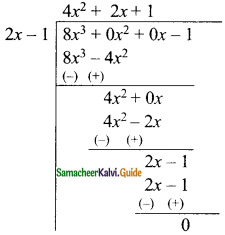
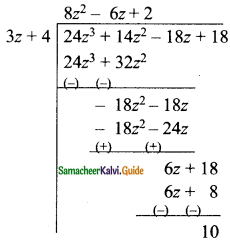
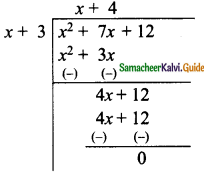
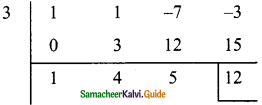
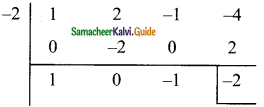
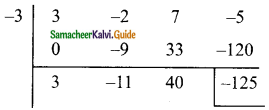
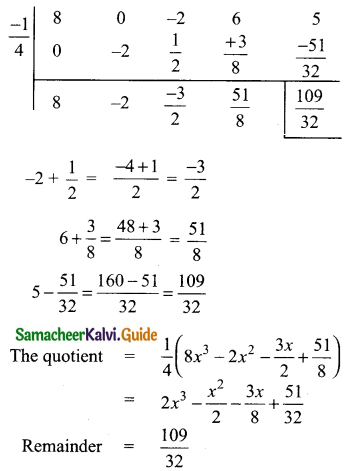
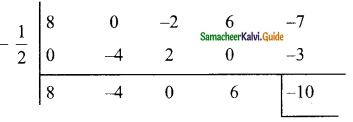
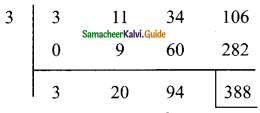
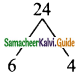
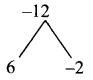
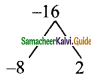
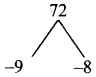
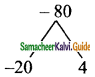
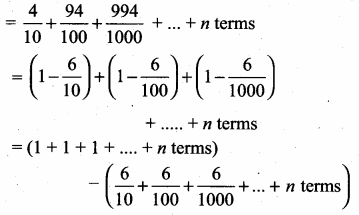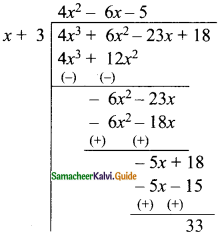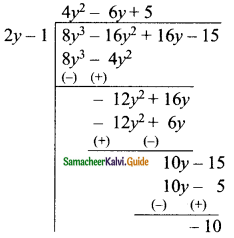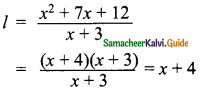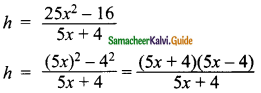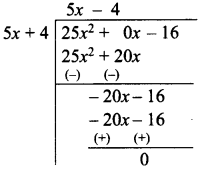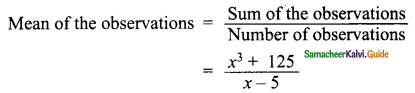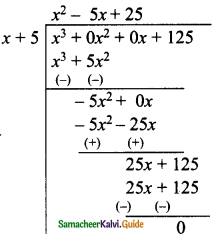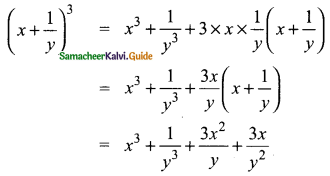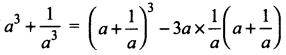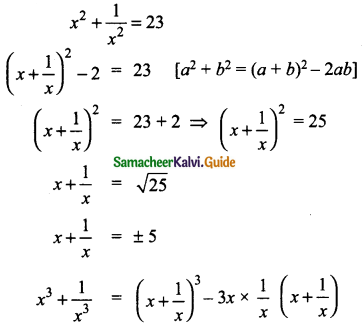Students can download Maths Chapter 5 Coordinate Geometry Ex 5.1 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Coordinate Geometry Ex 5.1
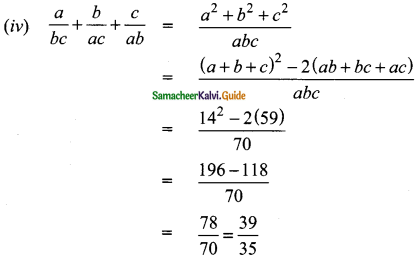
Question 1.
Plot the following points in the coordinate system and identify the quadrants P(-7, 6), Q(7, -2), R(-6, -7), S(3, 5) and T(3, 9)
Solution:
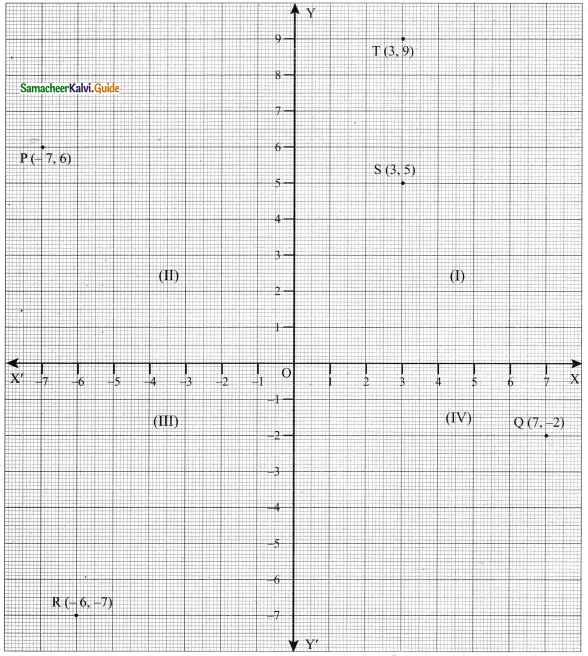
(i) P(-7, 6) lies in the II quadrant because the x-coordinate is negative and y-coordinate is positive.
