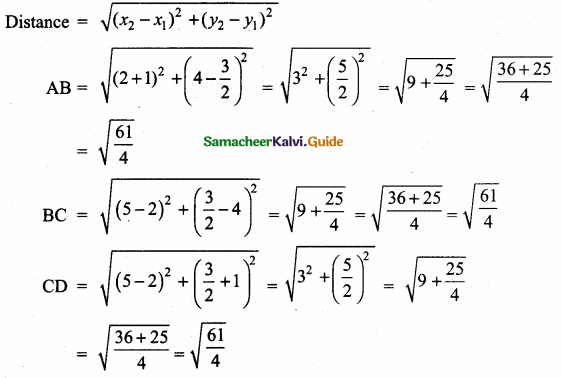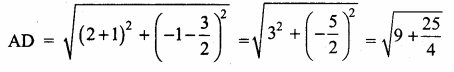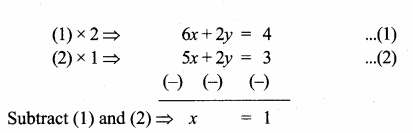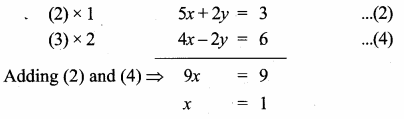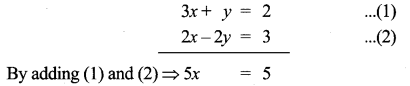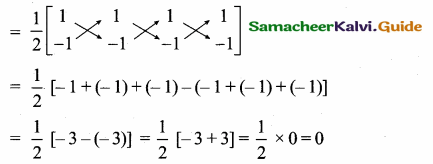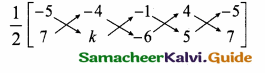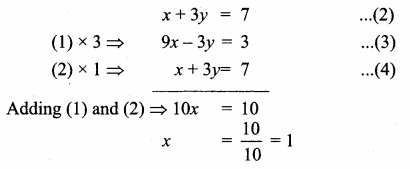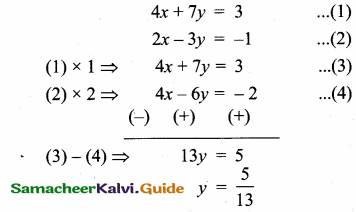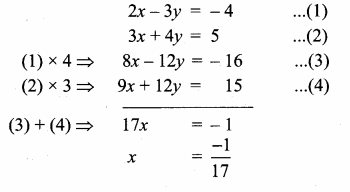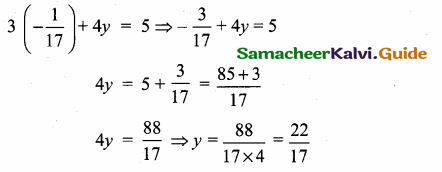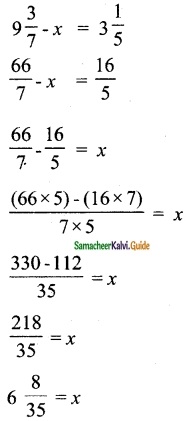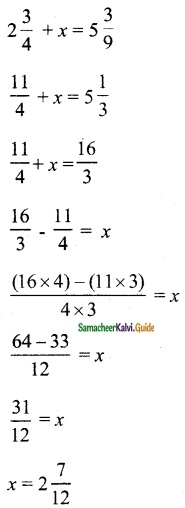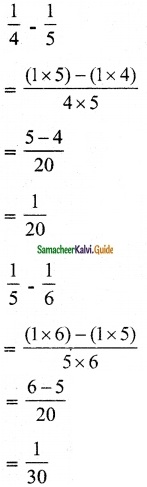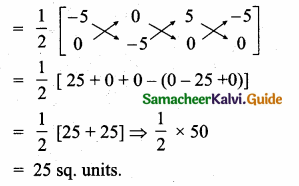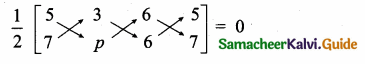