Students can download Maths Chapter 1 Set Language Ex 1.4 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Set Language Ex 1.4
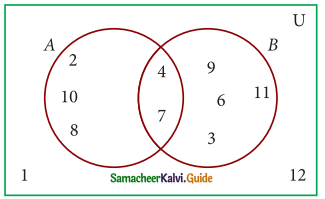
Question 1.
If P = {1, 2, 5, 7, 9}, Q = {2, 3, 5, 9, 11}, R = {3, 4, 5, 7, 9} and S = {2, 3, 4, 5, 8} then find
(i) (P∪Q)∪R
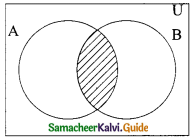
(ii) (P∩Q)∩S
(m) (Q∩S)∩R
Solution:
P = {1, 2, 5, 7, 9}; Q = {2, 3, 5, 9, 11}; R = {3, 4, 5, 7, 9} and S = {2, 3, 4, 5, 8}
(i) P∪Q = {1, 2, 5, 7, 9} ∪ {2, 3, 5, 9, 11}
= {1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11}
(P∪Q)∪R = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11} ∪ {3, 4, 5, 7, 9}
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11}
(ii) P∩Q = {1, 2, 5, 7, 9} ∩ {2, 3, 5, 9, 11}
= {2, 5, 9}
(P∩Q)∩S = {2, 5, 9} ∩ {2, 3, 4, 5, 8}
= (2, 5}
(iii) Q∩S = {2, 3, 5, 9, 11} ∩ {2, 3, 4, 5, 8}
= {2, 3, 5}
(Q∩S)∩R = {2, 3, 5} ∩ {3, 4, 5, 7, 9}
= {3, 5}
![]()
Question 2.
Test for the commutative property of union and intersection of the sets
P = {x : x is a real number between 2 and 7} and
Q = {x : x is an irrational number between 2 and 7}
Solution:
P is a real number set
Q is a set of irrational number
∴ Q⊂P
P∪Q= Q∪P = P
∴ Union of sets is commutative.
P∩Q = Q∩P = Q
∴ Intersection of sets is commutative.
![]()
Question 3.
If A = {p, q, r, s}, B = {m, n, q, s, t} and C = {m, n, p, q, s}, then verify the associative property of union of sets.
Solution:
When union of sets is associative
A∪(B∪C) = (A∪B)∪C
(B∪C) = {m, n, q, s, t) ∪ {m, n, p, q, s}
= {m, n, p, q, s, t}
A∪(B∪C) = {p, q, r, s} ∪ {m, n, p, q, s, t}
= {m, n, p, q, r, s, t} ……..(1)
(A∪B) = {p, q, r, s} ∪ {m, n, q, s, t}
= {m, n, p, q, r, s, t}
(A∪B)∪C = {m, n, p, q, r, s, t} ∪ {m, n, p, q, s}
= {m, n, p, q, r, s, t} ……….(2)
From (1) and (2) it is verified that A∪(B∪C) = (A∪B)∪C
![]()
Question 4.
Verify the associative property of intersection of sets for A = {-11, √2, √5, 7},
B = {√3, √5, 6, 13} and C = {√2, √3, √5, 9}.
Solution:
When intersection of sets is associative
A∩(B∩C) = (A∩B)∩C
(B∩C) = {√3, √5, 6, 13} ∩ {√2, √3, √5, 9}
= {√3, √5}
A∩(B∩C) = {-11, √2, √5, 7} ∩ {√3, √5}
{√5} ………(i)
(A∩B) = {-11, √2, √5, 7} ∩ {√3, √5 ,6, 13}
= {√5}
(A∩B)∩C = {√5} n {√2, √3, √5, 9}
= {√5}……..(2)
From (1) and (2) it is verified that A∩(B∩C) = (A∩B)∩C
![]()
Question 5.
If A={ x : x = 2n, n ∈ W and n < 4}, B = {x : x = 2n, n ∈ N and n ≤ 4} and C = {0, 1, 2, 5, 6}, then verify the associative property of intersection of sets.
Solution:
A = {x : x = 2n, n ∈ W and n < 4}
A = {1, 2, 4, 8}
B = {x : x = 2n, n ∈ N and n ≤ 4}
B = {2, 4, 6, 8}
C ={0, 1, 2, 5, 6}
When intersection of sets is associative
A∩(B∩C) = (A∩B)∩C
(B∩C) = {2, 4, 6, 8} ∩ {0, 1, 2, 5, 6}
= {2, 6}
A∩(B∩C)= {1 ,2, 4, 8} ∩ {2, 6}
= {2}……….(1)
(A∩B) = {1, 2, 4, 8} ∩ {2, 4, 6, 8}
= {2, 4, 8}
(A∩B)∩c= {2, 4, 8} n {0, 1, 2, 5, 6}
= {2}………..(2)
From (1) and (2) we get A∩(B∩C) = (A∩B)∩C
![]()