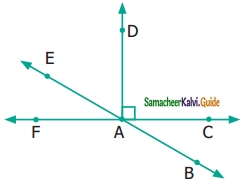
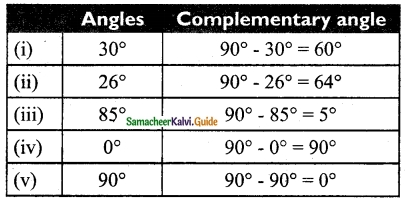
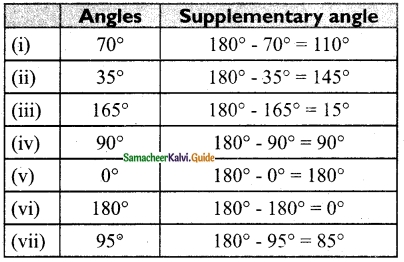
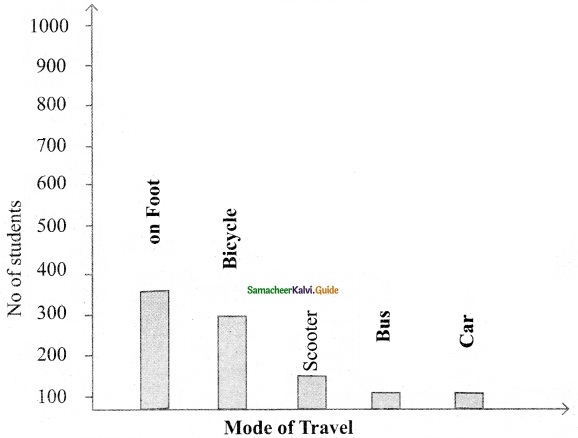
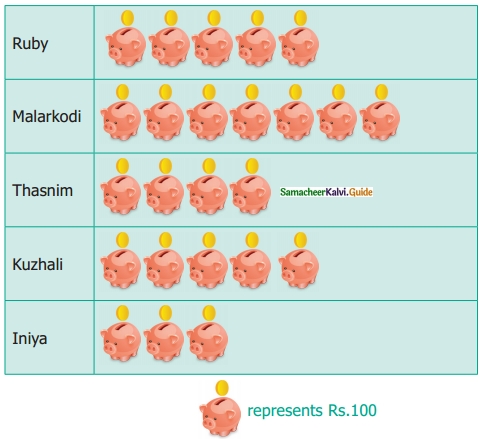
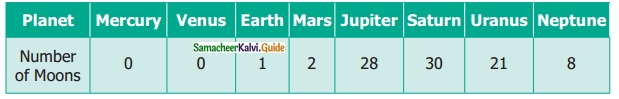
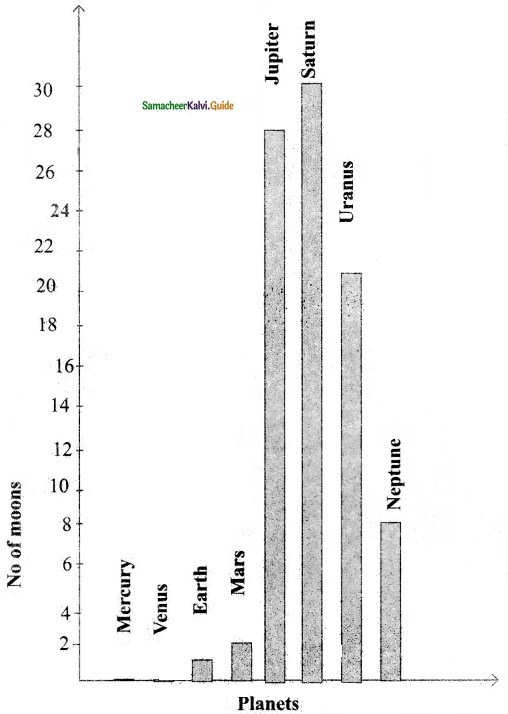
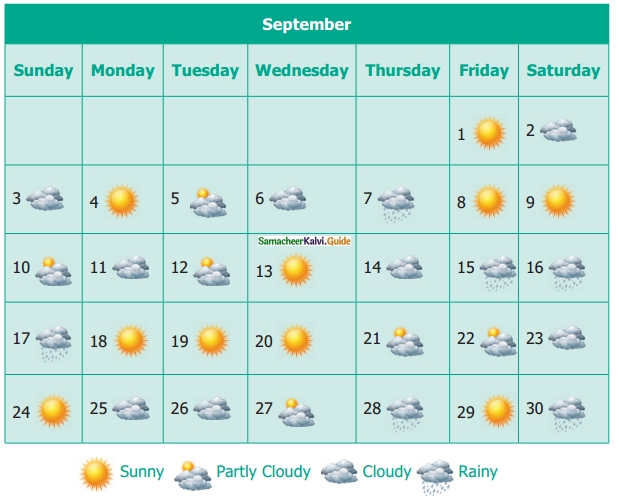
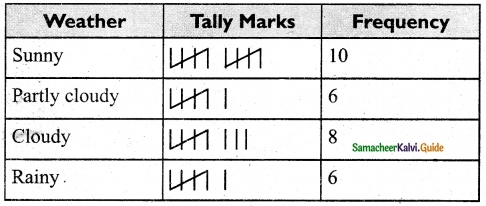
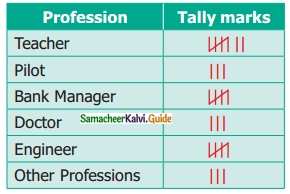
