Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 5 Molecular Genetics which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 5 Molecular Genetics
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Define gene.
Answer:
A gene is defined as a basic physical and functional unit of heredity.
Question 2.
What is the main aim of the Hershey and Chase experiment on T2 bacteriophage?
Answer:
The main objective of the Hershey and Chase experiment on T2 bacteriophage is to prove whether it was DNA or protein that acts as genetic material.
Question 3.
What are the components of a nucleotide?
Answer:
Each nucleotide consists of three components namely nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
![]()
Question 4.
Define genophore.
Answer:
Genophore is defined as the DNA of prokaryotes, which is almost circular and lacks chromatin organization.
Question 5.
Explain histone octamer.
Answer:
In nucleosome, Z molecules of four histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 are organized to form a unit of eight molecules called histone octamer.
Question 6.
Name any two enzymes involved in DNA replication.
Answer:
- DNA Polymerase
- DNA ligase.
Question 7.
Define Transcription.
Answer:
Transcription is a process through which the copying of genetic information from one strand of DNA into RNA takes place.
Question 8.
What is a promoter unit?
Answer:
The promoter region is located towards the 5 ends. It is a DNA sequence in which RNA polymerase binds.
![]()
Question 9.
Define genetic code.
Answer:
The genetic code is the sequence relationship nucleotide in genes (or mRNA) and the amino acids in a protein, they encode.
Question 10.
Define ‘Non-sense’ codon.
Answer:
‘Non-sense’ codons are defined as the codons designated as termination (stop) codons.
Question 11.
Define translation.
Answer:
The translation is a process in which the polymerization of amino acids to form a polypeptide chain takes place.
Question 12.
What is meant by reading frame?
Answer:
A reading frame is a codon that is formed by dividing up a sequence of bases in DNA or RNA.
Question 13.
Define operon.
Answer:
Operon is defined as a cluster of genes with related functions.
Question 14.
Mention any two enzymes involved in the metabolism of lactose in E.Coli.
Answer:
- p – galactosidase
- Transacetylase
![]()
Question 15.
What is pharmacogenomics?
Answer:
Pharmacogenomics is the study of genes, affecting a person’s response to drugs.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between one gene-one enzyme hypothesis and one gene-one polypeptide hypothesis.
Answer:
| One gene – one enzyme hypothesis | One gene -one polypeptide hypothesis |
| One gene – one enzyme hypothesis states that one gene control the production of one enzyme. This hypothesis is postulated by George Breadle and Edward Tatum. |
One gene – one polypeptide hypothesis states that a gene can code for only one polypeptide and more than one polypeptide chain may compose an enzyme. Thus one gene controls the production of only one polypeptide chain of an enzyme. |
Question 2.
Mention any three properties of Mendelian rules of inheritance.
Answer:
- Genes are arranged in a single linear order on chromosomes.
- A specific position called a locus, where the genes occupy the chromosome.
- Gene may exist in several alternate forms called alleles.
Question 3.
Distinguish between Nucleoside and nucleotide.
Answer:
| Nucleoside | Nucleotide |
| Nucleoside is formed by a chemical linkage of nitrogenous base with one molecule of sugar at one carbon atom. | Nucleotide is formed by attaching a phosphate group to the 5′ carbon of same sugar. Nucleotides are polymerized to form polynucleotides. |
![]()
Question 4.
Differentiate DNA and RNA based on nitrogenous bases.
Answer:
- DNA and RNA both have four bases (two purines and two pyrimidines)
- Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) are the purines.
- Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and uracil (U) are the pyrimidines.
- In DNA molecule, Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T), and Cytosine are present.
- In RNA molecule, instead of Thymine (T), Uracil (U) is present.
- Therefore, the nitrogenous base Thymine is unique for DNA, while uracil is unique for RNA.
Question 5.
Differentiate monocistronic mRNA from polycistronic mRNA.
Answer:
| Monocistronic mRNA | Polycistronic mRNA |
| Each mRNA carrys only a single gene. | Cluster of related genes form operon. |
| Each mRNA encodes information for the synthesis of only a single protein. | They transcribed together to give a single mRNA. |
| It is present in eukaryotes. | They are present in prokaryotes. |
Question 6.