(ii) Q(7, -2) lies in the IV quadrant because the x-coordinate is positive and y-coordinate is negative.
(iii) R(-6, -7) lies in the III quadrant because the x-coordinate is negative and y-coordinate is negative.
(iv) S(3, 5) lies in the I quadrant because the x-coordinate is positive and y-coordinate is also positive.
(v) T(3, 9) lies in the I quadrant because the x-coordinate is positive and y-coordinate is also positive.
![]()
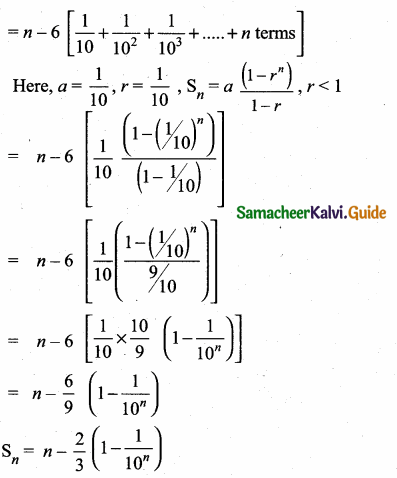
Question 2.
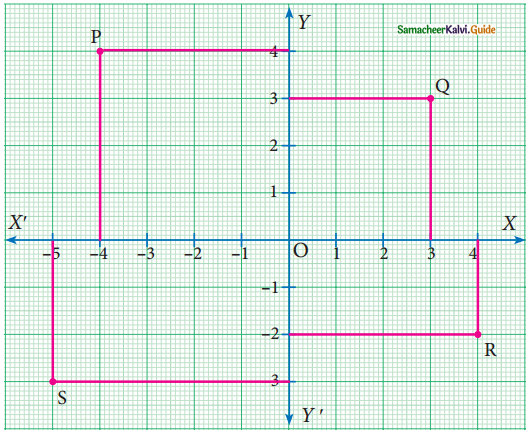
Write down the abscissa and ordinate of the following.
(i) P
(ii) Q
(iii) R
(iv) S
Solution:
(i) P is (-4, 4) [-4 is abscissa and 4 is ordinate]
(ii) Q is (3, 3) [3 is abscissa and 3 is ordinate]
(iii) R is (4, -2) [4 is abscissa and -2 is ordinate]
(iv) S is (-5, -3) [-5 is abscissa and -3 is ordinate]
![]()
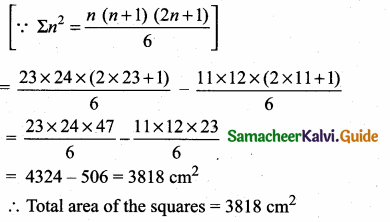
Question 3.
Plot the following points in the coordinate plane and join them. What is your conclusion about the resulting figure?
(i) (-5, 3) (-1, 3) (0, 3) (5, 3)
Solution:
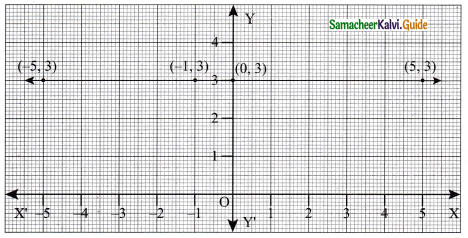
Straight line parallel to x-axis.
![]()
(ii) (0, -4) (0, -2) (0, 4) (0, 5)
Solution:
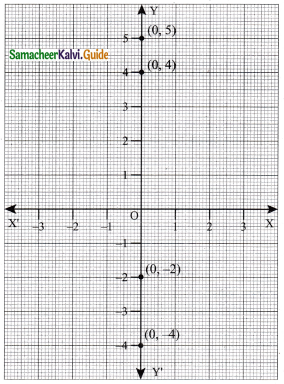
The line is on the y-axis.
![]()
Question 4.
Plot the following points in the coordinate plane. Join them in order. What type of geometrical shape is formed?
(i) (0, 0) (-4, 0) (-4, -4) (0, -4)
Solution:
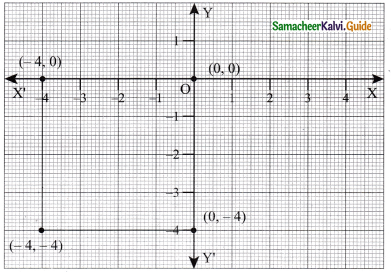
The geometrical shape of the figure is square.
![]()
(ii) (-3, 3) (2, 3) (-6, -1) (5, -1)
Solution:
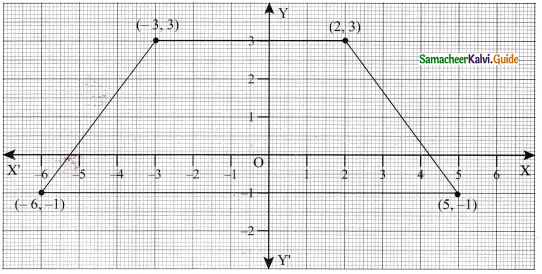
The shape of the geometrical figure is Trapezium.
![]()