Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 6 Principles of Ecology which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 6 Principles of Ecology
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is paleoclimatology?
Answer:
Paleoclimatology is a branch of climatology, which helps to reconstruct past climates of our planet and flora, fauna, and ecosystem in which they lived.
Eg: Air bubbles trapped in ice for tens of thousands of years with fossilized pollen, coral, plant, and animal debris.
Question 2.
What is meant by Heliophytes? Give example.
Answer:
Heliophytes are light-loving plants. Eg: Angiosperm.
Question 3.
What is Timberline?
Answer:
Timberline or tree line is an imaginary line in a mountain or higher areas of land, beyond which trees do not grow. This limit is calculated to be about 3000 to 4000m.
![]()
Question 4.
Name the gases present in the atmosphere.
Answer:
- Nitrogen – 78%
- Oxygen – 21%
- Carbon dioxide – 0.03%
- Argon and other gases – 0.93%
Question 5.
Name any two plants that used for phytoremediation of cadmium.
Answer:
- Rice
- Eichhomia
Question 6.
What is pyrophilous fungi? Give an example.
Answer:
Pyrophilous fungi are the fungi that grow in the soil of burnt areas after the fire.
Eg: Pyroriema confluence.
Question 7.
Explain briefly about the Edaphic factor.
Answer:
Edaphic factors are abiotic factors of soil.
It includes the composition of the soil in an area, including the physical and chemical composition of the soil.
Question 8.
What are soil organisms?
Answer:
The soil organisms are the living organisms, which live in the soil.
Eg: Bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoans, nematodes, insects, earthworms, etc.
Question 9.
Define cryptophytes.
Answer:
Cryptophytes are the plants that live below the surface of the soil.
![]()
Question 10.
Define Edge effect.
Answer:
Edge effect is defined as the phenomenon in which an organism or species are seen in ecotone areas due to the effect of an environment of two habitats.
Eg: Owl present between the forest and grassland area.
Question 11.
Name any two nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Answer:
- Anabaena
- Nostoc
Question 12.
What is the negative interaction of species?
Answer:
In negative interaction of species, one species is benefited and the other is harmed.
Question 13.
Mention any two plants, which show defensive mechanisms against their predators.
Answer:
- Tobacco produces nicotine
- Opuntia has spines.
![]()
Question 14.
Define Amensalism.
Answer:
Amensalism is the phenomenon of the interaction of two species, in which one is inhibited by the secretion of certain chemical substances. The other species is neither harmed nor benefited.
Question 15.
Name any two amphibious plants.
Answer:
- Typha
- Sagittaria
Question 16.
Mention any two root morphological adaptations in hydrophytes.
Answer:
- Roots are totally absent in Wolffia and Salvinia.
- The root pockets replace root caps. Eg: Eichhornia.
Question 17.
Mention any two stem modifications in xerophytes for example.
Answer:
- Cladode in Asparagus
- Phylloclades in Opuntia
Question 18.
What are Tropophytes?
Answer:
Tropophytes are plants that act as xerophytes during summer and act as mesophytes or hydrophytes during the rainy season.
![]()
Question 19.
Define Autochory. Give example.
Answer:
Autochory is a process through which seed disperse takes place by a sudden burst of fruit with a force enabling to throw the seeds little away from the parent plant.
Eg: Impatients, crossandra.
Question 20.
Explain briefly about pneumatophores.
Answer:
Pneumatophores are special types of roots present in halophytes. They are negatively geotropic and respiratory in function.
Eg: Avicennia.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between Autecology and synecology.
Answer:
| Autecology | Synecology |
| Autecology is the ecology of an individual species. | Synecology is the ecology of population or community. |
| It is also called as species ecology. | It is also called as community ecology. |
Question 2.
Explain commensalism with a suitable example.
Answer:
Commensalism is an interaction between two organisms. In this type, one organism is benefited, while the other is neither harmed nor benefited. The organism, that is benefited is called the commensal, and other organisms are the host.
Eg: The plants like Vanda, growing on other plants without harming the host. These plants are called epiphytes and are commonly seen in the tropical rain forest.
![]()
Question 3.
Give examples of tolerance to cadmium toxicity in the soil.
Answer:
- Plants like soybean and tomato can tolerate high concentrations of cadmium in the soil. They isolate cadmium and storing into few groups of cells. This in turn prevents the cadmium from affecting other cells.
- Plants like rice and Eichhomia can tolerate cadmium but binding it to their proteins.
