Students get through the TN Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 26 Export and Import Procedures which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 26 Export and Import Procedures
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is taking delivery of goods?
Answer:
Importer takes delivery of goods from the Railway/Carrier after producing the Railway Receipt or Lofry Receipt.
Question 2.
What Is a trade enquiry?
Answer:
Having obtained IEC, the intending importer has to make enquiry from the exporter or his agents.
Question 3.
What are import documents?
Answer:
- Import License,
- Indent,
- Letter of Credit,
- Bill of Entry,
- Bill of sight,
- Port Trust Dues Receipt,
- Bill Of Lading,
- Bill of Exchange,
- Advice Note.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a short note on the export trading house.
Answer:
Export trade house has been established to increase the export, strengthen the global market, capacity and get necessary facilities for increasing the export performance of our country.
Question 5.
Explain – Forwarding Agent.
Answer:
Forwarding Agent is appointed by the exporter to fulfill the customs and shipping-related formalities and certain logistic functions.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
What is the settlement of the import bill?
Answer:
The importer settles the import bill in the following ways.
- Importer collects shipping documents after payment.
- Importer gets shipping documents after payment of bills of exchange in the case of Documents against payments (D/P).
- Importer gets shipping documents after giving acceptance on bills of exchange in the case of Documents against Acceptance(D/A).
Question 2.
What are the contents of Bill lending?
Answer:
- Name of the ship,
- Date of shipment,
- Place of Bearding,
- Port of destination,
- Name address of exporter,
- Name and address of the importer,
- Description of Goods,
- Number of package,
- Distinctive mark on good,
- Amount of freight.
![]()
Question 3.
What are intermediaries involved in export trade?
Answer:
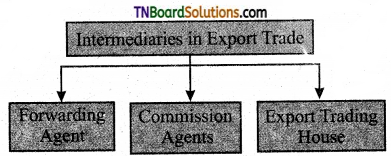
Question 4.
What is a commission agent?
Answer:
Commission Agent is an international agent who is paid a certain percentage of commission for the order booked by him abroad. He offers products to potential customers in the territory allotted to him in accordance with the terms and conditions specified by the principal. However, there is no employment relationship between the agent and the principal and the relationship is purely temporary. The agents get an only commission at the end of the deal.
Question 5.
Explain the intermediaries in import trade.
Answer:
- Indent Houses/ Import Agent: This intermediary is specialized in a particular trade. He charges fees for his service. The importer has to enter into a contract with the indent house to avail himself of his service.
- Clearing Agent: Clearing Agent is specialized in clearing the goods from the port of discharge destination and transport them over to the importer. They fulfill the various custom formalities on behalf of the importer and get the goods cleared from the port. They charge commission for their service.
Question 6.
What is the insurance of goods?
Answer:
Exporter has to arrange for getting the goods insured to protect them against the various risks like deterioration, collision, immersion, fire, entry of seawater, etc., as per the instructions of importer if any.
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the types of indent?
Answer:
- Open Indent: It gives complete freedom to the exporter to choose the type of goods, price, quality, method of packing, etc.
- Closed Indent: It does not give any freedom to the exporter. Importer specifies climates the type of goods, price, quality, packing method, and so on which should be strictly observed by the exporter.
- Confirmatory Indent: An indent is to be confirmed by the importer/ his agent and the final indent is sent by the importer thereafter.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What are the objectives of Export trade?
Answer:
The important objectives of the export include –
- Facilitating selling of goods to countries which desperately need such goods.
- Expanding the market for goods by producing them on a large scale.
- Earning foreign exchange through exports.
- Helping a country increase the national income.
- Creating employment opportunities in a country by promoting export-oriented and export-related enterprises.
- Generating revenue for the Government in the form of customs and excise duties.
- Promoting mutual understanding and co-operation among the nations.
- Achieving optimum utilization of resources by large-scale production of goods.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the EXIM bank’s main functions?
Answer:
The main functions of EXIM bank are:
- It provides direct financial assistance to exporters of plants, machinery, and related services.
