Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 2 Classical Genetics which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 2 Classical Genetics
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Define Heredity.
Answer:
Heredity is defined as a phenomenon in which the transmission of characters from parents to offspring takes place.
Question 2.
Define Variation.
Answer:
Variationisthedifferenceinthecharacteristics of the organisms belonging to the natural population or species.
Question 3.
Name any two scientists, who re-discovered Mendel’s experiments.
Answer:
- Hugo de Vries
- Carl Correns
![]()
Question 4.
Explain back cross.
Answer:
The back cross is the crossing of F1 hybrids with any one of the parental genotypes.
Question 5.
Enumerate the explanation for the monohybrid cross.
Answer:
- The expression of only one character of parental characters in F1 generation.
- The expression of both characters in the F2 generation.
Question 6.
Define genotype.
Answer:
Genotype is defined as the genetic constitution of an individual.
Question 7.
Mention any two characters in Pea plants selected by Mendel.
Answer:
- Plant height.
- Flower color.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain Codominance.
Answer:
Codominance is a phenomenon in which two alleles are both expressed in the heterozygous individual.
Question 9.
Define Pleiotropy.
Answer:
Pleiotropy is defined as a phenomenon in which a single gene affects multiple characters.
Question 10.
Explain briefly dominant Epistasis.
Answer:
Dominant epistasis is a gene interaction in which two alleles of a gene at one locus interfere and suppress or mask the phenotypic expression of a different pair of alleles of another gene at another locus.
Question 11.
Give two examples of Inter-genic interaction.
Answer:
- Inhibitor genes
- Duplicate genes.
Question 12.
Mention any two examples of Incomplete dominance.
Answer:
- Flower colour in Mirabilis jalapa.
- Flower colour in snapdragon.
Question 13.
Define Lethal genes.
Answer:
A lethal gene is an allele that has the potential to cause the death of an organism.
![]()
Question 14.
Mention any two types of lethal genes.
Answer:
- Conditional lethal gene
- Balanced lethal gene.
Question 15.
Define Molecular Genetics.
Answer:
Molecular genetics is defined as a branch of genetics, which deals with the structure and function of a gene at the molecular level.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between population genetics and quantitative genetics.
Answer:
| Population Genetics | Quantitative Genetics |
| Population Genetics deals with heredity in groups of individuals for a traits, determined by a few genes. | Quantitative Genetics deals with heredity of traits in groups of individuals. The traits are governed by many genes simultaneously. |
Question 2.
Explain briefly about Discontinuous Variation.
Answer:
In a discontinuous variation, two or more allelic forms of one or two major genes control the characteristic of an individual within a population. These characteristics show a limited form of variations, which are genetically determined by inheritance factors. In this type of variation, the individual shows differences without an intermediate form between the parents and there is no overlapping between the two phenotypes. Environmental factors do not affect phenotypic expression. This variation is otherwise called qualitative inheritance. Eg: Style length in Primula and Plant height of garden pea.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain Mendel’s law of heredity.
Answer:
Heredity is the process of transformation of characters from parents to offspring. Two rules on heredity were proposed by Mendel, based on the observations on monohybrid cross. The first rule is the law of dominance and the second one is the law of segregation. These rules play an important role in the history of evolution.
Question 4.
What are the types of dominant relationships?
Answer:
- Complete dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- Codominance
- Overdominance
Question 5.
Distinguish between Intragenic and intergenic gene interactions.
Answer:
| Intragenic | Intergenic |
| Intragenic gene interactions take place between the alleles of the same gene at same locus. This is otherwise known as intra allelic interactions. | Intergenic gene interactions take place between alleles of different genes at different loci. This is otherwise called as inter allelic interactions. |
Question 6.
List out three plants, that exhibit codominance.
Answer:
- Camillia
- Gossypium hirsutum
- Gossypium sturtianum
![]()
Question 7.
Mention three examples of non-allelic interactions.