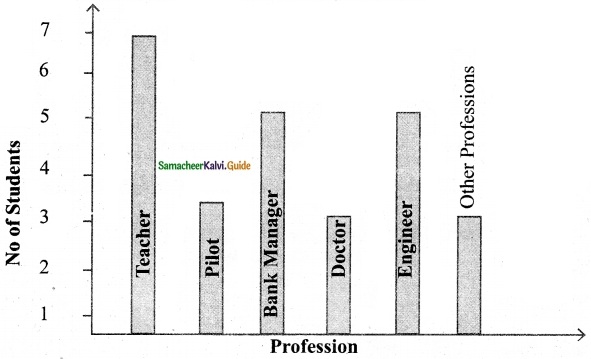
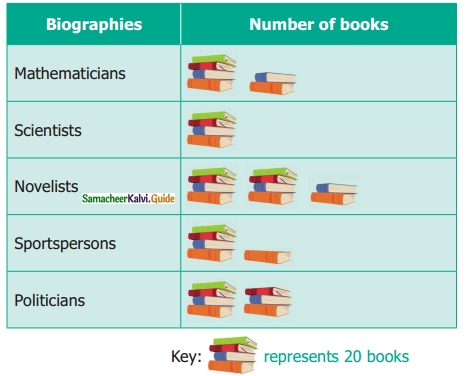
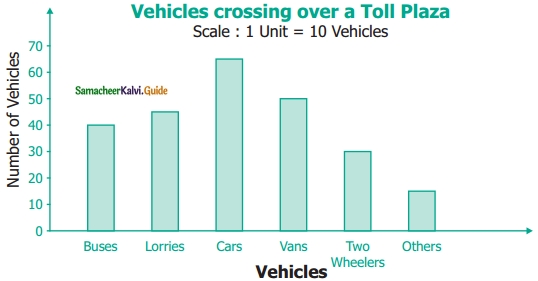
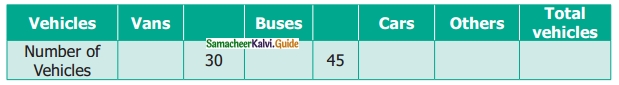
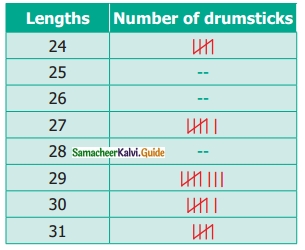
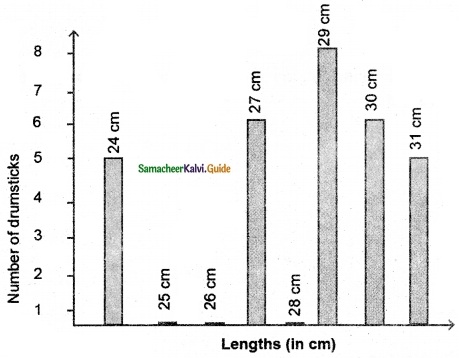
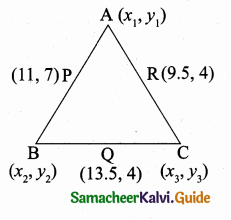
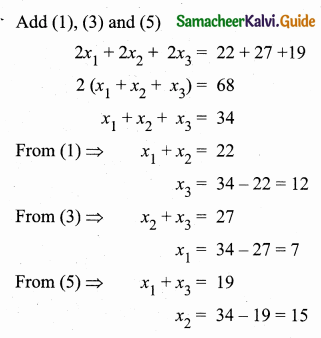
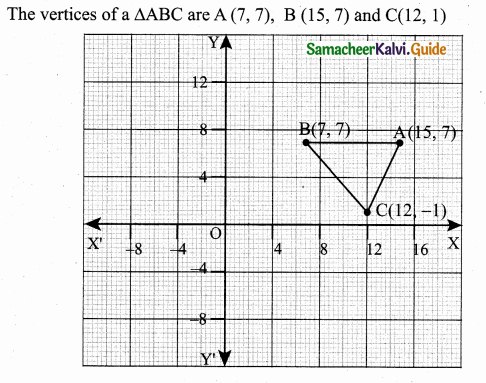
