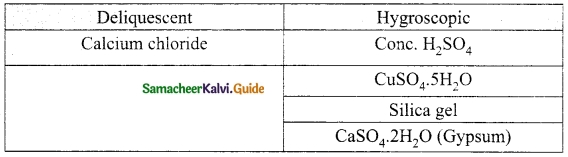
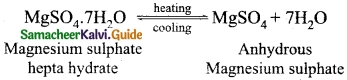
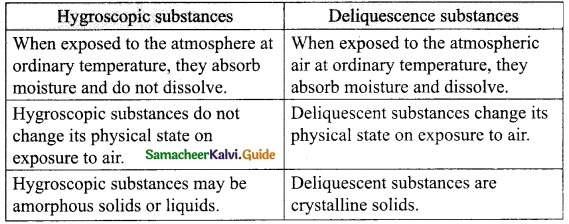
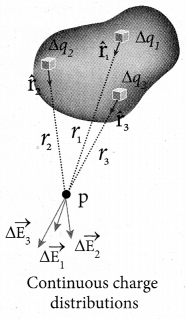
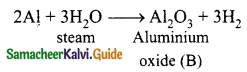
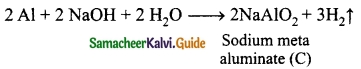
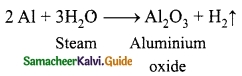
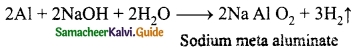
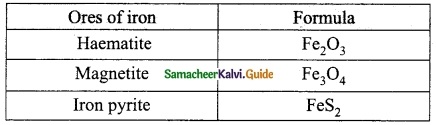
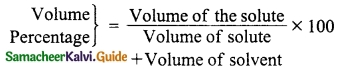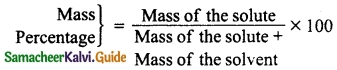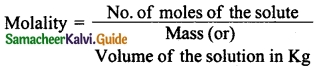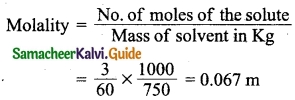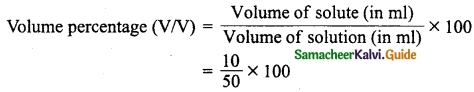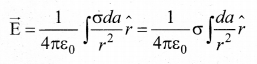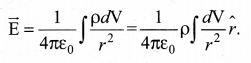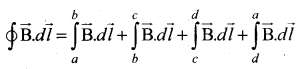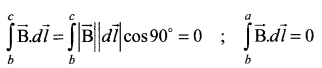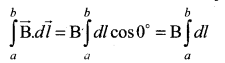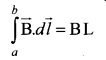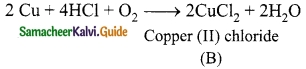Students can download 10th Science Chapter 14 Transportation in Plants and Circulation in Animals Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 14 Transportation in Plants and Circulation in Animals
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Transportation in Plants and Circulation in Animals Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
Active transport involves:
(a) movement of molecules from lower to higher concentration
(b) expenditure of energy
(c) it is an uphill task
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
Question 2.
Water which is absorbed by roots is transported to aerial parts of the plant through ______.
(a) cortex
(b) epidermis
(c) phloem
(d) xylem.
Answer:
(d) xylem.
Question 3.
During transpiration there is loss of:
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) oxygen
(c) water
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) water
![]()
Question 4.
Root hairs are ______.
(a) cortical cell
(b) projection of the epidermal cell
(c) unicellular
(d) both b and c.
Answer:
(b) projection of the epidermal cell
Question 5.
Which of the following process requires energy?
(a) active transport
(b) diffusion
(c) osmosis
(d) all of them
Answer:
(a) active transport
Question 6.
The wall of the human heart is made of ______.
(a) Endocardium
(b) Epicardium
(c) Myocardium
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question 7.
Which is the sequence of correct blood flow?
(a) ventricle – atrium – vein – arteries
(b) atrium – ventricle – veins – arteries
(c) atrium – ventricle – arteries – vein
(d) ventricles – vein – atrium – arteries
Answer:
(c) atrium – ventricle – arteries – vein
Question 8.
A patient with blood group O was injured in an accident and has blood loss. Which blood group the doctor should effectively use for transfusion in this condition?
(a) O group
(b) AB group
(c) A or B group
(d) all blood group.
Answer:
(d) all blood group.
Question 9.
‘Heart of heart’ is called:
(a) SA node
(b) AV node
(c) Purkinje fibres
(d) Bundle of His
Answer:
(a) SA node
Question 10.
Which one of the following regarding blood composition is correct?
(a) Plasma – Blood + Lymphocyte
(b) Serum – Blood + Fibrinogen
(c) Lymph – Plasma + RBC + WBC
(d) Blood – Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets.
Answer:
(d) Blood – Plasma + RBC+ WBG + Platelets.
II. Fill in the blanks:
- ……….. involves evaporative loss of water from aerial parts.
- Water enters the root cell through a ………. plasma membrane.
- Structures in roots that help to absorb water are …………
- Normal blood pressure is …………
- The normal human heartbeat rate is about ……….. time per minute.