- It underwrites the shares, debentures, and bonds of the companies engaged in exports.
- It provides a re-discount facility in respect of export bills for a period not exceeding 90 days against a short-term export bill discounted by a commercial bank.
- It gives overseas buyer credit to foreign exporters for the import of Indian capital goods which are used for manufacturing export products.
- It finances export-oriented industries.
- It collects and provides market and credit information about foreign trade to those engaged in international business.
Question 3.
What are the procedures relating to import trade?
Answer:
- Obtaining Import License: The importer has to secure Import and Export Code (IEC) from the Director-General of Foreign Trade or its Regional Authority. The Indian Institute classification (ITC) -Harmonized System (HS) classified the goods into three categories, namely Restricted, Canalised, and Prohibited. Goods not specified in the above categories can be freely imported without any restrictions. An import license is not required to import the goods not mentioned in the above classification. An import license is valid for 24 months for capital goods and 18 months for other goods. The importer has to submit a copy of the IEC to customs authorities at the time of clearance of goods. The second copy of IEC is used to obtain foreign exchange from RBI.
- Trade Enquiry: Having obtained IEC, the intending importer has to make enquiry from the exporter or his agents. The importer makes the request by e-mail or postal mail to supply the details given below,
- Specification of goods like size, design, quality, etc.
- Quantity goods available,
- Price per unit,
- Terms of shipping,
- Terms of payments i.e. Letter of credit Documents against Acceptance (D/A) or Documents against Payment (D/P),
- Probable delivery time,
- Validity of offer period.
Importer responds to enquiry by sending proforma invoice.
- Obtaining Foreign Exchange: Since the importer has to settle import bills in foreign j currency, he has to obtain foreign exchange.j Importer has to provide IEC code in the! form supplied by an authorized dealer to get foreign exchange. The importer has to submit an application along with necessary j documents to the Exchange Control I Department of RBI. After scrutinizing the said application, the Reserve Bank of India will sanction the release of foreign exchange.
- Placing an Indent Order: importer places j an order either directly or through an indenting house. The indent contains the details like type of goods, design of goods, price, quantity, grade, packing instructions, insurance, delivery mode, desired delivery period, mode of the period, mode of shipment, etc.
- Opening Letter of Credit (L/C): Where foreign exporter does not know Indian; importer, he may like to ensure the! the creditworthiness of the unknown importer. In such a case, the exporter may advise the importer to arrange for a letter of credit in his favour. Letter of credit is a document under which issuing bank undertakes to make payment on behalf of the importer or to the order of the importer in exchange for specified documents from the exporter’s bank. The letter of credit is issued only for the financially sound importers. Exporter’s bank eventually sends the document to issuing bank which releases the payment.
![]()
Question 4.
Share of top five commodities in India’s exports.
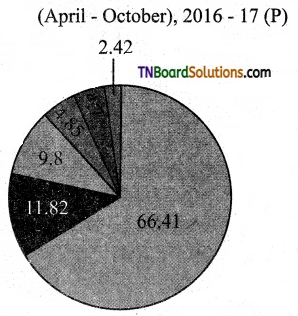
Answer:
■ Petroleum products
■ Peral precious semi-precious stone
■ Gold and other precious metals jewelry
■ Drug formulations biological
■ RMC cotton including accessories
■ Others
Question 5.
Write a note on (i) Customs clearance. (ii) payment of dock dues.
Answer:
(i) Customs Clearance: The exporter or his agent prepares three copies of the shipping bill in printed form. The Shipping bill contains the details like name and address of exporter, description of goods, value of goods, volume of goods, identification marks on the goods, port of destination, and port of loading. There are three types of shipping bills for three different categories of goods namely, dutiable goods, dutyfree goods, and duty draw-back goods Forwarding agent proceeds to pay export duty calculated by customs officers in the case of dutiable goods.
(ii) Payment of Dock Dues: After the payment of export duty, the forwarding agent arranges for transporting the goods to docks. The agent fills two copies of challan and submits it to the dock authorities along with one copy of the shipping bill. Then the agent pays dock charges. Dock authorities retain one copy of challan and return the second copy to the forwarding agent. This signed copy is called Dock Receipt or Port Trust Receipt.
