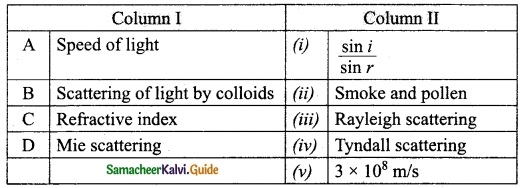
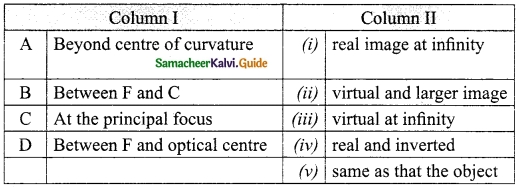
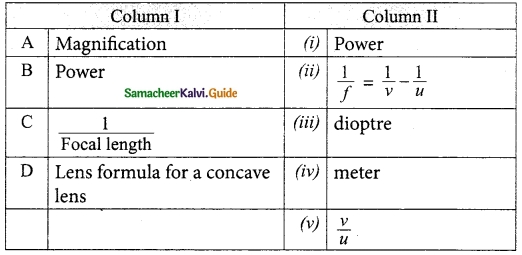
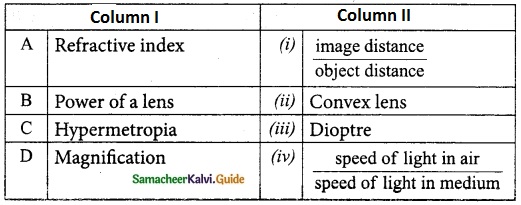
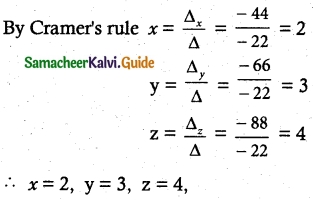
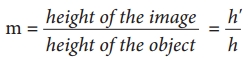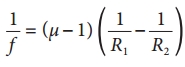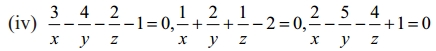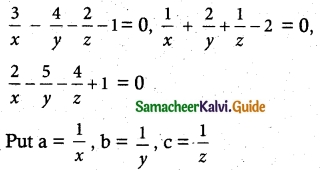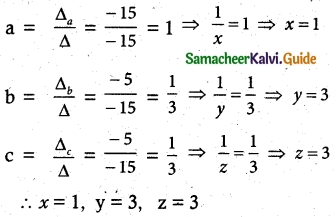Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th English Model Question Paper 4 Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th English Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 12th English Model Question Paper 4
![]()
Time: 2 1/2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the sections in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding option code.
- Part II has got two sections. The questions are of two marks each. Question numbers 21 to 26 in Section I and Question numbers 27 to 30 in Section II are to be answered in about one or two sentences each.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are of three marks each and have been divided in three sections. These are to be answered as directed.
- Question numbers 41 and 47 in Part IV are of five marks each. These are to be answered as directed.
![]()
Part -1
I. Answer all the questions. [20 x 1= 20]
Choose the correct synonyms for the underlined words from the options given:
Question 1.
Of the rest, many will end up as mental or physical cripples.
(a) rare gifts (b) able-bodied (c) disabilities (d) perfect health
Answer:
(c) disabilities
Question 2.
Little dangling baskets under the spout to catch the stray leaves.
(a) loose (b) gathered (c) harmful (d) fresh
Answer:
(a) loose
Question 3.
They were doing brisk business in the public square.
(a) dull (b) indolent (c) lethargic (d) active
Answer:
(d) active
![]()
Choose the correct antonyms for the underlined words from the options given:
Question 4.
The trolley was commandeered by the two boys.
(a) snatched (b) abandoned (c) usurped (d) hijacked
Answer:
(b) abandoned
Question 5.
The advent of brain-machine interfaces is certain to blur the boundary between humans and machines.
(a) departure (b) danger (c) drawback (d) dispute
Answer:
(d) dispute
Question 6.
Makalu was unexplored.
(a) expelled (b) explained (c) explored (d) expedited
Answer:
(c) explored
Question 7.
Choose the correct combination for the compound word light show.
(a) Noun + Verb (b) Verb + Noun (c) Noun- + Gerund (d) Preposition + Noun
Answer:
(a) Noun + Verb
![]()
Question 8.
