Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Name any two viral diseases.
Answer:
- Chickenpox
- Dengue fever.
Question 2.
Name the causative agents of diseases: cholera and measles.
Answer:
- Cholera – Vibrio cholerae,
- Measles-Rubella virus.
![]()
Question 3.
Mention any two fungal diseases.
Answer:
- Ringworm disease
- Dermatomycosis
Question 4.
Give the scientific names of roundworm and filarial worm.
Answer:
- Round worm – Ascaris lumbricoides.
- Filarial worm – Wuchereria bancrofti
Question 5.
Define immune response.
Answer:
The immune response is defined as the mechanisms used by the body for protection from environmental agents that are foreign to the body.
Question 6.
What is innate immunity?
Answer:
Innate immunity is the natural phenomenon of resistance to infection which an individual possesses right from birth.
Question 7.
Define cell-mediated immunity.
Answer:
Cell-mediated immunity is defined as an immunological phenomenon through which the pathogens are destroyed by cells without producing antibodies.
![]()
Question 8.
Define humoral immunity.
Answer:
Humoral immunity is defined as a process through which the pathogens are destroyed by the production of antibodies.
Question 9.
What is the spleen?
Answer:
The spleen is a secondary lymphoid organ, located in the upper part of the abdominal cavity close to the diaphragm. It brings humoral and cell-mediated immunity and contains B and T cells.
Question 10.
What are the functions of immunoglobulins?
Answer:
The functions of immunoglobulin include agglutination, precipitation, opsonization, and neutralization.
Question 11.
Define vaccine therapy.
Answer:
Vaccine therapy is defined as a method of treatment of disease by the use of vaccines.
Question 12.
Who developed the polio vaccine and rabies vaccine?
Answer:
- The Polio vaccine is first developed by Dr. Jonas Salk.
- The rabies vaccine is developed by Louis Pasteur.
![]()
Question 13.
What is the latest contribution of vaccines?
Answer:
The latest contribution in vaccines is the DNA vaccine or recombinant vaccine.
Question 14.
Define Anaphylaxis.
Answer:
Anaphylaxis is defined as a classical, sudden, systematic, severe hypersensitivity reaction occurring as a result of rapid generalized mast-cell degranulation.
Question 15.
Define Autoimmunity.
Answer:
Autoimmunity is defined as an abnormal immune response, in which the body produces antibodies cytotoxic T cells in response to self-antigens and destroys the individual’s own tissue.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
What are types of autoimmune diseases? Explain.
Answer:
Autoimmune diseases in humans are divided into two categories namely organ-specific and non-organ specific auto-immune diseases. The organ-specific immune disease is mostly directed against one organ. The functions performed by the organ are blocked by the antibodies produced.
Eg: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Grave’s disease, and Addison’s disease (adrenal gland).
The non-organ specific disorders are otherwise known as systemic disorders in which autoimmune activity is widely spread throughout the body.
Eg: Rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain Immunotherapy.
Answer:
Immunotherapy is otherwise called biological therapy, in which the substances made by the body or in a laboratory (monoclonal antibodies) are used to improve or to resist the immune system’s function. The immunotherapy of cancer involves different approaches. After the removal of the gross tumor, the patient is given immunotherapy to get nd of residual malignant cells. An integrated approach of treatment by combining surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy is the best treatment for cancer.
Question 3.
List the symptoms of mental depression.
Answer:
- Loss of self-confidence and self-esteem,
- Showing anxiety.
- Not being able to enjoy things that are usually pleasurable or interesting.
Question 4.
List the causative agents, mode of transmission, and symptoms of the diseases – Cholera, Pneumonia, and Tuberculosis.
Answer:
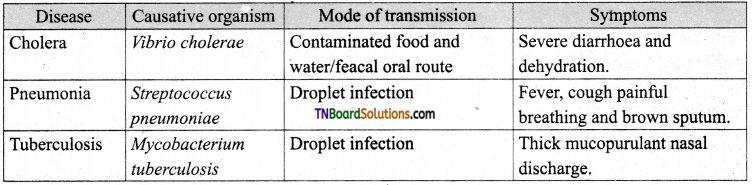
Question 5.
