Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 1 Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants
12th Bio Botany Guide Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants Text Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Choose the correct statement from the following
a) Gametes are involved in asexual reproduction
b) Bacteria reproduce asexually by budding
c) Conidia formation is a method of sexual reproduction
d) Yeast reproduce by budding
Answer:
d) Yeast reproduce by budding
Question 2.
An eminent Indian embryologist is
a) S.R.Kashyap
b) P.Maheswari
c) M.S. Swaminathan
d) K.C.Mehta
Answer:
b) P.Maheswari
Question 3.
Identify the correctly matched pair
a) Tuber – Allium cepa
b) Sucker – Pistia
c) Rhizome – Musa
d) Stolon – Zingiber
Answer:
c) Rhizome – Musa
![]()
Question 4.
Pollen tube was discovered by
a) J.G.Kolreuter
b) G.B.Amici
c) E.Strasburger
d) E.Hanning
Answer:
b) G.B.Amici
Question 5.
Size of pollen grain in Myosotis
a) 10 micrometer
b) 20 micrometer
c) 200 micrometer
d) 2000 micrometer
Answer:
a) 10 micrometer
Question 6.
First cell of male gametophyte in angiosperm is
a) Microspore
b) megaspore
c) Nucleus
d) Primary Endosperm Nucleus
Answer:
a) Microspore
![]()
Question 7.
Match the following
| I. External fertilization | i. pollen grain |
| II. Androecium | ii. anther wall |
| III. Male gametophyte | iii. algae |
| IV. Primary parietal layer | iv stamens |
Answer:
a) I—iv; ll—i; III—ii; I’V—iii
b) 1—iii; J1—iv; III—i; V—ii
c) I—iii; I1—iv; III—ii, IV—i
d) I—iii; II—i; III—iv; IV—ii
Answer:
b) I—iii;II—iv;III—i;1 V—ii
![]()
Question 8.
Arrange the layers of anther wail from locus to periphery
a) Epidermis,middle layers, tapetum, endothecium
b) Tapetum, middle layers, epidermis, endothecium
c) Endothecium, epidermis, middle layers, tapetum
d)Tapetum, middle layers endothecium epidermis
Answer:
d) Tapetum, middle layers endothecium epidermis
Question 9.
Identify the incorrect pair
a) sporopollenin – exine of pollen grain
b) tapetum – nutritive tissue for developing microspores
c) Nucellus – nutritive tissue for developing embryo
d) obturator – directs the pollen tube into micropyle
Answer:
c) Nucellus – nutritive tissue for developing embryo
![]()
Question 10.
Assertion : Sporopollenin preserves pollen in fossil deposits.
Reason : Sporopollenin is resistant to physical and biological decomposition.
a) Assertion is true; reason is false
b) Assertion is false; reason is true
c) Both Assertion and reason are not true
d) Both Assertion and reason are true
Answer:
d) Both Assertion and reason are true
Question 11.
Choose the correct statement(s) about tenuinucellate ovule
a) Sporogenous cell is hypodermal
b) Ovules have fairly large nucellus
c) sporogenous cell is epidermal
d) ovules have single layer of nucellus tissue
Answer:
a) Sporogenous cell is hypodermal and d)ovules have single layer of nucellus tissue
![]()
Question 12.
Which of the following represent megagametophyte
a) Ovule
b)Embryo sac
c) Nucellus
d)Endosperm
Answer:
b) Embryo sac
Question 13.
In Haplopappus gracilis, number of chromosomes in cells of nucellus is 4. What will be the chromosome number in Primary endosperm cell?
a) 8
b) 12
c) 6
d) 2
Answer:
C) 6 (3n)
![]()
Question 14.
Transmitting tissue is found in
a) Micropylar region of ovule
b) Pollen tube wall
c) Stylar region of gynoecium
d) Integument
Answer:
c) Stylar region of gynoecium
Question 15.
The scar left by funiculus in the seed is
a) tegmen
b) radicle
c) epicotyl
d) hilum
Answer:
d) hilum
Question 16.
A Plant called X possesses small flower with reduced perianth and versatile anther. The probable agent for pollination would be
a) water
b) air
c) butterflies
d) beetles
Answer:
b) air
![]()
Question 17.
Consider the following statement(s)
i) In Protandrous flowers pistil matures earlier
ii) In Protogynous flowers pistil matures earlier
iii) Herkogamy is noticed in unisexual flowers
iv) Distyly is present in Primula
a) i and ii are correct
b) ii and iv are correct
c) ii and iii are correct
d) i and iv are correct
Answer:
b) ii and iv are correct
Question 18.
Coelorhiza is found in
a) Paddy
b)Bean
c) Pea
d) Tridax
Answer:
a) Paddy
![]()
Question 19.
Parthenocarpic fruits lack
a) Endocarp
b) Epicarp
c) Mesocarp
d) seed
Answer:
d) seed
Question 20.
In the majority of plants, pollen is liberated at
a) 1 celled stage
b) 2 celled stage
c) 3 celled stage
d) 4 celled stage
Answer:
b) 2 celled stage
Question 21.
What is reproduction?
Answer:
Reproduction is the biological process of producing young ones of their own kind. It is a vital process for the existence of a species and it also brings suitable changes through variation in the offsprings for their survival on ear
Question 22.
Mention the contribution of Hofmeister towards Embryology.
Answer:
- He worked on flowering plant embryology.
- Discovered alternation of generation in plants.
- He described the structure of pollen tetrad.
![]()
Question 23.
List out two sub-aerial stem modifications with example.
Answer:
Subaerial stem modifications.
The stem is partly aerial and partly underground.
a) Runner. (Ex. oxalis, Centella Asiatica)
- It is running horizontally on the soil surface.
- Nodes have axillary buds, scale leaves, and adventitious roots.
- Runner arises from the axillary bud.
- Mother plant produces many runners in all directions.
- They break off and grow into individual plants.
b) Sucker. (Ex. Musa (banana), chrysanthemum)
Grows horizontally for a distance under the soil. Then it emerges obliquely upwards.
c) Stolon (Ex. Strawberry, Vallisneria)
Develop from underground stems.
They grow horizontally outwards.
d) Offset (condensed runners)
Unlike runners, they produce tilt of leaves above and duster of roots below Ex. Pistia, Eichhornia.
![]()
Question 24.
What is layering?
Answer:
- It is an artificial method of vegetative propagation.
- The stem of the parent plant is allowed to develop roots while still intact.
- The root develops. The rooted part is cut. It is planted to grow as a new plant.
- Ex. Ixora, Jasminum.
Question 25.
What are clones?
Answer:
Individuals developed by asexual reproduction are morphologically and genetically identical. Such individuals are called clones.
Question 26.
A detached leaf of Bryophyllum produces new plants. How?
Answer:
- Bryophyllum undergoes vegetative reproduction in the leaf.
- The succulent leaf is notched in its margin.
- Adventitious buds develop at these notches. They are called epiphyllous buds.
- These buds develop a root system. When the leaf decays, they become independent plants.
Question 27.
Differentiate Grafting and Layering.
Answer:
Grafting:
- In grafting, two different plants (stock & scion) are used to develop new plants.
- The new plant will support to possess the characters of both the parents or new variation can be noticed.
Layering:
- In layering, only one plant is used to develop a new plant.
- Variation cannot be expected. The new individual is exactly similar to the parent plant.
Question 28.
“Tissue culture is the best method for propagating rare and endangered plant species” Discuss.
Answer:
Micropropagation.
The growth of plant tissue in special culture medium under suitable controlled conditions is known as “tissue culture”.
it is the regeneration of a whole plant from a single cell or tissue.
Advantages.
- Rare, Endangered plants are propagated.
- In a short duration, plants with desirable characteristics can be multiplied.
- Produce Genetically identical plants.
- Done in any season.
- Plants without viable seeds (or) difficult to germinate can be propagated.
- Meristem culture produces disease-free plants.
- Cells can be genetically modified or transformed.
![]()
Question 29.
Distinguish mound layering and air layering.
Answer:
Mound Layering:
In mound layering, a lower flexible branch with leaves is bent to the ground and a part of the stem is buried in the soil and the tip of the branch is exposed above the soil. After the roots emerge from the buried stem, a cut is made in the parent plant so that the buried plant grows into a new plant.
Question 30.
Explain the conventional methods adopted in the vegetative propagation of higher plants.
Answer:
Conventional methods of vegetative propagation.
a) Cutting (Ex. Hibiscus)
- Plant parts like stem, leaf are cut from the parent plant.
- Cut part is placed in suitable medium,
- It produces root and grows into a new plant.
b) Grafting (Ex. Citrus, Mango)
- Two different plants are joined.
- They grow as one plant.
- Plant in soil is called stock.
- Plant used for grafting is the scion.