Choose the correct expansion of NSC.
(a) National Savings Certificate (b) National Service Certificate (c) National Savings Career (d) National Service Certificate
Answer:
(a) National Savings Certificate
Question 9.
Choose the meaning of the foreign word in the sentence: My cousin Charlotte is a real klutz.
(a) stranger (b) thief (c) clumsy fool (d) coward
Answer:
(c) clumsy fool
Question 10.
Choose the right combination for the blended word Bionic.
(a) Bio + Electric (b) Biology + Electronic (c) Bio + Nic (d) Biology + Nic
Answer:
(b) Biology + Electronic
Question 11.
Choose the clipped word for dormitory.
(a) dormi (b) doritory (c) dory (d) dorm
Answer:
(d) dorm
![]()
Question 12.
A craze for establishing banks is known as …………………… .
(a) monotonist (b) islomania (c) bancomania (d) barbarian
Answer:
(c) bancomania
Question 13.
Form a derivative by adding the right prefix to the word ‘open’.
(a) re- (b) en- (c) un (d) dis-
Answer:
(a) re-
Question 14.
Fill in the blanks with a suitable relative pronoun.
I have a friend …………………….. cat is very cute.
(a) which (b) whom (c) whose (d) when
Answer:
(c) whose
![]()
Question 15.
Fill in the blanks with a suitable preposition.
I heard that news …………………….. the radio.
(a) in (b) on (c) at (d) through
Answer:
(b) on
Question 16.
Choose the correct question tag for the following statement.
He reads a lot of comics, ……………………..?
(a) should he (b) won’t he (c) will he (d) doesn’t he
Answer:
(d) doesn’t he
Question 17.
Choose the suitable meaning or idiom found in the following sentence.
Sumathi was sick of bending over backwards to entertain her nieces.
(a) doing gymnastics (b) dancing (c) trying very hard (d) doing yoga
Answer:
(c) trying very hard
![]()
Question 18.
Substitute the underlined word with the appropriate polite alternative.
Till the next trial, the suspects will be kept in the prison camp.
(a) relocation center (b) jail (c) dungeon (d) dormitory
Answer:
(a) relocation center
Question 19.
Choose the correct sentence pattern for the following sentence.
We aren’t complaining.
(a) SVIODO (b) SVC (c) SVO (d) SVCA
Answer:
(b) SVC
Question 20.
Fill in the blank with a suitable phrasal verb.
The following afternoon we …………………….. the tiny village set high upon the hillside.
(a) set aside (b) called on (c) got away (d) drove to
Answer:
(d) drove to
![]()
Part II
Section -1
Read the following sets of poetic lines and answer any four from it. [4 x 2 = 8]
Question 21.
“For what, we thought, had we to fear
With our arms and provender, load on load,”
(a) What was the mood of the soldiers?
(b) What made the soldiers confident?
Answer:
(a) The soldiers were confident of winning the war.
(b) They had enough grains to survive a siege and plenty of arms to fight the war. These things made them confident.
Question 22.
“…………….. Free imaginations
Bringing changes into a world resenting change.”
(a) How does free imagination help the world?
(b) Identify the figure of speech.
Answer:
(a) Free imagination brings changes in the world.
(b) Personification
![]()
Question 23.
“Death closes all: but something ere the end,
Some work of noble note, may yet be done,
Not unbecoming men that strove with Gods.”
(a) The above lines convey the undying spirit of Ulysses. Explain.
(b) Pick out the words in alliteration in the above lines.
Answer:
(a) Ulysses is aware of ageing and substantial decrease in his physical strength. He knows that will close in on him sooner or later. But before that happens, he wants to sail beyond the sunset/horizon and if possible meet warriors like Achilles. He wants to achieve something worthy of those who challenged and fought with Gods. Thus these lines show the undying spirit of Ulysses.
(b) ere, end noble, note are the words that alliterate.
Question 24.
“And then the lover,
Sighing like furnace, with a woeful ballad
Made to his mistress’ eyebrow.”
(a) What does the lover do for his mistress?
(b) Explain, ‘sighing like furnace’.
Answer:
(a) The lover is always sighing and longing for his beloved. He writes a sad ballad describing the eyebrow of his mistress.
(b) It means moaning, breathing deeply and sadly like a fire place.
![]()
Question 25.
