores include:
(a) Arctic hare
(b) Snowy owl
(b) Arctic fox
(d) Bob cat
Answer:
(a) Arctic hare
9. Choose the odd one out:
(a) Light
(b) Temperature
(c) Water
(d) Soil microbes
Answer:
(d) Soil microbes
10. Identify the odd one:
(a) Polar bear
(b) Elephant
(c) Gaur
(d) Antelope
Answer:
(a) Polar bear
11. Find out the odd one:
(a) Trachea
(b) Gills
(c) Air bladder
(d) Lungs
Answer:
(c) Air bladder
![]()
12. Choose the odd one:
(a) Population density
(b) Ecological density
(c) Crude density
(d) Fecundity
Answer:
(d) Fecundity
13. Choose the correct pair.
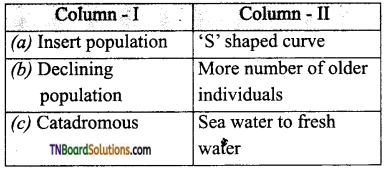
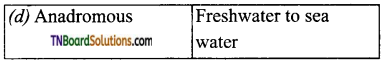
Answer:
(b)
14. Find out the correct pair.
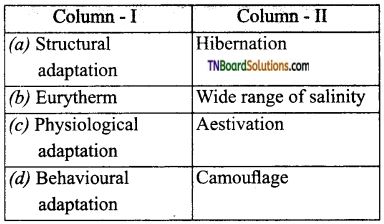
Answer:
(c)
15. Choose the incorrect pair.
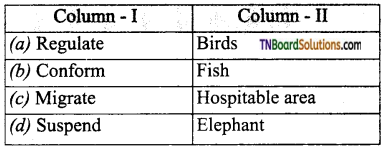
Answer:
(d)
16. Which of the following is incorrect pair?
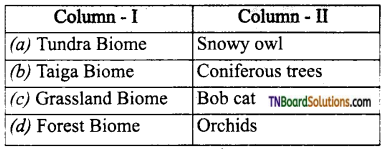
Answer:
(c)
![]()
17. Assertion: In a tropical forests, the soil nutrient-poor and acidic.
Reason: Decomposition is rapid and soils are subject to heavy leaching.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is wrong, Reason is correct.
(d) Assertion is correct, Reason is Wrong.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
18. Assertion: Grassland biome often is characterized by high winds.
Reason: Dense tree cover is not present in the Grassland biome.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is wrong, Reason is correct.
(d) Assertion is correct, Reason is Wrong.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
19. Assertion: Clay soil has a high water retention capacity due to high porosity.
Reason: The pore space between soil particle are more in clay soil.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is wrong, Reason is correct.
(d) Assertion is correct, Reason is Wrong.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
![]()
20. Assertion: in aquatic media, maintaining homeostasis and osmotic balance is a challenge.
Reason: Marine animals have appropriate adaptations to prevent cell shrinkage.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is wrong, Reason is correct.
(d) Assertion is correct, Reason is Wrong.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
21. Choose the correct statement:
(a) Light does not influence reproduction.
(b) Light does not influence the growth of an organism.
(c) Light influences pigmentation.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Light influences pigmentation.
22. Find out the incorrect statement:
(a) Water holding capacity of soil is directly dependent on soil porosity.
(b) Water holding capacity of soil is inversely dependent on soil porosity.
(c) Soil permeability is directly dependent on pore size.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Water holding capacity of soil is directly dependent on soil porosity.
23. Choose the correct statement:
(a) Tundra biomes have long summers and short winters.
(b) Tundra biomes have long winters and short summers.
(c) Tundra biomes have little daylight in summer and long daylight in winter.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Tundra biomes have long winters and short summers.
![]()
24. Which of the following statement is not correct?
(a) In aquatic animals, respiration is by gills.
(b) Presence of air bladders filled with air helps buoyancy.
(c) In fish, pectoral fins and dorsal fins act as balancers.
(d) None of the above statements is correct.
Answer:
(d) None of the above statements is correct.