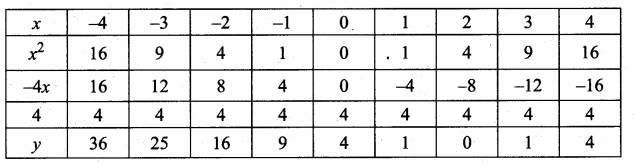
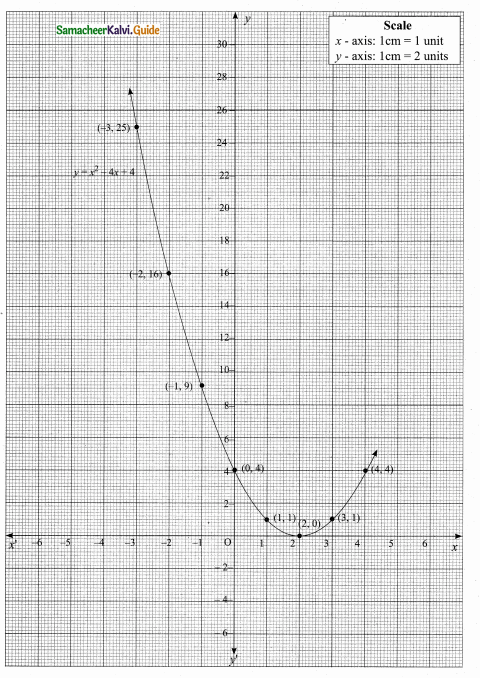
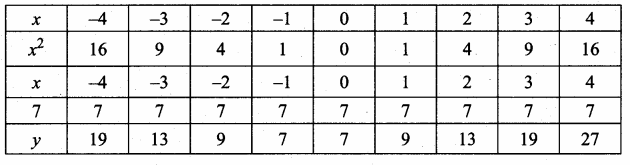
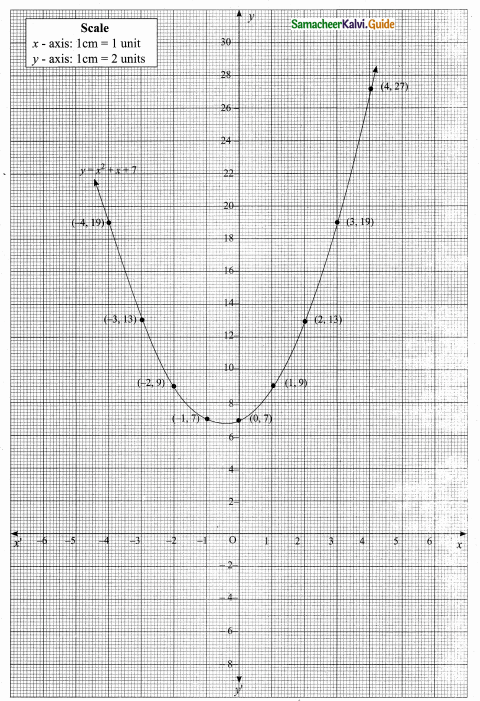
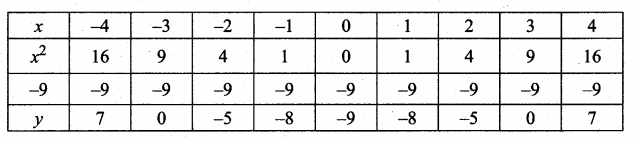
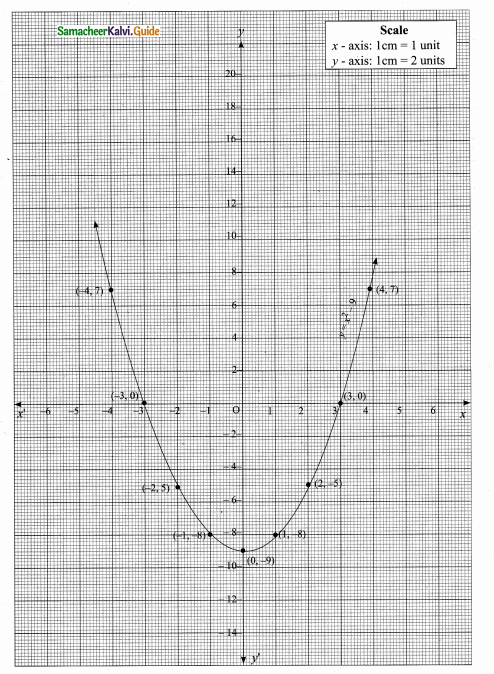
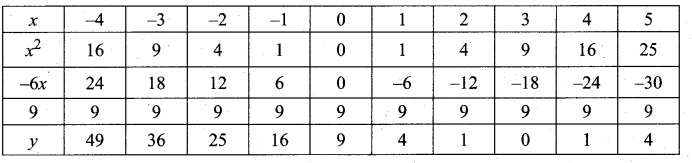
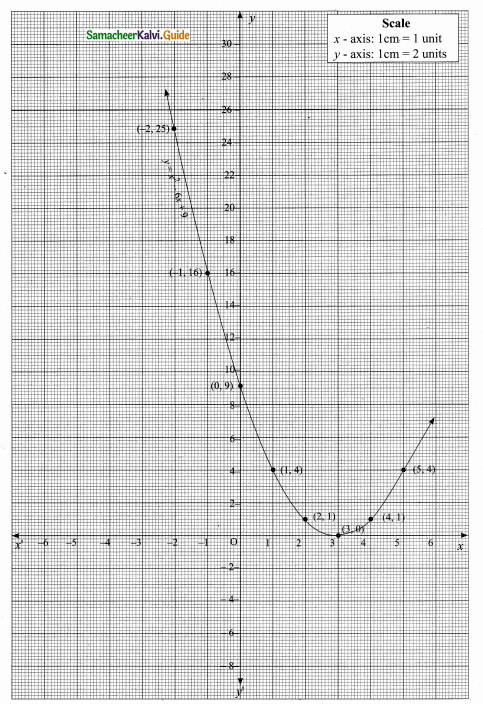
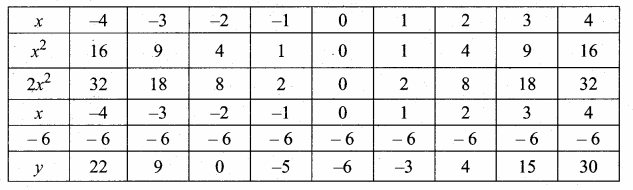
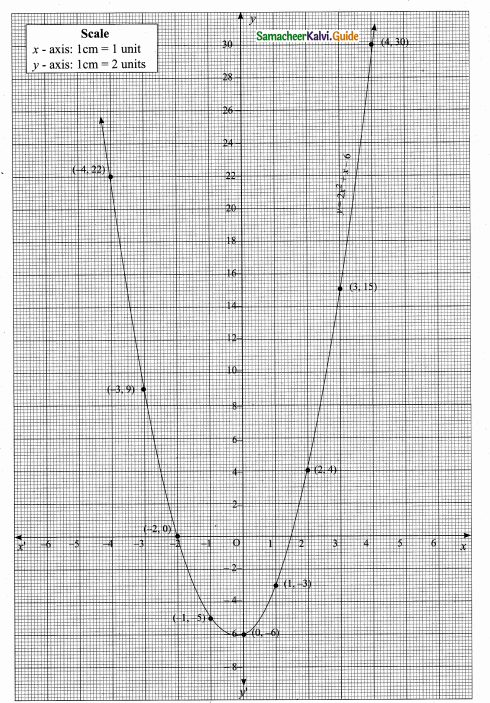
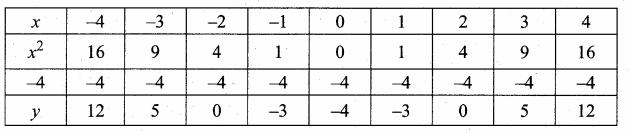
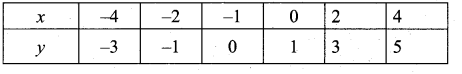