“But not because of its magnificence Dear is the Casuarina to my soul:
Beneath it we have played; though years may roll,”
(a) What is not the cause for Toru Dutt’s love for the Casuarina tree?
(b) What makes the tree dear to the poet?
Answer:
(a) As children, the poet and her friends had played under the tree. This experience has made the tree dear to the poet.
(b) The poet is unable to forget the wonderful time she had under the tree with her friends.
Question 26.
“Just as perhaps he mused, ‘My plans’
That soar, to earth may fall,”
(а) What may hamper the soaring plans of Napoleon?
(b) What is the figure of speech employed in these lines?
Answer:
(a) The negative outcome of battle at Ratisbon may hamper his soaring plans.
(b) ‘plans that soar’ – Metaphor.
![]()
Section – 2
Answer any three of the following questions. [3 x 2 = 6]
Question 27.
Report the following dialogue:
Answer:
Lady to the Judge : This man is responsible for the accident.
Man : No, my Lord. This lady does not know how to drive a car.
The lady told the Judge that, that man was responsible for the accident. The man denied the lady’s statement respectfully and said that that lady did not know how to drive a car.
Question 28.
Obey the traffic rules. Otherwise, you will be prosecuted, (combine using if)
Answer:
If you do not obey the traffic rules, you will be prosecuted.
Question 29.
Rewrite the sentence making an inversion in the conditional clause.
If you don’t wish to sign the contract, you must let them know by the end of this month.
Answer:
Should you not wish to sign the contract, you must let them know by the end of this month.
![]()
Question 30.
When he walked through the wood, he saw a fox that was following him.(Change the following into a simple sentence)
Answer:
Walking through the wood, he saw a fox following him.
Part-III
Section -1
Explain any two of the following with reference to the context. [2 x 3 = 6]
Question 31.
Unto thy honor, Tree, beloved of those Who now in blessed sleep for aye repose,
Answer:
Reference: These lines are from the poem, ‘Our Casuarina Tree’ written by Torn Dutt.
Context: The poet says this while consecrating the memories of the tree to the dear departed.
Explanation: The poet wants to freeze the love for the Casuarina tree in her poem. She remembers with pain three younger Dutts who had succumbed to Tuberculosis. She remembers with poignance the numerous days they had spent under the Casuarina tree.
![]()
Question 32.
We are not now that strength which in old days Moved earth and heaven;
Answer:
Reference: These lines are from the poem, ‘Ulysses’ written by Alfred Tennyson.
Context: The poet says these words through Ulysses when he wants to justify the reasons for resuming the daring voyage.
Explanation: Ulysses admits the decline in the compatriots’ physical strength with which they were able to move heaven and earth in their youth. He asks his compatriots to ignore the infinity of age and draw on their inner spiritual strength to resume their voyage beyond sunset.
Question 33.
Then off there flung in smiling joy,
And held himself erect
Answer:
Reference: These words are from the poem, ‘Incident of the French Camp” written by Robert Browning.
Context: The narrator says these words while describing the arrival of a boy soldier at the mound where Napoleon was anxiously awaiting news about the battle.
Explanation: Even though the boy-soldier was split into two, he sped fast in a horse amidst the smoke of cannon fire. On seeing Napoleon he jumped off the horse with a beaming face. Being at the verge of embracing death, he declared the good news that they had won the battle.
![]()
Section – 2
Answer any two of the following questions in about 30 words. [2 x 3 = 6]
Question 34.
What were the boys doing at night in a deserted square?
Answer:
The boys were resting on the stone pavement in the windy and deserted square beneath the street light. They were waiting for the last bus from Padua to sell the unsold newspapers.
Question 35.
What are the subsidiary uses of tea leaves?
Answer:
Telling fortunes, predicting the arrival of visitors, feeding rabbits, healing bums and sweeping the carpet are some of the subsidiary’s uses of tea leaves.
Question 36.
When did Hillary feel a sense of freedom and well being?
Answer:
Firsdtly, their partly-filled bottle of oxygen got exhausted. They had only one oxygen bottle to carry. With reduced load of 20 litre bottle, Hillary cut steps down off the South Summit. So, he felt a sense of freedom and well-being.
![]()
Section – 3
Answer any three of the following questions in about 30 words. [3 x 3 = 9]
Question 37.
Study the pie chart given and answer the questions that follow.