Answer:
- Fruit colour in summer squash
- Flower colour in sweet peas
- Grain colour in maize
Question 8.
Give three examples of polygenic inheritance.
Answer:
- Skin colour in human being.
- Wheat kernel colour.
- Height of human being.
Question 9.
What is polygenic inheritance?
Answer:
Polygenic inheritance is a phenomenon in which a group of genes together determine the phenotypic expression of a single character. The polygenic inheritance was first demonstrated by H. Nilsson-Ehle in 1909 in wheat kernels.
![]()
Question 10.
What is meant by extra chromosomal inheritance?
Answer:
Chromosomes are the location of genes, which determine the characters of the individual. But in certain traits, the DNA present in chloroplast and mitochondria decide certain characters. It is a kind of Non-Mendelian inheritance. As this involves cytoplasmic organelles like chloroplast and mitochondria, that act as inheritance vectors, it is called extrachromosomal inheritance through independent, self-replicating plasmalogens.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Explain the analytical and empirical approach of his experiments.
Answer:
In all Mendel’s experiments, be chose two contrasting characters of a single locus. He assumed that two distinct factors exist for a single trait. The recessive trait does not disappear in the F generation and it is hidden or marked in the F1 generation and reappear in F2 generation, in which it contributes to 25% of offspring. Mendel got a 3:1 ratio in F2 generation when he crossed a homozygous dominant and recessive trait. Hence he concluded that tall and dwarf alleles of F heterozygote segregate randomly into gametes. Mendel is the first biological scientist to use quantitative analysis in biological research.
Mendel’s analytical approach is an outstanding scientific achievement. His breeding experiments are planned meticulously and precisely executed to show that the hereditary materials are transmitted from one generation to another. Though he was not aware of genes during his experiments, he attributed factors, which are responsible for deciding characters. Now the factors are called genes. His approach is empirical and the laws arrived through this approach are known as empirical laws.
Question 2.
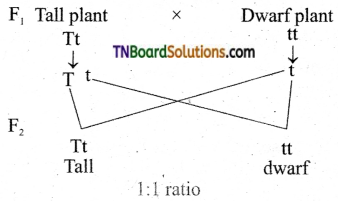
Define test cross. Explain it with an example.
Answer:
A test cross is defined as a cross between an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive.
In F1 generation of Mendel’s monohybrid cross of tall and dwarf pea plants, he got only tall plants. In F2 generation the tall and dwarf plants were in the ratio 3:1. He self-pollinated the dwarf F2 plants and he got only dwarf plants in F3 and F4 generation so he concluded that the genotype of the dwarf plant was homozygous recessive (tt). But the genotype of tall plants TT or Tt cannot be predicted. Mendel crossed the tall plants of F2 with the homozygous recessive dwarf plant. This is known as a test cross. From the progenies of the test cross, the genotype of tall plants can easily be identified. Thus a typical test cross is to cross an organism showing dominant phenotype is crossed with the recessive parent instead of self crossing. Therefore test cross can be used to identify whether an individual is homozygous or heterozygous for the dominant character.
![]()
Question 3.
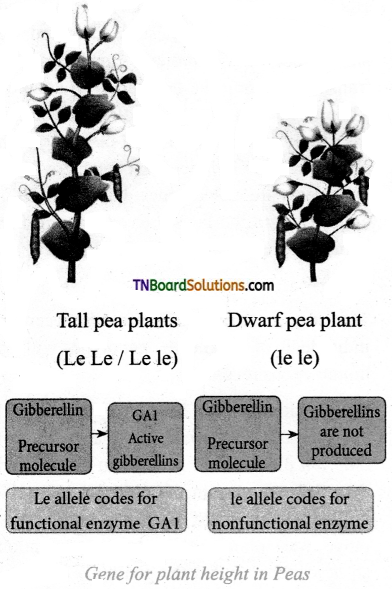
What is the molecular explanation for Mendel’s tall and dwarf planets?
