Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th English Model Question Paper 1 Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th English Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 11th English Model Question Paper 1
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3:00 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
PART – I
I. Answer all the questions. [20 × 1 = 20]
Choose the correct synonym for the underlined words from the options given.
Question 1.
A peaceful pallor spread on his face.
(a) paleness
(b) rosiness
(c) ruddy
(d) rejuvenation
Answer:
(a) paleness
Question 2.
It was indeed a sensational bid.
(a) astounded
(b) ordinary
(c) sensitive
(d) exciting
Answer:
(a) astounded
![]()
Question 3.
I had a sumptuous meal to sate my hunger.
(a) sadden
(b) suppress
(c) satisfy
(d) struggle
Answer:
(c) satisfy
Choose the correct antonym for the underlined words from the options given.
Question 4.
The vessels dropped and scattered all over.
(a) speckled
(b) sprinkled
(c) gathered
(d) grew
Answer:
(c) gathered
Question 5.
There a curious smothering noise from my friend.
(a) suppressed
(b) expressed
(c) smoothened
(d) suffocated
Answer:
(b) expressed
Question 6.
Her face was wrinkled and weird.
(a) smooth
(b) creased
(c) lined
(d) crippled
Answer:
(a) smooth
Question 7.
Choose the clipped form of “percolate”.
(a) perk
(b) per
(c) perc
(d) colate
Answer:
(a) perk
Question 8.
Choose the right definition for the given term “plagiarist”.
(a) A student of bees
(b) One who accumulates; one who collects
(c) One who purloins the words, writings, or ideas of another, and passes them off as his own; a literary thief
(d) One who is tenacious of a strict adherence to official formalities
Answer:
(c) One who purloins the words, writings, or ideas of another, and passes them off as his own; a literary thief
Question 9.
Choose the meaning of the idiom ‘Beat around the bush’.
(a) Indirectly talking about an issue
(b) Do or say something exactly right
(c) To go to bed
(d) Without any hesitation; instantly
Answer:
(a) Indirectly talking about an issue
Question 10.
Choose the meaning of the foreign word in the sentence.
I’d like to learn taekwondo though it might not be the best option for me.
(a) Japanese language
(b) Chinese preparation
(c) Floor dancing
(d) Kick fist martial art
Answer:
(d) Kick fist martial art
![]()
Question 11.
Choose the word from the options given to form a compound word with “goat”.
(a) male
(b) female
(c) scape
(d) major
Answer:
(c) scape
Question 12.
Form a new word by adding a suitable suffix to the root word, “hero”?
(a) ity
(b) ism
(c) ness
(d) ish
Answer:
(b) ism
Question 13.
Choose the expanded form of “NSC”.
(a) National Savings Certificate
(b) National Service Certificate
(c) National Savings Career
(d) National Service Certificate
Answer:
(a) National Savings Certificate
Question 14.
The correct syllabification of the word “psychology” is…………..
(a) psych-ol-ogy
(b) psy-chol-ogy
(c) ps-ycho-logy
(d) psy-chol-o-gy
Answer:
(d) psy-chol-o-gy
Question 15.
A craze for establishing banks is known as …………..
(a) Etymology
(b) Stampomania
(c) Eulogomania
(d) bancomania
Answer:
(d) bancomania
Question 16.
Fill in the blank with the suitable preposition.
Ramesh went……….. Tom’s place to settle the bills.
(a) to
(b) on
(c) in
(d) from
Answer:
(a) to
Question 17.
Add a suitable question tag to the following statement.
He never fails in his duty,………..?
(a) isn’t he
(b) won’t-he
(c) will he
(d) does he
Answer:
(d) does he
Question 18.
Substitute the underlined word with the appropriate polite alternative.
Sagar’s cat had to be killed because it had cancer.
(a) put in
(b) put down
(c) put up
(d) put out
Answer:
(b) put down
![]()
Question 19.
Substitute the phrasal verb in the sentence with a single word.