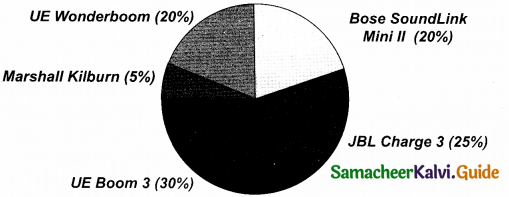
Popular Brands of Bluetooth Speakers
(a) Which is the most favourite brand of bluetooth speaker?
(b) Name the brand preferred by the least number of customers?
(c) Which two brands have equal number of customers?
Answer:
(a) UE Boom 3 is the most favourite brand preferred by the customers.
(b) Marshall Kilburn is the least preferred brand.
(c) UE Wonderbbom and Bose SoundLink Mini II.
Question 38.
Write a dialogue of minimum 3 exchanges between two friends discussing about a Book Fair.
Answer:
Rajini : Did you visit the Book Fair that started last week?
Ravi : Yes, I did. I was in fact waiting for the Book Fair to start.
Rajini : I know that you are a Voracious reader. How many did you buy?
Ravi : I bought a couple of mystery and detective novels by Tamizhvanan, Agatha Christie and Sujatha. What are you planning to buy?
Rajini : I need to buy a good set of Encyclopedias
Ravi : Do you want me to accompany you? I too want to buy some books published by Scholastic India.
![]()
Question 39.
Describe the process of making ice cream.
Answer:
Boil one litre of milk till it becomes thick and creamy and is reduced to one fourth its quantity. Add sugar to taste.
Keep aside five tablespoons of cold milk and mix two heaped spoons of ice cream powder. Pour the ice cream powder mixed milk to the boiling milk and stir continuously till it thickens. Add two drops of vanilla, strawberry or chocolate essence to taste and stir well.
After it cools, freeze for four hours.
Question 40.
Complete the proverbs using the word given below.
(a) He who hesitates is (gone, lost, dead)
(b) If God had meant us to fly, he would have given us (wings, cars, tails)
Answer:
(c) Little pitchers have big (ears, mouths, bottom)
(a) lost (b) wings (c) bottom
![]()
Part – IV
Answer the following questions: [7 x 5 = 35]
Answer in a paragraph in about 150 words.
Question 41.
What are the aspects that contribute to humour in the essay?
Answer:
The author claims the best manner of making tea is the subject matter of violent disputes. He compliments china tea for being economical but also says one does not feel rejuvenated after drinking it. One doesn’t feel braver, wiser, more optimistic or stimulated after drinking the Chinese tea. He says army tea tastes of grease and white wash. In Britain there are two schools of thought (i.e.) milk first school and tea first school (i.e.) one school claiming that milk must be poured first and tea added later and another school claiming that tea must be poured first and milk to be added next.
He says those who take tea with sugar for its sweetness alone as misguided people. He says that they could very well add salt and pepper to tea and drink it. He claims that there are some mysterious social etiquette surrounding teapot. It is vulgar to drink tea out of one’s saucer. There are some subsidiary uses of tea leaves such as telling fortunes, predicting the arrival of visitors, feeding rabbits, healing burns and sweeping the carpet.
![]()
[OR]
“My right to swing my fist ends, where your nose begins.” Elucidate with reference to, ‘On the Rule of the Road’.
Answer:
Rights are not completely individual affairs. In order to enjoy one’s rights one has to respect the rights of others too. The lady in Petrograd had the right to walk on the pavement. The right to move stops when the other person’s right to drive starts. A person may have a walking stick and roll it too. But his right just stops where the other person’s nose begins. No one has the right to violate the rights of others. The right, one exercises, must not affect or erode the rights of others.
One should not think of one’s own rights but also the rights of others. A.G.Gardiner beautifully illustrates this idea by emphasising the metaphor of traffic rules. Rules of road are in fact rules of politeness and unselfishness. One may have absolute freedom in the choice of food, religion, fashionable dress, up keep of hair, funny hairstyle, etc. But one must be conscious of the rights of others. So, the statement “my right to swing my fist ends, where your nose begins” fits well with the central theme of the essay ‘ On the Rule of the Road’.
![]()
Question 42.
Human greed led to the mighty fall of the citadel. Explain.
Answer:
The loyal soldiers and their brave captain expected enemies from outside the castle. Their arms and army was ready to fight them. But they could not identify the enemy within. The soldiers were proud that no might would tear their castle down. But they were unaware of the invisible soul-dead enemy within. The ingredients of personal downfall went unnoticed by them.