- It is of 5 types.
i) Bud grafting – scion is placed in the incision of stock.
ii) Approach grafting – Cut surfaces of stock scion are tied together.
iii) Crown Grafting – Wedge-shaped scion is inserted into the cleft of stock.
iv) Tongue grafting – Stock and scion are cut obliquely scion is fit into stock and bound with tape.
v) Wedge grafting – Twig of the scion is inserted into slot in the stock.
![]()
c) Layering
Stem of parent plant is allowed to develop roots while still intact. The root develops. The rooted part is cut and planted to grow as a new plant.
I) Mound Layering
- Flexible branch is buried in soil.
- Roots emerge from buried stem. It grows into a new plant.
ii) Air Layering
- Nodal region is girdled.
- Hormones are applied.
- Rooting is promoted.
- This area is covered by moist soil.
- Roots emerge in 2-4 months.
- Roots branches are removed from parent. They are grown separately.
Question 31.
Highlight the milestones from the history of plant embryology.
Answer:
- 1682 – Nehemiah Grew mentioned stamens as the male organ of a flower.
- 1694 – R.J. Camerarius described the structure of a flower, anther, pollen, and ovule
- 1761 – J.G. Kolreuter gave a detailed account of the importance of insects in pollination.
- 1824 – G.B. Amici discovered the pollen tube.
- 1848 – Hofmeister described the structure of pollen tetrad.
- 1870 – Hanstein described the development of embryos in Capsella and Alisma.
- 1878 – E. Strasburger reported polyembryony.
- 1884 – E. Strasburger discovered the process of Syngamy.
- 1899 – S.G. Nawaschin and L. Guignard independently discovered Double fertilization.
- 1904- E. Hanning initiated embryo culture.
- 1950 – D.A. Johansen proposed classification for embryo development.
- 1964 – S. Guha and S.C. Maheswari raised haploids from Datura pollen grains
- 1991 – E.S. Coen and E.M. Meyerowitz proposed the ABC model to describe the genetics of initiation and development of floral parts
- 2015 – K.V. Krishnamurthy summarized the molecular aspects of pre and post-fertilization reproductive development in flowering plants.
Question 32.
Discuss the importance of Modern methods in reproduction of plants.
Answer:
The genetic ability of a plant cell to produce the entire plant under suitable condition is said to be totipotency.
- This characteristic feature of a cell is utilized in horticulture, forestry and industries to propagate plants.
- The mature phloem parenchyma cells removed from the carrot were placed in a suitable medium under controlled conditions.
- It stimulate to start dividing again to produce a new carrot plant.
Importance of modern methods of reproduction in plants.
- Rapid Multiplication of desired plants in short duration.
- Genetically identical plants are produced.
- Tissue culture can be done at any season
- Plants without viable seeds (or) difficult to germinate can be propagated.
- Rare, Endangered plants are propagated.
- Meristem culture produces disease-free plants.
- Cells are genetically modified or transformed.
![]()
Question 33.
What is Cantharophily?
Answer:
- It is the cross-pollination of flowers by beetles. They feed on pollen or juicy tissues of their flower.
- The plants using this mode of pollination
- Er. Nymphaea species of plants – Rhinoceros beetle.
- Giant Water lily – Scarab beetle
- Illicium plant – Diptera files.
Question 34.
List any two strategy adopted by bisexual flowers to prevent self-pollination.
Answer:
1) Dichogamy
Anthers and stigmas mature at different times.
- Protandry – Stamens mature earlier.
- Protogyny – Stigmas mature earlier.
2) Herkogamy
- Self pollination is impossible by the arrangement of stamens and stigmas.
- Ex: In Hibiscus, stigmas project above the stamens.
- In some plants, when the pollen grain of a flower reaches the stigma of the same.
- It is unable to germinate or prevented to germinate on its own stigma.
- It is a genetic mechanism.
Example: Abutilon, passiflora.
Question 35.
What is the endothelium?
Answer:
In the Asteraceae species, the inner layer of the integument gets specialized for nourishing the embryosac and this is called the integumentary tapetum or endothelium.
![]()
Question 36.
“The endosperm of angiosperm is different from gymnosperm”. Do you agree? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Endosperm of Angiosperms
- Triploid Endosperm
- Endosperm is formed by triple fusion.
- Endosperm surrounds the embryo.
Endosperm of Gymnosperm
- Haploid endosperm.
- The endosperm is formed before fertilisation.
- Gymnosperms (Ex; pine) produce embryos. It provides nutrition as starch. with many cotyledons. Primary Endosperm is used as food.
Question 37.
Define the term Diplospory.
Answer:
Diplospory is a condition where a diploid embryosac is formed from megaspore mother cells without a regular meiotic division.
E.g: Eupatorium.
Question 38.
What is polyembryony? How can it be commercially exploited?
Answer:
Polyembryony
- The occurrence of more than one embryo in a seed is called poly embroyony.
Practical Applications.
- Seedlings from nucellar tissue of citrus are better clones for orchards.
- Embryos from polyembryonic are virus-free.
Question 39.
Why does the zygote divide only after the division of the Primary endosperm cell?
Answer:
The primary endosperm nuclear (PEN) divides prior to zygotic division and form endosperm. Endosperm acts as a nutritive tissue and nourishes the developing embryo.
![]()
Question 40.
What is Mellitophily?
Answer:
Pollination by honeybee is called mellitophily (Latin word mellitus= honey or sweet), Among the insects the bees are the main flower visitors and dominant pollinators.
Question 41.
“Endothecium is associated with dehiscence of anther” Justify the statement.
Answer:
The inner tangential wall develops bands (sometimes radial walls also) of cellulose (sometimes also slightly lignified). The cells are hygroscopic. The cells along the junction of the two sporangia of an anther lobe lack these thickenings. This region is called stomium. This region along with the hygroscopic nature of endothecium helps in the dehiscence of anther at maturity.
Question 42.
List out the functions of tapetum.
Tapetum is the innermost layers of anther wall.
Answer:
- Supplies nutrition to developing microspores.
- Contributes sporopollenin through ubisch bodies. They play role in pollen wall formation.
- Pollenkitt material is contributed by tapetal cells. It is layer transferred to pollen surface.
- Exine proteins for rejection reaction are derived from tapetal cells.
Question 43.
Write a short note on Pollen kitt.
Answer:
Pollenkitt is contributed by the tapetum and coloured yellow or orange and is chiefly made of carotenoids or flavonoids. It is an oily layer forming a thick viscous coating over pollen surface. It attracts insects and protects damage from UV radiation.
![]()
Question 44.
Distinguish tenuinucellate and crassinucellate ovules.
Answer:
Tenuinucellate ovule
- The sporogenous cell is hypodermal
- It has single layer of nuclear tissue.
- It has very small nucellus
Crassinucellate ovule
- These ovules have sub-hypodermal sporogenous cell
- They have large nucellus.
- Many layers of cells are seen.
Question 45.
‘Pollination in Gymnosperms is different from Angiosperms’ – Give reasons.
Answer:
In gymnosperms, the ovules are exposed and the pollens are deposited directly on it. Hence the pollution is direct in a gymnosperm. Whereas in angiosperms it is said to be indirect, as the pollens are deposited on stigma or the pistil.
![]()
Question 46.
Write a short note on Heterostyly.
Answer:
- Heterostyly is a mechanism to promote cross-pollination.
- Different forms of flowers with different lengths of stamen and style.
- Pollination takes place between organs of same length.
a) Distyly. (Ex. Primula)
- Thrum-eyed flowers have short styles. Anthers of pin have short stamen.
- Anthers of thrum-eyed flowers and stigma of the pin are of the same height (both are long). This helps in effective pollination.
b) Tristyly (Ex. Lythrum)
3 kinds of flowers are there, with respect to the length of style and stamens. Flower of one type can’t pollinate their own type. They pollinate the other 2 types.
Question 47.
Enumerate the characteristic features of Entomophilous flowers.
Answer:
The characteristic features of entomophilous flowers are as follows:
- Flowers are generally large or if small they are aggregated in dense inflorescence. Example: Asteraceae flowers.
- Flowers are brightly coloured. The adjacent parts of the flowers may also be brightly coloured to attract insects. For example in Poinsettia and Bougainvillea, the bracts become coloured.
- Flowers are scented and produce nectar.
- Flowers in which there is no secretion of nectar, the pollen is either consumed as food or used in building up of its hive by the honeybees. Pollen and nectar are floral rewards for visitors.
- Flowers pollinated by flies and beetles produce foul odour to attract pollinators.
- In some flowers, juicy cells are present which are pierced and the contents are sucked by the insects.
![]()
Question 48.