Distinguish between promoters and operators.
Answer:
| Promoters | Operators |
| Promoters are the single sequences of DNA that initiate RNA synthesis. | Operators are present between promoters and structural genes. |
| Prior to the initiation of transcription, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter. | The repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon. |
Question 7.
What are genes present in lac operon? Mention their function.
Answer:
The genes present in lac operon and their function include the following:
- One inhibitor gene (i) present is between promoter site (p) and operator site (o).
- Three structural genes namely lac z, y, and lac a gene are present.
- lac 2 gene codes for B galactosidase enzyme.
- lac y gene codes for permease enzyme.
- lac gene codes for transacylase enzyme.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain negative control of transcription initiation.
Answer:
- The repressor protein binds to the operator of the operon, preventing RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon.
- When an inducer such as lactose is present, the repressor protein is inactivated by the interaction with the inducer.
- This allows RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter site and transcribe the operon to produce lac mRNA.
- This enables the formation of all required enzymes for lactate metabolism.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Mention any five salient features of the human genome project.
Answer:
- The encoded proteins are only 5% even though more than 3 billion nucleotide bases are present in the human genome.
- The largest human gene is dystrophic with 2.4 million bases.
- The transposable elements such as LINE and ALU sequence form about 50% of the functional genome in human beings.
- chromosome 19 has the highest gene density, while chromosome 13 and y chromosomes have the lowest gene densities.
- Chromosome 1 has 2968 genes while the ‘Y’ chromosome has only 231 genes.
Question 2.
Explain the wobble hypothesis with an example.
Answer:
Crick in 1966 proposed this hypothesis, which states:
- tRNA anticodon has the ability to wobble at its 5′ and by pairing with even non-complementary base of mRNA codon.
- In anticodon pairing, the third base may not be complementary.
- The third base of the codon is called wobble base and the position is known as wobble position.
- At the first two positions, actual base pairing occurs.
- According to this hypothesis, it reduces the number of tRNAs required for the synthesis of the polypeptide.
- It also overcomes the effect of code degeneracy.
Eg:
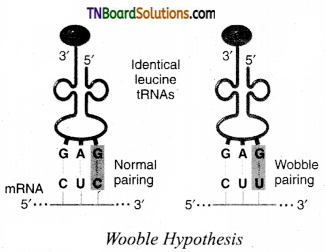
In this example, the codons and anticodons do not match perfectly.
Yet, the required amino acid is produced perfectly. This helps the economy of tRNA – GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG code for valine amino acid.
![]()
Question 3.
Give the diagrammatic representation of semi conservation mode of DNA replication based on Meselson and Stahl experiments.
Answer:
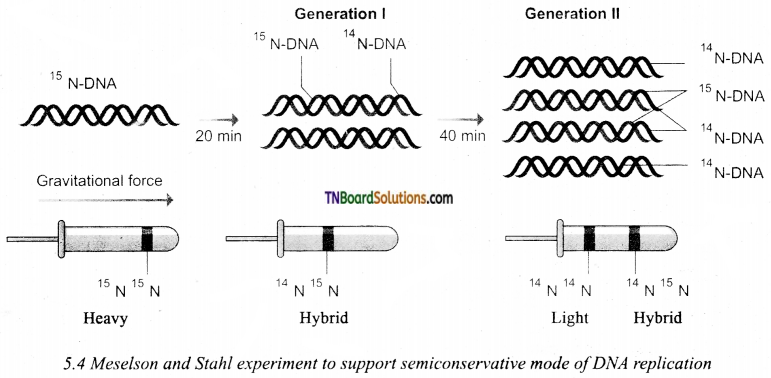
Question 4.
Draw the schematic representation of the lac operon model.