Answer:
- Transpiration
- Semipermeable
- Root hairs
- 120 mm / 80 mm Hg
- 72 – 75 times
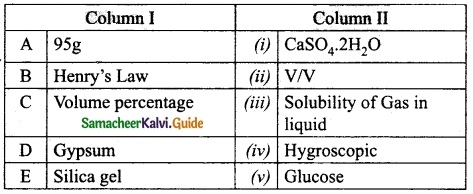
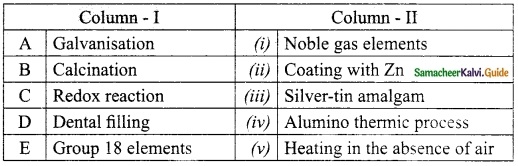
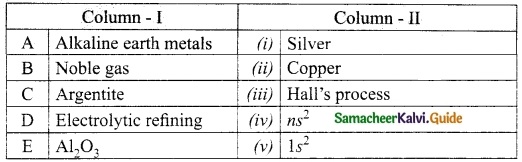
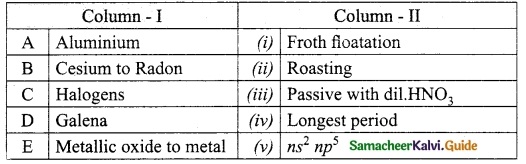
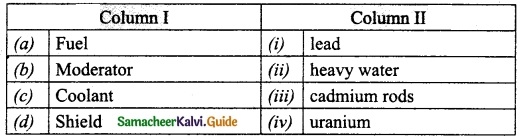
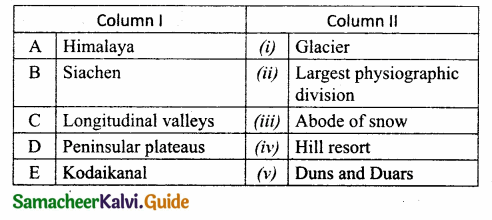
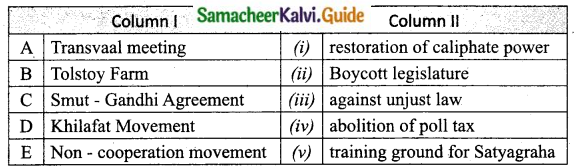
III. Match the following:
Section – I
Answer:
A. (ii)
B. (i)
C. (iv)
D. (iii)
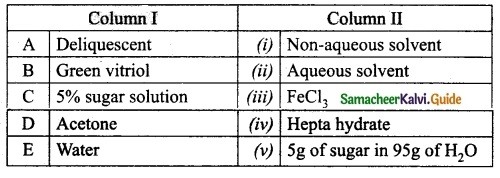
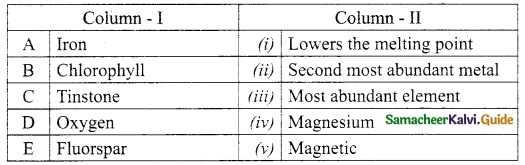
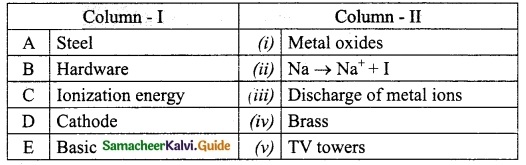
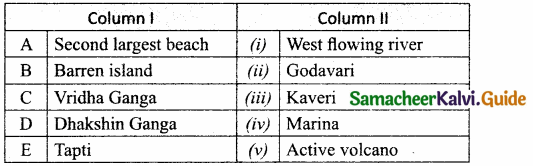
Section – II
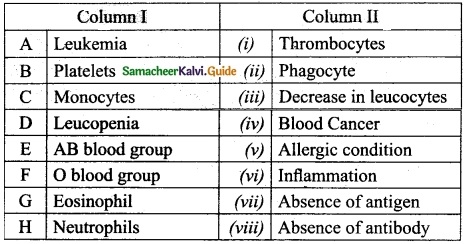
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (i)
C. (ii)
D. (iii)
E. (viii)
F. (vii)
G. (v)
H. (vi)
![]()
IV. State whether True or False. If false write the correct statement:
- The phloem is responsible for the translocation of food.
- Plants lose water by the process of transpiration.
- The form of sugar transported through the phloem is glucose.
- In apoplastic movement the water travels through the cell membrane and enter the cell.
- When the guard cells lose water the stoma opens.
- Initiation and stimulation of heart beat take place by nerves.
- All veins carry deoxygenated blood.
- WBC defend the body from bacterial and viral infections.
- The closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves at the start of the ventricular systole produces the first sound ‘LUBB’.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False – The form of sugar transported through the phloem is sucrose.
- False – Apoplastic movement does not involve crossing the cell membrane.
- False – When the guard cells lose water the stoma closes.
- False – Initiation and stimulation of heart beat take place by Sino-atrial node.
- False – All veins carry deoxygenated blood except the pulmonary veins,
- True
- True.
V. Answer in a word or sentence:
Question 1.
Name two layered protective covering of human heart.
Answer:
Pericardium is the two layered protective covering of human heart.