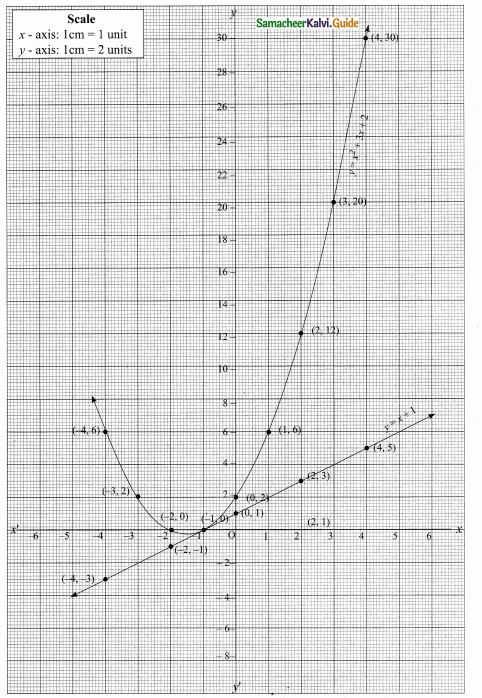
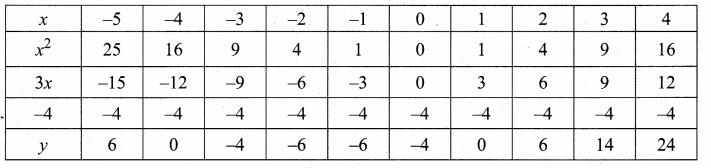
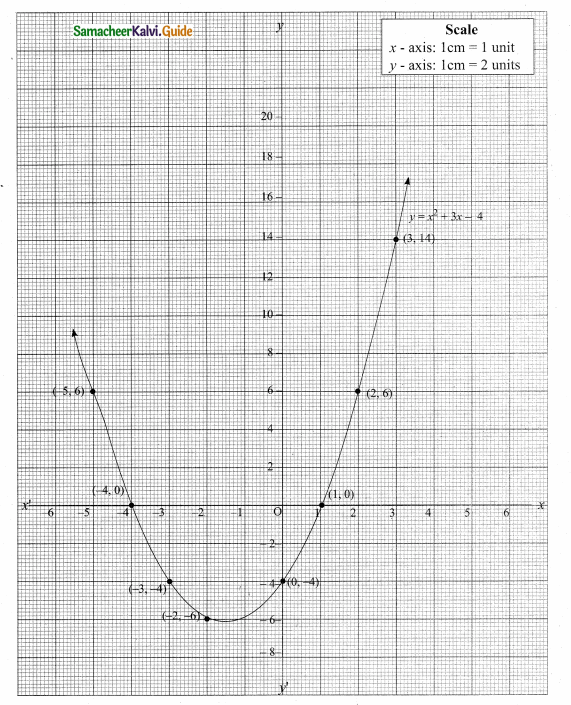
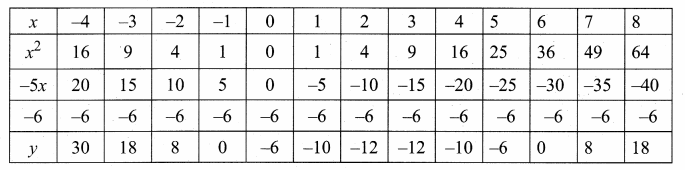
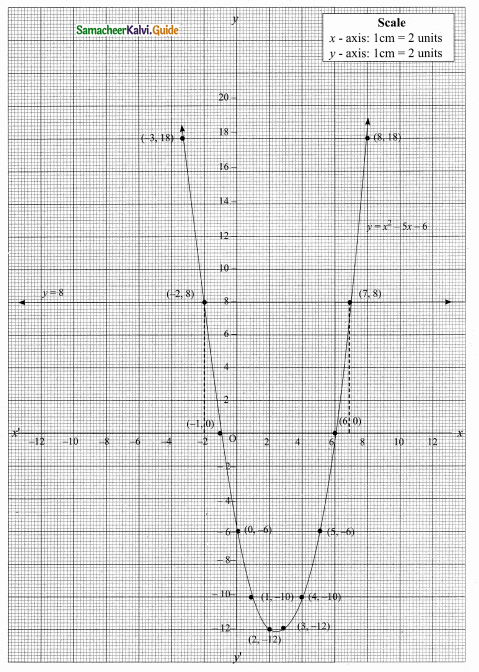
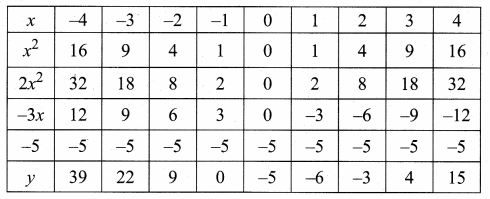
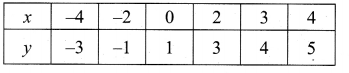
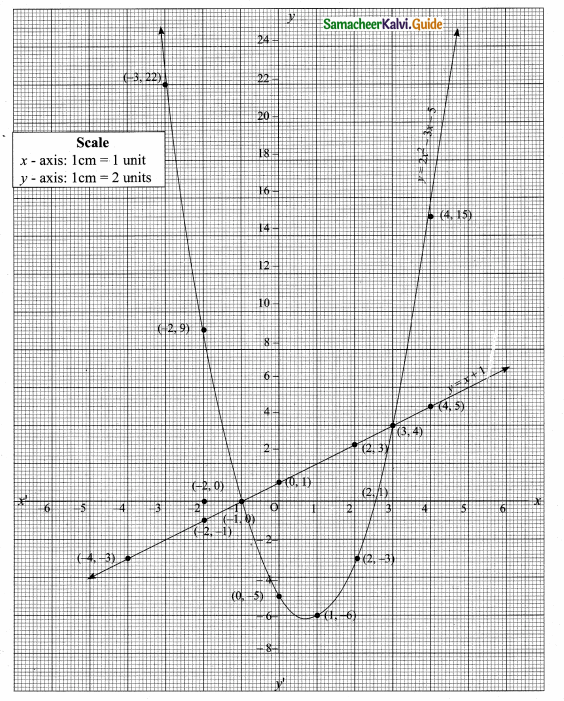
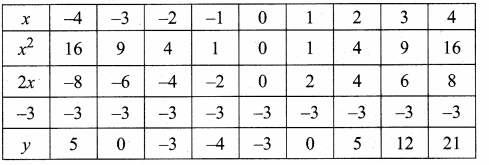
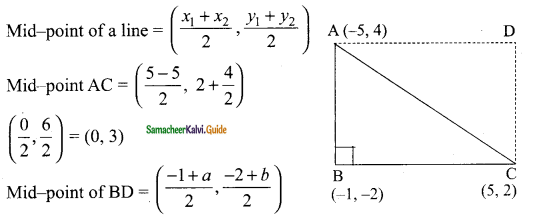
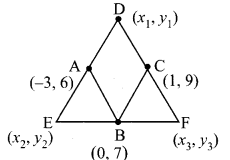
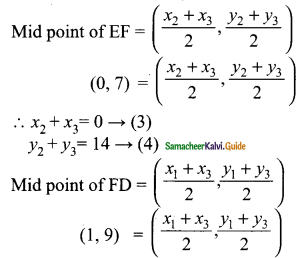
