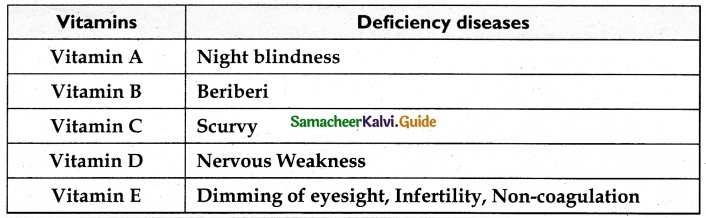
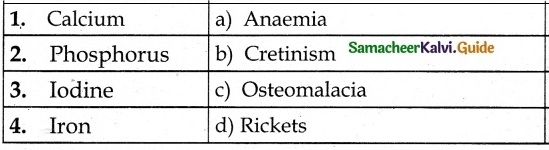
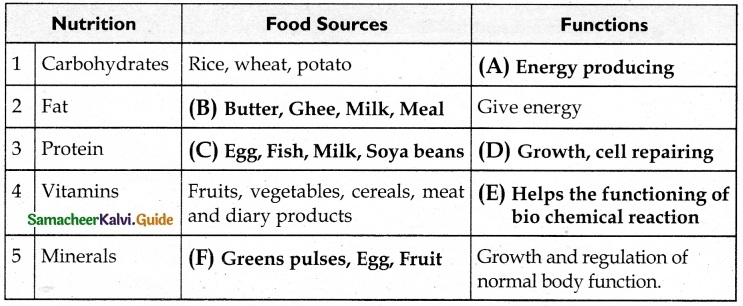
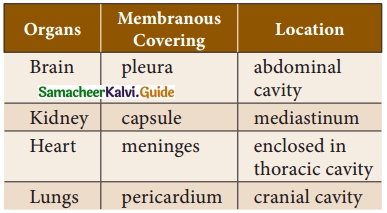
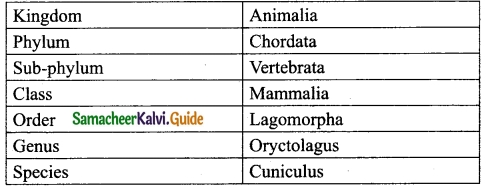
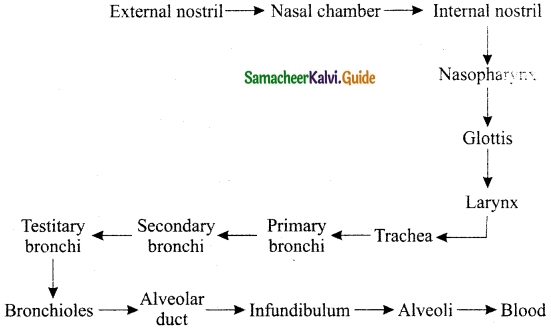
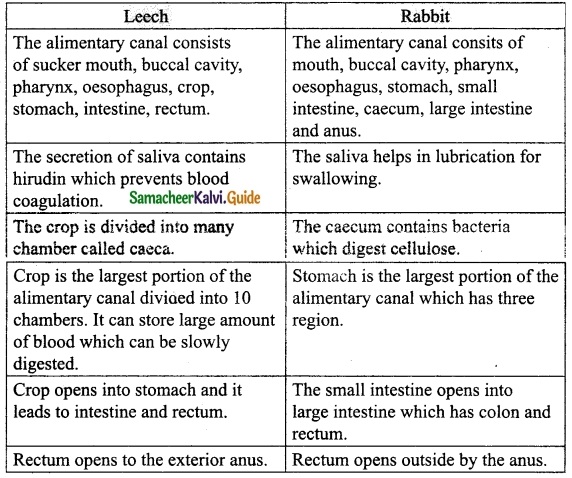
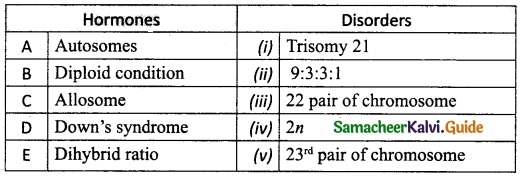
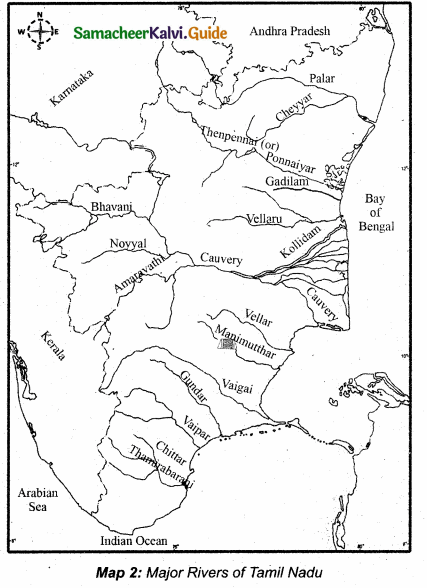
Students can download 10th Social Science Civics Chapter 5 India’s International Relations Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 5 India’s International Relations
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science India’s International Relations Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
McMahon Line is a border between
(a) Burma and India
(b) India and nepal
(c) India and China
(d) India and Bhutan
Answer:
(c) India and China
Question 2.