Answer:
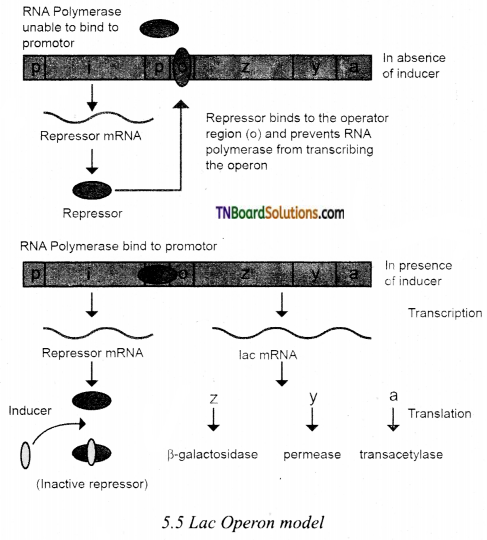
Question 5.
List out any five applications of the human genome project.
Answer:
- Mapping the human genome provides information on DNA sequence, which makes it possible to identify genetic abnormalities.
- This helps to diagnose diseases and to provide counseling to those planning to have children. (Hi) This kind of information provides clues to understand human biology and learning non¬human organisms for comparison.
- This helps to create possibilities for new gene therapies.
- Another important advantage of this kind of information is that it provides a new era of molecular medicine characterized by looking into the most fundamental causes of diseases than treating the symptoms.
![]()
Question 6.
Give the sequential steps involved in DNA fingerprinting.
Answer:
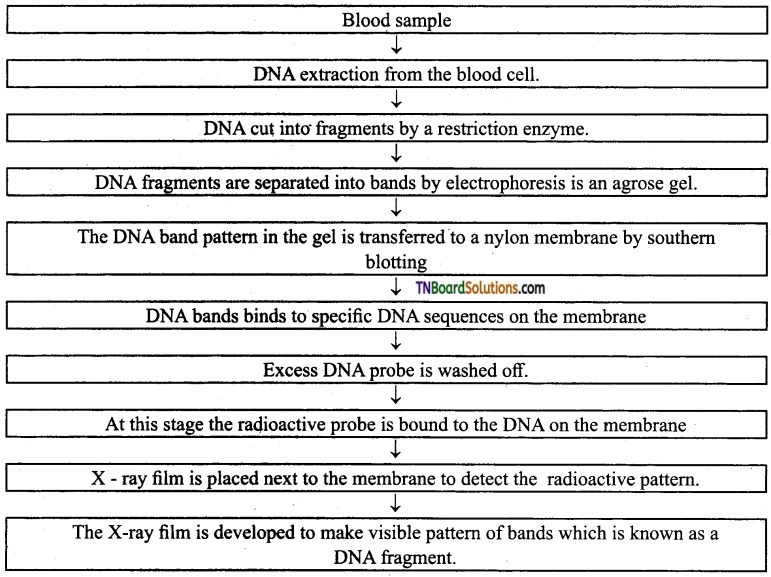
Choose the correct answers.
1. Match the following:
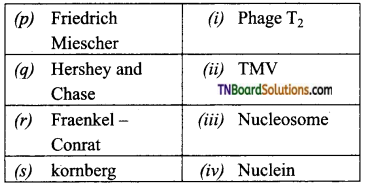
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
2. Match the following:
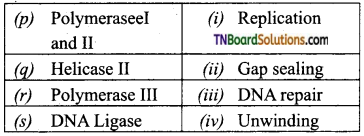
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
3. Match the following:
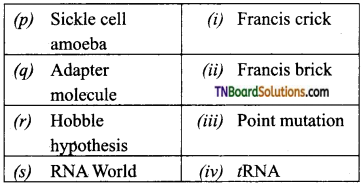
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
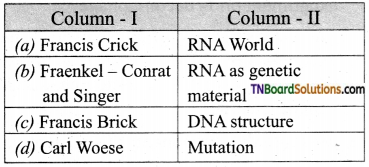
4. Match the following:


(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(iii); (r)-(iv); (s)-(i)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
5. Gene is the functional unit of:
(a) Inheritance
(b) Human genome
(c) Human history
(d) DNA
Answer:
(a) Inheritance
6. Several biochemical reactions are catalyzed by RNA and such RNA is known as:
(a) Ribosome
(b) RNA ase
(c) Ribozyme
(d) RNA Hydrogenase
Answer:
(c) Ribozyme
7. The functional phosphate group (PO4) gives DNA and RNA the property of acid by releasing:
(a) a neutron in solution
(b) H+ ion in solution
(c) OH- ion in solution
(d) an electron in solution
Answer:
(b) H+ ion in solution
![]()
8. International human genome project was launched in the year:
(a) 1969
(b) 1978
(c) 1992
(d) 1990
Answer:
(d) 1990
9. Choose the odd man out:
(a) P-Galactosidase
(b) Permease
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) Transacetylase
Answer:
(c) DNA polymerase
10. Find out the odd one:
(a) Replication
(b) Transcription
(c) Translation
(d) Termination
Answer:
(a) Replication
11. Indicate the odd one:
(a) Adenine
(b) Guanine
(c) Uracil
(d) Thymine
Answer:
(c) Uracil
12. Choose the odd man out:
(a) Rosalind Franklin
(b) Janies Watson
(c) Maurice Wilkins
(d) Walter Gilbert
Answer:
(d) Walter Gilbert
![]()
13. Choose the correct pair:
Answer:
(b)
