Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 9 Plant Breeding which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 9 Plant Breeding
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Define organic farming.
Answer:
Organic fanning is defined as an alternative agriculture system, that sustains the health of soils, ecosystem and people, using natural inputs like organic manure, bio-pesticides etc.
Question 2.
Mention any two advantage of biofertilizers.
Answer:
- Biofertilizers are eco-friendly organic agro-inputs.
- They are more efficient and cost-effective than chemical fertilizers.
![]()
Question 3.
Name any two free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria:
Answer:
- Azotobactor
- Clostridium
Question 4.
What is the importance of root nodule?
Answer:
The root nodules are the place, where the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacteria, Rhizobium resides and converts the atmospheric nitrogen into a bioavailable form to the plants.
Question 5.
Define Arbuscular Mycorrhizae.
Answer:
Arbuscular mycorrhizae (AM) is defined as the symbiotic association between certain phycomycetous fungi and angiosperm roots.
Question 6.
Explain Bio-pesticides.
Answer:
Bio-pesticides are biologically based agents j used for the control of plant pests.
![]()
Question 7.
Name any two green manure crops.
Answer:
- Crotalaria juncea
- Indigofera tinctoria
Question 8.
Define plant breeding.
Answer:
Plant breeding refers to the science of improvement of crop varieties with a higher yield, better quality, resistance to diseases and shorter duration for yield.
Question 9.
Define Mutagenesis.
Answer:
Mutagenesis is defined as the process by which developing new genetic diversity by exposing crop plants to chemical agents or radiation.
Question 10.
Explain hybridization.
Answer:
Hybridization refers to the method of producing new crop varieties, in which two or more plants of varying genetic constitution 1 are crossed to produce a hybrid.
Question 11.
Define Pseudoheterosis.
Answer:
Pseudoheterosis is defined as a hybrid I possessing superiority over parents in vegetative growth, but not in yield and adaptation, usually sterile or poorly fertile.
Question 12.
What are polyploids?
Answer:
Polyploids are plants that possess more than two sets of chromosomes.
Question 13.
Define green revolution.
Answer:
The green revolution is defined as the cumulative result of a series of research, development, innovation and technology transfer initiatives j in order to increase crop production.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain Biofortification.
Answer:
Biofortification is referred to as a process by which crops with high levels of vitamins and minerals or high protein and healthier fats are produced.
Question 15.
Mention any two methods of New Plant Breeding Techniques (NBT).
Answer:
The two methods of New Plants Breeding Techniques are:
- Genetic Engineering
- Plants tissue culture
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Explain organic agriculture.
Answer:
An alternative type of agriculture in which the agro-inputs are natural and ecofriendly is known as agro farming. It is originated early in the twentieth century. It is an agricultural production system that sustains the health of the soils, ecosystems and people. It relies on natural ecological processes, biodiversity and cycles adapted to local conditions rather than the use of inputs with adverse effect.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the characteristics of biofertilizers?
Answer:
- The biofertilizers are the preparations of living cells or latent cells of microorganisms.
- They should help the plants uptake of nutrients by their interactions. Eg: Mycorrhiza.
- Biofertilizers are eco-friendly, cost-effective and more efficient than chemical fertilizers.
Question 3.
What are the advantages of Arbuscular mycorrhizae (AM)?
Answer:
- Arbuscular mycorrhizae are the process of the symbiotic association between phycomycetous fungi and angiosperm roots.
- They have the ability to mobilise the phosphate found in the soil abundantly.
- They also provide the necessary strength to resist diseases, germs and unfavourable weather conditions.
Question 4.
Distinguish between Mass selection and Pureline selection.
Answer:
| Mass selection | Pureline selection |
| Bulk of phenotypically similar plants are selected. | Single plant’s offsprings are selected. |
| They are heterogeneous cultivers. | Different purelines of cultivers are segregated. |
| They are registered and marketed. | They are homogenous cultivers. |
Question 5.
Who coined the term mutation breeding? Write its advantages.
Answer:
The term “Mutation breeding” was coined by Muller and Stadler in 1927-28.
They have the advantage of improving the defect without losing an agronomic and quality character in agriculture and crop improvement. Gene mutations provide essential inputs for evolution as well as for recombination and selection. Seedless crops are developed by this method.
![]()
Question 6.
What are vegetables fortified with nutrients released by the Agricultural Research Institute?
Answer:
- Vitamin A enriched carrot, spinach, pumpkin.
- Vitamin C enriched bitter guard, bathua, mustard and tomato.
- Iron and calcium-enriched spinach and bathura.
- Protein-enriched beans, broad beans, lablab, French and garden peas.
Question 7.
List the plant’s resistance to insect pests developed through plant breeding.