Differentiate between normal cells and cancer cells.
Answer:
| Normal cell | Cancer Cell |
| Normal cells are small having uniformly shaped nuclei and relatively large cytoplasmic volume. | Cancer cells are large having variable shaped nuclei and relatively small cytoplasmic volume. |
| Cell size and shape are confirmed and form discrete tissues. | They are variable in cell size and shape. Disorganized arrangement of cells. |
| They may possess differentiated cell structures. Normal presentation of cell surface markers. | Loss of normal specialized features Elevated expression of certain cell markers. |
| Lower levels of dividing cells, clearly demarkated cell tissues. | Large number of dividing cells and poorly defined tumor boundaries. |
![]()
Question 6.
Write briefly about swine flu.
Answer:
Swine flu is caused by the HINI virus strain. This flu was first recognized in the year 1919. Fever, cough, sore throat, chills, weakness, and body ache are the common symptoms of this flu. Children, pregnant women, and elderly people are highly susceptible to infection.
Question 7.
Draw and label the structure of Trypanosoma gambiense.
Answer:
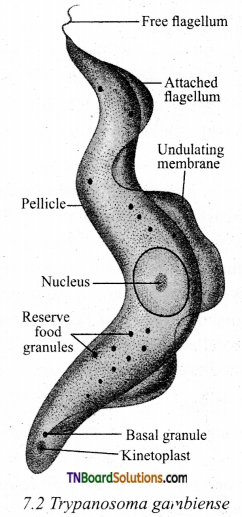
Question 8.
Explain adenoids and their function.
Answer:
Adenoids are glands located at the roof of the mouth, the place where the nose connects to the throat. The main function of adenoids is the production of antibodies, which help to resist infections. The adenoids shrink during adolescence and may disappear during adulthood.
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Draw the structure of HIV and label the parts.
Answer:
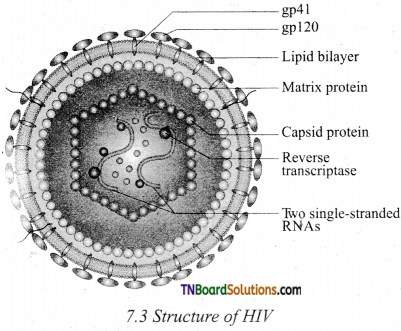
Question 2.
Give an account of fungal diseases in humans.
Answer:
Fungal diseases are known before bacterial diseases in humans. The fungal genera, Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton cause a skin infection in human being called Dermatomycosis.
Ring Worm is also one of the most common diseases in humans. The main symptoms of this disease include the appearance of dry, scaly lesions on the skin, nails, and scalp. Generally, these fungi grow in skin folds such as those in-between toes and in the groin due to heat and moisture. Tenea pedis causes ringworms of feet called Athlete’s feet. The infection of ringworms is acquired from the soil. The transmission of this disease may also be carried by using clothes, towels, and comb used by infected persons.
Question 3.
Distinguish between primary immune response and secondary immune response.
Answer:
| Primary immune response | Secondary immune response. |
| Primary immune response occurs as a result of primary contact with as antigen. | Secondary immune response happens as a result of second or subsequent contact with the same antigen. |
| During 7 to 10 days of infection, antibody level reaches the peak. | Within 3 to 5 days the antibody level reaches the peak. |
| Long period is to establish immunity. | Short time is required to establish immunity. |
| In this, there is rapid decline in antibody level. | Antibody level remain high for longer period. |
| Primary immune response mainly in lymph nodes and spleen. | Secondary immune response generally appears is bone marrow, followed by spleen and lymph nodes. |
![]()
Question 4.
List the different groups of drugs along with their effects.