India is not a member of which of the following …………..
1. G20
2. ASEAN
3. SAARC
4. BRICS
Select the correct option
(a) 4 only
(b) 2 and 4
(c) 2, 4 and 1
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer:
2 only
![]()
Question 3.
OPEC is:
(a) An international insurance Co.
(b) An international sports club
(c) An Organisation of Oil Exporting Countries
(d) An international company
Answer:
(c) An Organisation of Oil Exporting Countries
Question 4.
With which country does India share its longest land border?
(a) Bangladesh
(b) Myanmar
(c) Afghanistan
(d) China
Answer:
(a) Bangladesh
Question 5.
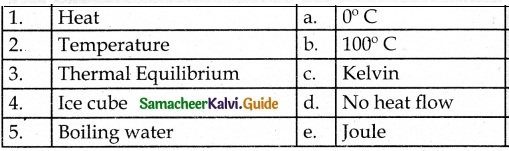
Match the following and choose the correct answer form the codes given below.
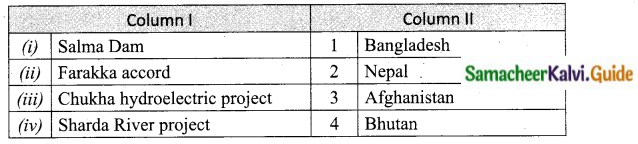
(a) 3 14 2
(b) 3 12 4
(c) 3 4 12
(d) 4 3 2 1
Answer:
(a) 3 14 2
Question 6.
How many countries share its border with India?
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer:
(c) 7
Question 7.
Which two island countries are India’s neighbours?
(a) Sri Lanka and Andaman island
(b) Maldieves and Lakshadweep island
(c) Maldieves and Nicobar island
(d) Sri Lanka and Maldieves
Answer:
(d) Sri Lanka and Maldieves
![]()
Question 8.
Which Indian state is surrounded by three countries?
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Meghalaya
(c) Mizoram
(d) Sikkim
Answer:
(a) Arunachal Pradesh and (d) Sikkim
Question 9.
How many Indian states have their boundary with Nepal?
(a) Five
(b) Four
(c) Three
(d) Two
Answer:
(a) Five
Question 10.
Who drew up the borders for newly independent Pakistan?
(a) Lord Mountbatten
(b) Sir Cyril Radcliffe
(c) Clement Atlee
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Sir Cyril Radcliffe
II. Fill in the blanks
- ………………. is a small Himalayan kingdom.
- India’s gateway to South East Asia is ……………….
- ………………. is a buffer country between India and China.
- A strip of land ………………. belongs to India on West Bengal and Bangladesh border.
- ………………. is known as the Land of thunderbolt.
- India and Sri Lanka are separated by ……………….
Answer:
- Bhutan
- Myanmar
- Nepal
- Teen Bigha Corridor
- Bhutan
- Palk strait
![]()
III. Consider the following statement and tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
The Kaladan transport project by India and Myanmar consists of which of the following modes of transport?
1. Roads
2. Railways
3. Shipping
4. Inland water transport
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1,3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer:
(b) 1,3 and 4 only
Question 2.
Assertion (A): India and France launched International Solar Alliance.
Reason (R): It was done to bring together countries between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn for co-operation of solar energy.
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is wrong and R is correct
(d) Both are wrong
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 3.
Which of the following statements are true?
Statement 1: ICCR has initiated a Tagore Chair in University of Dhaka.
Statement 2: Myanmar is India’s gateway to western countries.
Statement 3: Nepal and Bhutan are land locked nations.
Statement 4: Sri Lanka is one of the partner in Nalanda University Project of India.
(a) 1,2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 1,2 and 4
Answer:
(c) 1, 3 and 4
Question 4.
Assertion (A): OPEC has vested interest in India’s economic growth.