These plants can be used to remove cadmium from contaminated soil.
Question 4.
Vegetation at different altitudes varies, showing distinct zonation why?
Answer:
Vegetation at different altitudes varies because of the following reasons:
- The velocity of wind remains high at high altitudes.
- The atmospheric temperature and air pressure decrease with an increase in height in high altitudes.
- The timidness and intensity of light increase at high altitudes.
Question 5.
Name any three plants which show a defense mechanism against predators. Mention their mechanisms.
Answer:
- Cinchona – Produces a chemical compound, quinine.
- Bougainvilla – has thorns that produce it from animals.
- Cacti – Produces latex, which protects them from predators.
Question 6.
Give any three examples of Amensalism.
Answer:
- Penicillin produced by Penicillium notation inhibits the dying growth of a variety of bacteria, especially Staphylococcus.
- The growth of fungus, Aspergillus is inhibited by Trichoderma.
- An alkaloid, the jungle is secreted by roots and hulls of black walnut, Juglans nigra, inhibits the growth of seedlings of apple, tomato, and Alfalfa around it.
![]()
Question 7.
Name any three plants, which are called rooted submerged hydrophytes.
Answer:
- Vallisneria
- Hydrilla and
- Isoetes.
Question 8.
What are the stem adaptations in hydrophytes?
Answer:
In hydrophytes the stem is adapted to suit the aquatic mode of life as follows:
- In submerged plants, the stem is long, slender, spongy, and flexible.
- In free-floating plants, a thick, short, stoloniferous, and spongy stem is present while in rooted floating forms, the stem is modified as a rhizome.
- The vegetative propagation is also done through stem cuttings and their modifications like a rhizome, runners, etc.
Question 9.
What are the different types of xerophytic habitat? Explain them.
Answer:
There are two types of xerophytic habitats namely physical and physiological.
- Physical dryness: In these habitats, the soil has a little amount of water due to low rainfall and the inability of the soil to retain water.
- Physiological dryness: In this habitat, the plants are unable to absorb water, because of the absence of capillary spaces, even though sufficient water is available.
Eg: Plants in salty and acidic soil.
Question 10.
Mention any three adaptations in the seeds and fruits of hydrochory plants.
Answer:
The plants which grow in or near water bodies, disperse their seeds, fruits through the water. They have certain adaptations for the dispersal of seeds and .fruits and they are:
- The fruits of some plants like, Nelumbo have open coel receptacle with prominent air Space for floating.
- In plants like coconut, the presence of fibrous mesocarp and light percap aids the fruits to float in water.
- In plants like Heritiera littoralis, the fruits may be inflated, so that it can float in water.
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What is Autochory? Give an account of adaptations in fruits of autochory plants.
Answer:
Autochory is one of the types of seed dispersal, through which the seeds are dispersed by a sudden burst of fruits with a force. Autochory shows the following adaptations.
- In some plants, the ripened fruits explode suddenly and seeds are dispersed with of great force by the mere touch of the plant. Eg: Inpatient (Balsam), Hura
- In some plants, the fruits burst with noise and scatter the seeds, when they come in contact with water due to a shower of rain. Eg: Ruellia and Crassandia.
- Some long pods explode with a loud noise like a cracker, dispersing the seeds in all directions. Eg: Bauhinia viable.
- In some fruits, the dispersal of seeds takes place due to a high turgor pressure developed inside the fruit, when tissues around seeds are converted into a mucilaginous fluid. Eg: Ecballium elaterium, Gyrocarpus, and Dipterocarpus.
Question 2.
List out the anatomical adaptions of epiphytic plants. Draw and label the T.S section of the aerial root of an orchid.
Answer:
- The roots of these plants have multilayered epidermis. The Exodermis layer is present inner velamen tissue.
- The transpiration is reduced due to the presence of thick cuticle and sunken stomata.
- Well-developed parenchymatous cells to store water is present in succulent epiphytes.
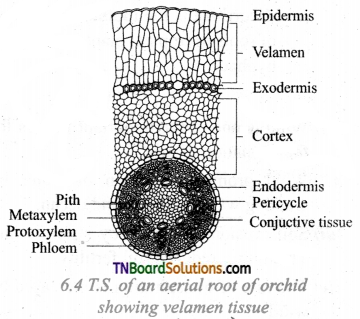
Question 3.
Give an account of an Example of Mutualism in the plant kingdom.
Answer:
Mutualism is an interaction between two species in which both species are benefited from obligate association. The common examples of mutualism are as follows.