If a person never looks within, the faults that can be their doom go overlooked. Their reality could crumble while they gaze outward and pride themselves on their sureness. This is what happened precisely with the soldiers of the castle. They only focused on the strength of their physical surroundings and what was beyond the castle. Human greed-propelled betrayal from within caused the castle’s downfall.
[OR]
Explain how the poet guides his son who is at the threshold of manhood, to face the challenges of life.
Answer:
The poet shares his wisdom with his son who is at the threshold of manhood. He persuades his son to be hard like steel or rock to withstand challenges and unforeseen betrayals in life. A person with soft heart will crumble before a breach of trust. Similarly he wants his son to be discerning enough to be soft when needed to grow like a frail flower plant splitting a rock.
![]()
Occasionally one has to go with the current because life is at times fertile with a lot of opportunities to grow even among the harshest circumstances. ‘Rich soft wanting’ can help a person to win against all odds. He reiterates this idea by explaining how gentleness can reform a hardened criminal when lashes would, in contrast, harden them further.
Question 43.
Write a paragraph of about 150 words by developing the following hints:
Pi convinced – water on board – divining rod – Pi’s mind – genuine regulation lifeboat – outfitted with supplies – captain – ensure safety and survival – ship chandler – extra money-saving lives – water on board.
Answer:
Pi had never before experienced physical hell than that putrid taste and pasty feeling in the mouth. It was an unbearable pressure at the back of his throat. The divining rod in Pi’s mind dipped sharply and spring gushed forth. He remembered that he was on a genuine regulation lifeboat and such a lifeboat was surely outfitted with supplies. A captain would never fail in so elementary way of preserving water to ensure safety and survival of his crew in the event of a disaster. Besides, it is natural that a ship chandler would think of making a little extra money under the noble pretext of saving lives. It was settled beyond doubt that there was water on board.
![]()
[OR]
Bond of friendship – Baldwin and Gresham – boyhood chums – school together – lifetime bondage – thirty five years – baptism – 60 dollars a week – Governor of the private bank – Gresham siphoning money – loyalty and honesty – part ways – upright character – close the bank – return the deposit – reorganization of the bank – arrest – court could not nail Gresham – one hundred thousand dollars – three words – slapped him – body language – not compromise with conscience.
Answer:
Baldwin and Gresham were boyhood chums. They went to school together. Their friendship flowered into a lifetime bondage as it was sustained for thirty five years. When Baldwin’s son was being baptised in the church, Gresham was present. Baldwin expressed his wish that his son John Gresham Baldwin grew up to Gresham’s standard in life. Baldwin was paid only 60 dollars a week for working as a Governor of the private bank founded by Gresham.
Accidentally, Baldwin found out how Gresham was siphoning money very cleverly from the deposits technically without really causing any loss to the depositors. But Baldwin was loyal to Gresham only as long as he was honest. Once he parted ways with honesty, Baldwin would also part ways with Gresham. By the force of his upright character, Baldwin advised him to close the bank and return the deposit to the customers.
![]()
Third National Bank was ready to help the reorganization of the bank. Meanwhile, Gresham was arrested. The court could not nail Gresham as there was not a shred of evidence to prove his guilt. If Baldwin testified, the court would indict him. Just before being arrested Gresham offered him one hundred thousand dollars to just say “I don’t remember”. The three words to let him off the hook. He claimed it was the difference between the salary he had been paid and what he ought to have received. Had it been someone else, Baldwin would have slapped him.
But it was Gresham who understood his body language and did not press the matter further. He was proud of the fact that Gresham understood how he could not compromise with his conscience. His family members Martha, Evie and John felt that it was a compliment that cost him one hundred thousand dollars. Baldwin said that Gresham’s compliment about his uprightness was worth a hundred thousand dollars.
Question 44.
Write a summary or Make notes of the following passage.
Answer:
Occasional self-medication has always been part of normal living. The making and selling of drugs has a long history and is closely linked, like medical practice itself, with belief in magic. Only during the last hundred years or so, as the development of scientific techniques made it possible, diagnosis has become possible. The doctor is now able to follow up the correct diagnosis of many illnesses – with specific treatment of their causes. In many other illnesses of which the causes remain unknown, he is still limited, like the unqualified prescriber, to the treatment of symptoms.