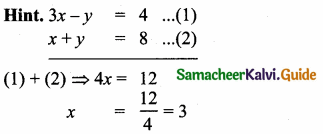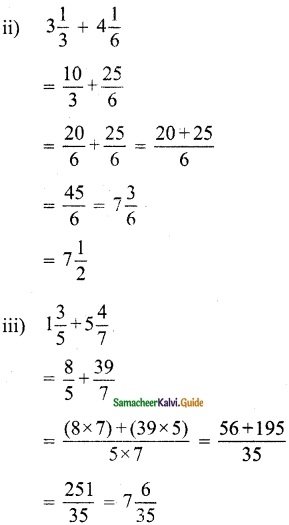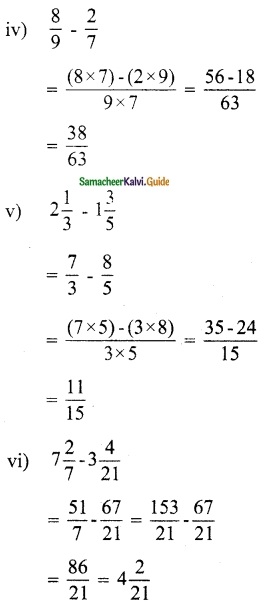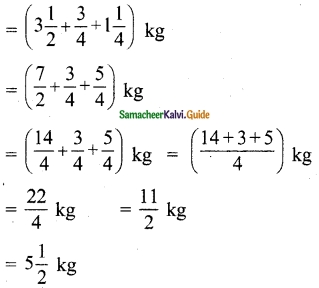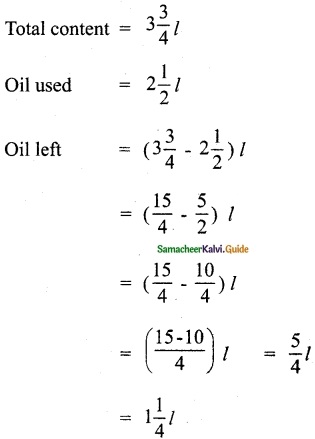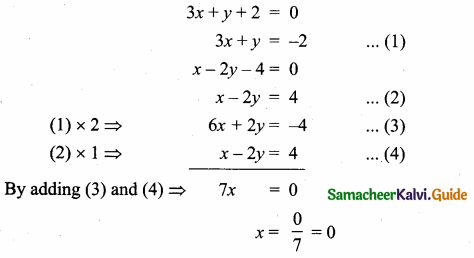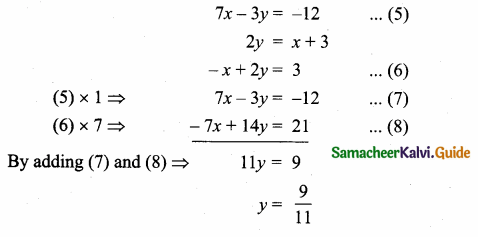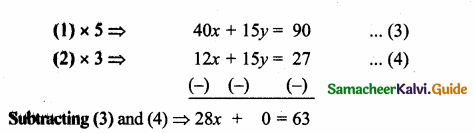Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Applications of Matrices and Determinants Ex 1.3 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Applications of Matrices and Determinants Ex 1.3
Question 1.
Solve the following system of linear equations by matrix inversion method.