- The bacteria, Rhizobium lives in the nodules of leguminous plants, establishing a symbiotic association. The bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrate for the leguminous plant, which in turn supplies food to the bacteria.
- The association of water fem (Azolla) and nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium (Anabaena) is a mutualism, in which the bacteria harbors in the water fem will fix atmospheric nitrogen for the Azolla.
- The nitrogen-fixing Anabaena is present in coralloid roots of cycas (Gymnosperm) fixes atmospheric nitrogen into nitrate, making it available for the host cycas. The cycas provide food for the bacteria.
- The association of cyanobacterium (Nostoc) found in the thalloid body of. Bryophyte (Anthoceros) is a mutual association. In this, the bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and the Bryophyte into supplies shelter and food to the cyanobacterium.
- Other mutual associations are:
(a) Wasps present in fruits of fig.
(b) The association of algae and a fungus is the Lichen.
Micorrhiza is the mutual association of roots of tropical plants and fungal hyphae.
![]()
Question 4.
List out the effects of wind on plants.
Answer:
- The wind is one of the important factors for the formation of rain.
- Wind promotes the aeration of water by creating waves in lakes and the ocean.
- Soil erosion is caused by strong wind. This in turn reduces soil fertility.
- The rate of transpiration is increased by the wind.
- It helps in pollination in anemophilous plants.
- The dispersal of fruits, seeds, spores, etc., is carried out by the wind.
- The uprooting of the big trees may be caused by a strong wind.
- The development flag forms in trees are caused by unidirectional wind.
Question 5.
List out the important edaphic factors which affect vegetation in an area.
Answer:
- Soil moisture: Plants absorb water from the soil. Some plants absorb moisture from the atmosphere.
- Soil water: The distribution of plants greatly depends on the soil water. The main source of soil water is rain. In soil, water is held between pore spaces of soil particles and angles between them and this forms the most important form of water available to the plants for absorption.
- Soil reactions: The availability of soil nutrients mainly depend on the pH of the soil. Soil may be acidic, alkaline, or neutral in its reaction. The pH range of 5.5 to 6.8 is ideal for the cultivation of crop plants.
- Soil nutrients: All essential plant nutrients such as mineral and organic nutrients in the form of ions decide the fertility of the soil, which determines the plant growth and vegetation.
- Soil temperature: As low temperature reduces the use of water and solute absorption by roots, the geographical distribution of plants is mainly decided by soil temperature.
- Soil atmosphere: The spaces between soil particles are occupied by oxygen and carbon-di-oxide. This forms soil aeration or soil atmosphere.
- Soil Organisms: Many organisms like bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoans, nematodes, insects, earthworms, etc., are present in the soil. They are responsible for making the soil suitable for plant growth.
TN Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions
Choose the correct answers:
1. Match the following:
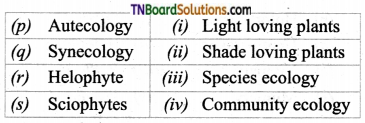
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
2. Match the following:
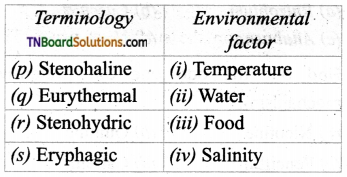
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
3. Match the following:
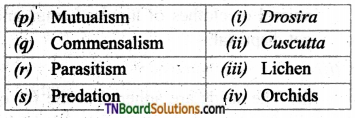
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
4. Match the following:
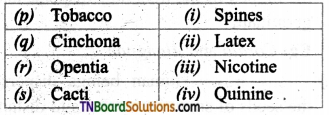
(a) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
5. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(iii); (r)-(iv); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
6. Choose the odd one out.
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Cuscuta
(c) Anabaena
(d) Nostoc
Answer:
(b) Cuscuta
7. Find out the odd one out (Defensive mechanism).
(a) Nicotine
(b) Quinine
(c) Penicillin
(d) Caffeine
Answer:
(c) Penicillin
8. Indicate the odd one out.
(a) Mimicry
(b) Myrmecophily
(c) Co-evolution
(d) Epiphyte
Answer:
(d) Epiphyte
![]()