However hard she tried, she could not figure out the meaning of the proverb.
(a) appreciate
(b) condemn
(c) understand
(d) faint
Answer:
(c) understand
Question 20.
Fill in the blank with a suitable relative pronoun
The children ……… shouted in the street are not from our school.
(a) which
(b) whose
(c) who
(d) that
Answer:
(c) who
PART – II
II. Answer any seven of the following: [7 × 2 = 14]
(i) Read the following sets of poetic lines and answer any four of the following. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 21.
“I have learned to wear many faces like dresses”
(а) State the figure of speech in the above line.
(b) Who does the term ‘I’ refer to?
Answer:
(a) Simile
(b) 1 refers to the poet, Gabriel Okara.
Question 22.
“ When swollen eye meets gnarled fist
When snaps the knee, and cracks the wrist”
(a) What is the figure of speech employed in the second line.
(b) Why are the eyes swollen?
Answer:
(a) Onomatopoeia
(b) The eyes are swollen as they were injured by the opponent.
Question 23.
“Or the greenhouse glass is broken, and the trellis past repair
Ay, there’s the wonder of the thing! Macavity’s not there!”
(a) What is a greenhouse and a trellis?
(b) What is a wonder after the greenhouse glass is broken?
Answer:
(a) Greenhouse is a glass building in which plants that need protection from cold weather are grown. Trellis is a framework of light wooden or metal bars used as a support for fruit trees or creeper.
(b) Macavity is to be found nowhere when one finds out that the greenhouse glass is broken.
Question 24.
“Let’s talk of graves, of worms, and epitaphs,
Make dust our paper, and with rainy eyes
Write sorrow on the bosom of the earth.”
(a) What do you understand by rainy eyes?
(b) Identify the figure of speech in the first line.
Answer:
(a) Eyes shedding tears is said to be rainy eyes.
(b) Metaphor
![]()
Question 25.
“And I must think, do all I can,
That there was pleasure there…”
(a) What did the poet notice about the twigs?
(b) What was the poet’s thought about then?
Answer:
(a) The budding twigs spread out their fan to catch the breezy air.
(b) The poet thought the twigs were experiencing the j oy of their contact with the breezy air.
Question 26.
“The height you reach is not that we care;”
(a) How different is the poet’s perception of success?
(b) How does the poet use the word ‘height’?
Answer:
(a) Those who reach great heights in terms of scholarship, wealth and positions are not deemed great. Those who have competence and merit alone are respected.
(b) In terms of mountain climbing, climbing Everest is said to be the highest achievement.
But even scaling a small hillock is an achievement. Every human effort to succeed needs to be appreciated.
(ii) Do as directed (any three) [3 × 2 = 6]
Question 27.
Rewrite the following dialogue in reported form.
Kiran : Will you exchange the defective torch I had bought from you yesterday?
Shopkeeper : Do you have the receipt with you?
Answer:
Kiran asked the shopkeeper if he would exchange the defective torch he had bought from him the day before. The shopkeeper enquired if Kiran had the receipt with him.
Question 28.
Rewrite the following sentence in its passive form.
She had already cooked the food.
Answer:
The food had already been cooked by her.
Question 29.
Convert the following complex sentence to a compound sentence.
I called for Arjun who came at once.
Answer:
I called for Aijun and he came at once.
Question 30.
Hurry up. You will miss the flight. (Combine using ‘Unless’)
Answer:
Unless you hurry up, you will miss the flight.
PART – III
III. Answer any seven of the following: [7 × 3 = 21]
(i) Explain any two of the following with Reference to the Context: [2 × 3 = 6]
Question 31.
“Have I not reason to lament What Man has made of Man?”
Answer:
Reference: These lines are from the poem “Lines Written in Early Spring” written by William Wordsworth.
Context: Amidst happy nature, William Wordsworth couldn’t help feeling sad. At that occasion, he said these words.