Question 6.
Explain the objectives of import trade.
Answer:
- Achieving Rapid Industrialization: Developing countries can achieve rapid industrialization by importing advanced technology scarce raw materials, capital goods like machinery equipment, etc., and talents from other countries.
- Meeting Consumer Demand: Certain goods are either not available or cannot be manufactured/produced adequately to meet the growing demand in the home country. Hence import is necessary to meet the short supply of those goods.
- Upgrading Standard of Living of the People: Consumers are able to use a wide variety of goods like cell phones, car laptops, television audio systems, washing machines, perfume, soaps, etc., manufactured in foreign countries and enhance their standard of living through import trade.
- Meeting Shortage Situation: During famine, earthquake, flood drought, tsunami, abnormal price-increase situations, and so on food grains, vegetables, and other essential commodities are imported from foreign countries and the bad situation arising from the above situations are thus overcome.
- Lengthening Defence: Many countries around the world import defense equipment for their armed force. Such imports enable the country to ensure its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
![]()
For Future Learning
1. Import Trade Procedures.
Answer:
- Trade enquiry.
- Obtain import license
- Obtaining foreign exchange.
- Placing the indent.
- Arranging letter of credit.
- Obtaining shipping documents.
2. Agencies involved in Import Trade.
Answer:
- Indent houses.
- Clearing agents.
For Own Thinking
1. You should be able to think to simplify Import Trade Procedures.
Answer:
- Trade enquiry,
- Arranging letter of credit.
- Receiving payments.
2. Create interest in International Business for yourself.
Answer:
- Take interest in International business.
- To get more profit.
- To give employment opportunities to the public.
![]()
Multiple-choice questions
1. Which of the following documents are not required for obtaining an export license?
(a) IEC number
(b) Letter of credit
(c) Registration cum membership certificate
(d) Bank account number
Answer:
(b) Letter of credit
2. Which of the following documents is not required in connection with an import transaction?
(a) Bill of lading
(b) Shipping bill
(c) Certificate of origin
(d) Shipment advice
Answer:
(a) Bill of lading
3. Which of the following do not form part of the duty drawback scheme?
(a) Refund of excise duties
(b) Refund of customs duties
(c) Refund of export duties
(d) Refund of income dock charges at the port of shipment
Answer:
(d) Refund of income dock charges at the port of shipment
4. Which one of the following is not a document related to fulfilling the customs formalities?
(a) Shipping bill
(b) Export license
(c) Letter of insurance
(d) Proforma invoice
Answer:
(d) Proforma invoice
5. Which one of the following is not a part of – export documents?
(a) Commercial invoice
(b) Certificate of origin
(c) Bill of entry
(d) Mate’s receipt
Answer:
(c) Bill of entry
![]()
6. A receipt issued by the commanding officer of the ship when the cargo is loaded on the ship is known as:
(a) shipping receipt
(b) mate receipt
(c) cargo receipt
(d) charter receipt
Answer:
(b) mate receipt
7. Which of the following document is prepared by the exporter and includes details- of the cargo in terms of the shippers name the number of packages the shipping bill. Port of destination name of the vehicle carrying the cargo?
(a) Shipping bill
(b) Packaging list
(c) Mate’s receipt
(d) Bill of exchange
Answer:
(a) Shipping bill
8. The document containing the guarantee of a bank to honour drafts draw on it by an exporter is:
(a) letter of hypothecation
(b) letter of credit
(c) bill of lading
(d) bill of exchange
Answer:
(b) letter of credit
9. Which of the following does not belong to the world bank group?
(a) IBRD
(b) IDA
(c) MIGA
(d) IMF
Answer:
(d) IMF
![]()
10. TRIP is one of the WTO agreements that deal with:
(a) trade in agriculture
(b) trade in services
(c) trade-related investments measures
(d) none of these
Answer:
(d) none of these