Reason (R): Devoid of necessary oil resources India strongly focuses on agriculture and industrial production.
(a) A is correct and R explains A
(b) A is wrong and R is correct
(c) Both are correct
(d) Both are wrong
Answer:
(c) Both are correct
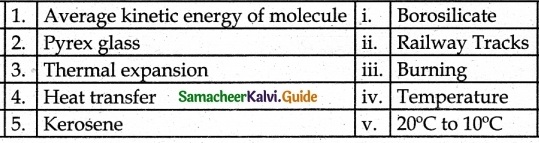
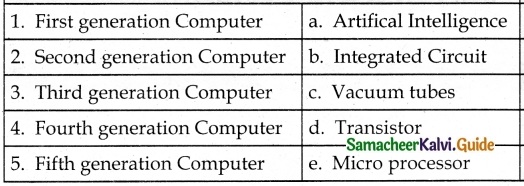
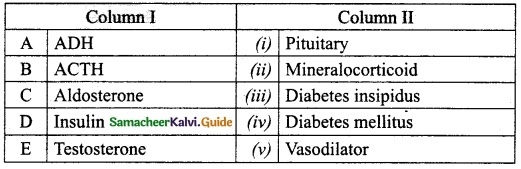
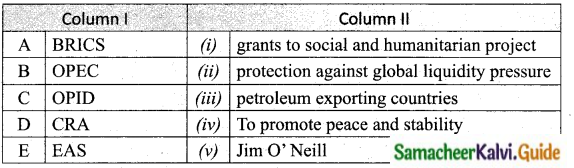
IV. Match the following
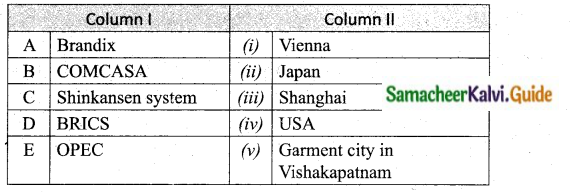
A. (v)
B. (iv)
C. (ii)
D. (iii)
E. (i)
![]()
V. Give Short Answers
Question 1.
Name the neighbouring countries of India.
Answer:
- India is a vast country with Pakistan and Afghanistan to the north-west
- China, Nepal, Bhutan to the north
- Bangladesh to the east
- Myanmar to the far east
- Sri Lanka (from south-east) and Maldives (from south-west) are two countries that lie close to India separated by the Indian Ocean.
Question 2.
Write a short note on Strategic partnership Agreement (SPA).
Answer:
- Indo – Afghan relation was strengthened by the strategic partnership , agreement.
- SPA provide assistance to rebuild Afghan’s infrastructure, institutions, agriculture, water, education, health and providing duty – free access to the Indian market.
Question 3.
Mention the member countries of BRICS.
Answer:
- Brazil
- Russia
- India
- China
- South Africa
Question 4.
What do you know about Kaladan Multi-Model Transit Transport?
Answer:
- India is building the kaladan multi – model transit transport, a road-river- port cargo transport project to link kolkata to Sittwe in Myanmar.
- A project aiming to connect Kolkata with Ho chi minh city on the south sea for the formation of an economic zone will have a road pass through Myanmar, Cambodia and Vietnam and work on the first phase connecting Guwahati with Mandalay is currently underway.
Question 5.
How do you assess the importance of Chabahar agreement?
Answer:
A trilateral agreement called the Chabahar Agreement was signed between India, Afghanistan . and Iran, which has led to the establishment of transit and transport corridor among three countries using Chabahar port. This port is seen as golden gateway for India to access landlocked markets of Afghanistan and Central Asia by passing Pakistan.
Question 6.
List out any five global groupings in which India is a member.
Answer:
IBSA, BCIM, MGC, BBIN, and SCO.
Question 7.
What is the role of Japan India Institute of Manufacturing (JIM)?
Answer:
In the manufacturing sector Japan announced its co-operation of training 30,000 Indian people in the Japan India Institute of Manufacturing (JIM) providing Japanese style manufacturing skills to enhance India’s manufacturing industry base and contribute to ‘Make in India’ and ‘Skill India’ initiatives. In 2017, the first four JIMs were started in the states of Gujarat, Karnataka, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu.
![]()
VI. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Highlight India and International organisation with special reference to any three India’s global groupings.
Answer:
- India is a potential superpower and has a growing international influence all around the world.
- India has is a member of formal groupings like UNO, NAM, SAARC, G20 and the commonwealth.