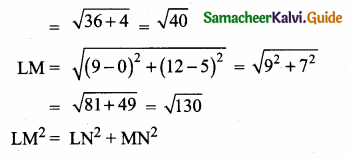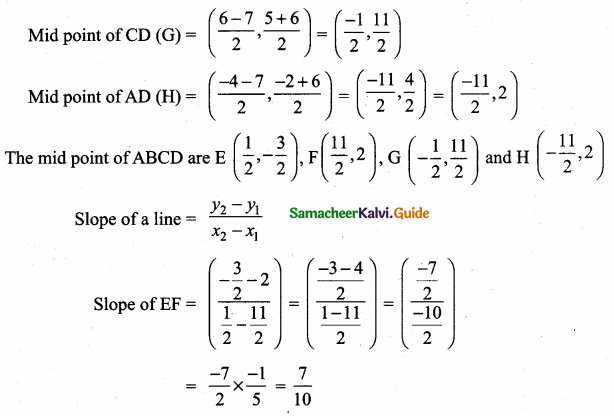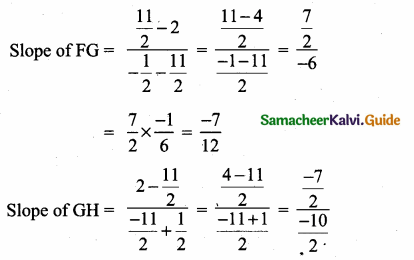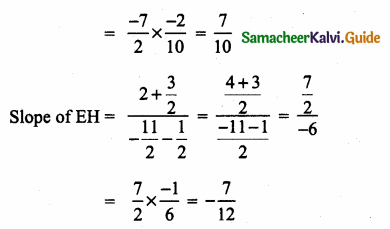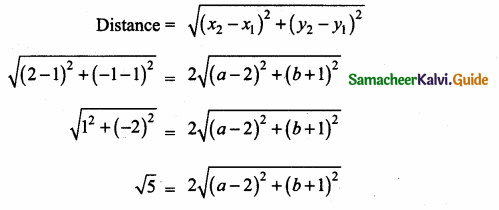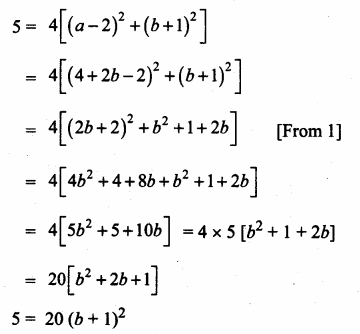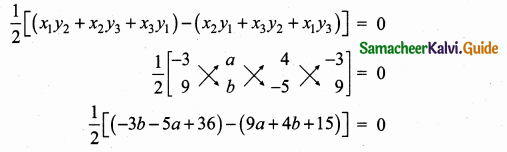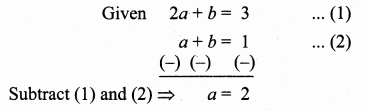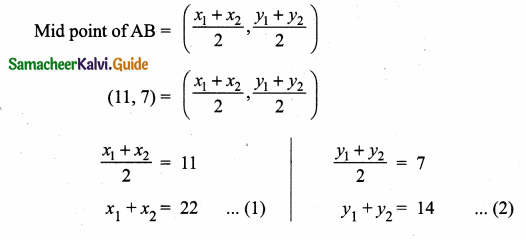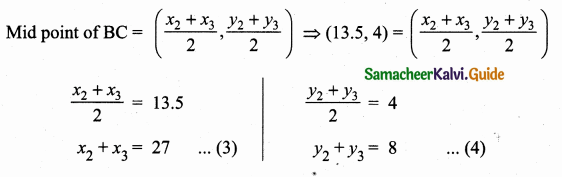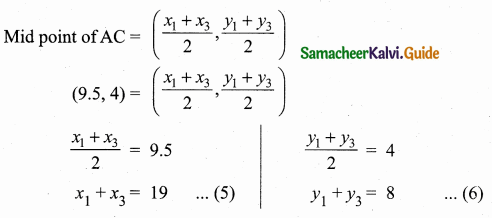