Discuss the steps involved in
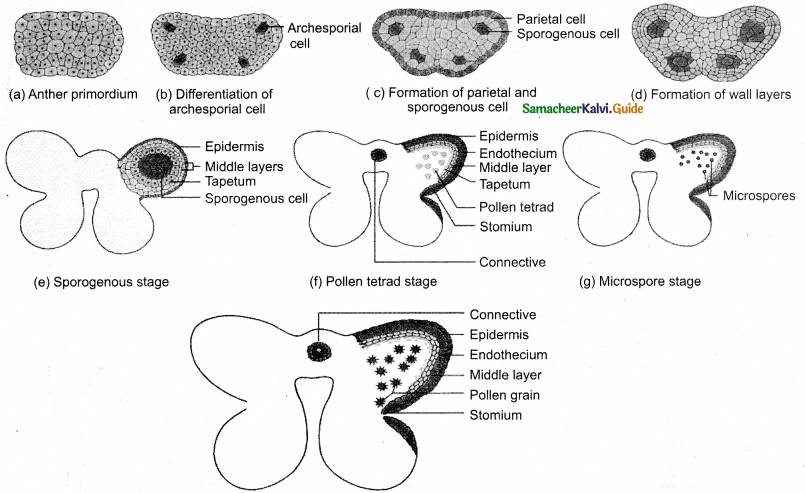
Microsporogenesis.
Microsporogenesis.
Answer:
Formation of haploid microspores from diploid microspore mother cell by meiosis.
- The primary sporogeneous cells undergo mitosis to form sporogenous tissue. ‘
- Sporogenous tissue functions as microspore mother cells.
- Microspore mother cell divides meiotically to form a tetrad (4 haploid microspores)
- Microspores get separated. They remain free in the anther locule. They develop into pollen grains.
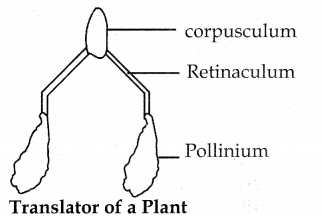
- Microspores are held together by pollinium. Filament (or thread) like part form pollinium is called retinaculum. Through retinaculum pollinia are attached to clip like corpusculum. This structure is called Translator (Y shapled).
Question 49.
With a suitable diagram explain the structure of an ovule.
Structure of ovule (Megasporangium)
Answer:
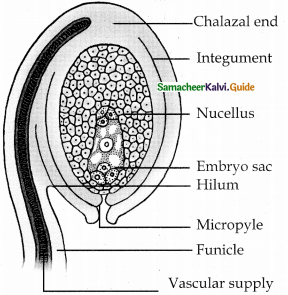
- Ovule of ovule (Megasporangium)
- It has a stalk and a body.
- stalk (funiculus) is at the base of ovule. It attaches ovule to the placenta.
- Hilum is the junction (point of attachment) between ovule and funicle.
- In an inverted ovule, the funicle is fused to the body of ovule. Thus a ridge called raphe is formed.
- Body of ovule has central mass of reserve food called nucellus.
- Nucellus is covered by 2 layers, called integuments.
- Integument covers the nucellus completely except at the top. This forms a pore called micropyle.
- Ovule with single integument is called unitegmic.
- At the base of body, nucellus, integument and funicle meet. This is called chalaza.
- Sac like structure in nucellus towards micropylar end is called embryosac (or) female gametophyte. It is formed from functional megaspore of nucellus.
- The nutritive inner intergument layer is called integumentary tapetum or endothelium.
- Tenuinucellate type ovule has hypodermal sporogenous cell. It has single layer of nucellar tissue.
- Crassinucellate type, ovule has subhypodermal sporogenous cell.
- Group of cells between chalaza and embryosac is called hypostase.
- Thick walled cells above micropyle are called epistase.
![]()
Question 50.
Give a concise account on steps involved in the fertilization of an angiosperm plant.
Answer:
Steps in the fertilization of Angiosperms
1. Germination of pollen to form pollen tube in the stigma.
- Pollens fall on receptive stigma.
- Compatible pollen germinates to form a tube.
- This is helped by stigmatic fluid in wet stigma and pellicle in dry stigma.
- Compatibility is decided by recognition, rejection protein reaction, between pollen and stigma surface.
- Pollen undergoes hydration. Pollen wall proteins cire released.
- The entire content moves into pollen tube.
- Growth is at the cytoplasmic contents at the tip.
- The remaining part of pollen tube is occupied by a vacuole.
- It is cut off from tip by callose plug.
- The hemispherical, transparent pollen tip of pollen tube is called ‘cap block.
- The “cape block” disappears and the growth of the pollen tube stops.
2. Growth of pollen tube in the style.
- Hollow style glandular canal cells secrete mucilaginous substance. These secretions are nutrition for growing pollen tube. They control compatibility of style and pollen tube.
- In solid style the pollen tube grows through the intercellular space of transmitting tissue. Semisolid style is intermediate between solid and open type.
3. Entry of the pollen tube into the ovule.
- Propgamy – Pollen tube enters through the micropyle.
- Chalazogamy – Pollen tube enters through chalaza.
- Monogamy – Pollen tube enters through integument.
4. Entry of pollen tube into the embryo sac.
- Pollen tube enters embryosac at the micropylar end. It is guided by an obturator.
- Pollen tube enters into one of the synergids.
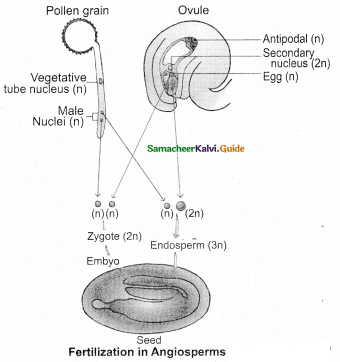
5. Double fertilization and Triple fusion.
- In Angiosperms, both the male gametes are involved in fertilization, it is called double fertilisation.
- One of the male gametes fuses with the egg nucleus (syngamy). Thus zygote is formed.
- The second gamete migrates to central cell. It fuses with polar nuclei (or) secondary nucleus. Thus primary Endosperm nucleus is formed. This involves the fusion of 3 nuclei so it is called Triple fusion.
![]()
Question 51.
What is endosperm. Explain the types. (OR) Write the three fusion of Antisper- mous plant fertilization.
The zygote divides into an endosperm.
The primary Endosperm Nucleus is the regulatory structure. It nourishes the developing embryo.
These types of endosperms are based on the mode of development.
a) Nuclear Endosperm. (Ex.Arachis)
- Primary Endosperm Nucleus undergoes mitosis.
- No cell wall formation.
- A free nuclear condition exists
b) Cellular Endosperm (Ex. Helianthus)
- Primary Endosperm Nucleus divides into 2 nuclei.
- It is followed by wall formation.
c) Helobial Endosperm. (Ex. Vallisneria)
- Primary Endosperm Nucleus moves towards the base of the embryo sac. It divides into 2 nuclei.
- Cell wall is formed. It divides large micropylar chamber into form the small chalazal chamber.
- Nucleus of micropylar chamber divides. The Chalazal chamber nucleus does not divide.
Question 52.
Differentiate the structure of Dicot and Monocot seed.
Answer:
Structure of Dicot seed
- Two cotyledons
- Two seeds may be seen
- The seed coat has outer coat testa and inner tegmen.
- In pea the cotyledons store the food. In castor the endosperm, stores reserve food.
- Coleoptile (sheath of plumule) coleorhiza (sheath of radicle) are absent.
Structure of Monocot seed :
- Only one cotyledon
- Paddy is one-seeded.
- Seed is enclosed by husk. The brown membranous seed coat closely adheres to grair
- Scutellum supplies embryo with food from endosperm through epithelium
- Coleoptile and coleorhiza are seen.
![]()
Question 53.
Give a detailed account of parthenocarpy. Add a note on its significance.
Answer:
In some plants, fruit-like structures may develop from the ovary without the act of fertilization. Such fruits are called parthenocarpic fruits. Invariably they will not have true seeds. Many commercial fruits are made seedless.
Examples: Banana, Grapes, and Papaya. Nitsch in 1963 classified the parthenocarpy into the following types:
- Genetic Parthenocarpy: Parthenocarpy arises due to hybridization or mutation.
Examples: Citrus, Cucurbita. - Environmental Parthenocarpy: Environmental conditions like frost, fog, low temperature, high temperature etc., induce Parthenocarpy. For example, low temperature for 3-19 hours induces parthenocarpy in Pear. Chemically
- induced Parthenocarpy: Application of growth-promoting substances like Auxins and Gibberellins induces parthenocarpy.
- Significance: The seedless fruits have great significance in horticulture.
- Seedless fruits have great commercial importance.
- Seedless fruits are useful for the preparation of jams, jellies, sauces, fruit drinks, etc.
- A high proportion of edible parts is available in parthenocarpic fruits due to the absence of seeds.