- India is an activity engaged in general economic diplomacy, which is evident in the country being part of several economic coalitions, as listed in the table below.
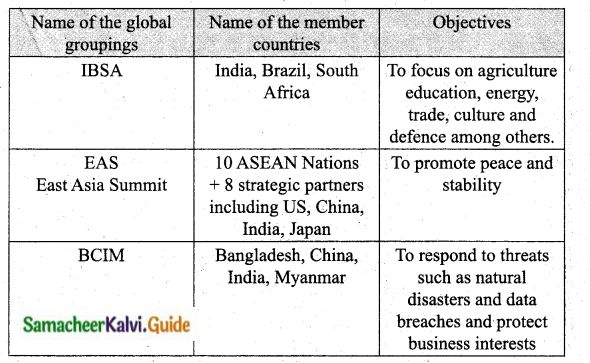
Question 2.
Trace the reason for the formation of BRICS and write its objectives.
Answer:
Reason for the formation of BRICS To be an alternative to World Bank and IMF to challenge U.S. supremacy.
To provide self-owned and self-managed organisations to carry out developmental and economical plans in its member nations.
Objectives of BRICS
- To achieve regional development
- It acts as a bridge between developed and developing countries
- To contribute extensively to development of humanity
- To establish a more equitable and fair world
- Boost intra BRICS trade in their local currencies to increase trade cooperation and cope with the current international financial crisis.
- To promote the technological information exchange among the member states
- To enhance inclusive economic growth that will lead to an increase in the creation of jobs, fight against poverty and accelerate the economic transformation of members.
![]()
Question 3.
Mention OPEC missions and how does it help other countries?
Answer:
OPEC’S Mission:
- To coordinate oil policies in its member countries.
- Help stabilise oil markets.
- To secure fair and stable income to petroleum producers.
- An efficient, economic and regular supply of oil to consuming nations.
- A fair return on capital to those investing in the petroleum industry.
How does OPEC help other countries?
- The OPEC, fund for International Development (OPID) is an institution that help finance projects with low interest loans.
- It also provides grants to social and humanitarian projects..
- OPEC has an information centre with over 20,000 volumes including books reports, maps and conference, proceedings related to petroleum energy and the oil markets.
- The information centre is open to the public and is often used by researchers and students.
VII. Project and Activity
Question 1.
Students can be asked to collect information from newspapers about India’s relation with world countries.
Answer:
Students should find any article from Tamil (or) English newspaper about India’s relation with world countries.
Eg: Foreign Minister’s visit to India.
[OR]
Indian Prime Minister or President’s visit to foreign countries. After finding the information, cut down the article with its date and year of publication and the name of the newspaper. A minimum of five such news articles can be collected and can be pasted in a notebook to prepare an album to submit as project to the subject teacher.
A sample news taken from the English newspaper.
Times of India
Date: Sep. 17,2019
AGARTALA: Bangladesh Information Minister Hasan Mahmud said ties between India and Bangladesh is becoming better by the day under the leadership of Narendra Modi and Sheikh Hasina.
Inaugurating a 3 – day film festival here, the Minister said Bangladesh believes in having good relations with its neighbours and films play a great role in that. The film festival will feature 20 films made on the Bangladesh Liberation war.
Question 2.
Group project involving students to prepare an album with pictures on India’s latest projects with its neighboring countries.
Answer:
India’s latest project with its neighbouring countries: The Government of India gives high importance to strengthen the friendly relations and to promote understanding with neighbouring countries. As part of this policy, the Government has undertaken several development projects with our neighbouring countries. Details of projects (a sample) is given below.
Note: Students should find and collect information (or) pictures related to the project of Gol (Government of India) with its neighbouring countries taking the sample few projects given here (or) other projects also. Students should paste the pictures in a note book underlining the project, prepare it as an album, submit to the subject teacher.
Projects
Bhutan: Projects completed in Bhutan with GOI assistance include Paro airport, Bhutan broadcasting station, major highways, and construction of Mini – Hydel projects. Penden cement plant with 300 tonnes capacity was completed in 1982 with GOI assistance.
Bangladesh: India is gifting 10 ambulances to Bangladesh.
Maldives: The 200 – bed Indira Gandhi Memorial Hospital (IGMH) was set up in Maldives in 1995 at a cost of about ₹40 crores.
Nepal: The recently completed projects include 22 bridges on the East – West Highway. Setting up of trauma – center at Bir hospital in Kathmandu.
Sri Lanka: GOI has committed US $ 7.5 million to set up an India cancer centre in Colombo.