Answer:
A single gene with two alleles controls the height of the pea plant. The difference in height of the plant is due to:
- The pea plant cells have the ability to convert a precursor molecule of gibberellins into an active form (GA1).
- The dominant allele of the gene (Le), which codes for a protein, a functional enzyme, which helps in the gibberellin synthesis pathway and catalyzes the production of gibberellins (GA1). When the allele is dominant even if it is double (Le Le) or single (Le le) it produces gibberellins resulting in tall plants. The dwarf pea plants, which have two recessive alleles (le le) cannot code for functional protein resulting in dwarf plants.
Question 4.
Tabulate examples of Inter-genic interaction with their F2 ratio.
Answer:
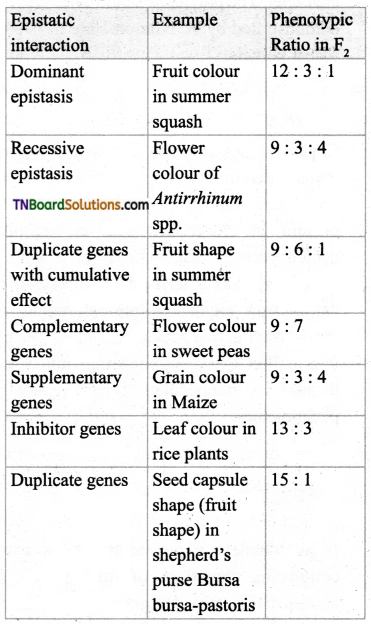
![]()
Choose the correct answers:
1. Match the following:
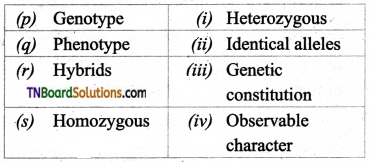
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(ii); (r)-(iv); (s)-(i)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
2. Match the following:
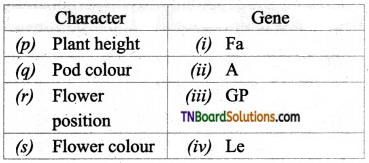
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
3. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
4. Match the following:
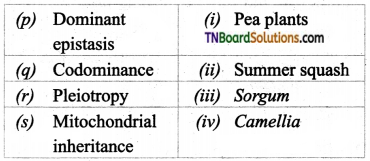
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(iii)
5. Choose the odd man out:
(a) Phenotype
(b) Homozygous
(c) Heterozygous
(d) Allele
Answer:
(a) Phenotype
6. Choose the odd one out:
(a) Complete dominance
(b) Lethal genes
(c) Multiple alleles
(d) Epistatic
Answer:
(d) Epistatic
![]()
7. Identify the odd man out:
(a) Hugo de Vries
(b) Linnaeus
(c) Carl Correns
(d) Erich Von Tschermak
Answer:
(b) Linnaeus
8. Choose the odd one out:
(a) Codominance
(b) Complementary
(c) Supplementary
(d) Inhibitory
Answer:
(a) Codominance
9. Choose the correct pair.
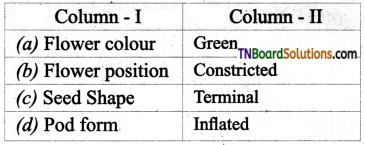
Answer:
(d)
10. Find out the incorrect pair.

Answer:
(c)
![]()
11. Choose the correct pair.
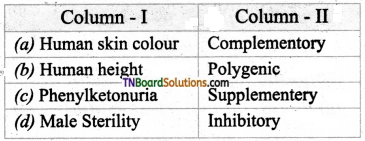
Answer:
(b)