12th Bio Botany Guide Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants in Animals Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Match the following
| A) Camerarius | 1. structure of a flower |
| B) Hofmeister | 2. Pollen Tetrad. |
| C) Hanning | 3. Discovery of the pollen tube. |
| D) Amici | 4. Embryo culture |
a) A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
b) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
c) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
d) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Answer:
A-1,B-2,C-4,D-3
![]()
Question 2.
Find the Matching pair
a) Rhizome – Zingiber
b) Corm – Solanum
c) Tuber – Lilium
d) Bulb – Tuber
Answer:
a) Rhizome – Zingiber.
Question 3.
Find the mismatching pair
a) Runner – Centella
b) Sucker – Chrysanthemum
c) Stolon – Fragaria
d) Offset – Bryophyllum
Answer:
d) Offset – Bryophyllum.
Question 4.
Epiphyllous buds are in
a) Chrysanthemum
b) Agave
c) Curcuma
d) Scilla
Answer:
d) Scilla
![]()
Question 5.
Eyes of potato are referred to
a) adventitious roots
b) axillary buds
c) terminal buds
d) intercalary buds
Answer:
b) axillary buds
Question 6.
The T-shaped incision is made in grafting.
a) Bud
b) Approach
c) Tongue
d) Crown
Answer:
a) Bud
Question 7.
Plants propagated economically by vegetative propagation
a) Solanum tuberosum
b) Ixora
c) Jasminum
d) Chrysanthemum
Answer:
a) Solanum tuberosum
![]()
Question 8.
Steward produced……………plant from phloem
a) Beetroot
b) Carrot
c) Solanum
d) Radish
Answer:
b) Carrot
Question 9.
Arrange from the periphery to centre in another wall.
a) Endothecium, Middle layer, tapetum
b) Tapetum, middle layer, Endothecium
c) Endothecium, tapetum, middle layer
d) Middle layer, endothecium, tapetum
Answer:
a) Endothecium, Middle layer, tapetum
Question 10.
Microspores are held together by pollinium in
a) Hibiscus
b) Calotropis
c) Ixora
d) Datura
Answer:
b) Calotropis
![]()
Question 11.
…………… cells are hygroscopic in anther wall.
a) Epidermis
b) Endothecium
c) Middle layer
d) tapetum
Answer:
b) Endothecium
Question 12.
Find the wrong statement
a) Invasive tapetum is peri plasmodial.
b) Amoeboid tapetum is associated with male sterility
c) Middle layer is ephemeral.
d) Epithelium is hygroscopic
Answer:
d) Epithelium is hygroscopic
Question 13.
Find the correct statement
a) Carrot grass causes allergy
b) Bee pollen is an artificial substance.
c) Palynology is the study of honey pollen.
d) Mellitopalynology is the study of pollen grain.
Answer:
a) Carrot grass causes allergy
![]()
Question 14.
Not a shape of pollen grain
a) Globose
b) Ellipsoid
c) crescent-shaped
d) Cubical
Answer:
d) Cubical
Question 15.
…………… protects pollen grain from UV
radiation.
a) Sporopollenin
b) pollenkitt
c) Exine
d) callose.
Answer:
b) pollenkitt
Question 16.
Not in exine of pollen grain
a) Cellulose
b) Sporopollenin
c) Pollenkitt
d) Callose
Answer:
d) Callose
![]()
Question 17.
………………….. % of angiosperm pollen is liberated in 2 cell stage
a) 50
b) 60
c) 40
d) 30
Answer:
b) 60
Question 18.
Which one of the following is a dioecious plant?
a) Coconut
b) Bitter gourd
c) Pea plant
d) Date palm
Answer:
d) Date palm
Question 19.
Match the following
| A) Orthotropous | 1. Leguminosae. |
| B) Anatropous | 2. Primulaceae |
| C) Hemianatropous | 3. Dicot, Monocot |
| D) Campylotropous | 4. Piperaceae |
a) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
b) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
c) A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
d) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Answer:
a) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
![]()
Question 20.
Horseshoe shaped nucellus is in …………… ovule.
a) Circinotropous
b) Amphitropous
c) Anatropous
d) Hemianatropous
Ans:
b) Amphitropous
Question 21.
Find the mismatching pair
a) Tetrasporic – Peperomia
b) Bisporic – Allium
c) Monosporic – Polygonum
d) Trisporic – Cactaceae
Ans :
d) Trisporic – Cactaceae
Question 22.
Homogamy is in ……………………….
a) Mirabilis
b) Commelina
c) Viola
d) Oxalis.
Answer:
a) Mirabilis
Question 23.
Protogyny is in ………………………..
a) Aristolochia
b) Helianthus
c) Viola
d) Oxalis.
Answer:
a) Aristolochia
![]()
Question 24.
Distyly is in ……………………….
a) Primula
b) Lythrum
c) Abutilon
d) Hibiscus
Answer:
a) Primula
Question 25.
Find the mismatching following
a) Passiflora – self sterility
b) Gloriosa – Herkogamy
c) Sugarcane – Anemophily
d) Urtica – Hydrophily
Answer:
d) Urtica – Hydrophily
Question 26.
Find the matching pair
a) Epihydrophily – Elodea.
b) Ornithaphily – Lemna
c) Entomophily – Vallisneria
d) Hydrophily – Kigelia.
Answer:
a) Epihydrophily – Elodea
Question 27.
Find the odd one
Not dealing with entry of pollen tube
a) Herkogamy
b) Porugamy
c) Mesogamy
d) chalozogamy
Answer:
a) Herkogamy
![]()
Question 28.
Not a post-fertilization change
a) Endosperm
b) Embryo development
c) Seed formation
d) Triple fusion
Answer:
d) Triple fusion.
Question 29.
Matching
| A) Apple | 1. Edible receptacle |
| B) Jack fruit | 2. Beet root |
| C) Juicy flower stalk | 3. Anacardium |
| D) Perisperm | 4. Fleshy perianth |
a) A-1, B-4, C-3, D-2
b) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
c) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
d) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Answer:
a) A-1, B-4, C-3, D-2
![]()
Question 30.
Matching the following
| A) Ovary | 1. zygote |
| B) Ovule | 2. Endosperm |
| C) Secondary nucleus | 3. Seed |
| D) Egg | 4. Fruit |
a) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
b) A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
c) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
d) A-3, B-2, C-1, D-4
Answer:
a) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
Question 31.
Which one of the following statements is not true regarding sporopollenin? I a
a) Sporopollenin is contributed by both pollen cytoplasm and tapetum.
b) It helps the pollen to withstand strong acid.
c) Sporopollenin is derived from phycobilins
d) It helps pollen during long period perservation in fossil deposits.
Answer:
a) Sporopollenin is contributed by both pollen cytoplasm and tapetum.
Question 32.
True (or) False
1) Beetles show Palaenophily
2) Bees show Cantharophily
3) Snails show Malacophily
4) Ants show Myrmecophily
a) 1,2,3 true 4 is false
b) 1,2 are true, 3,4 are false
c) 1,2,3 are true, 4 true
d) 1 is true 2,3,4 are false
Answer:
a) 1,2, 3 true 4 is false
![]()
Question 33.
Find the mismatching pair
a) Trap mechanism – Aristolochia.
b) Pit fall mechanism – Arum.
c) Clipmechanism – Aeclepiadaceae
d) Piston mechanism – Salvia
Answer:
d) Piston mechanism – Salvia
Question 34.
Find the mismatching pair
a) Obligate mutualism – Tridax
b) Pollen robber – Amurphophallus.
c) Pseudo copulation – Ophyrus.
d) Fig pollination – Wash.
Answer:
a) Obligate mutualism – Tridax
Question 35.
Fritillaria imperialis shows vegetative propagation by
a) Bulb
b) Runner
c) Bulbils
d) Sucker
Answer:
c) Bulblis
![]()
Question 36.
Generative apospory is in
a) Aerva
b) Ulmus
c) Balanophova
d) Allium
Answer:
a) Aerva
Question 37.
Terror of Bengal is
a) Eichhornia
b) Centella
c) Lilium
d) Murraya
Answer:
a) Eichhornia
Question 38.
Allium cepa is an example for ………………….
a) Corm
b) Tuber
c) Tunicated bulb
d) Naked bulb
Answer:
c) Tunicated bulb
Question 39.
Jasminum shows…………………….
a) Bud grafting
b) Approach grafting
c) Crown grafting
d) None
Answer:
d) None
![]()
Question 40.
Endangered plants can be produced by
a) Layering
b) Grafting
c) Micropropagation
d) Cutting
Answer:
c) Micropropagation
Question 41.
Disease free plants can be produced by
a) Meristem, culture
b) Grafting
c) Cutting
d) Layering
Answer:
a) Meristem, culture
Question 42.
