Students get through the TN Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 19 Sources of Business Finance which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 19 Sources of Business Finance
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What are External sources?
Answer:
External sources of funds include all those sources which generate funds from outside the business enterprise. For example issue of shares and debentures, borrowings from banks and financial institutions, public deposits, factoring, leasing, hire purchase, etc.
Question 2.
What are mutual funds?
Answer:
An individual investor who wants to invest in equities and bonds with a balance of risk and return generally can invest in mutual funds. Nowadays people invest in stock markets through a mutual fund. A systematic investment plan is one of the best investment options in India.
Question 3.
Business finance on the basis of ownership types of categories.
Answer:
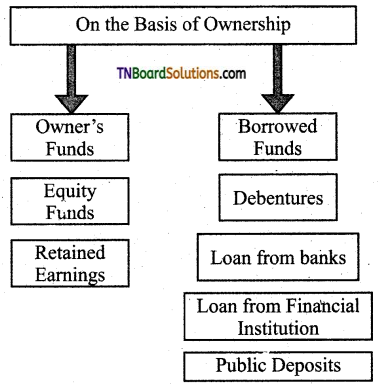
![]()
Question 4.
Expand ULIP?
Answer:
ULIP is a life insurance-linked product, which provides risk cover for the policyholder along with investment options to invest in any number of qualified investments such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Explain PPF?
Answer:
Public Provident Fund (PPF): It is the safest long-term investment option for investors in India. It is totally tax-free. PPF account can be opened in a bank or post office. The money deposited cannot be withdrawn before 15 years and an investor can earn compound interest from this account. However, the investor can extend the time frame for the s next five years if the investor does not opt to withdraw the amount matured for payment at the maturity date. PPF investor can take a loan against PPF account when he/she experiences financial difficulties.
Question 2.
What is the post office saving scheme?
Answer:
There are different types of postal small savings schemes namely Post Office Savings Account, Post Office Recurring Deposit Account (RD), Post Office Fixed Deposit Account (FD/TD), Post Office Monthly Income Account Scheme (MIS), Senior Citizens Saving Scheme (SCSS) Public Provident Fund Account (PPF), National Savings Certificates (NSC), Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP), Sukanya Samriddhi Account (SSA). Investors can choose the appropriate postal schemes as per their needs. Postal investment schemes are the safest investments.
Question 3.
What are public deposits?
Answer:
Public deposits are more beneficial than the fixed deposit in the bank, in the matter of yielding good returns. An investor has to select the investment period very carefully. He/she is not allowed to withdraw money before maturity. However, the public deposits collected by companies and institutions do not offer any insurance benefits. It does not come under the control of the Reserve Bank of India. Investors who are willing to invest for the long term can opt for public deposits.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Bonds?
Answer:
Bonds are one of the ideal investment options for those investors who would like to invest their hard-earned money safely. Bonds are issued both by government and public and private sector companies and financial institutions. Mostly there are four types of bonds sold in ‘India namely Government bonds, Corporate bonds, Banks and other financial institutions bonds, and Tax saving bonds. The term bond is used for the debt collected by the government while the term debenture is used when the corporates collect debt capital from the public. Investment in bonds is totally risk-free.
Question 5.
Explain bank deposits.
Answer:
Fixed deposits (FD) enable the investor to invest the money for a specific period. The Fixed deposit can be opened from a minimum period of 7 days to a maximum period of 10 years. The fixed deposit holder can take a loan against the fixed deposit receipt. The depositor cannot withdraw the fixed deposits before the maturity date.
A recurring deposit (RD) account is another investment option for those people who earn regular income. This deposit can be opened for a minimum period of 1 year to a maximum period of 10 years. The Recurring deposit holder can take a loan against the installments paid.
Question 6.
Explain the terms- Bank overdraft?
Answer:
Bank overdraft refers to an arrangement whereby the bank allows the customers to overdraw the required amount from its current deposit account within a specified limit. Interest is charged only on the amount actually overdrawn.
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the term-Share.
Answer:
Corporate enterprises generally obtain capital mainly from share capital which is divided into small units called shares. Each share has a nominal value. The Indian Companies Act 2013 describes a share as “to be a share in the share capital of a company”. The person holding a share is called a shareholder.
Question 8.
Write about savings.
Answer:
The concept of savings plays an important role in the economic development of any country. Saving is defined as the difference between income and consumption. In other words, it points to sacrifices of some sort. Earning money may be easy, but using it in the right way as well as saving it for the future is pretty tough. Savings is important for each and every one of us to lead a peaceful life. Saving paves way for a happier future. “World Savings Day” was promoted all over the world to emphasize the value Of savings. October 31 has been declared as the “World Savings Day” by. the International Savings Bank Congress.
Question 9.
Write about Estate Investment.
Answer:
Real estate is one of the fastest-growing sectors in India. Buying a flat or plot is supposed to be the best decision amongst the investment options. The value of the real asset may increase substantially depending upon the area of location and other support facilities available therein. However, an investor in real estate has to be cautious and circumspect in verifying the genuineness of the title deeds before investing in real estate assets and also the reputation of the seller of real assets.
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Do the following points highlight the importance of savings?
Answer:
Importance of Savings: Money invested in a deposit account, small savings schemes, mutual funds, life insurance policies, Bonds of Government companies, shares, etc. lead to the overall economic development of a country.
- Money invested in bank deposits facilitates employment generation in various sectors of the economy and poverty alleviation.
- The savings invested in bank deposits lead to credit creation in the country which in turn promotes industrial and agricultural development in a country.
- Savings invested in government bonds and various institutions help in great measure in building in strengthening the infrastructure facilities in a country.
- A country with higher savings can easily face the consequences of an economic recession.