The above mentioned are only guidelines that could help a student to find what type of projects are generally undertaken.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science India’s International Relations Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Independent India has been consistently fostering.
(a) World peace
(b) International co-operation
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 2.
………… development of nations can be achieved only through world peace.
(a) Economic
(b) Social
(c) Political
Answer:
(a) Economic
Question 3.
How many kilometre that Pipeline between Siliguri in West Bengal and ‘ Parbatipur (Bangladesh).
(a) 130
(b) 150
(c) 170
(d) 190
Answer:
(a) 130
Question 4.
China became republic in ……………
(a) 1947
(b) 1949
(c)1950
Answer:
(b) 1949
Question 5.
How many hydro electric projects the Government of India has constricted in Bhutan.
(a) 1
(b) 5
(c) 3
(d) 2
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 6.
…………….. is located South of Lakshadweep islands in the Indian ocean.
(a) Sri Lanka
(b) Myanmar
(c) Maldives
(d) none
Answer:
(c) Maldives
![]()
Question 7.
India’s second-largest border is shared with:
(a) Maldives
(b) Myanmar
(c) Nepal
(d) Bhutan
Answer:
(b) Myanmar
Question 8.
In …………… a 25 years treaty of friendship, co-operation and peace was signed by India and Bangladesh at …………..
(a) 1971, New Delhi
(b) 1972, Dacca
(c) 1982, Lahore
Answer:
(b) 1972, Dacca
Question 9.
The 204 – kilometre long Mahendra Raj marg to link …………….. and India
(a) Kathmandu
(b) Kalandan
(c) Sittwe
(d) none
Answer:
(a) Kathmandu
Question 10.
In which agreement India tried to bring positive change in the relationship of Pakistan.
(a) Strategic Partnership Agreement
(b) Shimla Agreement
(c) International Agreement
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Shimla Agreement
Question 11.
Which king had sent his son and daughter to ceylon (Sri Lanka) for the propagation of Buddhism.
(a) Chandra Gupta Mourya
(b) Ashoka
(c) Kanishka
(d) none
Answer:
(b) Ashoka
Question 12.
The cease fire line determined in ……………………….. was called the LOC.
(a) 1947
(b) 1945
(c) 1949
(d) 1943
Answer:
(c) 1949
Question 13.
……………… gives India access to advance communication technology used in U.S defence equipment.
(a) COMCASA
(b) AVSINDEX
(c) JIM
(d) MAHSR
Answer:
(a) COMCASA
Question 14.
India and France launched the international ……………… between Tropic of cancer and Tropic of capricorn.
(a) Solar Alliance
(b) Railway
(c) domestic development
(d) none
Answer:
(a) Solar Alliance
![]()
Question 15.
Which country decided to introduce the Japan’s Shikansen system.
(a) Australia
(b) India
(c) West Asia
(d) Europe
Answer:
(b) India
Question 16.
Which institute providing manufacturing skills to enhance India’s manufacturing industry (Make in India).
(a) JIM
(b) JEC
(c) MAHSR
(d) COMCASA
Answer:
(a) JIM
Question 17.
Which course was introduced in engineering colleges was established in Andhrapradesh.
(a) JIM
(b) JEC
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none
Answer:
(b) JEC
Question 18.
Which port is seen as golden gate way for India?
(a) Chabahar
(b) Kandla
(c) Gwadar
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Chabahar
Question 19.
Mention the C of the BRICS:
(a) China
(b) Vienna
(c) Japan
(d) Europe
Answer:
(a) China
Question 20.
Which economist was coined BRICS?
(a) British
(b) French
(c) German
(d) Russian
Answer:
(a) British
Question 21.
NDB gives priority to projects aimed at developing ……………… sources.
(a) Renewable
(b) Non – Renewable
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none
Answer:
(a) Renewable
Question 22.
The contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) for providing protection against ……………… pressures.
(a) liquidity
(b) currency issues
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) Trade
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
![]()
Question 23.
Which centre has cover 20,000 volumes including books, maps related to petroleum.
(a) Information centre (OPEC)
(b) Research Centre (OPEC)
(c) Universities (OPEC)
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Information centre (OPEC)
Question 24.
……………… is one of the biggest consumers of crude oil.
(a) Nepal
(b) China
(c) India
(d) Pakistan
Answer:
(c) India
Question 25.
India strongly focuses on production.
(a) Agriculture
(b) industrial
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) rural
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
Question 26.
India extend its support to the in all her efforts.
(a) U.N.O
(b) W. T. O
(c) world bank
(d) none
Answer:
(a) U.N.O
Question 27.