![]()
The doctor is trained to decide when to treat symptoms only and when to attack the cause. This is the essential difference between medical prescribing and self-medication. The advance of technology has brought about much progress in some fields of medicine, including the development of scientific drug therapy. Parallel with such beneficial trends are two which have an adverse effect. One is the use of high pressure advertising by the pharmaceutical industry which has tended to influence both patients and doctors and has led to the overuse of drugs generally.
The other is emergence of eating, insufficient sleep, excessive smoking and drinking. People with disorders arising from faulty habits such as these, as well as from unhappy human relationships, often resort to self-medication. Advertisers go to great lengths to catch this market. Clever advertising, aimed at chronic sufferers who will try anything because doctors have not been able to cure them, can induce such faith in a preparation, particularly if steeply priced, that it will produce -by suggestion- a very real effect in some people.
It is doubtful whether taking these things ever improves a person’s health, it may even make it worse. Worse, because the preparation may contain unsuitable ingredients; worse because the taker may become dependent on them; worse because they might be taken excess; worse because they may cause poisoning, and worst of all because symptoms of some serious underlying cause may be asked and therefore medical help may not be sought. Self-diagnosis is a greater danger than self-medication.
![]()
Summary
No. of words given in the original passage: 347
No. of words to be written in the summary: 347/3 = 115 ± 5
Rough Draft
Self-medication is part of normal living. Medicinal experts are required for diagnosis and treatment of diseases according to symptoms and causes. The development of drug therapy and improvement in public health organizations and nutritional standards have helped progress in medicinal science. Excessive advertising by pharmaceutical companies and emergence of the sedentary society are two counter trends. Self-medication is dangerous as the preparation may be toxic or contain unsuitable ingredients; the user becomes dependent and consumes medicine in excess. Self-diagnosis is worse than self-medication.
No. of words in the summary: 83
Notes:
Title: Self-Medication
1. Self-medication
(a) Part of normal living—last 100 yrs
(b) Advance in diagnostic technology
(c) Doctors required – diagnosis & treatment of disease
(d) Self-medication differs from medical prescription
2. Technological Advmnt in medicine
(a) Drug therapy
(b) Improvement in public health organizations
(c) Increase in nutritional standards
![]()
3. Clever advertising by pharmaceutical companies
(a) Take advantage of people’s need
(b) Chronic sufferers
(c) Faulty lifestyle
(i) Lack of exercise, overeating, insufficient sleep, etc.
(ii) Stress, unhappy rela’ps, etc.
4. Dangers of self-medication
(a) Preparation of some drugs contains unsuitable ingredients
(b) Taker becomes dependent
(c) Taker consumes medicine in excess
(d) Preparations may cause poisoning .
(e) Real cause of illness gets suppressed or untreated
Abbreviations used: yrs – years; Advmnt – Advertisement; rela’ps – relapses
Question 45.
Write a letter to the Port Trust, Chennai, asking permission for a group of 25 students of your school to visit a ship that has collection of books of all languages of the world. The ship would remain in Chennai only for a fortnight. Get permission mentioning the date, time and the number of visitors the teachers in – charge of the bona fide students of your school.
Answer:
14th January, 2020
From
The Principal
TM Hr. Sec. School
Chennai – 45
![]()
To
The Naval Officer
Port Trust of India
Chennai
Respected Officer,
Sub: Reg. Permission for visiting the Ship – Queen Mary
Given to understand that the Ship named Queen Mary with a collection of books of all languages of the world has arrived at the Chennai Port for public viewing, I hereby request permission for our school children to visit the ship on one of the working days.
We would be grateful if you can permit us to view the books in the ship on Friday, 6th February, 2020 at 10 a.m. There will be 15 students from Std IX accompanied by two teachers with one male office staff.
Please find enclosed the bona fide certificates and Photocopy of the staff identity card accompanying them.
Staff in-charge: Mrs. Shalini Varma and Mrs. Sharmila Das.
Students of Std IX:
- Anitha.M
- Asha.L
- Balaji.G
- Bharath.U
- Chandhini.G
- Christopher. Y
- rthy.T
- Firoz.P
- Janaki.R
- Kalai.A
- Lalitha.G
- Leena.B
- Mohan.C
- Niranjan.F
- Rohit.R
Looking forward to an enriching experience and safe visit. Kindly send us a reply acknowledging our request.