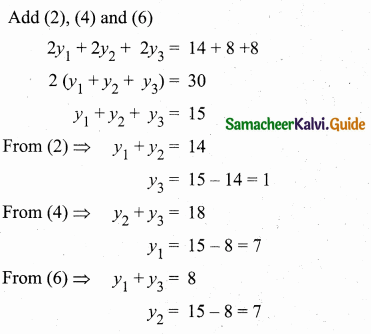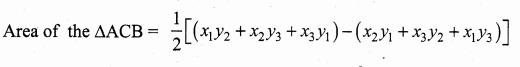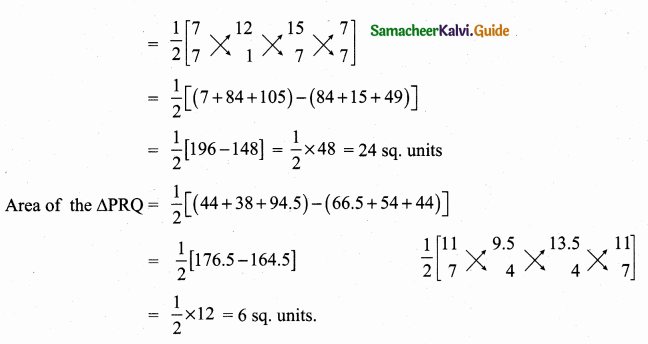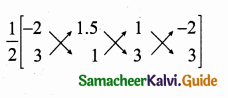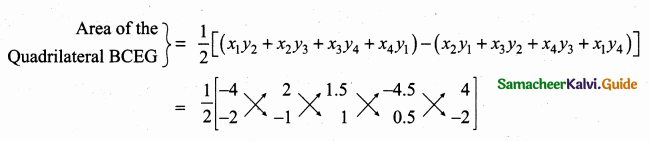Students can download Maths Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.3 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.3
Miscellaneous Practice Problems
Question 1.