Which one of the following is not an advantage of micro propagation?
a) Plants produced are genetically identical
b) Endangered plants can be propagated
c) Sometimes undesirable genetical changes occur.
d) Disease free plants can be produced.
Answer:
c) Sometimes undesirable genetical changes occur.
Question 43.
…………………………. has underground and aerial flowers
a) Scrophularia
b) Catharanthus
c) Commelina
d) Clerodendron
Answer:
c) commelina
![]()
Question 44.
Juicy cells are in the …………………. flowers
a) Ornithophilous
b) Hydrophilous
c) Entomophilous
d) Malacophilous
Answer:
c) Entomophilous
Question 45.
The central mass of parenchyma in ovule is
a) Nucellus
b) Chalaza
c) Endothelium
d) Embryosac.
Answer:
a) Nucellus
Question 46.
From the following which one is the column of sterile tissue surrounded by the anther lobe.
a) Periplasodium
b) pollen chamber
c) connective tissue
d) tapetum
Answer:
c) connective tissue
Question 47.
Oxalis shows …………………
a) Cleistogamy
b) Homogamy
c) Incomplete dichogamy
d) Geitonogamy
Answer:
a) Cleistogamy
![]()
Question 48.
Brightly coloured bracts attract insects in……………..
a) Poinsettia
b) Bougainvillea
c) Lemna
d) Both a,b
Answer:
d) Both a,b
Question 49.
In a male gametophyte, the chromosomal number of generative nucleus is (A)
a) (A)-(n);(B)-(2n)
b) (A)-(2n);(B)-(n)
c) (A)-(2n);(B)-(2n)
d) (A)-(n);(B)-(n)
Answer:
b) (A)-(2n);(B)-(n)
Question 50.
Endosperm is formed from …………………..
a) Ovary
b) Ovule
c) egg
d) Secondary nucleus
Answer:
d) secondary nucleus
![]()
Question 51.
First cell of Male gametophyte in angio…………………..
a) Primary endosperm
b) Microspore
c) Megaspore
d) Nucleus
Answer:
b) Microspore
Question 52.
Malus shows ………………….. cutting
a) Root
b) stem
c) leaf
d) Flower
Answer:
a) Root
![]()
Question 53.
Polygonaceae has …………………..type of ovule
a) Orthotropous
b) Anatropous
c) Hemianatropous
d) Campylotropous.
Answer:
a) Orthotropous
Question 54.
Not an animal pollinater
a) Lemur
b) Gecko Lizard
c) Garden lizard
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 55.
This shape is not seen in Tridax embryo
a) Globular
b) Heart
c) torpedo shape
d) Cuboidal
Answer:
d) cuboidal
![]()
Question 56.
Kigelia africana shows
a) Cheiropterophily
b) Malacophily
c) Entomophily
d) Zoophily
Answer:
a) Cheiropterophily
Question 57.
The pollen of Myosotis is micrometers.
a) 10
b) 100
c) 1
d) 20
Answer:
a) 10
![]()
Question 58.
Rhizome is not in
a) Musa paradisiaca
b) Zingifer officinale.
c) Curcuma longa
d) Colocasia
Answer:
d) Colocasia
Question 59.
The pollen of Nyctaginaceae is of microns
a) 50
b) 100
c) 200
d) 300
Answer:
c) 200
Question 60.
Does not show vegetative reproduction by root
a) Murraya
b) Dalberigia
c) Millinagtonia
d) Spinifex.
Answer:
d) spinifex
![]()
II. Two Marks
Question 1.
Which characteristic feature of a plant cell in used in horticulture, forestry and industries to propagate plants
Answer:
The Genetic ability of plant cell to produce entire plant under suitable conditions is called totipotency.
Question 2.
Define tissue culture?
Answer:
The growth of plant tissue in special culture medium suitable controlled conditions.
Question 3.
Name the 3 types of gametic fusions in sexual reproduction of plants?
Answer:
Isogamy, Anisogamy and Oogamy.
Question 4.
What is microsporogenesis?
Answer:
Formation of haploid microspores from diploid microspore mother cell by meiosis.
Question 5.
Comment on amoeboid tapetum?
Answer:
- It is a third type of tapetum.
- The cell wall is not lost.
- Cells protrude into the anther cavity, by amoeboid movement.
- It is connected to male sterility. It is not periplasmodial type.
![]()
Question 6.
What are Ubisch bodies?
Answer:
Tapetum contributes to sporopollenin through ubisch bodies. They play an important role in pollen wall formation.
Question 7.
Differentiate Exine and Intine?
Answer:
Exine Intine:
- Outer wall layer of pollen
- Thick
- Not uniform. Made of cellulose, sporopollenin, pollenkitt.
Intine :
- Inner wall layer.
- Thin
- Uniform made of pectin, hemicellulosc, cellulose, callose.
Question 8.
Comment on the sculpturing pattern of pollengrains?
Answer:
- The exine is sculptured as rod, groove, wart, punctuation etc.
- This pattern is used in plant identification and classification.
Question 9.
Mention the various shapes of pollengrains?
Answer:
Globose, ellipsoid, fusiform, lobed, angular, crescent shaped.
![]()
Question 10.
What do you know of Palynology?
Mention its uses.
Answer:
- It is the study of pollengrains.
- It helps to identity the coal, oil fields.
- It reflects the vegetation of that area.
Question 11.
How can we preserve pollengrains?
Answer:
Pollen is preserved in liquid nitrogen (-196°C) in viable condition for prolonged duration. It is called cryopreservation. This pollen of economically important plants are stored in pollen bank.
Question 12.
What is Mellitopalynology?
Answer:
Study of flower honey and pollen.
Question 13.
Comment on Carrot Grass?
Answer:
- Parthenium hysterophorus of Asteraceae family is called as carrot grass.
- It is introduced as a contaminant with cereal from Tropical America.
- Pollen of this plant causes allergy.
Question 14.
Differentiate hypostase from Epistase?
Answer:
Hypostase
Group of cells in the ovule between chalaza and embryosac.
Epistase :
Thick walled cells above the micropylar end above the embryosac.
![]()
Question 15.
What is Archesporium?
Answer:
In the ovule, a single hvpodermal cell in the nucellus become enlarged. “I his functions as Archesporium. In some plants it functions as megaspore mother cell directlv. It mev divide.
Question 16.
Prove that there is a co.evolution between plants and animals?
Answer:
Many plants are pollinated hv a particular animal species. The flowers are modified accordingly. This proves their co.evolution.
Question 17.
Draw this diagram and table the parts.
Answer:
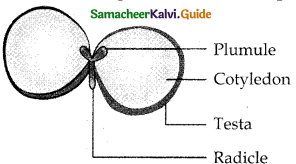
Question 18.
Define pollination?
Answer:
Transfer of pollengrains from anther to stigma of a flower.
![]()
Question 19.
Differentiate pollination in gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Answer:
Pollination in Gymnosperms
- Direct
- Pollens are directly deposited on the exposed ovules.
Pollination in Angiosperms :
- Indirect
- Pollens are deposited on the stigma of pistil.
Question 20.
What is chasmogamy?
Answer:
In many angiosperms, the flowers open. They exposure mature anther and stigma for pollination. This phenomenon is chasmo¬gamy. These are chasmogamous flowers.
Question 21.
Define cleistogamy?
Answer:
In some plants, pollination occurs without exposing or opening the sex organs. This phenomenon is called cleistogamy. Such flowers are called cleistogamous flowers.
![]()
Question 22.
Differentiate Autogamy and allogamy?
Answer:
Autogamy
Transfer of pollen on the stigma of the same flower
Allogamy :
Transfer of pollen of one flower to the stigma of another flower.
Question 23.
Name the abiotic agents of pollination?
Answer:
- Pollination by wind (or) Anemophily.
- Pollination by water (or) Hydrophily.
Question 24.
Define Zoophily?
Answer:
Pollination through animals (Ex. insects) is called as Zoophily.
Question 25.
What is cheiropterophily? Give example?
Answer:
Pollination by bats. Such plants are kigelia africana, Adansonia digitata.
Question 26.
Malacophily – Comment?
Answer:
Pollination by slugs and snail. Ex. Plants of Araceae, Water snails pollinate Lemna.
![]()
Question 27.
What is Myrmecophily?
Answer:
Pollination by ants Ex. Eegnminosae, plants.
Question 28.
Redraw the diagram and lable the parts.
Answer:

Question 29.
What is cap block?
Answer:
The Hemispherical, transparent tip of pollentube is called cap block. It is seen by microscope. When it disappears the growth of pollen tube stops.
![]()
Question 30.
What is the significance of obtruator?
Answer:
In the ovary locule, the obtruator guides pollen tube towards the micropyle, of ovule.
Question 31.
Suggest the events after fertilization ?