Answer:
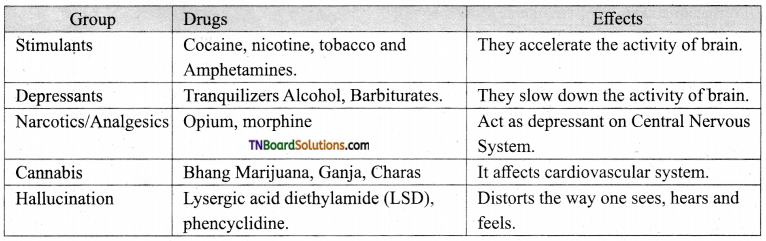
Question 5.
Mention any five viral diseases and what is the mode of their transmission and symptoms?
Answer:


Activities
Activity 1: Students examine the impact of microorganisms in our daily life and consider their applied potential. They can also conduct independent research and communicate their findings.
- Examine the microorganisms in curd – Lactobacillus sp.
- Examine the microorganisms in baking – yeast.
- Examine the microorganism present in the root nodules of the pea plant – Rhizobium.
Students can do experiments with curd fermentation. The boiled and cooled milk can be inoculated with little curd as an experiment and another part without inoculum serves as a control. Observe both with and without inoculum after 12 hrs, Examine the organisms in both, and report the findings.
Activity 2: Students prepare wet mounts to observe the microbes found in curd.
Observation: Lactobacillus sp.
Activity 3: The leader will blow bubbles at the group of students to demonstrate how some diseases can be airborne?
Observation: Bubbles spread in all directions in the air, simulating the airborne pathogen.
![]()
Activity 4: Which parasite acts as a transporter host for other parasites? Discuss.
Trypanosoma brucei is a protozoan known to cause sleeping sickness in humans but actually uses tests fly as its definite host, as that is where it develops into maturity and reproduces. The definite host for a Plasmodium, the genus of parasite that causes malaria, is the female Anopheles mosquito.
Activity 5: Your friends call you a ‘sissy boy’ because you do not smoke or chew tobacco. What answer will you give? How will you prove your strength?
- Smoking and tobacco chewing lead to lung cancer and check cancer respectively due to the presence of carcinogenic nicotine.
- Lung diseases caused by smoking include COPD, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis smokers are 12 to 13 times more likely to die from COPD than non-smokers. Tobacco chewers are more vulnerable to the onset of cancer.
Choose the correct answers.
1. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
2. Match the following:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(iif; (s)-(i)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
![]()
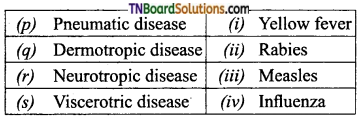
3. Match the following:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
4. Match the following (in relation to drugs):
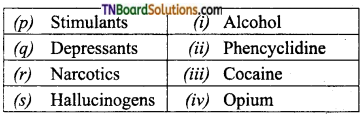
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
5. Match the following:
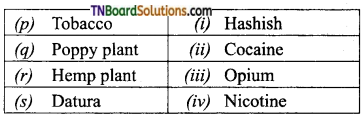
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
6. The ring worm disease is caused by:
(a) A worm
(b) Bacteria
(c) Fungi
(d) Virus
Answer:
(c) Fungi
7. The duration of the Erythrocytic cycle in quartan malaria is:
(a) 48 hours
(b) 72 hours
(c) 36 hours
(d) 40 hours
Answer:
(b) 72 hours
8. The cholera is a bacterial disease and the site of infection is:
(a) Liver
(b) Lungs
(c) Skin
(d) Intestine
Answer:
(d) Intestine
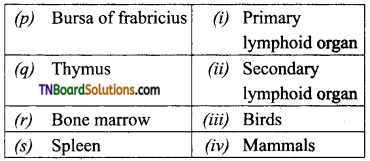
9. Which of the following is the primary lymphoid organ?
(a) Thymus
(b) Lymph node
(c) Spleen
(d) Pancreas
Answer:
(a) Thymus
10. Regular use of morphine effects:
(a) Intestine
(b) Central Nervous system
(c) Cardiovascular system
(d) Liver
Answer:
(b) Central Nervous system
![]()
11. Choose the odd man out:
(a) Cocaine
(b) Nicotine
(c) Cannabis
(d) Amphetamine
Answer:
(c) Cannabis
12. Find the odd one out:
(a) Precipitin
(b) Agglutinin
(c) Opsonin
(d) Creatin
Answer:
(d) Creatin
13. Indicate the odd one out:
(a) Lymphocytes
(b) Monocytes
(c) Red Blood cells
(d) Neutrophils
Answer:
(c) Red Blood cells
14. Choose the odd one out:
(a) Bursa of fabricius
(b) Spleen
(c) Peyer’s patebes
(d) Lumph node
Answer:
(a) Bursa of fabricius
![]()
15. Identify the odd one out:
(a) Cholera
(b) Elephantiasis
(c) Diphtheria
(d) Malaria
Answer:
(b) Elephantiasis
16. Choose the correct pair:
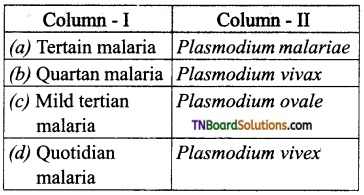
Answer:
(c)
17. Which of the following is an incorrect pair?
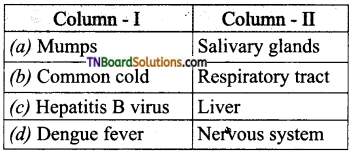
Answer:
(d)
![]()
18. Choose the correct pair:

Answer:
(a)
19. Find out the incorrect pair:
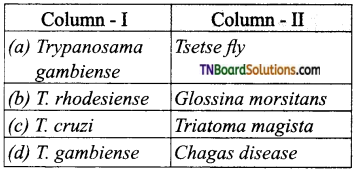
Answer:
(d)
20. Which of the following is a correct pair?
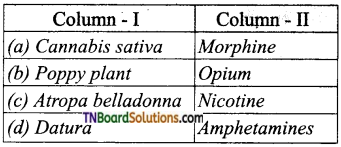
Answer:
(b)
21. Assertion: Alcohol is a psychoactive drug, affecting a person’s mind and behavior.
Reason: Alcohol acts on the brain and slows down the activity of the brain.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
![]()
22. Assertion: When a cell undergoes malignant transformation, it acquires a new surface antigen and may also lose some normal antigens.
Reason: These antigens are present on the membranes of malignant cells.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
23. Assertion: The third-generation vaccine contains the purest and the highest potential vaccine.
Reason: Because they are natural potential vaccines.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong.
![]()
24. Assertion: B lymphocytes leave the bone marrow and mature in the thymus gland.
Reason: Once mature, they accumulate in the same areas of T cells.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
25. Assertion: Active immunity is acquired through the use of a person’s immune responses, which lead to the development of memory cells.
Reason: Active immunity results from an infection or an immunization.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is wrong.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
26. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) The unique feature of acquired immunity is antigenic specificity.
(b) The unique feature of acquired immunity is diversity.
(c) The unique feature of acquired immunity is recognition of self and non-self and immunological memory.
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
27. Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Innate immunity is the natural phenomenon of resistance to infection.
(b) These defense mechanisms are non-specific.
(c) This type of immunity results from an infection.
(d) It is otherwise known as natural immunity.
Answer:
(c) This type of immunity results from an infection.
![]()
28. Indicate the correct statement.
(a) Filariasis is a viral disease
(b) Filariasis is a bacterial disease
(c) Filariasis is a fungal disease
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
29. Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Neurotropic disease includes rabies and polio.
(b) Yellow fever and dengue fever are grouped under viscerotropic diseases.
(c) Dermotropic diseases include chickenpox and measles.
(d) None of the above statements is correct.
Answer:
(d) None of the above statements is correct.
30. Find out the correct statement:
(a) In the primary immune response, antibody level reaches a peak in 8-12 days.
(b) Primary immune response occurs as a result of primary contact with an antigen.
(c) In this, there is a rapid increase in antibody level.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Primary immune response occurs as a result of primary contact with an antigen.