Question 2.
What is the shape of RBC in human blood?
Answer:
The shape of RBC in human blood is biconcave and disc – shaped.
Question 3.
Why is the colour of the blood red?
Answer:
The blood is red in colour due to the presence of respiratory pigment – haemoglobin.
Question 4.
Which kind of cells are found in the lymph?
Answer:
Lymphocytes in the lymph, which defend the body from infection.
Question 5.
Name the heart valve associated with the major arteries leaving the ventricles.
Answer:
Aortic valve present at the base of aorta.
Question 6.
Mention the artery which supplies blood to the heart muscle.
Answer:
Coronary arteries.
VI. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
What causes the opening and closing of guard cells of stomata during transpiration?
Answer:
The general mechanism of stomatal movement is based on entry and exit of water molecules in guard cells. When the turgidity increases within the guard cells the stomata open. When the guard cells lose water it becomes flaccid and the stomata closes.
![]()
Question 2.
What is cohesion?
Answer:
The force of attraction between molecules of water is called Cohesion.
Question 3.
Trace the pathway followed by water molecules from the time it enters a plant root to the time it escapes into the atmosphere from a leaf.
Answer:
Soil → root hair → cortex → endodermis → Pericycle → xylem → stem → leaves.
Question 4.
What would happen to the leaves of a plant that transpires more water than its absorption in the roots?
Answer:
When transpiration exceeds than water absorption by roots, the plant dehydrates. It affects plant processes such as growth, Photosynthesis and transpiration.
Question 5.
Describe the structure and working of the human heart.
Answer:
The heart is thick muscular organ located in the thoracic cavity. It is covered by a two layered sac called pericardium. The heart is four chambered with two auricles and two ventricles. Right Auricle receives deoxygenated blood from superior and inferior vena cava and passes to right ventricles from right ventricles impure blood passes to pulmonary artery and reaches the lungs.
Question 6.
Why is the circulation in man referred to as double circulation?
Answer:
The blood circulates twice, through the heart in one complete cycle, in the circulation of blood in man. So it is called double circulation.
Question 7.
What are heart sounds? How are they produced?
Answer:
‘Lubb’ and ‘Dupp’ are the sounds of the heart. ‘Lubb’ sound is produced by the ventricle- contraction. It arises due to closing of mitral and tricuspid valve.
‘Dupp’ is produced by ventricular diastole. This arises due to the closing of the semi-lunar valves of two auricles.
Question 8.
What is the importance of valves in the heart?
Answer:
The valves are the muscular flaps, that regulate the flow of blood in a single direction and prevent backflow of blood.
Question 9.
Who discovered Rh factor? Why was it named so?
Answer:
Landsteiner and Wiener discovered Rh factor of blood in 1940. Rh factor is a protein CD antigen present on the surface of the red blood cells in majority of humans. This protein is similar to the protein present in Rhesus monkey, hence the term Rh.
Question 10.
How are arteries and veins structurally different from one another?
Answer:
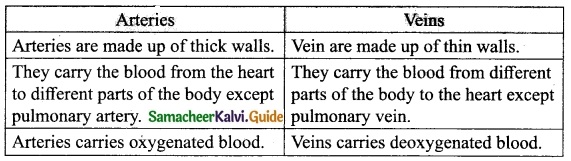
Question 11.
Why is the Sinoatrial node called the pacemaker of the heart?
Answer:
Sinoatrial node is called the pacemaker of the heart because it is capable of initiating impulse, which can stimulate the heart muscles to contract.
![]()
Question 12.
Differentiate between systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation.
Answer:
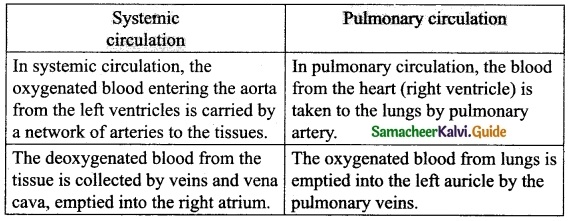
Question 13.
The complete events of the cardiac cycle last for 0.8 sec. What is the timing for each event?
Answer:
- Atrial Systole: Contraction of auricles (0.1 sec)
- Ventricular Systole: Contraction of ventricles (0.3 sec)
- Ventricular diastole: Relaxation of Ventricles (0.4 sec).
VII. Give reasons for the following statements:
Question 1.
Minerals cannot be passively absorbed by the roots.
Answer:
All minerals cannot be passively absorbed by the roots because, minerals are present in the soil as charged particles that cannot move across the cell membranes and the concentration of minerals in the soil is usually lower than the. concentration of minerals in the root. So, the minerals enter the root by active absorption through the cytoplasm of epidermal cells which needs energy.
Question 2.
Guard cells are responsible for opening and closing of stomata.
Answer:
Guard cells are responsible for the opening and closing of stomata because, during transpiration, the movement of ions (Potassium) in and out of the guard cells causes the opening and closing of Stomata. When the water moves inside the guard cells, causing them to swell up and become turgid making the stomata open. When guard cells cause water to move out of the cell and make guard cells shrunk and stomata pores close.