Explanation: The mixed feelings of happiness and sadness is well brought out in these lines. He was inspired by a small woodland grove, a landscape of beauty. He came upon this spot when walking near Alford village. While sensing the blissful mood and happiness of birds, plants, creepers and the murmuring brook, he juxtaposed what humans did to their kind in Napoleonic wars.
![]()
Question 32.
“I am just glad as glad can he
That I am not them, that they are not me. ”
Answer:
Reference: The poet Ogden Nash says these words in the poem “Confession of a Bom Spectator’.
Context: While discussing about the athletes he admires, the poet says these words.
Explanation: The poet was a bom spectator. Right from his boyhood, he had seen boys aspire for sports championships. He had wondered at their ability to specialize in horse riding, to play hockey or basketball. He had seen young ones trying to play center in the football or be a tackle or offender in a game like kabaddi. But he has been absolutely glad that he is not them and they are not him.
Question 33.
We deem it our duty and mission in life,
To bless and praise the deserving ones
Answer:
Reference: These lines are from the poem “Everest is not the Only Peak” written by Kulothungan.
Context: The poet says these words highlighting the virtues of unsung heroes.
Explanation: The unsung heroes adhere to their ethical principles in life. Even if they have not reached great heights. They consider it their duty and mission to identify deserving people with natural talents and appreciate them.
(ii) Answer any two of the following questions briefly: [2 × 3 = 6]
Question 34.
Why was the author left with his grandmother in the village?
Answer:
The author was left with his grandmother in the village because his parents had to go to the city for work.
Question 35.
What difficulty did Mary Kom experience while eating Chinese preparation?
Answer:
Once Mary Kom and her team mates were given chopsticks to eat their food in China. Other friends, asked for spoons and managed. But Mary Kom ended up using both her hands to hold the chopsticks to pick up the food and push it into her mouth. She managed the complex work and satisfied her hunger.
Question 36.
What were the contents of Bryson’s bag?
Answer:
The contents of the bag were frequent flyer card, newspaper cuttings, loose papers, tobacco pipe, magazines, passport, English money and film.
(iii) Answer any three of the following: [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 37.
Re-arrange the shuffled words and frame into meaningful sentences, (change to pie chart/graph or table)
- pillars/there/human life/man/of/woman/and/are/two
- uppermost/soil layer/is/earth/the/of/the
- it/palnts/which/supports/food/provide/all/living things/to/planet/on/this
Answer:
- There are two pillars of human life – man and woman.
- Soil is the uppermost layer of the earth.
- It supports plants which provide food to all living things on this planet.
Question 38.
Describe the process of pitching a tent.
Answer:
- Select a location free of debris and an area that is as level as possible for your camp site. Lay down your footprint or ground cloth.
- Position the tent over the footprint with the doors facing away from the wind for the best ventilation.
- Lay out the poles and assemble them.
- Insert the tent poles and secure it to take up the tension in the poles.
- Pull the tent upright.
![]()
Question 39.
Expand the following news headlines:
- Scientists Develop Synthetic Cornea.
- World Leaders Meet at Geneva.
- ATMs Without Security Guards to Close.
Answer:
- A newly developed implant made of plastic may soon offer patients the chance to see again as Scientists from Germany have developed synthetic corneas.
- German Chancellor Angela Merkel and US President Donald Trump will converge upon the snowy Swiss town of Davos this week for the World Economic Forum’s Annual Meeting.
- The Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi has requested all ATM’S without proper security to be closed down.
Question 40.
Complete the proverbs choosing the suitable words given in brackets.
- A stitch in ………. saves nine, (tear, time, line)
- A thing begun is ……….. done, (half, full, not)
- Beauty is in the ………… of the beholder, (imagination, mind, eye)
Answer:
- time
- half
- eye
PART – IV
IV. Answer the following: [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41.
Describe Mary Kom’s personal experiences during her first International Championship match from the time of selection to winning the medal.