14. Which of the following pair is incorrect?
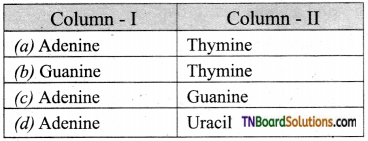
Answer:
(c)
15. Choose the correct pair:
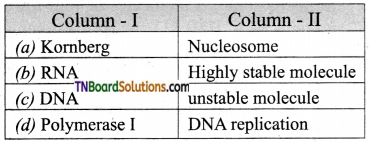
Answer:
(a)
16. Indicate the incorrect pair:
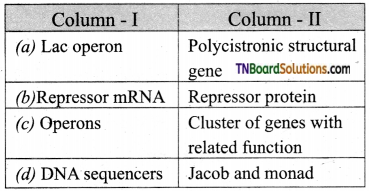
Answer:
(d)
17. Assertion: In the lac operon, a polycistronic structural gene is regulated by a common promoter and regulator.
Reason: It is an example of negative control of transcription initiation.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
18. Assertion: Hershey and chase in their experiments, allowed the phages to infect bacteria in a culture medium which contains the radioactive isotopes 35S or 35P.
Reason: The bacteriophage that grew in the presence of 35S had labeled proteins and bacteriophages grown in presence of 82P had labeled DNA.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true. The reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
![]()
19. Assertion: The bases of nitrogen-containing molecules having the chemical properties of a base are the nitrogenous bases of DNA. Reason: Because they release H+ ions or protons in solution.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
20. Assertion: The mode of DNA replication was first demonstrated in 1956 by Meselson and stahl.
Reason: They designed an experiment to distinguish between DNA and protein as genetic material.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
21. Which of the following statement is true?
(a) Watson and Crick proposed a semi-conservative replication hypothesis.
(b) Watson and Crick proposed a conservative replication hypothesis.
(c) Watson and Crick proposed imperative replication hypothesis.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Watson and Crick proposed semi conservative replication hypothesis.
22. Indicate the incorrect statement:
(a) A transcriptional unit in DNA is defined by three regions namely a promoter, a structural gene and a terminator.
(b) The promoter is located at the 3′ end.
(c) The presence of promoter in a transcription unit defines the template and coding “strands.
(d) Besides promoter Eukaryotes need an enhancer for transcription.
Answer:
(b) The promoter is located at the 3′ end.
![]()
23. Choose the correct statement:
(a) The genetic codon is a quadruplicate code.
(b) The genetic code is not universal.
(c) The genetic code is a triplet code.
(d) In Non-ambiguous code, more than one codon is needed for one amino acid.
Answer:
(c) The genetic code is a triplet code.
24. Which of the following statement is not correct?
(a) Human genome contains 3 billion nucleotide bases.
(b) Average human gene consists of 3000 bases.
(c) In humans, chromosome 19 has the highest gene density.
(d) All the above statements are not correct.
Answer:
(d) All the above statements are not correct.