Question 3.
The movement of substances in the phloem can be in any direction.
Answer:
Phloem transports food from the source to sink. The source is part in which plant synthesize food, sink is the part that needs or stores food. Since the source-sink relationship is variable, the direction of movement in the Phloem can be upwards or downwards, i.e., bidirectional.
Question 4.
Minerals in the plants are not lost when the leaf falls.
Answer:
Minerals like Phosphorus, Sulphur, Nitrogen and Potassium are remobilised in the soil from older dying leaves to younger leaves. This phenomenon is seen in deciduous plants. So minerals in the plants are not lost, when the leaf falls.
Question 5.
The walls of the right ventricle are thicker than the right auricles.
Answer:
Because the right ventricle have to pump out the deoxygenated blood with force away from the heart through pulmonary artery to lungs.
![]()
Question 6.
Mature RBC in mammals does not have cell organelles.
Answer:
Mature RBC in mammals does not have cell organelles because
- The lack of Nucleus in RBC makes the cells, biconcave and disc – shaped. RBC involved in the transport of oxygen from lungs to tissues.
- They do not have cell organelles in order to accommodate maximum space for haemoglobin.
- The loss of endoplasmic reticulum allows more flexibility, for RBC to move through narrow capillaries.
VIII. Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
How do plants absorb water? Explain.
Answer:
Water present in the soil must reach the xylem of roots. Root hair is in contact with soil water. Their cell wall is thin and water easily diffuses in the passage of water from the soil to leaf is
Soil water → Root hair → Epidermis → Cortex → Endodermis → Pericycle → Xylem → Stem and leaf.
Once water is absorbed by the root hairs, it can move deepers into root layers by two pathways. Apoplast and Symplast.
- Apoplast : This is the non living path in plants. It occurs through the intercellular spaces and walls of the cells. This movement dependent on the gradient.
- Symplast : This is the living passage. The movement of water from cell to cell through plasmodesmato and cytoplasm, Movement is again down a potential gradient.
Question 2.
What is transpiration? Give the importance of transpiration.
Answer:
Transpiration is the evaporation of water in plants through stomata in the leaves.
Importance of Transpiration
- Creates transpirational pull for the transport of water.
- Supplies water for photosynthesis.
- Transports minerals from the soil to all parts of the plant.
- Cools the surface of the leaves by evaporation.
- Keeps the cells turgid; hence, maintains their shape.
Question 3.
Why are leucocytes classified as granulocytes and agranulocytes? Name each cell and mention its functions.
Answer:
Depending on the presence and absence of granules, leucoytes are divided into two types Granulocytes and Agranulocytes.
Granulocytes : They are characterised by the presence of granules in cytoplasm. The granulocytes include neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils.
- Neutrophils : They constitute about 60-65% of total WBC’s. They are large and have many lobed nucleus. They are phagocytic in nature and appear in large,number in and around the infected tissue.
- Eosinophils : They have bilobed nucleus and constitute about 2-3% of total WBC’s. Eosinophil increase during certain types of parasitic infection and allergic reaction. It bring about detoxification of toxin.
- Basophils: Basophil have lobed nucleus. They form 0.5 – 1.0% of the total leucocytes. They release chemicals during the process of inflammation.
Agranulocytes : They are characterised by the absence of granules in the cytoplasm. These are of two types Lymphocytes and Monocytes.
- Lymphocytes: These are about 20-25% of the total leucocytes. They produce antibodies during bacterial and viral infections.
- Monocytes: They are the largest leucocytes and amoeboid in shape. These cells form 5-6% of the total leucocytes. They are phagocytic and can engulf bacteria.
Question 4.
Differentiate between systole and diastole. Explain the conduction of the heartbeat.
Answer:
One complete contraction (Systole) and relaxation (diastole) of the atrium and ventricles of the heart constitutes Heartbeat. The human heart is myogenic. Contraction is initiated by the sino – atrial (SA) node, which is situated in the wall of the right atrium, near the opening of the superior vena cava. SA node is broader at the top and tapering below and made up of thin fibres.
SA node acts as the ‘pacemaker’ of the heart because it is capable of initiating impulse which can stimulate the heart muscles to contract. The impulse spreads like a wave of contraction over the right and left atrial wall, pushing the blood, through the atrioventricular valves into the ventricles and the same wave from SA node reaches the atrioventricular node (AV), to emit an impulse of contraction, spreading to the ventricular muscle, through the atrioventricular bundle and the Purkinje fibres. The expansion of the artery every time, the blood is forced into the arteries, is called pulse. Normal pulse rate ranges from 70 – 90 / min.
![]()
Question 5.
Enumerate the functions of blood.
Answer:
- Transport of respiratory gases (Oxygen and CO2).
- Transport of digested food materials to the different body cells.
- Transport of hormones.
- Transport of nitrogenous excretory products like ammonia, urea and uric acid.
- It is involved in protection of the body and defense against diseases.
- It acts as buffer and also helps in regulation of pH and body temperature.
- It maintains proper water balance in the body.
IX. Assertion and Reasoning:
Direction: In each of the following questions a statement of assertion (A) is given and a corresponding statement of reason (R) is given just below it. Mark the correct statement as.