Answer:
| Crop | Variety | Insect pest |
| Brassica (Rapeseed mustard) |
Pusa Gaurav |
Aphids |
| Flat bean | Pusa sem2, pusa sem3 | Jassids, aphids and fruit borer |
| Okra (Bhindi) | Pusasawani pusa A-4 | Shoot and Fruit borer |
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Write about polyploids breeding.
Answer:
Polyploids are plants, that possess more than two sets of chromosomes. Diploids (2n) number of chromosomes are present in the majority of flowering plants. Polyploids often exhibit increased hybrid vigour by increasing heterozygosity Polyploidy increase the tolerance to both biotic and abiotic stresses. It offers a buffering effect of deleterious mutations. The production of seedless varieties is possible due to meiotic error, Polyploidy often results in reduced fertility and is considered to be a major force in the evolution of both wild and cultivated plants.
Autopolyploidy and Allopolyploids are the two types of polyploids.
Autopolyploidy: The doubling of the chromosome by themselves in the same plant is called autopolyploidy.
Eg: Triploid condition in sugar beets, apple and pear. In tomato, it leads to seedless variety. Polyploidy can be induced by a chemical called colchicine.
Allopolyploids: The multiplication of chromosome sets that are initially derived from two different species, is called allopolyploidy.
Eg: Triticale (Triticum durum X Secale cereal), Raphanobrassica (Brassica oleraceae X Raphanus satious).
Question 2.
List out the objectives of plant breeding.
Answer:
The followings are the objectives of plant breeding.
- The increase in crop yield, plant vigour and increase in the fertility of the plant are the main objectives of plant breeding.
- Raise plants with increased tolerance to environmental factors like salinity, temperature and drought.
- To prevent the premature falling of buds, fruits etc.
- The synchronous maturity of gametes should be improved.
- To develop plants that develop resistance to pathogens and pests.
- To develop photosensitive and thermosensitive varieties of plants
![]()
Question 3.
What are the changes that take place in a plant species due to domestication?
Answer:
- They have to adapt to a greater diversity of environments and a wider geographical range.
- They may have simultaneous uniform flowering and Suiting.
- Lack of shattering or scattering of seeds.
- They may have increased the size of fruits and seeds.
- They have to change from a perennial to an annual habit.
- Change in the breeding system.
- They may change to increased yield.
- Increased resistance to disease and pest.
- Parthenocarpic seedless fruits may be developed.
- Enhancing colour, appearance palatability and nutritional composition.
Question 4.
Draw the diagram showing the benefits of Am colonization and label.
Answer:
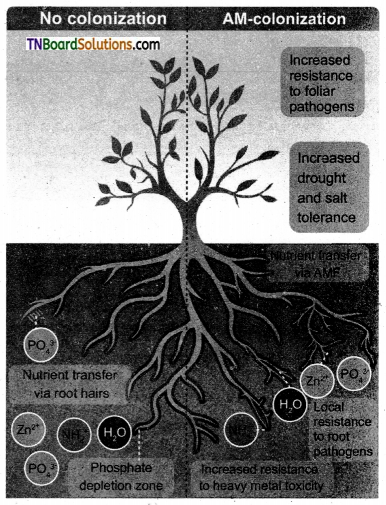
Question 5.
Liquid seawater fertilizer is not only organic but also eco-friendly. Justify.
Answer:
Seaweed liquid fertilizer (SLF) contains organic nutrients, like cytokinin, gibberellins and auxin. It also contains macro and micronutrients. Seaweed liquid fertilizer is made from kelp (brown algae), which contains alginate. This alginate reacts with metals in the soil and forms long, cross-linked polymers, which improve the crumbling of soil, swell up when they get wet. It retains moisture for a long time. They are especially useful in organic gardening, which provides carbohydrate for plants.
This manure has more than 70 minerals, vitamins and enzymes which promote vigorous growth in plants. The plants grown in seaweed liquid fertilizer have improved resistance to frost and disease, indicating that this fertilizer is ecofriendly-pesticide.
![]()
Choose the correct answer.
1. Match the following:
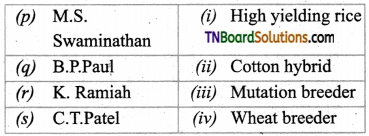
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
2. Match the following (Vavilov’s centres):
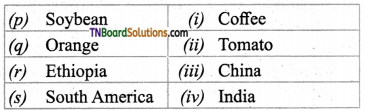
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv);(s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
3. Match the following:
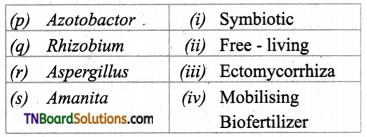
(a) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
4. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
5. The method of creation of genetic variation includes:
(a) Mutation
(b) Hybridization
(c) Vegetative propagation
(d) Tissue culture
Answer:
(c) Vegetative propagation
6. Objective of plant breeding is:
(a) to increase yield
(b) to decrease tolerance to disease
(c) to increase sensitivity toi salinity
(d) to prevent synchronous maturity.