9. Choose the odd one out.
(a) Balanophora
(b) Loranthus
(c) Nepenthes
(d) Sandalwood
Answer:
(c) Nepenthes
10. Identify the odd one out:
(a) Nelumbo
(b) Morsilea
(c) Nymphaea
(d) Utricularia
Answer:
(d) Utricularia
11. Which of the following is the correct pair:
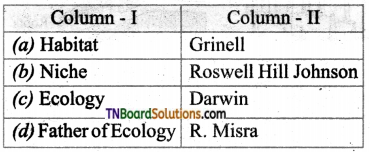
Answer:
(b)
12. Which of the following in the incorrect pair?

Answer:
(c)
13. Which of the following in the correct pair?
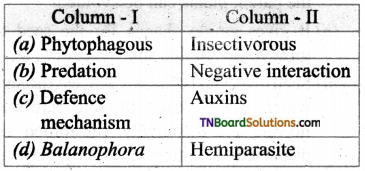
Answer:
(b)
![]()
14. Choose the incorrect pair:
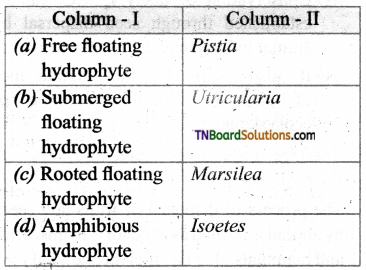
Answer:
(d)
15. Which of the following in the correct pair seed dispersal?

Answer:
(a)
16. Assertion: Mango plants cannot grow in temperate countries like Canada.
Reason: They are stenothermal plants and they cannot tolerate a wide range of temperatures.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is correct.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
17. Assertion: Temperature affects all biochemical reactions in the plant body.
Reason: It influences CO2 and O2 solubility in biological systems.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is correct.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
![]()
18. Assertion: Gases let out to the atmosphere causes climate change.
Reason: It is due to the Albedo effect.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct. The reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct. The reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is correct.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct. The reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
19. Assertion: Epiphytic plants like orchids get their nutrients and water from the atmosphere.
Reason: Because they have hygroscopic roots, which contain a special type of spongy tissue called velamen.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is correct.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
20. Assertion: Vallisneria is adapted to both aquatic and terrestrial modes of life.
Reason: It is an amphibious hydrophyte.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is correct.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
21. Eichhornia is a:
(a) Rooted floating hydrophyte
(b) Free-floating hydrophyte
(c) Submerged floating hydrophyte
(d) Amphibious hydrophyte
Answer:
(b) Free-floating hydrophyte
![]()
22. The interaction between mango free and ants called:
(a) Mimicry
(b) Co-evolution
(c) Myrmecophily
(d) Amensalism
Answer:
(c) Myrmecophily
23. Forest fire is classified under:
(a) Climatic factor
(b) Edaphic factor
(c) Topographic factor
(d) Biotic factor
Answer:
(a) Climatic factor
24. Organisms that can live in water with a wide range of salinity is called:
(a) Stenothemal
(b) Eurythermal
(c) Euryhaline
(d) Stenohaline
Answer:
(c) Euryhaline
25. Seed dispersal in Gyrocarpus in by:
(a) Hydrochoiy
(b) Zoochory
(c) Autochory
(d) Anemochory
Answer:
(d) Anemochory
26. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) The pneumatophores are a special type of positively geotropic roots in Avicennia.
(b) They absorb water and nutrients from the atmosphere.
(c) The pneumatophores are a special type of negatively geotropic roots in Avicennia.
(d) They are called hydrographic roots.
Answer:
(c) The pneumatophores are a special type of negatively geotropic roots in Avicennia.
![]()
27. Indicate the incorrect statement.
(a) Phylloclades are present in Opuntia.
(b) Phyllode is present is Acacia
(c) Cladode is seen in Asperagus.
(d) All the above statements are not correct.
Answer:
(d) All the above statements are not correct.
28. Choose the correct statement.
(a) In desert plants the root system is not well developed.
(b) In xerophytes, the stems and leaves are covered with wax coating.
(c) In xerophytes, the vascular bundles are not well developed.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) In xerophytes, the stems and leaves are covered with a wax coating.
29. Find out the incorrect statement.
(a) Cuscuta is a total stem parasite
(b) Balanophora is a hemi parasite
(c) Rafflesia is a total root parasite
(d) Viscum is a partial stem parasite
Answer:
(b) Balanophora is a hemi parasite
![]()
30. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) The nitrogen filing bacteria Rhizobium is present in the coralloid roots in cycas.
(b) The cyanobacterium Anabaena is present in the root nodules of leguminous plants,
(c) The interaction of water fern Azolla and nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium is an example of mutualism.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) The interaction of water fern Azolla and nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium is an example of mutualism.