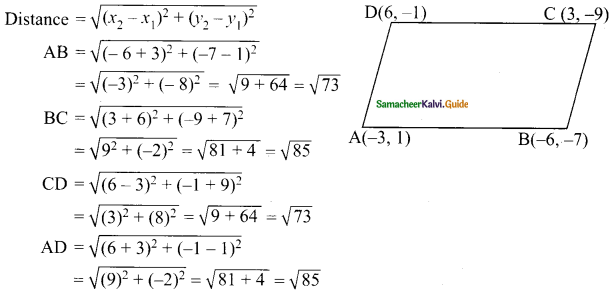
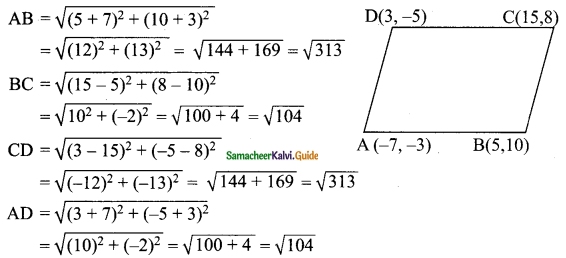
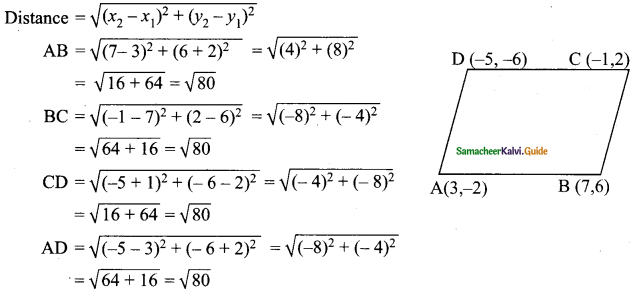
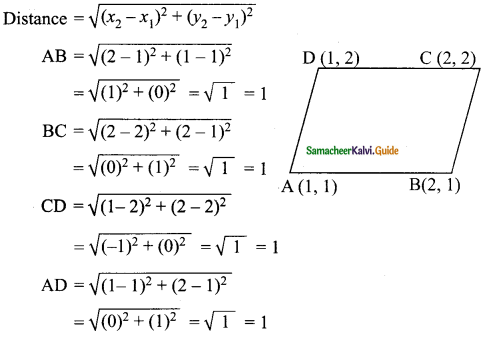
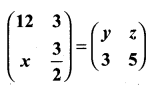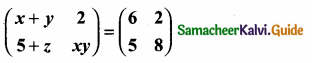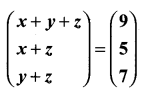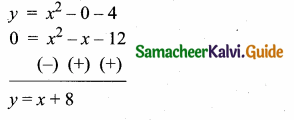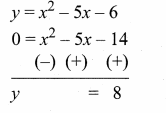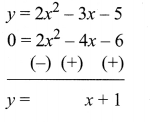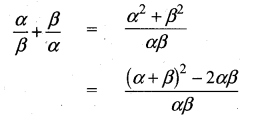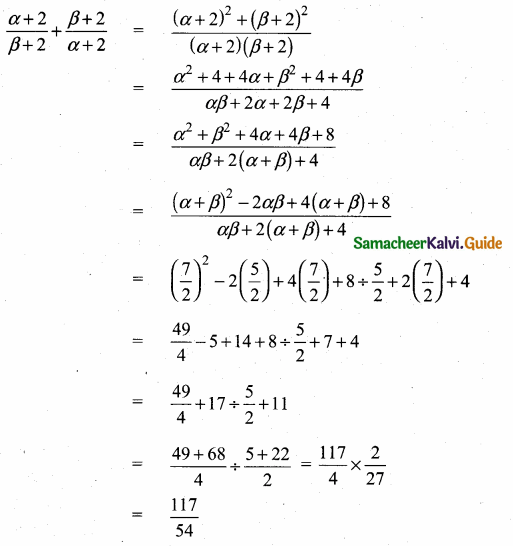