Who is an active member of BRICS.
(a) Nepal
(b) Pakistan
(c) India
(d) Bangladesh
Answer:
(c) India
Question 28.
Which bank is lending for infrastructure project?
(a) The New Development Bank
(b) Contingent Reserve Arrangement
(c) global liquidity currency
(d) none
Answer:
(a) The New Development Bank
Question 29.
How many seats per year to Indian national for a master’s degree in university of Japan.
(a) 30
(b) 20
(c) 10
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 20
Question 30.
Who is a super power and has a growing international influence all around the world.
(a) China
(b) Japan
(c) Pakistan
(d) India
Answer:
(d) India
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks
- ……………….. has always been known as a peace – loving country.
- India’s position is ……………….. in its neighbourhood.
- ……………….. is surrounded by many neighbouring countries.
- Indo – Afghan relation was strengthened by the ………………..
- ……………….. of Baluchistan active supporter of the Indian National congress.
- ……………….. has built kandahar international cricket stadium.
- India and ……………….. share 54 common rivers and a bilateral joint River commission is working to maximise benefits.
- ……………….. has initiated a Tajore chair in university of Dhaka (Scholarship).
- ……………….. is India’s gate way to Western countries.
- ……………….. one of the partner in Nalanda university project of India.
- ……………….. represents one of the main indicators of bilateral co-operation between India and Bhutan.
- India declared the bilateral trade relation known as ………………..
- China being the ……………….. of the world.
- ……………….. is a small land locked country.
- Nepali and Indian people visit each other’s country for religions ………………..
- India included ……………….. in the VIII schedule of the constitution.
- There are a number of ……………….. along Indo- Nepal border.
- A joint hydropower project is being built on the ……………….. River.
- The Government of India and Nepal have signed ……………….. agreements.
- ……………….. remains our core concern in the relationship with Pakistan.
- The cross-border firing between India and ………………..
- ……………….. is the bone of contention between India and Pakistan.
- ……………….. is a major irritant.
- India and Pakistan under the ……………….. of 1972.
- Sri Lankan investments in India include ……………….. (garment city)
- COMCASA is valid for a period of ………………..
- French space launch pads are used by ………………..
- ……………….. broadens the relationship raising awareness and promoting exchanges between two countries.
- ……………….. is one of most successful examples of Japanese co-operation.
- JIM providing training for Indian-people in ………………..
- Trade relations were established between civilisation of Mesopotemia and ………………..
- ……………….. gateway to land locked and energy rich
- In trading routes ran from ancient Sumeria to the Indus civilisation called ………………..
- The acronym BRICS was coined by ……………….. a famous British economist.
- ……………….. is a multilateral development Bank.
- ……………….. are defining changes to have huge geo – economic and geo – political impact.
- ……………….. mission to co-ordinate oil policies in its member countries.
- ……………….. is an institution that help finance projects with low interest loans.
- ……………….. doesn’t have enough oil reserves.
- India – Japan join laboratories in the area of ………………..
Answers:
- India
- unique
- India
- Strategic Partnership Agreement (SPA)
- Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan
- India
- Bangladesh
- Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR)
- Myanmar
- Sri Lanka
- Hydel power sector
- Bharat to Bhutan B2B
- Manufacturing hub
- Nepal
- Pilgrimage
- Nepalese language
- Tiger reserves
- Sharda
- Three-sister-city
- Terrorism
- Pakistan
- Kashmir
- Cross border terrorism
- Shimla Agreement
- Brandix
- 10 years
- ISRO
- The Australia India council
- Delhi metro
- Manufacturing sector
- The Indus valley
- West Asia, Central Asia
- Meluna
- Jim O’Neill
- NDB (New Development Bank)
- The Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA)
- OPEC 38. OPID
- India
- Information and communication Technology
![]()
III. Consider the following statement and tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The Farakka accord on sharing of Ganga waters signed in 1977 is a historic agreement.
Reason (R): India and Bangladesh share 54 common rivers and a bilateral joint river commission is working to maximise benefits.
(a) A is correct and R explains A.
(b) A is wrong and R is correct
(c) Both are correct
(d) Both are wrong
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R explains A.
Question 2.
Which of the following statements are false?
Statement 1: India’s position is unique in its neighbourhood.
Statement 2: Myanmar is a land locked nations.
Statement 3: The cross border firing between India and Nepal.
Statement 4: Kashmir is the bone of contention between India and Pakistan.
(a) 1,2, and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1,2 and 4
(d) 2 and 3
Answer:
(d) 2 and 3
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Maldives is located South of Lakshadweep Islands in the Indian oceans.