Answer:
(a) to increase yield
7. The introduction of foreign genes into DNA of a plant for the first time in the year:
(a) 1940
(b) 1985
(c) 1994
(d) 2000
Answer:
(c) 1994
8. Bacterial blight resistance was achieved in;
(a) Wheat
(b) Cowpea
(c) Chilli
(d) Cauliflower
Answer:
(b) Cowpea
![]()
9. Choose the odd man out.
(a) E.Borlaug
(b) M.S.Swaminathan
(c) Nel jayaraman
(d) N.G.P.Rao
Answer:
(c) Nel jayaraman
10. Find out the odd one out.
(a) Mutation
(b) Gene transfer
(c) Cytoplasmic fusion
(d) Polyploidy
Answer:
(c) Cytoplasmic fusion
11. Indicate the odd one out (Bio fortification)
(a) Protein content
(b) Fat content
(c) Vitamin content
(d) Gibberellin content
Answer:
(d) Gibberellin content
12. Choose the odd one out (NBT)
(a) Plant tissue culture
(b) Genetic Engineering
(c) Heterosis
(d) Somatic hybridization
Answer:
(c) Heterosis
![]()
13. Choose the correct pair.
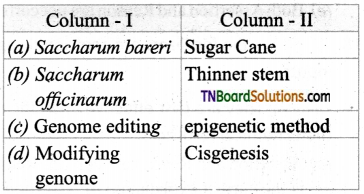
Answer:
(a)
14. Choose the incorrect pair.
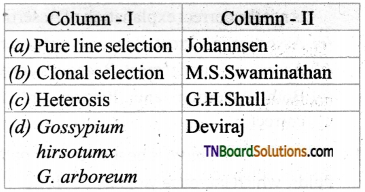
Answer:
(b)
15. Choose the correct pair.

Answer:
(b)
16. Choose the incorrect pair.
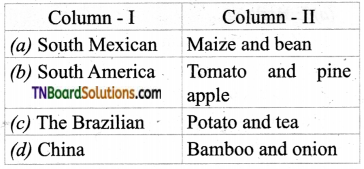
Answer:
(c)
17. Assertion: Organic agriculture is a production system that sustains the health of the soils, ecosystem and people.
Reason: Organic agriculture relies on ecological processes, biodiversity and cycles adapted to local conditions rather than the use of inputs with adverse effect.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
(d) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
![]()
18. Assertion: Biofertilizers are eco-friendly agro-inputs.
Reason: They are cost-effective and efficient than chemical fertilizers.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
(d) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
19. Assertion: Rhizobium is best suited for paddy fields, which increase yield by 15-40%.
Reason: This nitrogen-fixing bacterium when applied in soil undergoes multiplication in billions and fix nitrogen into a usable form for plants.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
(d) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
20. Assertion: Trichoderma is symbiotic fungi, that are common in soil and root ecosystem.
Reason: They have been recognized as bio-control agent for plant disease.
(a) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
(d) Assertion is not correct, Reason is correct.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are not correct.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is not correct.
21. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Most important green manure crops are Vinca rosea, Crotalaria and Thespecia.
(b) Most important green manure crops are Indigotera, Abitelon and Banian tree.
(c) Most important green manure crops are Crotalaria juncea, Tephrosia purpurea, and Indigofera tinctoria.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Most important green manure crops are Crotalaria juncea, Tephrosia purpurea, and Indigofera tinctoria.
![]()
22. Choose the incorrect statement.
(a) The aim of plant breeding is to increase yield.
(b) The aim of plant breeding is to increase the fertility of crop.
(c) The aim of plant breeding is to increase tolerance to environmental conditions.
(d) All the above statements are not correct.
Answer:
(d) All the above statements are not correct.
23. Find out the correct statement.
(a) William S. Gaud coined the term mutation breeding.
(b) Muller and Stadler coined the term green revolution.
(c) M.S.Swaminathan is a pioneer mutation breeder.
(d) Nel Jayaraman hails from Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
(c) M.S.Swaminathan is a pioneer mutation breeder.
24. Indicate the incorrect statement.
(a) Wheat variety Atlas 66 have high protein content.
(b) Wheat variety Atlas 66 have less protein content.
(c) Wheat variety Atlas 66 have been used as a donor for improving cultivated wheat.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Wheat variety Atlas 66 have less protein content.