Answer:
Mary Kom flew to Pennsylvania, USA to compete under 48 kg World Women’s Boxing Championship in 2001. On landing, she rushed to the sports arena and weighed. She was lucky as she could rest enough to face her opponent the following day. As soon as she won her opponent in the first match, she gained enormous confidence. Her fear of facing new opponents in the ring vanished completely. While her team-mates went on losing one after another, she went on to reach the finals.
She was even hopeful of winning gold. She had defeated Nadia Hokmi of Poland by RSC. She also defeated Jamie Behai of Canada by 21-9. The greatest disadvantage just before finals was that she lost her appetite. She was not accustomed to American food. However hard she tried, she could not eat. She lost her weight. She was just 46 kg before the finals. This cost her, her long cherished dream of gold medal and she lost to Hula Sahin of Turkey 13-5. She won her silver but was very sad. But the biggest thing she took home from Pennsylvania was not the medal but the conviction that she could take on any boxer in the world.
[OR]
Trace the thoughts that went on in the mind of the narrator when picture after picture was put up and sold at the auction.
Answer:
The author was enthusiastically participating in the bid at Christie with very little money on him. He sailed smooth for a long time raising the stakes on many paintings and carefully staying behind other competitors. It was fun watching till he got trapped in a net, set by his own tongue. When one particular painting was offered for 4000 guineas, the bidders maintained an uncomfortable silence when the author heard himself foolishly saying “and fifty”. The auctioneer banged the hammer finalizing the deal in the narrator’s favour.
It was then the narrator realized with alarm that he had no money on him. Suddenly he lost interest in fun- bidding. He started thinking fast for a way out of the tight comer he had created for himself. Many small and big paintings were offered and sold out fast. The Barbizon pictures were selling fast like hot cakes for 2000 to 3000 guineas. The author was running over the names of friends, relatives and even money lenders who might bail him out of the tight comer. He even speculated on the possibility of confessing his poverty to the staff of Christie and request them to put up the picture again for sale. Such a genuine mistake could have been rectified at the early stages of auction.
As he had enthusiastically participated in the bid for many paintings, the auctioneers wouldn’t buy his justification for the “genuine mistake”. As bidders stood in a queue to hand in their cheques/cash to collect their paintings, the narrator stood deliberately at the end. He never felt such a fool or had colder feet all his life.
![]()
Question 42.
According to the poet what contributes most to the injuries sustained by the athletes?
Answer:
According to the poet, zealous athletes play so rough that they do not even consider one another’s feelings in their dealings with other players. The players are mostly goaded by prize money or glory from the media’s light on them. They maim each other as they romp. Cracking vertebrae and spines don’t stop the rough players. Most of the players don’t have sportsmanship.
They don’t treat success and failure equally. In order to get the light of fame on their face, they are ready to permanently disable a rival player too. The crazy desire for championship titles and the light of fame on them leads them to ignore swollen eyes, snapping of knee joints or cracking of wrists. In short, the poet believes the apathy of zealous players and obvious indifference to the pain and debilitating injury contribute most to the injuries sustained by athletes.
[OR]
Explain how ‘Lines Written in Early Spring’ stresses the fact that Nature is meant for Man’s joy and pleasure to be preserved by Man.
Answer:
Nature’s holy plan is to offer joy and peace to all forms of life on earth. He firmly believes that man is meant to spend his days blissfully taking part in the vitality and joy surrounding him. The poet believes that the harmonious, peaceful and happy co-existence of birds, plants, trees and brooks soothes the troubled mind of man. But he remembered the depravity of man which was evident in Napoleonic wars. He was fed up with man’s capacity to destroy innocent lives and property.
The poet is unhappy with unnatural aspects of industrial revolution, the misery caused by wars, greedy and aggressive behaviour causing suffering in humans. Man has lost his sensitivity to listen to the joyful lessons of nature and has gone to the extent of denuding the forest which really sustains life on earth. The poet stands to reason that nature functions on God’s plan but the man changes the holy plan wrecking the natural joy of human life.
Question 43.
Write an essay of about 150 words by developing the following hints.