Reason (R): The relationship with Maldives is important for India given its strategic location and geo – graphical proximity.
(a) A is correct and R is correct explanation of A.
(b) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is wrong and R is correct
(d) Both are wrong
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R is correct explanation of A.
Question 4.
Assertion (A): McMahon line is the boundary line between India and China.
Reason (R): The secretary of state for India (in British cabinet) Arthur Henry McMahon represented British India at the conference.
(a) A is correct and explains A
(b) A is wrong and R is correct
(c) Both A and R are correct
(d) A is correct and R is wrong.
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are correct
![]()
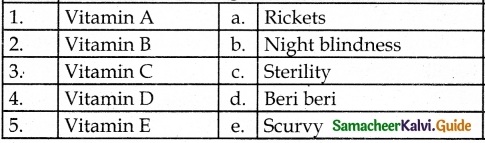
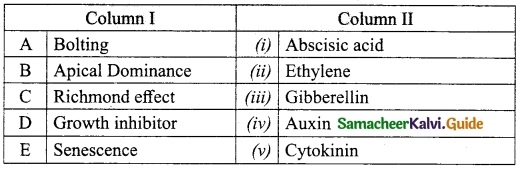
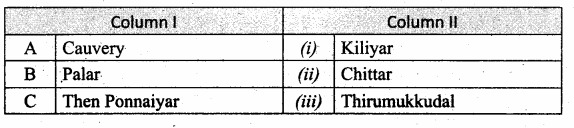
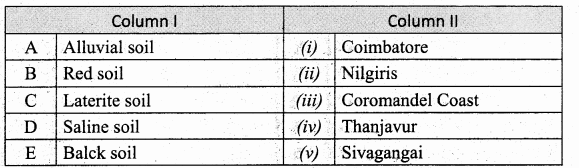
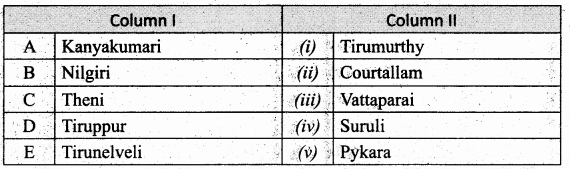
IV. Match the following
Question 1.
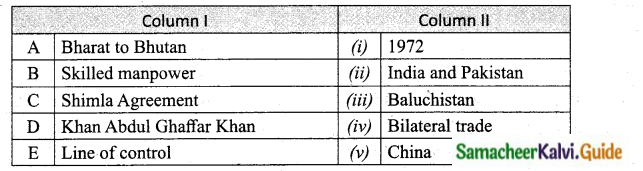
Match the Column I with Column II.
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (v)
C. (i)
D. (iii)
E. (ii)
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II.
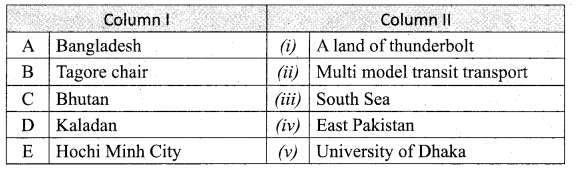
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (v)
C. (i)
D. (ii)
E. (iii)
Question 3.
Match the Column I with Column II.
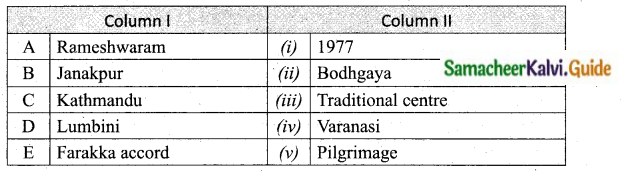
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (iii)
C. (iv)
D. (ii)
E. (i)
Question 4.
Match the Column I with Column II.
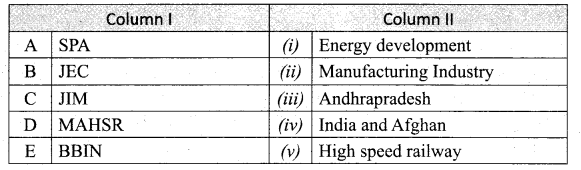
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (iii)
C. (ii)
D. (v)
E. (i)
Question 5.
Match the Column I with Column II.
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (iii)
C. (i)
D. (ii)
E. (iv)
![]()
V. Give Short Answer
Question 1.
What is the role of India as a Great Helper?