![]()
Yours sincerely,
Meena
(Principal)
Address on the envelope:
The Naval Officer
Port Trust of India
Chennai
[OR]
Write a paragraph of 150 words on “Punctuality”.
Answer:
It has been said, “Never put off for tomorrow what you can do today”. Yet there are many people who enjoy postponing things. Such people do not realize the dangers of delaying. Work does not disappear if we postpone it. The difficulty of the work does not get reduced by postponing it. The more we postpone, the more the work piles up. Finally, the load of work seems too much. We then have to work for many days at a stretch under great strain and tension. Finally we do it hurriedly and in a careless manner.
It is as bad as not doing the work at all. Again, when some work is delayed, the time which would have been profitably used is wasted. Time wasted is time lost forever. Hence procrastination, that is the habit of postponing things, is rightly called the thief of time. Precious time wasted means opportunities lost, and lost forever. By the time we realize how much time we have wasted and how many opportunities we have missed by delaying word, it may be too late.
![]()
And then nothing remains for us except to regret and repent. Sometimes a very heavy price has to be paid for delaying things. The person who delays insuring his factory will regret it when the factory is gutted by a sudden fire. Delay in the treatment of a disease may make it worse, and may even result in death. There are other proverbs conveying similar meaning. Thus we say: “Time and tide wait for no man” and “A stitch in time saves nine”. All these proverbs warn us against the dangers of delay in actions, and stress the importance of timely action and punctuality.
Question 46.
Spot the errors and rewrite the sentences correctly
(a) Many a man have been arrested at the meeting.
(b) Most of the work have been completed.
(c) Neither of the books are illustrated.
(d) One of the thieves, were arrested.
(e) Rani sat besides the new student.
Answer:
(a) Many a man had been arrested at the meeting.
(b) Most of the work has been completed.
(c) Neither of the books is illustrated.
(d) One of the thieves, was arrested.
(e) Rani sat beside the new student.
![]()
[OR]
Fill in the blanks correctly.
(а) Someone who decides to …………….. a car has committed a crime, but auto parts are made of aluminium and …………….. (steel/steal)
(b) They look just the same! I am sure that boy …………….. be his son. (Use a modal in the given blank.)
(c) All my clothes are dirty! I …………….. do some laundry, (use a semi-modal)
(d) He …………….. never …………….. (study) art before he came to college. (use a proper tense)
Answer:
(a) steal/steel (b) must (c) need to (d) had/studied
Question 47.
Identify each of the following sentences with the fields given below:
(a) Shakespeare’s plays are read by many people.
(b) The yield of wheat has increased.
(c) Fast food is a growing health hazard.
(d) My brother is planning to go to the US.
(e) Dhoni was declared the Man of the Series.
[Sports, Nutrition and Dietetics, Travel, Literature, Agriculture]
Answer:
(a) Literature
(b) Agriculture
(c) Nutrition and Dietetics
(d) Travel
(e) Sports
![]()
[OR]
Read the following passage and answer the questions in your own words.
Answer:
Housed in an 18th century style Heritage building with wooden paneling running through the thirty seat dining area, “Lean and Lovely” is the latest attraction in Siddhapuram Nagar. Says the owner Chef Virina “People come to us for the unusual fare that we serve. Fairly ordinary Indian recipes are ignited with a dash of sauce and spiced with colour. There is harmony and balance between taste, lightness and tradition. Wholly organically grown vegetables and flour are used. We use the freshest of ingredients that are cut and cooked so as to display their colour and individual texture.
Questions:
a. What is special about the vegetables and flour used by “Lean and Lovely”?
b. In which town is “Lean and Lovely” located?
c. Who is a ‘Chef’?
d. How do the people in “Lean and Lovely” make the ordinary Indian recipes more attractive?
e. How do they keep the colour and texture of the food items?
Answers:
(a) Wholly organically grown vegetables and flour is the speciality of “Lean and Lovely’.
(b) “Lean and Lovely” is located in Siddhapuram Nagar.
(c) A chef is a skilled cook, who prepares a variety of dishes in a restaurant and manages them.
(d) Fairly ordinary Indian recipes are ignited with a dash of sauce and spiced with colour in “Lean and Lovely”. There is also harmony and balance between taste, lightness and tradition attracting the people.
(e) Freshest of ingredients to retain the colour and texture of the food items.
![]()