12. Find out the incorrect pair.
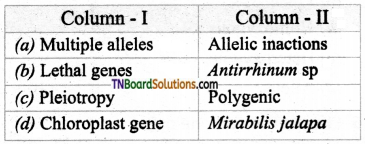
Answer:
(c)
13. Male sterility in pearl maize is due to:
(a) Independent inheritance
(b) Mitochondrial inheritance
(c) Chloroplast gene inheritance
(d) Codominance
Answer:
(b) Mitochondrial inheritance
14. The polygenic inheritance was first demonstrated by:
(a) E. Baur
(b) Carl Correns
(c) Hugo de Vries
(d) H. Nilsson – Ehle
Answer:
(d) H. Nilsson – Ehle
![]()
15. In dominant epistasis in summer squash, the F2 generation the phenotypic ratio is:
(a) 9:3:3:1
(b) 12:3:1
(c) 9:7
(d) 15:1
Answer:
(b) 12:3:1
16. In Polygenic inheritance the production of medium dark red color is due to:
(a) Four R genes
(b) Two R genes
(c) Three R genes
(d) Absence of R – gene
Answer:
(c) Three R genes
17. Intra-genic interaction includes:
(a) Dominant epistasis
(b) Duplicate genes
(c) Inhibitor genes
(d) Codominant genes
Answer:
(d) Codominant genes
18. Assertion: Two alleles of a gene at one locus suppress or mask the phenotypic expression of a different pair of alleles of another gene at another locus in dominant epistasis.
Reason: Inter locus interactions take place between the alleles at different loci i.e., between alleles of different genes.
(a) Assertion is true; Reason is wrong.
(b) Assertion is wrong; Reason is true.
(c) Both Assertion and Reason are true.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(c) Both Assertion and Reason are true.
![]()
19. Assertion: The phenomenon in which two alleles are both expressed in the heterozygous condition is known as codominance.
Reason: Thecodominancewasdemonstrated in plants with the help of electrophoresis.
(a) The Assertion is true; the Reason is false.
(b) The Assertion is false; the Reason is true.
(c) Both Assertion and Reason are true.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(a) The Assertion is true; the Reason is false.
20. Assertion: In a monohybrid cross, when two homozygous dominant and recessive traits are crossed, an intermediate character is found in F1 generation:
Reason: This may be due to the codominance of two alleles.
(a) Assertion is right; the Reason is wrong.
(b) Assertion is false; the Reason is true.
(c) Both Assertion and Reason are true.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
21. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) The dihybrid cross involves individuals differencing in one character.
(b) The recessive back cross helps to identify the homozygosity of the hybrid.
(c) The dihybrid cross is a genetic cross in which- individuals differing in two characters are involved.
(d) None of the above statements is correct.
Answer:
(c) The dihybrid cross is a genetic cross in which- individuals differing in two characters are involved.
22. ChoOse the incorrect statement.
(a) Two identical alleles of a gene are called heterozygous.
(b) Two different alleles of a gene are called heterozygous.
(c) Two identical alleles of a gene are called homozygous
(d) An individual with two dominant alleles is called homozygous dominant.
Answer:
(a) Two identical alleles of a gene are called heterozygous.
![]()
23. Find out the correct statement.
(a) Mendelian experiments prove that a single gene controls more than one character.
(b) Independent assortment leads to genetic diversity.
(c) Back cross involves the cross between the F2 offspring with F1 parents.
(d) Independent assortment leads to genetic homozygosity.
Answer:
(b) Independent assortment leads to genetic diversity.
24. Which of the following statement is false?
(a) Intragenic gene interaction takes place between the alleles of the same gene.
(b) Intragenic gene interaction takes place between the alleles at the same locus.
(c) Intergenic gene interaction takes place between alleles of different locus.
(d) All the above statements are wrong.
Answer:
(d) All the above statements are wrong.
25. Choose the correct statement.
(a) Codominance type of inheritance is found in snapdragon.
(b) The inheritance of sickle cell anemia is a typical example of pleiotropy.
(c) Polygenic inheritance is seen in the flower color of pea plants.
(d) The expression of inhibitor gene leads to male sterility in plants.
Answer:
(b) The inheritance of sickle cell anemia is a typical example of pleiotropy.