C.V. Burgess-master craftsman-reveals-few names-first patient Joe-wife Emily- surgical room-Emily apprehensive-two children-Dorothea-Dentist hospital becomes play area-snobbish woman-whole play resolves-dramatic irony of patients’ guess- the dentists’ room -opening the tool cabinet-The groaning noise-vexation of Emily- Joe add to the dramatic irony-nurse moves about-feigned seriousness-the fact of the misplacement of key-which adds comic.
Answer:
C.V. Burgess is a master craftsman who reveals only a’few names. The first patient Joe and his wife Emily are the most dominant characters. Joe is inside the surgical room. Emily is anxious about the husband. Among the two children the dramatist uses only the girl’s name Dorothea and the Dentist hospital becomes a play area for Dorothea and the little boy who claim the same magazine for reading. The snobbish woman who goes on showing her photo album gives us an impression if she came to see the doctor or to show her photos. The whole play revolves around the dramatic irony of patients’ guess as to what happened inside the dentists’ room and what really happened.
The pliers, hack saw and the huge hammer were taken inside the dentist’s room only for opening the tool cabinet. But the patients wondered how these would’be used in dental surgery. The groaning noise from inside the dentist’s rooms and the vexation of Emily Joe add to the fear of the patients waiting. A few women patients leave the waiting room scared of subjecting themselves to the torture of having their bad teeth extracted with carpentry tools. The nurse moves about with all feigned seriousness without disclosing the fact of the misplacement of key.
![]()
[OR]
Narrator – wants – photograph – photographer wait for an hour – comments – angry – called on Saturday – proof – Narrator shocked – photograph – not like him – worthless bauble.
Answer:
‘With the Photographer’ by Stephen Leacock is narrated in the first person. The narrator while sitting in the photographer’s studio begins, to read some magazines and sees how other people look and the narrator begins to feel insecure about his appearance. It is also noticeable that the photographer takes a dislike to his face judging it to be wrong.
What should have been a simple process of taking a photograph becomes something of a nightmare for the narrator. How confident the narrator becomes is noticeable when he returns to the photographer’s studio the following Saturday. He realises that the photograph that has been taken of him looks nothing like him. This angers the narrator as he was simply looking for a photograph that would show his likeness. He accepts that he may not be to everybody’s liking when it comes to his physical appearance but is angered by the changes made. The photographer has retouched the photograph so much that the narrator does not recognise himself.
The end of the story is also interesting as the reader realises that it is just a worthless bauble when he begins to cry. He has been judged solely by his appearance by the photographer whose job was to simply take a life like photograph.
Question 44.
Write a summary or Make notes of the following passage.
Goa is a vibrant, living entity and more than just a geographical sunspot on the western coast of India. Famous for its silver sands and mesmeric sunsets, its recorded history datesback to the 3rd century B.C. It is blessed with marvelous weather, fabulous beaches, picturesque hill-top forts, gracious people and awe inspiring cathedrals. Arombol, 50 km north of Panaji, is a unique beach, which is both rocky and sandy.
It was a sweet water pond right near the seashore that’s very pleasant to bask in. Goa not only has almost 120 km long silver beaches but also offers long, wide and picturesque rivers and scenic lakes. Aqua sports hold great attraction for tourists to Goa. Some of the most popular aqua sports are swift rides on water scooters and speedboats at the Bay of Doha Paula. The best time to visit Goa, the ideal Serene Beach Resort is during the relatively cool winter months between late September and mid-March.
Answer:
Summary
No. of words given in the original passage: 160
No. of words to be written in the summary: 160/3 = 51 ± 5
Rough Draft
Goa is in the western coast of India. It is famous for silver sands, sunsets, weather, beaches, forts, gracious people and eathedrals. Arombol is a rocky and sandy beach with a small water pond with sweet water. Aqua sports like swift rides on water scooters and speedboats are available at the Bay of Dona Paula. It is good to visit Goa between late September and mid March.