(a) If both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A.
(b) If both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) Both A and R are false.
1. Assertion: RBC plays an important role in the transport of respiratory gases.
Reason: RBC do not have cell organelles and nucleus.
Answer:
(a) If both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A.
2. Assertion: Persons with AB blood group are called an universal recipients, because they can receive blood from all groups.
Reason: Antibodies are absent in persons with AB blood group.
Answer:
(a) If both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A.
X. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS):
Question 1.
When any dry plant material is kept in water, they swell up. Name and define the phenomenon involved in this change.
Answer:
The process is imbibition’. The type of diffusion in which a solid absorbs water and gets swelled up is Imbibition.
Question 2.
Why are the walls of the left ventricle thicker than the other chambers of the heart?
Answer:
The walls of the left ventricle are about three times thicker than the right ventricle. The left ventricle gives rise to the aorta, which carries oxygenated blood, to various organs of the body. The ventricle walls are thick because they have to pump out blood with force away from the heart.
Question 3.
Doctors use stethoscope to hear the sound of the heart. Why?
Answer:
A stethoscope is an instrument used to detect the sound produced by the internal organs of human body. It is an useful diagnostic tool to identify and localize health problems and diagnose disease.
Question 4.
How do the pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein differ in their function when compared to a normal artery and vein?
Answer:
- All arteries carry oxygenated blood, except pulmonary arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- All veins carry deoxygenated blood, except pulmonary veins, which carry oxygenated blood from the lungs and to the left atrium of the Heart.
Question 5.
Transpiration is a necessary evil in plants. Explain.
Answer:
The water is lost from the leaves due to transpiration, pressure is created in, at the top to pull more water from the xylem to the leaves through the process of transpiration pull. This ensure the continuous flow of water from the roots of the leaves.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Transportation in Plants and Circulation in Animals Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Seed swells when placed in water due to:
(a) osmosis
(b) imbibition
(c) hydrolysis
(d) all of these
Answer:
(b) imbibition
Question 2.
Root hairs occurs in:
(a) Meristematic zone
(b) Cell elongation zone
(c) Cell maturation zone
(d) Old root
Answer:
(c) Cell maturation zone
The other name for Red blood corpuscles (RBC) is called ______.
Answer:
Erythrocytes.
Question 3.
Water in plants is transported by ascent of sap takes place through:
(a) cambium
(b) xylem
(c) phloem
(d) epidermis
Answer:
(b) xylem
Question 4.
Absorption of water is increased when:
(a) transpiration is increased
(b) photosynthesis is increased
(c) respiration is increased
(d) root pressure is increased
Answer:
(a) transpiration is increased
Question 5.
Opening of stomata is due to:
(a) Turgidity of guard cells
(b) Size of guard cells
(c) Number of guard cells
(d) Amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Answer:
(a) Turgidity of guard cells
Question 6.
Guard cells help in:
(a) Fighting against infection
(b) Guttation
(c) Protecting against grazing
(d) Transpiration
Answer:
(d) Transpiration
Question 7.
Photosynthetic food material is transported in the form of:
(a) Glucose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Starch
(d) Fructose
Answer:
(b) Sucrose
![]()
Question 8.
Coronary artery supplies blood to:
(a) Mammary glands
(b) Rib muscles
(c) Skin
(d) Heart
Answer:
(d) Heart
Question 9.
All arteries carry oxygenated blood except:
(a) systematic
(b) hepatic
(c) pulmonary
(d) cardiac
Answer:
(c) pulmonary
Question 10.
The colour of lymph is:
(a) white
(b) pale yellow
(c) colourless
(d) milky
Answer:
(c) colourless
Question 11.
An artery can be distinguished from a vein in having:
(a) thicker wall
(b) elastic vessels
(c) no valves
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
Question 12.
Purkinje fibres mainly help in contraction of:
(a) right auricle
(b) left auricle
(c) ventricles
(d) Aorta
Answer:
(c) ventricles
Question 13.
The ‘Lubb’ and ‘Dupp’ heart sound are due to:
(a) opening of heart valves
(b) action of papillary’ muscles
(c) closing of heart valves
(d) activity of pace maker
Answer:
(c) closing of heart valves
Question 14.
The closed circulatory system occurs in:
(a) cockroach
(b) fish
(c) mosquito
(d) house fly
Answer:
(b) fish
Question 15.
Normal pulse rate is:
(a) 80 mm Hg
(b) 120 mm Hg
(c) 40 mg Hg
(d) 90 mm Hg
Answer:
(d) 90 mm Hg
Question 16.
In the ABO system of blood groups, of both antigens are present but no antibody, the blood group of the individual would be?
(a) B
(b) O
(c) AB
(d) A
Answer:
(c) AB
Question 17.
Arteries are branches of:
(a) capillaries
(b) veins
(c) aorta
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) aorta
Question 18.
Which type of WBCs are found in maximum number?
(a) Monocytes
(b) Basophils
(c) Eosinophils
(d) Neutrophils
Answer:
(d) Neutrophils
![]()
Question 19.