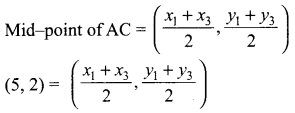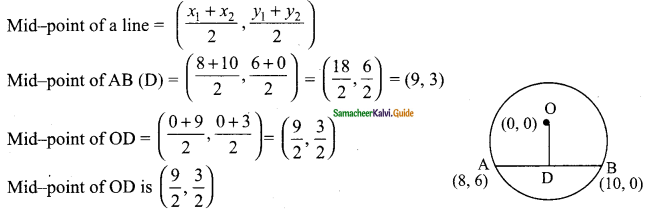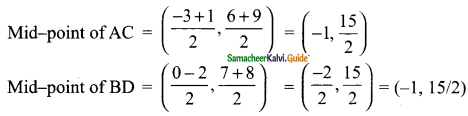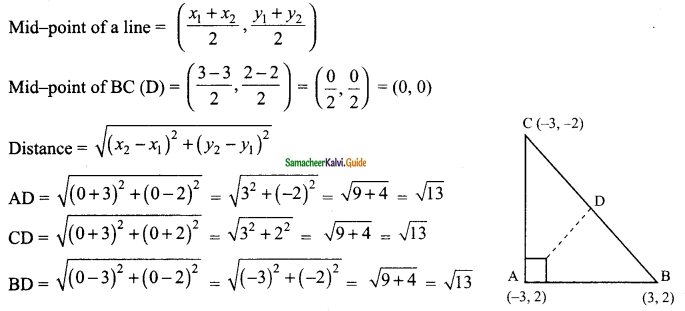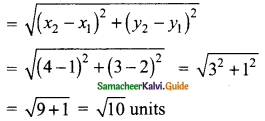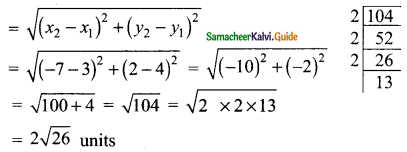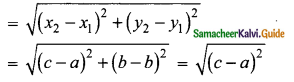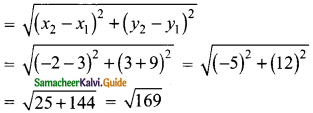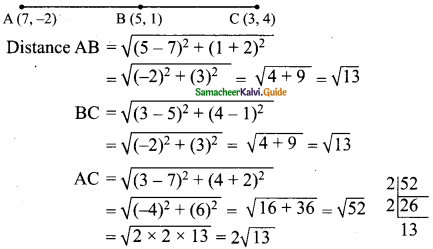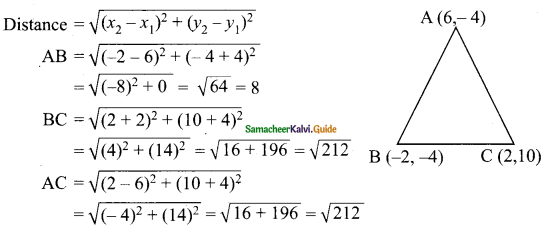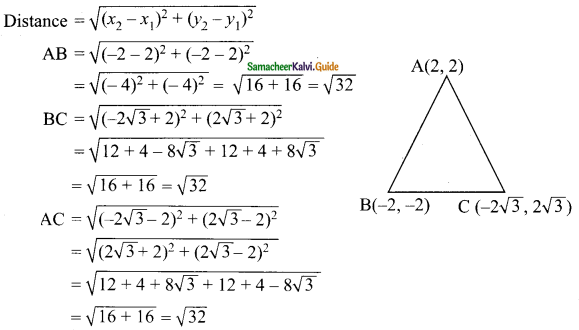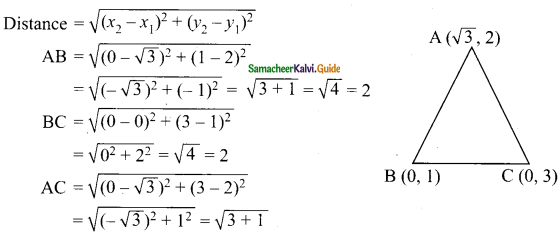