Answer:
- Endosperm, embryo development.
- Formation of seed, fruit. These are called post fertilization changes.
Question 32.
What is Suspensor ?
Answer:
- During the developement, the two cells of the basal cell undergoes several transverse division into form a six to ten called suspensor.
- The suspensor helps to push the embryo deep into the endosperm.
Question 33.
What is Callus?
Answer:
Undifferentiated mass of cells obtained through tissue culture.
![]()
Question 34.
Define Apomixis ?
Answer:
- It is defined as the substitution of the usual sexual system (Ampimixis) by a form of reproduction.
- It does not involve meiosis and syngamy.
Question 35.
What is Scutellum?
Answer:
- The seeds of paddy is one seeded and is called Caryopsis.
- The embryo is small and consists of one shield shaped cotyledon known as scutellum.
- It is present towards lateral side of embryonal axis.
Question 36.
Define Pollinium.
Answer:
In some plants, all the microspores in a microsporangium remain held together called pollinium.
Example: Calotropis
![]()
Question 37.
What is Amphitropous?
Answer:
- A type of ovule.
- It is between hilum and chalaza.
- The curvature of the ovule leads to horse – shoe shaped nucellus.
Example: Alismataceae.
Question 38.
Write the practical application of activation of nucellar tissue.
Answer:
- The activation of micellar tissue or an\ other cells (sporopln lie ceils of the ovule) can produce more’ Ilian one embryo, known as poly embryonv.
- The seedlings formed from the nucellar tissues in citrus are found belter clones lor orchards.
- They are Disease resistant (virus free) and are preferred by Agriculturists than the normal seedlings.
Question 39.
Differentiate pineyed flower and thrum eyed flower.
Answer:
Pineyed flower :
Pin or long stv!e, long stigma tic pa iliac, short stamens and small pollen grains.
Ex : primula
![]()
Thrum eyed flower :
Thrum-eved or short style, small stigmatic papillae, long stamens and large pollen gains.
Question 40.
Differentiate Coleoptile and
Answer:
Coleoptile Coleorhiza :
The plumule is surrounded bv a proteetive sheath called coleoptile.
Coleorhiza:
The radicle including root cap is also covered bv a protects e sheath called coleorhiza.
III. Three Marks
Question 1.
How does pollen tube grow through a solid style?
Answer:
- It is common among dicots. It is character¬ized by the presence of central core of elorgated highly specialised cells called transmitting tissue.
- This is equivalent to the lining cells of hollow style and does the same function.
- Its contents are also similar to the content of those cells. The pollen tube grows through inter-cellular spaces of the transmitting tissue.
![]()
Question 2.
Give the significance of pollen calendar?
Answer:
- It shows the production of pollen by plants during different seasons.
- This benefits the allergic persons.
- Pollen grains cause asthma, bronchitis, has fever, allergic rhinitis.
Question 3.
Comment on Caruncle?
Answer:
Cells at the tip of outer integument around micropyle develop into fleshy stucture. It is called caruncle. Ex. Ricinus communis.
Question 4.
What is perisperm?
Answer:
Remnant of nucellar tissue in the seed is called perisperm.
Ex. Black pepper, beet root.
![]()
Question 5.
What is Aril?
Answer:
The colourful, fleshy funiculus is called Aril. Ex. Myristica and Pithe cellobium.
Question 6.
Write about Endosperm?
Answer:
The Zygotas divides into endosperm. It is a nutritive tissue nourishing embryo. It is a regulatory structure.
Question 7.
Differentiate Endospermous and non-endospermous seeds?
Answer:
Endospermous seeds :
- Seeds with endosperm
- It is also called ex-albuminous seeds
- Ex-Pea, Ground nut, bean
Non-Endospermous seeds :
- Seeds without endosperm
- It is also called albuminous seeds
- Paddy, Coconut, Castor.
![]()
Question 8.
Comment on Aleurone Tissue.
Answer:
- These are layers of specialized cells around the endosperm, in cereals.
- They have sphaerosomes (Ex. Barley, Maize) During germination, they secrete hydrolytic enzymes amylase,
- protease. They digest reserve food of endosperm.
Question 9.
Mention the other interesting pollinating mechanism of plants?
Answer:
- Trap Mechanism Ex. Aristolochia.
- Pit fall mechanism Ex. Arum.
- Clip or Translator Mechanism
Ex. Asclepiadaceae - Piston Mechanism Ex. Papilionaceae.
Question 10.
Grafting is method of production of hybrid plants but not the method of reproduction. Do you agree this statement? Give logic reason for your answer.
Answer:
- Eventhough Grafting is considered as artifica! method of vegetative reproduction, it is realtv used to produce plants combining favourable stem characteristics with root characteristics.
- The stem of the plant to be grafted is known as scion and the root is called stock.
- Here, one fnbrid is produced unlike in other method where manv number of plants are produced.
Question 11.
Comment on pollen (nectar) robber?
Answer:
Amorphophallus provide floral rewards. They are the safe site for laying eggs, visitors consume pollen and nectar. They do not help in pollination. They are pollen robbers.
Question 12.
Describe pseudocopulations?
Answer:
- In Bee orchid (ophyrus) the morphology of flower is similar to female wasp (colpa).
- Male wasp mistakes the flower for female wasp, and try to copulate. This pseudocopulation helps in pollination.
- In pea cotyledons store food.
![]()
Question 13.
Write any two differences between male gametophyte and female gametophyte.
Anwer:
Male gametophyte :
- It is the pollen grain (microsporangium)
- It has two phases of growth – pro pollination and post pollination
- Pre pollination occurs in it.
- It is only 3 celled
- All cells of it are functional
Female gametophyte :
- it is t mbedded in side the ovum (megasporangium)
- All the cells are formed in single phase ol growth surrounded bv megaspore membrane.
- It is 7 celled and the growth occurs inside megasporangium
Question 14.
What are the disadvantages of self pollination?
Answer:
- Continuons self pollination produce weaker progeny
- Chance of producing new species and varieties are meagre.
Question 15.
Enlist the disadvantages of cross pollination?
Answer:
- The process is uncertain since it depends on external agencies.
- Various devices are needed to attract the pollinating agents.
Question 16.
Pollination is prerequisite for fertilisation. Discuss?
Answer:
- Fertilisation forms fruits and seeds.
- Pollination brings male and female gametes closer.
- Cross pollination produces variations, due to mixing of genes. Variations help the adaptation of plants to environment. It helps in specifiation.
Question 17.
How is the surface of endosperm ? Discuss?
Answer:
Endosperm with irregularity and uneven ness in its surface forms the ruminate endosperm. Ex. Areca catchu, Passiflora, Myristica.
Question 18.
Discuss the functions of Endosperm?
Answer:
- It is the nutritive tissue for the developing embryo.
- The zygote divides only after the develpment of endosperm.
- Endosperm regulates the embryo development.
Question 19.
Relate the role of cocount as endosperm?
Answer:
- Coconut milk is a nutrient medium.
- It induces the differentiation of embryo (embryoids), Plantlets of various plant tissues.
- Coconut water is free nuclear endosperm. The white kernel part is cellular.
IV. Five Marks
Question 1.
Illustrate the structure of cicer, a dicot seed?
Answer:
- Seeds are attached to fruits by funiculus.
- The scar of funiculus is called hilum.
- Micropyle is the small pore below hilum.
- O2 and water enters seed for germination through micropyle.
- Each seed has outer thick seed coat.seed coat develops from the integuments of ovule.
- Testa is the hard outer coat.
- Tegmen is the thin membranous inner coat.
- In pea testa, tegmen are fused.
- Two cotyledons are laterally attached to embryonic axis.
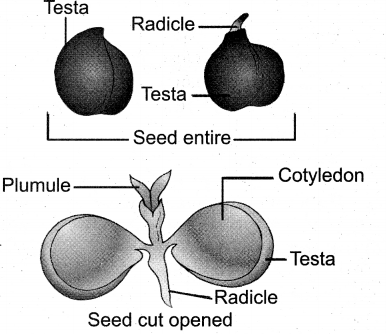
- In castor endosperm has reserve food.
- One end of embryonal axis projecting beyond the cotyledons. It is called radicle (embryonic root)
- The other end of embryonal axis called plumule (embryonic shoot)
- Embryonic axis above the cotyledons is epicotyl.
- Cylindrical region between the cotyledons is hypocotyl.
- Epicotyle terminates in plumule. Hypocotyl ends in radicle
Question 2.
Describe the structure of a monocot seed (Ex. Paddy)?
Answer:
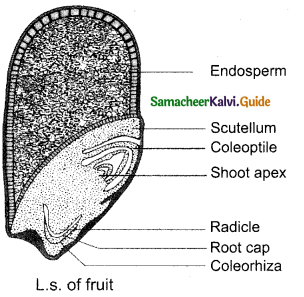
- Paddy is a one seeded caryopsis.