Which of the following are granular WBCs?
(a) Neutrophils, Basophils, Lymphocytes
(b) Eosinophil, Basophil, Monocytes
(c) Basophils, Monocytes, Lymphocytes
(d) Neutrophils, Eosinophil, Basophil
Answer:
(d) Neutrophils, Eosinophil, Basophil
Question 20.
RBCs are concerned with carriage of gases.
(a) CO2
(b) O2
(c) Respiratory
(d) CO2 and SO2
Answer:
(c) Respiratory
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. The contraction of heart is called ………..
2. Oxygenated blood is carried by ………..
3. Sphygmomanometer measures ………..
4. Heart of man is ………..
5. Pace maker of heart is ………..
6. The life span of RBC in human is ……… days.
7. Pulmonary artery carry ………….. blood.
8. ………. discovered the circulation of blood in man.
9. Semilunar valve is present at the base of ………….
10. Human heart beats ………. times in a minute at rest.
11. Red blood pigment is ………..
12. Transpiration helps in the absorption and ………… movement of water and minerals.
13. Water in plants is transported by ascent of sap takes place through ……….
14. The absorption water due to expenditure of energy is called ………….
15. In plants, the translocation of organic solutes takes place through ………….
Answer:
1. systole
2. pulmonary vein
3. blood pressure
4. myogenic
5. sino atrial node
6. 120
7. deoxygenated
8. William Harvey
9. Pulmonary artery
10. 72
11. Haemoglobin
12. upward
13. xylem
14. active absorption
15. phloem
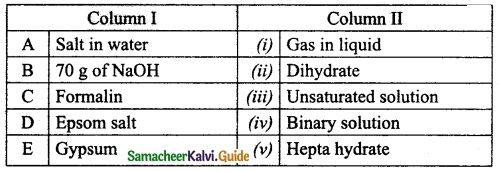
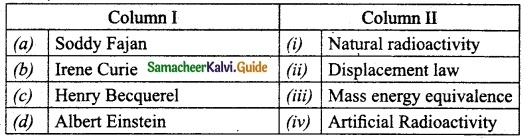
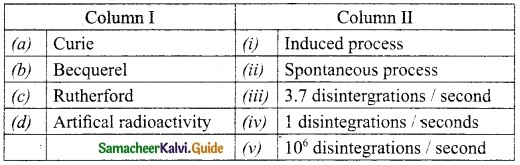
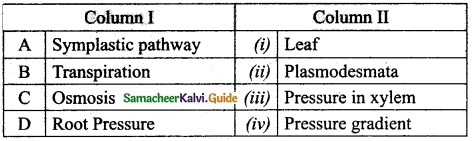
III. Match the following:
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II.
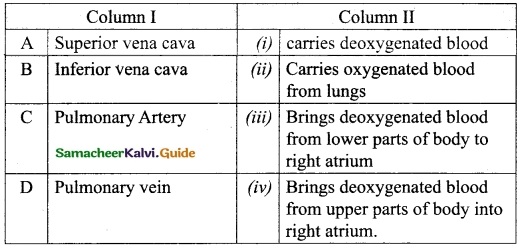
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (iii)
C. (i)
D. (ii)
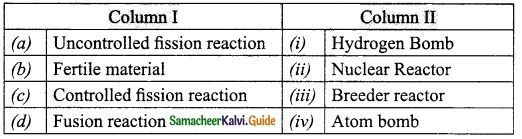
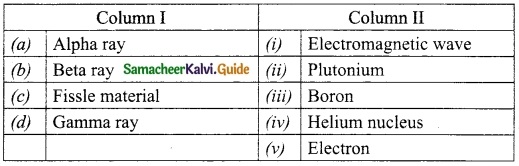
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II.
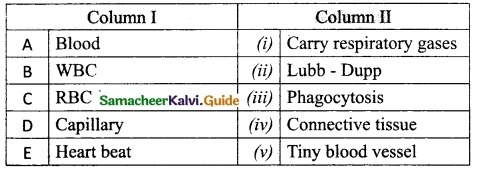
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (iii)
C. (i)
D. (v)
E. (ii)
IV. State whether true or false. If false write the correct statement:
- The human heart beats 72 times per minute.
- Right half of heart receives and pu mps off oxygenated blood.
- Between right auricle and right ventricle seen Mitral valve.
- The force of attraction between water molecule is cohesion.
- By passive transport sucrose moves into the cells where it is utilised or stored.
Answer:
- True
- False – Right half of heart receives and pumps off deoxygenated blood.
- False – Between right auricle and right ventricle seen tricuspid valve.
- True
- False – By active transport sucrose moves into the cells where it is utilised or stored.
![]()
V. Creative Question:
Question 1.
Origin of heart beat and its conduction is represented by:
(a) AV node → Bundle of His → SA node → Purkinje fibres
(b) SA node → Purkinje fibres → AV node → Bundle of His
(c) Purkinje fibres → Purkinje node → AV fibres → Bundle of His
(d) SA node → AV node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibres
Answer:
(d) SA node → AV node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibres
Question 2.