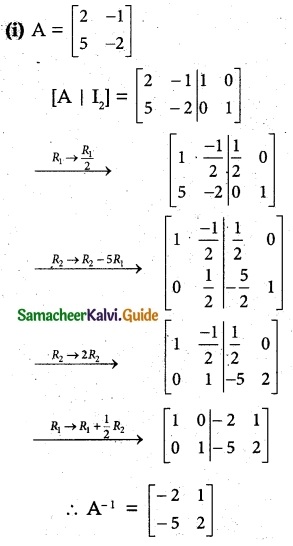
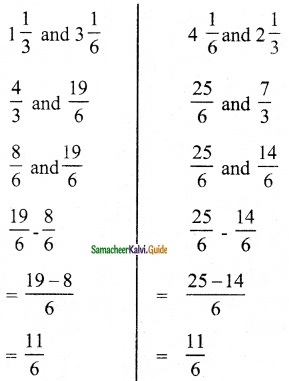
(i) 2x + 5y = -2, x + 2y = -3
Solution:

![]()
(ii) 2x – y = 8, 3x + 2y = -2
Solution:
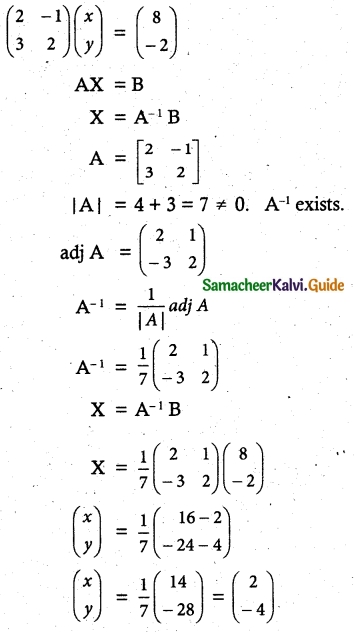
x = 2, y = -4
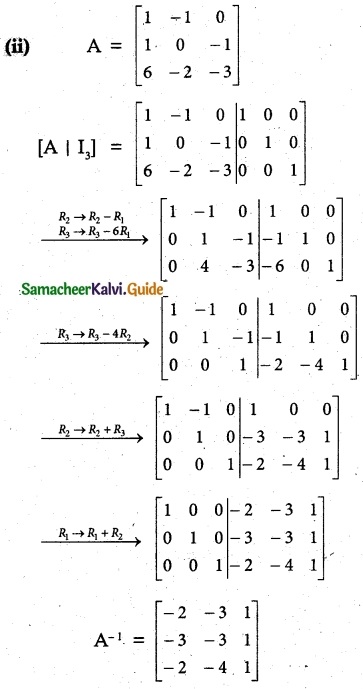
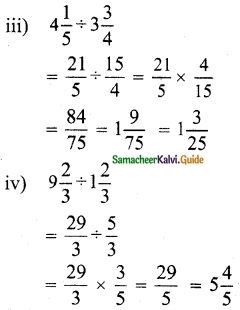
(iii) 2x + 3y – z = 9, x + y + z = 9, 3x – y – z = -1
Solution:
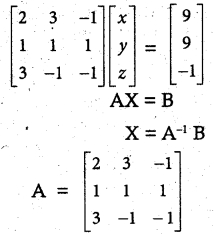
|A| = 2(-1+1)-3(-1-3)-1(-1-3)
= 0 + 12 + 4 =16 ≠ 0 A-1 exists.
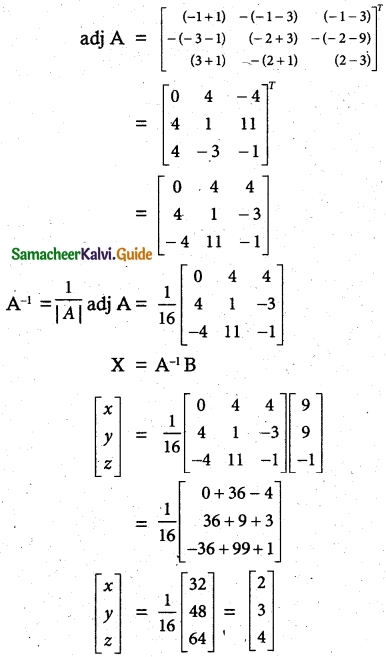
∴ x = 2, y = 3, z = 4
![]()
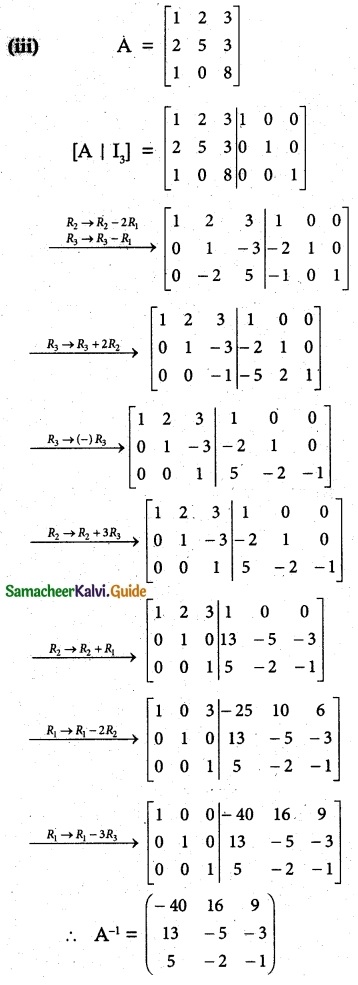
(iv) x + y + z – 2 = 0, 6x – 4y + 5z – 31 = 0, 5x + 2y + 2z = 13
Solution:
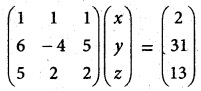
AX = B
X = A-1B
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 1 & 1 \\
6 & -4 & 5 \\
5 & 2 & 2
\end{array}\right]\)
|A| = 1(-8-10)-1(12-25)+1(12+20)
= 18 + 13 +32 = 27
≠ 0
A-1 Exists
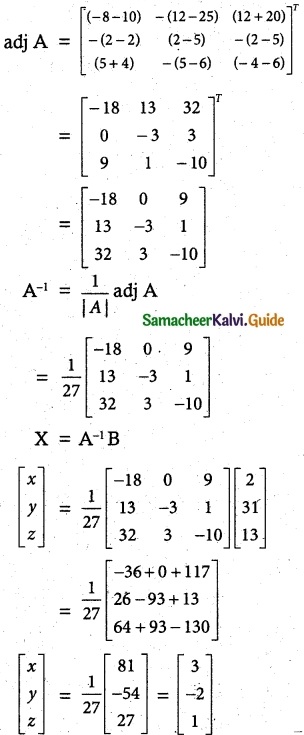
∴ x = 3, y = -2, z = 1
![]()
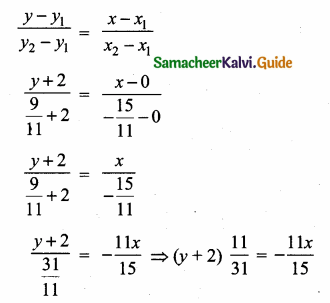
Question 2.
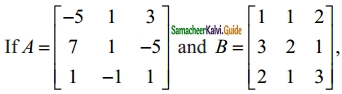
Find the products AB and BA and hence solve the system of equations x + y + 2z = 1, 3x + 2y + z = 7, 2x + y + 3z = 2