- The seed is enclosed by brown husk with 2 rows of glumes.
- The brown, membranous seed coat is attached to grain.
- Endosperm is the bulk of grain. It is the storage tissue.
- It is separated from embryo by epithelium.
- Embryo has one cotyledon called scutellum. It is later to embryonal axis.
- A short axis with plumule and radicle is protected by root ‘ cap.
- Coleoptile is a protective sheath of plumule.
- Coleorhiza is the protective sheath of radicle.
- Scutellum supplies food to embryo from endosperm through epithelium.
![]()
Question 3.
In some kinds of plant reproductions male, female gametes are not involved ? Justify? Apomixis.
Answer:
it is tile plant reproduction which does not involuo the union of male and female gametes.
A) Recurrent Apomixis.
Vegetative Reproduction and agamospernw.
B) Non recurrent Apomixis.
Alter meiosis, haploid embrvosoe is lormed.
It devleps into emhrvo without fertilization.
I) Vegetative Reproduction
Eiopagation of plants by parts other than seeds.
Ex. bulbil – I’riiiliaria imperialis.
Bulbs – Allium
Sucker – Chrysanthemum.
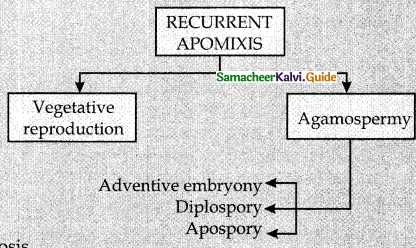
a) Agamospory
Embryos are rormed without syngamy and meiosis.
b) Advcntiver Embryony
Embrvo arises from diploid sporopln tic coll of nuceilus or integument, lt is called sporophytic budding, Gametophylic phase is completeh absent.
c) Diplospory (Generative apospory)
Megaspore mother ceils gives rise to diploid embrvosac without meiosis. ex. Eupatorium.
d.) Apospory
Nucellar cell develop into diploid emhryo sac. This is somatic apospory. Ex. Hieracium, parthenium.
![]()
Question 4.
Differentiate heterostyly from herkogamy
Answer:
Heterostyly :
- Some plants produce two or three different forms of flowers that are different in their length of stamens and style
- Pollination will take place only between organs of the same length. Distyly: Eg Primula Herkogamy:
Herkogamy
- Stamens and stigmas are arranged in such a way preventing self pollination.
- Stigmas project for above the stamens Eg: Hibiscus
Question 5.
An entire plant can be produced from a single cell – Justify?
Answer:
The genetic ability of a plant cell to produce entire plant in suitable condition is called Totipotency.
i) Tissue Culture
Growth of plant tissue in special cutture medium under suitable conditions is called tissue culture.
Ex. F.C steward of Cornell University developed a new carrot plant from the phloem parenchyma cell.
ii) Micropropagation
Regenerationof whole plant from a cell or tissue of vegetative structures.
- Advantages of Modern methods.
- Plants with desired characteristics are multiplied rapidly in short duration.
- Genetically identical plants are produced.
- Done at any season.
- Plants without viable seeds, difficult to germinate can be propagated.
- Rare, endangered plants are propagated.
- Meristem culture produces disease free plants.
- Cells are transformed by genetic modification.
Disadvantages of modem methods
- Labour intensive. It requires skilled workers.
- Maintenance of sterile condition increases cost.
- Genetically identical clones are susceptible to new diseases.
- Genetical changes in callus is not desirable for commercial use.
![]()
Question 6.
Elaborate an account on the T.S of anther.
Answer:
1. Anther Wall
a) Epidermis
- Protective single layer.
- Cells undergo anticlinal division to cope up enlarging internal tissue.
b) Endothecium
- Single layer of radially elongated cells.
- Bands of cellulose (or) lignin are seen in tangetial wall.
- At the junction of 2 sporangia these thickenings are absent. This region is called stomium.
- Hygroscopic nature of endothecium helps in dehiscence of anther.
c) Middle layer
- 2 to 3 layers next to endothecium.
- These are ephemeral. Disintegrate or crushed during maturity.
d) Tapetum
- It is dual in origin (from peripheral wall layer and connective tissue of anther lining.
- It nourishes sporogenous tissue, microspore mother cell, microspores.
- Cells are uninucleate, multinucleate with polyploid nucleus.
- It contributes to wall material, sporopollenin, pollen kitt, tryphine.
- It controls fertility or sterility of pollengrains. It is of 2 tvpes i) Secretory tapetum ii) Invasive tapetum
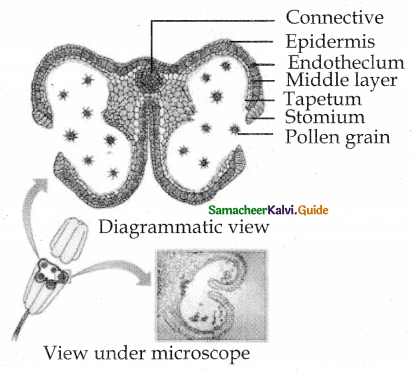
2. Anther cavity.
- It is filled with young microspores or mature pollengrains.
- Microspore mother cells form microspore by meiosis.
3) Connective.
- It is a colume of sterile tissue. It is surrounded by anther lobe. It has vascular tissue.
Question 7.
How does the male gametophyte develop?
Answer:
- Haploid microspore is the first cell.
- Development takes place at microsporangium.
- Microspore nucleus divides into vegetative and generative nucleus.
- Large vegetative cell and small generative cell is formed.
- At this 2 celled stage, pollens are liberated from anther.
- In some plants generative cell form 2 male gametes.
- Male gametophyte grows when the pollen reaches the right stigma.
- Pollen absorbs moisture and swells.
- Intine grows as pollen tube through germ pore.
- At the 2 celled stage, generative cells divides into 2 male cells at stigma.
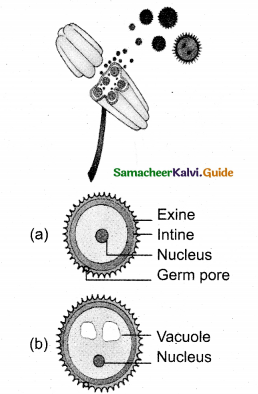
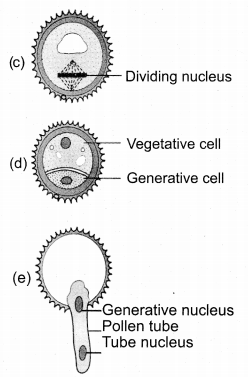
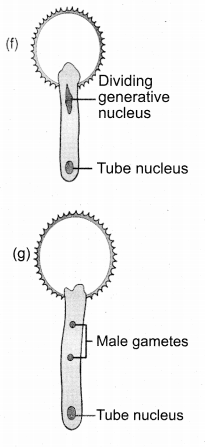
![]()
Question 8.
Ovules are of many types based on the orientation, form, position of micropyle with respect to funicle, chalaza – discuss?
Answer:
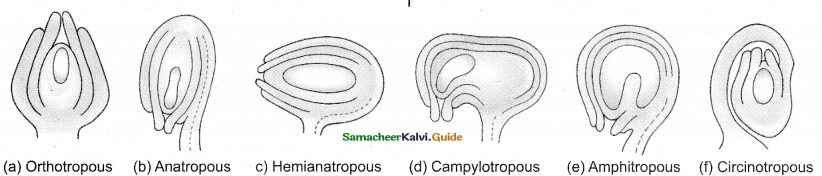
1. Orthotropous
- Micropyle is at distal end,
- Funicle and chalaza lie in one straight vertical line (Ex. Piperaceae)
2. Anatropous
- Body of ovule is inverted.
- Micropyle, funiculus lie close to each other Ex. Dicots, Monocots.
3. Hemianatropous
- Body is transverse
- It is at right angle to funicle. Ex. Primulaceae.
4. Campylotropous
- Body is curved at micropylar end. Embroysac is curved.
- Hilum, micropyle and chalaza are nearer. Ex.Leguminosae
5. Amphitropous
Less distance between hilum and chalaza. Nucellus is horse shoe shaped. Ex. Alismataceae.
6. Circinotropous. (Ex. Cactaceae)
Long funicle surrounds the ovule.
![]()
Question 9.
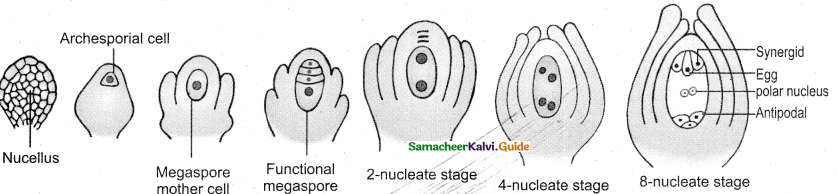
How does the monosporic embryosac develop?