The cardiac pacemaker in a patient fails to function normally. The doctors find that an artificial pacemaker is to be grafted in him. It is likely that it will be drafted at the site of:
(a) Purkinje system
(b) Sinu atrial node
(c) Atrio ventricular node
(d) Atrio ventricular bundle
Answer:
(b) Sinu atrial node
Question 3.
Doctor use stethoscope to hear the sounds produced during each cardiac cycle. The second sound is heard when:
(a) AV node receives signal from SA node
(b) AV valves open up
(c) Ventricular walls vibrate due to rushing in of blood from atria
(d) Semi lunar valves close down after the blood flows into vessels from ventricles
Answer:
(d) Semi lunar valves close down after the blood flows into vessels from ventricles
VI. Assertion and Reason:
(a) If both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
1. Assertion: RBC impart red colour to the blood due to the presence of respiratory pigment haemoglobin.
Reason: The young RBC contain nucleus in man.
Answer:
(b) If both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
2. Assertion: Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecule from higher concentration to lower concentration.
Reason: Osmosis is the active movement of water.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
VII. Answer in a Sentence:
Question 1.
Name the components of circulatory system.
Answer:
The circulation system consists of the circulating fluids, the blood and lymph, the heart and the blood vessels namely arteries, veins and capillaries.
Question 2.
What is the Ascent of Sap?
Answer:
The upward movement of water and minerals from roots to different plant parts is called ascent of sap.
Question 3.
Mention the composition of plasma.
Answer:
Organic substances like protein, glucose, urea, enzyme, hormones, vitamins and minerals are present in plasma.
![]()
Question 4.
Define Adhesion?
Answer:
The force of attraction between molecules of different substances is called adhesion.
Question 5.
Why are auricles and ventricles separated by auricular and ventricular septum?
Answer:
The separation of chamber avoids mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Question 6.
What is Single Circulation?
Answer:
In fishes, amphibians and certain reptiles, the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are mixed ‘ and pass through the heart only once, is called Single Circulation.
Question 7.
Name the instruments used to measure blood pressure.
Answer:
Sphygmomanometer is a clinical instruments used to measure blood pressure when a person is in a relaxed and resting condition. Normal blood pressure in human is 120 mm/ 80 mm Hg.
Question 8.
Which blood group is called as ‘Universal Donor’ and ‘Universal Recipient’.
Answer:
Person with ‘O’ blood group are called Universal Donor.
Person with ‘AB’ blood group are called Universal Recipient.
Question 9.
What is Pulse?
Answer:
During the expansion of the artery, every time, the blood is forced into the arteries is called pulse.
Question 10.
What is transpiration puil?
Answer:
Transpiration through stomata creates vacuum which creates a suction called transpiration pull.
Question 11.
What are Rh antibodies?
Answer:
Rh-negative persons do not have Rh antigen on the surface of RBC. Antibodies developed against this Rh antigen is called Rh antibodies.
Question 12.
What is Adhesion?
Answer:
The force of attraction between molecules of different substances is called . adhesion.
VIII. Short answer question:
Question 1.
What is blood pressure?
Answer:
Blood pressure is the force exerted during the flow of blood against the lateral walls of arteries. The blood pressure is high in the arteries gradually drop in the arterioles and capillaries and become very low in the veins. Blood pressure varies during conditions of physical exercise, anxiety, emotions, stress and sleep. Increase in blood pressure is known as hypertension and decrease in blood pressure is termed as hypotension.
Question 2.
Distinguish between open and closed circulation.
Answer:
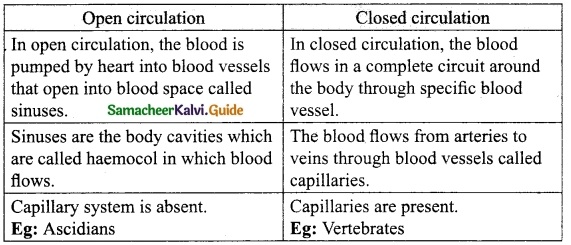
Question 3.
Explain the phenomenon of Guttation.
Answer:
The Guttation is a phenomenon caused due to root pressure. It takes place through a specialized cells called hydathodes. Dews on the leaves of grass seen in the early morning, when the climate is humid and excess of water in the soil is an example of Guttation.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Coronary circulation?
Answer:
The supply of blood to the heart muscles is called as coronary circulation. Cardiac muscles receives oxygenated blood from coronary arteries that originate from the aortic arch. Deoxygenated blood from the cardiac muscles drains into the right atrium by the coronary sinuses.
IX. Long answer questions:
Question 1.
What is lymph? Write its functions.
Answer:
Lymph is a colourless fluid formed when plasma, proteins and blood cells escape into intercellular spaces in the tissues through the pores present in the walls of capillaries.
Functions of Lymph:
- Supplies nutrition and oxygen to those parts where blood cannot reach.
- It drains away excess tissue fluid and metabolites and returns proteins to the blood from tissue spaces.
- The lymph also carries absorbed fats from small intestine to the blood. The lymphatic capillaries of intestinal villi (lacteals) absorb digested fats.
- Lymphocytes in the lymph defend the body from infections.
Question 2.
(a) Name the main two components of blood.