What are the angles of an isosceles right-angled triangle?
Solution:
Since it is a right-angled triangle
One of the angles is 90°
The other two angles are equal because it is an isosceles triangle.
The other two angles must be 45° and 45°
Angles are 90°, 45°, 45°.
Question 2.
Which of the following correctly describes the given triangle?
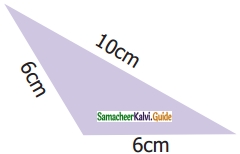
(a) It is a right isosceles triangle
(b) It is an acute isosceles triangle
(c) It is an obtuse isosceles triangle
(d) It is an obtuse scalene triangle
Solution:
(c) It is an obtuse isosceles triangle
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following is not possible?
(a) An obtuse isosceles triangle.
(b) An acute isosceles triangle.
(c) An obtuse equilateral triangle.
(d) An acute equilateral triangle.
Solution:
(c) An obtuse equilateral triangle.
Question 4.
If one angle of an isosceles triangle is 124°, then find the other angles
Solution:
In an isosceles triangle, any two sides are equal. Also, the two angles are equal.
Sum of three angles of a triangle = 180°
Given one angle = 124°
Sum of other two angles = 180° – 124° = 56°
Other angles are = \(\frac{56}{2}\) = 28°
28° and 28°.
Question 5.
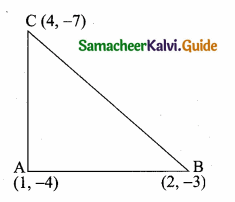
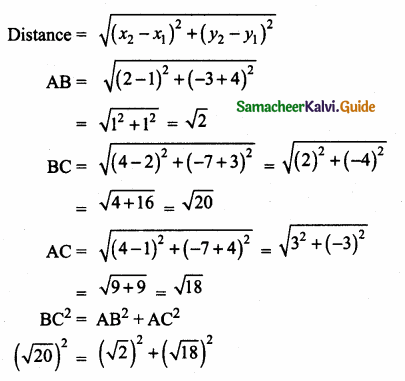
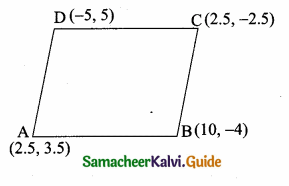
The diagram shows a square ABCD. If the line segment joins A and C, then mention the type of triangle so formed.
Solution:
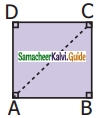
Isosceles right-angled triangles
![]()
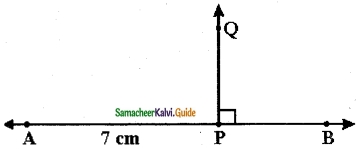
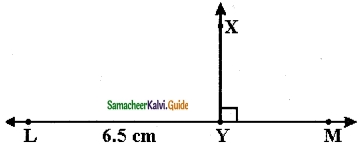
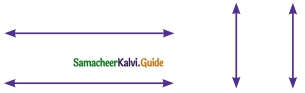
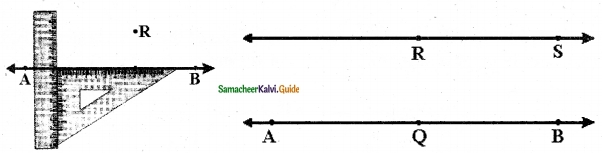
Question 6.
Draw a line segment AB of length 6 cm. At each end of this line segment AB, draw a line perpendicular to the line segment AB. Are these lines parallel?
Solution:
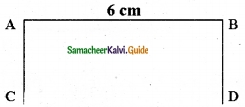
yes, they are parallel
Challenge Problems
Question 7.
Is a triangle possible with the angles 90°, 90°, and 0°, Why?
Solution:
No, a triangle cannot have more than one right angle.
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following statements is true? Why?
(a) Every equilateral triangle is an isosceles triangle.
(b) Every isosceles triangle is an equilateral triangle
Solution:
“(a)” is true, because an isosceles triangle need not have three equal sides
Question 9.