Answer:
- Functional megaspore is the first cell of embryosac or female gametophyte.
- Megaspore elongates along micropylar – chalaza! axis.
- Nucleus undergoes mitosis without wall formation.
- A central vacuole expands and pushed the nuclei towards the opposite poles.
- Each nucleus divide mitotically twice. Thus 4 nuclei are formed at each pole.
- Eight nuclei are in common cytoplasm.
- Of the 4 nuclei at micropylar end, 3 nuclei form 3 antipodal cells. Fourth one is the lower polar nucleus.
- Two polar nuclei fuse into secondary nucleus.
- Thus 7 celled, 8 nucleated embrovsac is formed.
Question 10.
Enlist the contrivances for crosspollination ?
Answer:
1) Dicliny or Unisexuality. ’
In unisexual flowers, only cross pollination is possible,
i) Monoecious (Ex. coconut)
- Male and female flowers on same plant
- Autogany is prevent in castor, maize. Geitonogamy takes place.
Dioecious.
- Male and female flowers are on different plants.
- Both autogamy, geitonogamy are prevented.
2) Monocliny or Bisexuality.
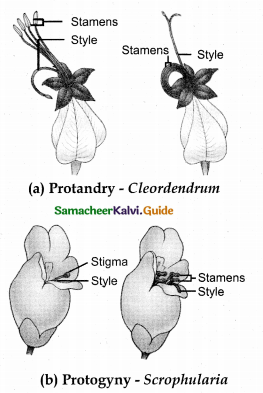
i) Dichogamy.
Anther and stigma mature at different times.
- Protandry (Ex. Helianthus)
Stamens mature earlier than stigma - Protogymy (Ex. Aristolochia)
Stigmas mature earlier than stamen.
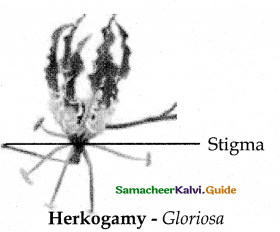
ii) Herkogamy.
Arrangement of stamen, stigma are different. Thus self pollination is prevented.
Ex . Hibiscus – Stigma project above stamen.
iii) Heterostyly,
Flowers differ in the length of stamen and style.
Pollination takes place between organs of the same length.
a) Distyly.
Pin flowers have long style. Thrum eyed flowers have long stamens. This same height helps in pollination.
Pin flowers have short stamens. Thrum eyed flowers have short style.
This helps in pollination.
b) Tristyly (Ex. Lythrum)
Plant produces 3 kinds of flowers with respect to length of style and stamens.
iv) Self sterility / Self incompatibility. Pollengrain of one flower is unable to germinate in the stigma of the same.
Ex. Passiflora
Question 11.
Enlist the characteristics of Anemophilous
Answer:
- Flowers in pendulous, catkin like, spike inflorescence.
- Inflorescence axis elongates. So, flowers are brought above leaf level.
- Reduced perianth (or) Absent.
- Small, colourless flowers do not / secrete nectar. The are not scented
- Long, exerted, versatile filaments.
- Enormous quantitv of pollen grains.
- Minute, light, dry pollen easily cart ied by wind to long distances.
- Violent bursting of anthers release the pollengrains. Ex. Urlica.
- Protruding, feathery, branched stigma catch pollengrains.
- Flowers are produced before leaves. So, they are carried without hindrance.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain pollination in maize?
Answer:
- Maize is monoecious and unisexual.
- Male inflorescence is at the terminal.
- Female inflorescence is at the lateral lower level.
- Heavy pollens cannot be carried by breeze.
- Male inflorescence is shaken by wind. The released pollens fall vertically below
- Male inflorescence (Tassel) Female inflorescence (Cob)
- The long stigma (23 cm) projects beyond the leaves.
- Pollens dropping from tassel is caught by the stigma.
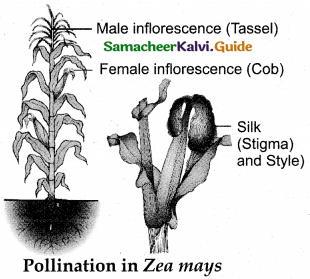
Question 13.
What do you know about the lever mechanism of pollination? Explain?
Answer:
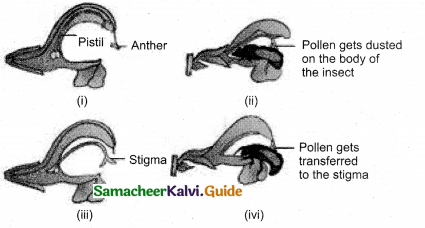
- Salvia is adapted for bee pollination.
- Bilabiate corolla has 2 stamens.
- Each anther has upper fertile lobe and lower sterile lobe separated by long connective. The anthers swing freely.
- The bee strikes against the sterile end of connective. So, fertile part of stamen descend. It strikes at the back of the bee.
- When the bee visits another flower, the pollen is rubbed on stigma. Thus pollination is
Question 14.
Describe the development of Dicot embryo?
Answer:
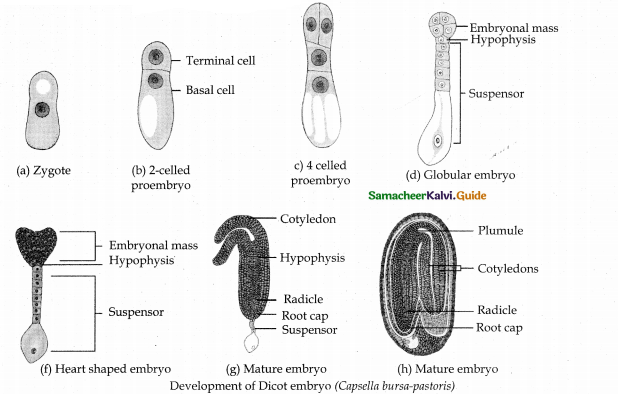
- The embryo develops at micropylar end of embryo sac.
- The zygote undergoes transverse division.
- An upper terminal cell and lower basal cell is formed.
- Divisions in zygote during development lead to the formation of embryo.
- Before mature stage, embryo undergoes globular, heart shaped stages.
- Mature embryo has a radicle, 2 cotyledons and a plumule.
![]()
Question 15.
Summarise the whole life cycle of an Angiosperm plant in the form of schematics diagram.
Answer:
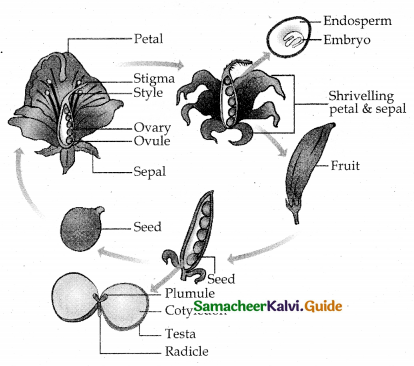
Question 16.
Explain epihy drophily with an example?
Answer:
Pollination occurs at water level Pollination in vallisneria.
- It is submerged rooted hydrophyte.
- At the time of pollination, the flowers come to water level by long coiled stalk.
- Cup shaped depression is formed in female flower.
- The detached male flower floats on water surface.
- Male flower gets settled on the depression of female flower. It contacts stigma and bring out pollination.
- Stalk of female flower coils. Thus the flower comes under water from surface. Then fruits are produced.
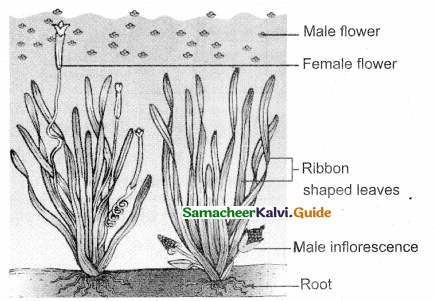
Question 17.
Enlist the advantages, disadvantages of conventional methods of vegetative propagation?
Answer:
Advantages of conventional Methods.
- Plants are genetically uniform.
- Plants are produced quickly.
- For plants with little or no seeds (or) when seeds do not germinate.
- Economical vegetative propagation. Ex. Solanum tuberosum,
- Plants with desirable characters like disease resistance, high yield can be grafted.
Disadvantages.
- Virus infected plants produce virus infected new plants.
- Bulky vegetative structures are difficult to handle.
![]()
Question 18.
Differentiate biosporic megaspore development from tetrasporic development.
Answer:
Biosporic megaspore :
- of the four megaspores if two are involved in Embryo Sac formation the development is called bisporic.
- Example: Allium
Tetrasporic megaspore
- If all the four megaspores are involved in Embryo Sac formation the . development is. called tetrasporic.
- Example: peperomia