(b) What does plasma contain?
Answer:
(a) 1. The fluid plasma
2. Formed elements (blood cells)
- RBC
- WBC
- Blood platelets
(b) Plasma is slightly alkaline, containing non – cellular substance, constitute 55 % of the blood. Organic substances like Proteins, Glucose, Urea, Enzymes, Hormones, Vitamins and Minerals are present in the Plasma.
Question 3.
Demonstrate the process of osmosis with thistle funnel.
Answer:
Aim : To demonstrate the process of osmosis, using Thistle funnel.
Materials Required : Beaker, Thistle funnel, semi permeable membrane, sucrose solution.
Procedure : A thistle funnel whose mouth is covered with a semipermeable membrane, is filled with sucrose solution. It is kept inverted in a beaker containing water.
Observation : The water will diffuse across the membrane due to osmosis and raise the level of the solution in the funnel.
Inference : Raise of liquid in the funnel indicates the process of osmosis.
Question 4.
Explain Double circulation.
Answer:
Diagrammatic representation of the double circulation.
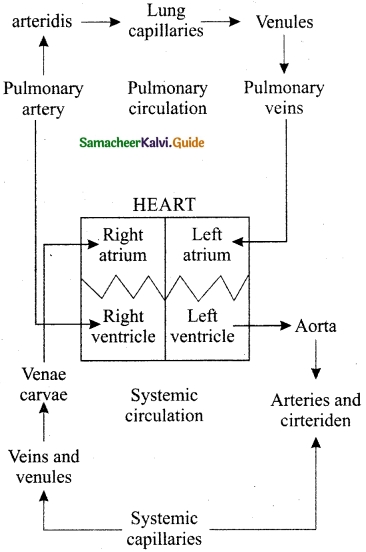
Question 5.
Explain the steps involved in Ascent of sap.
Answer:
The upward movement of water, and minerals from roots to different plant parts is called ascent of sap. A number of factors play a role in ascent of sap and it takes places in following steps.
Root Pressure : Water from soil enters the root hairs due to osmosis. Root pressure is responsible for movement of water up to the base of the stem.
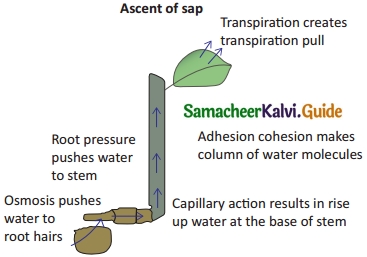
Capillary Action : Water or any liquid rises in a capillary tube because of physical forces, this phenomenon is called capillary action. In the same way, in stem water rises up to certain height because of capillary’ action.
Adhesion-cohesion of Water Molecules : Water molecules form a continuous column in the xylem because of forces of adhesion and cohesion among the molecules.
Cohesion : The force of attraction between molecules of water is called cohesion.
Adhesion : The force of attraction between molecules of different substances is called adhesion.Water molecules stick to a xylem because of force of adhesion.
Question 6.
Explain the causes of the sound of the Heart.
Answer:
The rhythmic closure and opening of the valves cause the sound of the heart.
- The first sound ‘LUBB’ is produced by the closure of the tricuspid and bicuspid valves, after the beginning of ventricular systole. It is a longer duration.
- The second sound ‘DUPP’ is produced by the closure of semilunar valves, at the end of ventricular systole. It is of short duration.
![]()
X. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
Question 1.
An unconscious patient is rushed into the emergency room and need a fast blood transfusion. Because there is no time to check her medical history or determine her blood type, which type of blood should you as her doctor, give?
Answer:
O+ve, it is universal donor. In O group individuals, Antigen A or B are absent on the surface of RBC. However the plasma contains both antibodies a and b.
Question 2.
What are the factors affecting the Ascent of Sap?
Answer:
- High Temperature
- Atmospheric Pressure
- Wind Velocity
- Low atmospheric humidity
- Soil water deficit.
Question 3.
Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements.
Answer:
Both processes can happen together because the diffusion co-efficient of water and CO2 is different.
Question 4.
Write a few Strategies, to prevent heart disease.
Answer:
- Exercise for about 30 minutes every day.
- Smoking or use of Tobacco should be avoided.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet – Avoid too much of salt or sugar, use of a diet rich in Vegetables and Fruits.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get enough quality sleep.
- Manage Stress.
- Get regular health screenings (B.P. monitoring, Cholesterol level, Diabetes Screening etc.).
XI. Give reason:
Question 1.
Valves are important in human heart. Give reason.
Answer:
The valves will prevent the back flow of blood.
Question 2.
During rainy season wooden door generally swells up – Give reason.
Answer:
It is due to imbibition. It is a type of diffusion in which a solid absorbs water and gets swelled up.
Question 3.
Para sympathetic neural signals affects the working of the heart. Give reason.
Answer:
It reduce both heart rate and cardiac output.
Question 4.
Grapes placed in salt solution shrink. Give reason.
Answer:
It is due to exosmosis.
![]()
Question 5.
Why WBC’s are known as phagocytes?
Answer:
WBC produce antibodies during bacterial and viral infection and engulf the germs.