Answer:
India is basically against colonization and wants to see all the countries of the world free from foreign domination. It played a great role in freeing Indonesia from the domination of Holland. In the same way, it has supported the freedom movements started by Egypt, Sudan, Indo-China, Ghana, Morocco and Bangladesh.
Question 2.
Name the formal groups in which India is a member.
Answer:
India is a member of formal groupings like U.N.O, NAM, SAARC, G-20 and the common wealth.
Question 3.
Explain India’s relationship with Pakistan.
Answer:
Inspite of part conflicts both India and Pakistan are trying to come closer. The Delhi-Lahore bus service was launched on March 10th 1999 to bring the people of the two countries closer. Negotiations for setting up Iran-Pakistan-India gas pipeline are taking place.
Question 4.
Mention the India’s relationship with OPEC.
Answer:
- India is one of the biggest consumers of crude oil.
- OPEC obviously has vested interest in India’s economic growth.
- We import 86% of crude oil, 70% natural gas, 35% of cooking gas from OPEC countries.
- India has been identified as a greater partner for OPEC mainly because of its high oil demand.
Question 5.
‘The relationship between India and Sri Lanka is smooth’-Justify.
Answer:
Sri Lanka is a Buddist country. The Mauryan emperor Ashoka spread Buddism there by sending his son and daughter. We have good trade relation with Sri Lanka India always support Sri Lanka on just and reasonable grounds. Thus the relationship between India and Sri Lanka is very smooth. It will be continued forever.
Question 6.
Write about Khan Abdual Ghaffar Khan.
Answer:
Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan of Baluchistan (a border province in 10 day’s Pakistan) was a prominent leader of the Indian independence movement and active supporter of the Indian national congress.
Question 7.
Why Buddhist saint went to Bhutan from India?
Answer:
Gur Padmasambhava, a Buddhist saint who want to Bhutan from India, played an influential role in spreading Buddhism and Cementing traditional ties between people of both nations.
Question 8.
List out the Indian states have their boundary with Nepal.
Answer:
Sikkim, west Bengal, Bihar, Uttarpradesh and Uttarakhand.
Question 9.
In what way JIM providing training to Indian people?
Answer:
The Japan India Institute of manufacturing(JIM) providing Japanese style manufacturing skills to enhance India’s manufacturing industry base and contribute to “Make in India” and “skill India” initiatives.
![]()
Question 10.
Write a short note on a joint hydro power project.
Answer:
- A joint hydropower project is being built on the Sharda river.
- This power plant helps both India and Nepal with respect to electricity production and irrigation facilities.
VI. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Explain the relationship of India with her neighbouring countries.
Answer:
India and Pakistan:
Insipite of port conflicts both India and Pakistan are trying to come closer. The Delhi-Lahore bus service was launched on March 16th 1999 to bring the people of the two countries closer. Negotiations for setting up Iran-Pakistan-India gas pipeline are taking place.
India and China:
When China became republic in 1949, India was the first country to recognize it. Both the countries have successfully attempted to restore the economic lines. China has formally declared that she will back India’s claim for becoming a permenent member of United Nation’s Security Council.
India and Srilanka:
Srilanka is a Buddhist country. The Mauryan emperor Ashoka spread Buddhism there by sending his son and daughter. We have good trade relation with Srilanka. India always support Srilanka on just and reasonable grounds. Thus the relationship between India and Srilanka is very smooth. It will be continued for ever.
India and Bangladesh:
It is due to the effort and support of Smt. Indira Gandhi, the Prime Minister of India, Bangladesh got freedom from Pakistan in 1971. In 1972, a 25 years treaty of friendship, co operation and peace was signed in Dacca by India and Bangladesh. The farakka Barrage issue regarding the distribution of Ganga water was settled amicably. Thus India is a very good friend of Bangladesh. Our friendship with Bangladesh will go on forever.
![]()
Question 2.
Write about India and Pakistan relationship?
Answer:
- Since the bifurcation of territory which demarcated India and Pakistan in 1947.
- The two nations have had strained relations due to disagreements over a number of key issues.
- Terrorism remains our core concern in the relationship with Pakistan.
- But India has made extreme efforts to improve and stabilise relations with Pakistan.
- The cross – border firing between India and Pakistan and the terrorist attacks combined have taken its toll on the Kashmiri’s who have suffered poor living standards and an erosion of human rights.
- Kashmir is the bone of contention between India and Pakistan, which has brought the two countries into open clash many times.
- Cross-border-terrorism is a major irritant.
- India tried bring a positive change in the relationship of the two countries through bilateral agreements such as Shimla Agreement and Lahore Declaration.