Solution:
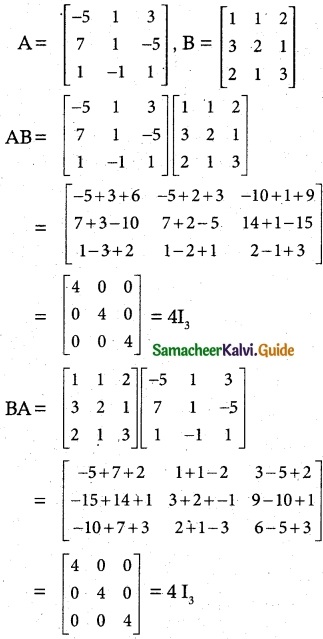
AB = BA = 4I3
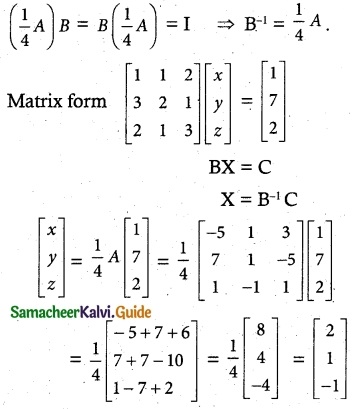
∴ x = 2, y = 1, z = -1
![]()
Question 3.
A man is appointed in a job with a monthly salary of a certain amount and a fixed amount of annual increment. If his salary was Rs 19,800 per month at the end of the first month after 3 years of service and Rs 23,400 per month at the end of the first month after 9 years of service, find his starting salary and his annual increment. (Use the matrix inversion method to solve the problem.)
Solution:
Let the man starting the salary be Rs x and his annual increment be Rs y.
Given x + 3y = 19,800
x + 9y = 23,400
The equation can be written as
\(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
1 & 3 \\
1 & 9
\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l}
x \\
y
\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{c}
19800 \\
23400
\end{array}\right]\)
AX = B
X = A-1B
A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ll}
1 & 3 \\
1 & 9
\end{array}\right]\)
To find A-1
|A| = 9 – 3 = 6 ≠ 0 A-1 Exists.