Fair Draft
Goa
Goa is in the western coast of India. It is famous for silver sands, sunsets, weather, beaches, forts, gracious people and cathedrals. Arombol is a rocky and sandy beach with a small water pond with sweet water. Aqua sports like swift rides on water scooters and speedboats are available at the Bay of Dona Paula. It is good to visit Goa between late September and mid March.
No. of words in the summary: 67
![]()
[OR]
Note-making
Title: Goa
Answer:
Location:
western coast of India
Tourist attraction:
silver sands, sunsets, weather, beaches, forts, gracious people and cathedrals Arombol beach – sweet water pond Aqua sports held at at the Bay of Dona Paula
Best time to visit:
between late September and mid-March
Question 45.
Read the following advertisement and respond to it with a resume/bio-data/CV considering yourself fulfilling the conditions specified:
[Write XXXX for your name and YYYY for your address]
Wanted:
Applications are invited for the post of a Typist in a reputed school of Madurai. The . candidate must have at least 5 years of experience. The applicant must have a pleasant personality. He/she should be good in English. Attractive salary. Interested candidates should apply to The Principal, AKS International, Indirapuram, Madurai within 10 days with detailed resume.
14th January, 2020
From
Savitha
2, Gandhi street
Madurai
To
The Correspondent
AKS International School
Indirapuram
Madurai
Respected Sir/Madam,
Sub: Application for the post of a Typist
With reference to your advertisement dated 8th January 2019,1 hereby wish to apply for the post of a typist. I have rich experience and can communicate well with a pleasing personality. If given an opportunity, I will satisfy my superiors to the best of my ability.
Please find enclosed my resume for your kind perusal.
Yours sincerely,
Savitha
Address on the Envelope To
The Correspondent
AKS International School
Indirapuram
Madurai
Resume:
Name : Savitha Rajeev
Date Of Birth : 8th May, 1991
Marital Status : Married
Husband’s Name : Mr. Rajeev
Address For Communication : Yyy
Contact Number – Mobile: 9988776655
Residence : 22445566
Mother Tongue : Tamil
Language Known : English and Tamil
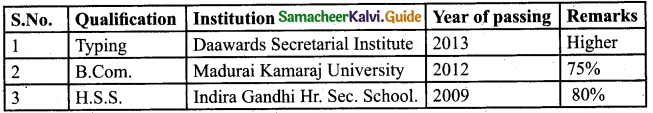
Educational Background:
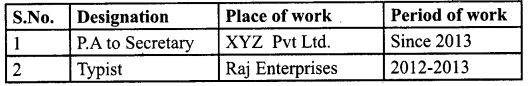
Professional Experience:
Hobbies : Photograph, Gardening, Reading, Travelling.
Expected Salary : 27,000/ per month
Salary Drawn : 23,000/ per month
Reference : 1. Mr. Ravi (Manager -no. 9998887777
2. Mrs. Rani (Manager-Raj Enterprises) 9900000222
Declaration
I hereby declare that the above given information is true to my knowledge.
Station: YYY
Date. 14.01.2020
Savitha
Signature of the Applicant
![]()
[OR]
Write an essay in about 150 words on ‘Convincing the public not to discriminate against those with AIDS’.
Answer:
Abolish discrimination against those with AIDS
People living with HIV infection and AIDS should have the same basic rights and responsibilities as those which apply to all citizens of the country. They have the same rights to liberty and autonomy, security of the person and to freedom of movement as the rest of the population. No restrictions should be placed on the free movement of HIV-infected people, and they may not be segregated, isolated or quarantined in prisons, schools, hospitals or elsewhere merely because of their HIV-positive status.
Only a sexual relationship without proper precautions will be a risk factor. Therefore they should be accepted whole heartedly without any discrimination. People with HIV infection or AIDS are entitled to the right to make their own decisions about any matter that affects marriage and child-bearing – although counselling about the consequences of their decisions should be provided. Due to the fear of isolation, ignorance, denial, and discrimination, people will allow HIV to develop into AIDS, further decreasing life expectancy, since the body’s immune system function will have been significantly lowered.