If one angle of an isosceles triangle is 70°, then find the possibilities for the other two angles.
Solution:
(i) Given one angle = 70°
Also, it is an isosceles triangle.
Another one angle also can be 70°.
Sum of these two angles = 70° + 70° = 140°
We know that the sum of three angles in a triangle = 180°.
Third angle = 180° – 140° = 40°
One possibility is 70°, 70°, and 40°
(ii) Also if one angle is 70°
Sum of other two angles = 180° – 70° = 110°
Both are equal. They are \(\frac{110}{2}\) = 55°.
Another possibility is 70°, 55° and 55°.
Question 10.
Which of the following can be the sides of an isosceles triangle?
(a) 6 cm, 3 cm, 3 cm
(b) 5 cm, 2 cm, 2 cm
(c) 6 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm
(d) 4 cm, 4 cm, 8 cm
Solution:
(c) 6 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm
![]()
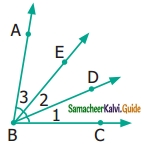
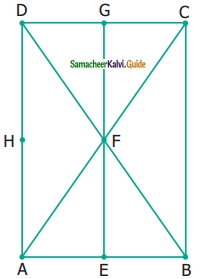
Question 11.
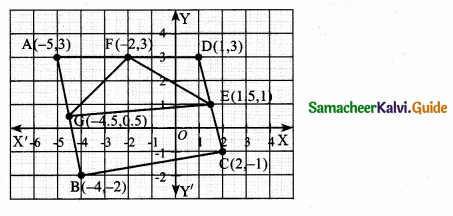
Study the given figure and identify the following triangles,
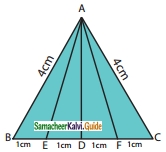
(a) equilateral triangle
(b) isosceles triangle
(c) scalene triangles
(d) acute triangle
(e) obtuse triangle
(f) right triangle
Solution:(a) BC = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4 cm
AB = AC = 4 cm
∆ABC is an equilateral triangle.
(b) ∆ABC and ∆AEF are isosceles triangles.
Since AB = AC = 4 cm Also AE = AF.
(c) In a scalene triangle, no two sides are equal.
∆AEB, ∆AED, ∆ADF, ∆AFC, ∆ABD, ∆ADC, ∆ABF, and ∆AEC are scalene triangles.
(d) In an acute-angled triangle all the three angles are less than 90°.
∆ABC, ∆AEF, ∆ABF, and ∆AEC are acute-angled triangles.
(e) In an obtuse-angled triangle any one of the angles is greater than 90°.
∆AEB and ∆AFC are obtuse angled triangles.
(f) In a right triangle, one of the angles is 90°.
∆ADB, ∆ADC, ∆ADE, and ∆ADF are right-angled triangles.
![]()
Question 12.
Two sides of the triangle are given in the table. Find the third side of the triangle.
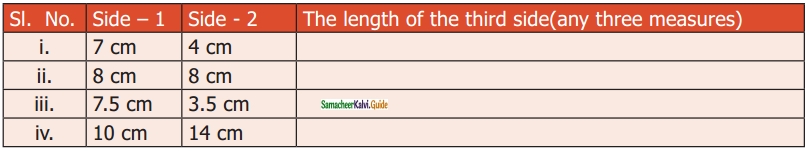
Solution:
(i) between 3 and 11
(ii) between 0 and 16
(iii) between 4 and 11
(iv) between 4 and 24
![]()
Question 13.
Complete the following table:
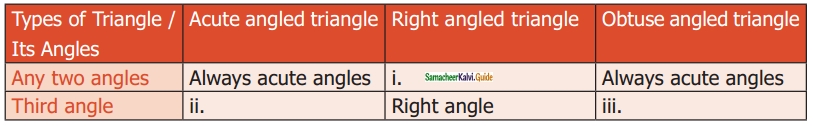
Solution:
(i) Always acute angles
(ii) Acute angle
(iii) Obtuse angle