- The bad consequences of inflation can be met easily with strong savings. As a result, the evil effect of soaring prices can be controlled.
Question 2.
Significance of business finance.
Answer:
The following points highlight the significance of business finance.
- A firm with adequate business finance can easily start any business venture.
- Business finance helps the business organization to purchase raw materials from the supplier easily to produce goods.
- The business firm can meet financial liabilities like prompt payment of salary and wages, expenses, etc., in time with the help of sound financial support.
- Sound financial support enables the enterprises to meet any unexpected or uncertain risks arising from the business environment efficiently. For example economic slowdown, trade cycles, severe competition, a shift in consumer preference, etc.
- A sound financial position empowers the enterprise to attract talented manpower and introduce the latest technology.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the nature of Business finance.
Answer:
Nature of Business Finance: The following characteristics can be derived from the above definitions.
- Business finance comprises all types of funds namely short, medium, and long-term used in business.
- All types of organizations namely small, medium and large enterprises require business finance.
- The volume of business finance required varies from one business enterprise to another depending upon its nature and size. In other words, small and medium enterprises require a relatively lower level of business finance than large-scale enterprises.
- The amount of business finance required differs from one period to another. In other words, the requirement of business finance is heavy during the peak season while it is at a low level during the dull season.
- The amount of business finance determines the scale of operations of business enterprises.
Case Study
Gokul Steel Ltd is a large and credit-worthy company that manufactures steel for the Indian market. It now wants to cater to the Asian market and decides to invest in new hi-tech machines. Since the investment is large, it requires long-term finance. It decides to raise funds by issuing equity shares. The issue of equity shares involves huge floatation costs. To meet the expenses of floatation cost, the company decides to tap the money market.
(a) Name and explain the money-market instrument the company can use for the above purpose.
They help the central bank in regulating liquidity in the economy. Money market help short-term fund user to fulfill their needs reasonable costs.
(b) What is the duration for which the com party can get funds through the instrument?
These instruments are short-term notes issued by state and municipal governments although they carry somewhat more risk than T-bills and tend to be less negotiable. They feature the added benefit that the interest is not subject to federal income tax. For this reason, corporations find that the lower yield is worthwhile on this type of short-term investment.
(c) State any other purpose for which this instrument can be used.
Financial instruments are assets that can be traded. They can also be seen as packages of capital that may be traded. Most types of financial instruments provide an efficient flow and transfer of capital all throughout the world investors. These assets can be cash a contractual right to deliver or receive cash or another type of financial instrument or evidence of one’s ownership of an entity.
![]()
For Own Thinking
Question 1.
Working of chit funds.
Answer:
Equity mutual funds are managed by professional and certified funds managers who have expertise and experience in financial markets. As mutual funds collect money from many investors the cost of asset management is divided between a larger number of people. Thus reducing the assets management fee per person.
Question 2.
Finance for bonded labor.
Answer:
“Debt bondage” also known as debt slavery or bonded labor is a person’s pledge of labour or service as security for the repayment for a debt or other obligation where there is no hope of actually repaying the debt.
For Future teaming
Question 1.
Export finance for small entrepreneurs.
Answer:
Exporting goods and services can bring significant opportunities for companies of all sizes. By tapping into new markets and new revenue streams. Companies can access a larger customer base and grow their business. Importantly these opportunities are not limited to large corporations.
![]()
Question 2.
Financing software companies run by young graduates.
Answer:
Even employees already working in the financial sector eyeing opportunities in tech; In a new study of over 800 financial services employees in partnership with Kronos. We found that one-fourth are more interested in working in the tech industry than finance. Finance as a career choice is down 22% from 2008 and graduates from the top 10 MBA schools are now 40% less likely to work’ in investment banking.
Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
Equity Shareholders are called:
(a) owners of the company
(b) partners of the company
(c) executives of the company
(d) guardian of the company
Answer:
(a) owners of the company
Question 2.
The term redeemable is used for:
(a) preference shares
(b) commercial paper
(c) equity shares
(d) public shares
Answer:
(a) preference shares
Question 3.
Funds required for purchasing current assets is an example of:
(a) fixed capital requirement
(b) plowing back of profits
(c) working capital requirement
(d) lease financing
Answer:
(c) working capital requirement
![]()
Question 4.
ADRS are issued in:
(a) Canada
(b) China
(c) India
(d) the USA
Answer:
(d) the USA
Question 5.
Under the lease agreement, the lessee gets the right to:
(a) share profits earned by the lessor
(b) participate in the management of the organization
(c) use the asset for a specified period
(d) sell the assets
Answer:
(c) use the asset for a specified period
Question 6.
Public deposits are the deposits that are raised directly from:
(a) the public
(b) the directors
(c) the auditors
(d) the owners
Answer:
(a) the public
Question 7.
Debentures represent:
(a) fixed capital of the company
(b) permanent capital of the company
(c) fluctuating capital of the company
(d) loan capital of the company
Answer:
(d) loan capital of the company
![]()
Question 8.
Under the factoring arrangement the sector:
(a) produces and distributes the goods or services
(b) makes the payment on behalf of the client
(c) collects the client’s debt or account receivables.
(d) transfer the goods from one place to another
Answer:
(c) collects the client’s debt or account receivables.
Question 9.
The maturity period of a commercial paper usually ranges from:
(a) 20 to 40 days
(b) 60 to 90 days
(c) 120 to 365 days
(d) 90 to 364 days
Answer:
(d) 90 to 364 days
Question 10.
Internal sources of capital are those that are:
(a) generated through outsiders such as suppliers
(b) generated through loans from commercial banks
(c) generated through the issue of shares.
(d) generated within the business
Answer:
(d) generated within the business