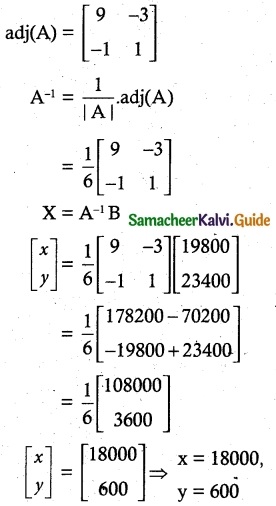
Monthly salary = Rs 18000
Annual increment = Rs 1800
![]()
Question 4.
4 men and 4 women can finish a piece of work jointly in 3 days while 2 men and 5 women can finish the same work jointly in 4 days. Find the time taken by one man alone and that of one woman alone to finish the same work by Using the matrix inversion method.
Solution:
Let the time taken by one man alone be x days and one woman alone be y days.
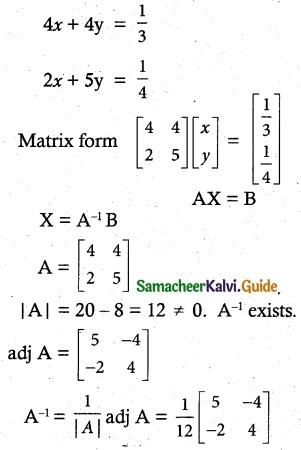
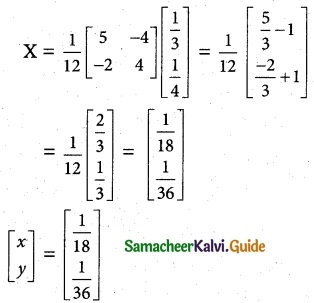
∴ One man can do 18 days
One woman can do 36 days
![]()
Question 5.
The prices of three commodities A, B, and C are Rs x,y, and z per unit respectively. A person P purchases 4 units of B and sells two units of A and 5 units of C. Person Q purchases 2 units of C and sells 3 units of A and one unit of B. Person R purchases one unit of A and sells 3 unit of B and one unit of C. In the process, P, Q and R earn Rs 15,000, Rs 1,000 and 14,000 respectively. Find the prices per unit of A, B, and C. (Use the matrix inversion method to solve the problem.)
Solution:
Let x, y, z are commodities of A, B, C
2x – 4y + 5z = 15,000 ………… (1)
3x + y – 2z = 1000 ………… (2)
-x + 3y + z = 4000 ………… (3)
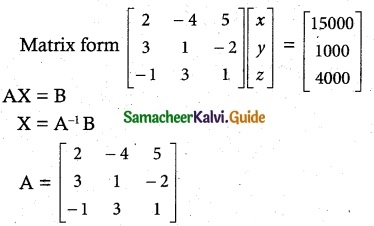
|A| = 2(1 + 6)+ 4(3 – 2) + 5(9 + 1)
= 2(7) + 4(1) + 5(10)
= 14 + 4 + 50 = 68
≠ 0
A-1 Exists.
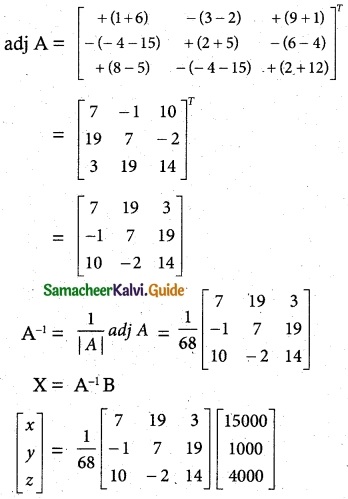
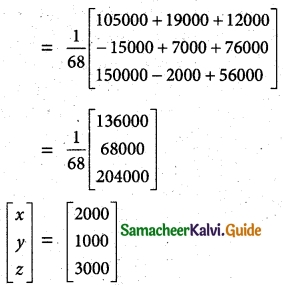
x = Rs 2000, y = Rs 1000, z = Rs 3000
The prices per unit of A, B, and C are Rs 2000, Rs 1000, Rs 3000
![]()