Along with family bonds and intimate relationships, a spiritual relationship is also strained. Fear and vulnerability included fear of punishment from God, fear of being discovered as HIV/ AIDS-positive and fear of the future and death. They should be given the love, warmth, psycho-social and emotional support.
Question 46.
Read the following sentences, spot the errors and rewrite the sentences correctly.
(a) People of diverse cultures lives in India.
(b) There is many people who exhibit unity on diversity.
(c) Water is needed to irrigating the fields.
(d) We live in times when incomes is rising.
(e) The opening ceremony for the 2016 Summer Olympic Games took place in Maracan stadium.
Answer:
(a) People of diverse cultures lives in India.
(b) There are many people who exhibit unity on diversity.
(c) Water is needed to irrigate the fields.
(d) We live in times when incomes are rising.
(e) The opening ceremony of the 2016 Summer Olympic Games took place in Maracana stadium.
![]()
[OR]
Fill in the blanks appropriately.
(a) They could ……….. untie the ………. (knot / not)
(.b) The world ………….. avoid war in the larger interest of human race. (Fill in with a modal verb)
(c) Every student …………. respect the national symbols, (use semi-modal)
(d) ……….. you have the hall ticket you can enter the examination hall. (Use a suitable link word).
Answer:
(a) not, knot
(b) should
(c) must
(d) If
Question 47.
Identify each of the following sentences with the fields given below.
(a) The flight was cancelled due to fog.
(b) Spicy food can cause acidity in the stomach.
(c) Meena stumbled upon a chance to practice running a race.
(d) The company has recommended a dividend of 75 percent.
(e) The monitor is not working. Get it repaired.
(Sports, Weather, Commerce, Nutrition and Dietetics, Computer)
Answer:
(a) Weather
(b) Nutrition and Dietetics
(c) Sports
(d) Commerce
(e) Computer
![]()
[OR]
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
For millions of people in India, river Ganga is the most sacred river. It is considered as mother and goddess. It is also a lifeline to millions of Indians who live along its course and depend on it for their daily needs. River Ganga is the third largest river in the world by the amount of water that flows through it. It is the longest river in India. The river water of Ganga is used for irrigation, transportation and fishing. The Gangetic plain formed by river Ganga is one of the most fertile lands on earth.
This is why almost 10% of the world population lives here and earns its livelihood. The Ganga, in India is the most worshipped body of water. The irony here is that in spite of being the most worshipped river, it is also the dirtiest one. It carries some metals thrown out by tanneries, waste produced by industries and urban waste from different cities. All this has made river Ganga the fifth most polluted river in the world. Another major reason that adds to the Ganga river pollution is the coal based power plants on its banks which burn tons of coal every year and produce tons of fly ash. This ash mixed with domestic waste water is released, in the river.
This bad situation calls for an urgent need to make efforts to reduce pollution and revive river Ganga. To achieve these objectives, Government of India has started a programme named “Namami Ganga Programme”. The main pillars of this programme are sewage treatment, river surface cleaning, afforestation, riverfront development and public awareness. The importance of the success of ‘Namami Gange Programme’ can be seen through the following lines; “If Ganga dies, India dies. If Ganga thrives, India thrives. No Ganga, No India.”
Questions.
- For whom is river Ganga a lifeline?
- For what purpose is the Ganga river water used?
- Most people in India consider the Gan^a as
- What are the pollutants that make the river dirty?
- Write any two pillars of the “Namami Gange”?
Answer:
- River Ganga is a lifeline for millions of Indians.
- The Ganga river water used for irrigation, transportation and fishing.
- Goddess
- Metals thrown out by tanneries, waste produced by industries and urban waste from different cities makes the river dirty.
- The pillars of this programme are sewage treatment, river surface cleaning, afforestation, riverfront development and public awareness.
![]()