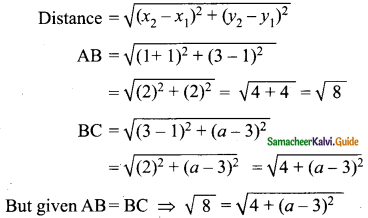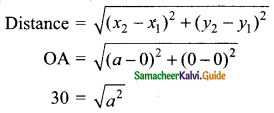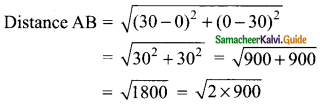Students can download Maths Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.5 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.5
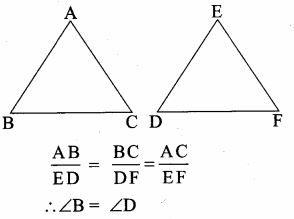
Question 1.
If in triangles ABC and EDF, \(\frac { AB }{ DE } \) = \(\frac { BC }{ FD } \) then they will be similar, when ……….
(1) ∠B = ∠E
(2) ∠A = ∠D
(3) ∠B = ∠D
(4) ∠A = ∠F
Answer:
(3) ∠B = ∠D
Hint:
![]()
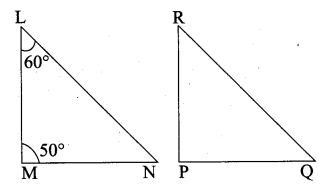
Question 2.
In ∆LMN, ∠L = 60°, ∠M = 50°. If ∆LMN ~ ∆PQR then the value of ∠R is ……………
(1) 40°
(2) 70°
(3) 30°
(4) 110°
Answer:
(2) 70°
Hint:
Since ∆LMN ~ ∆PQR
∠N = ∠R
∠N = 180 – (60 + 50)
= 180 – 110°
∠N = 70° ∴ ∠R = 70°
![]()
Question 3.
If ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle with ∠C = 90° and AC = 5 cm, then AB is ………
(1) 2.5 cm
(2) 5 cm
(3) 10 cm
(4) 5 \(\sqrt { 2 }\) cm
Answer:
(4) 5 \(\sqrt { 2 }\) cm
Hint:
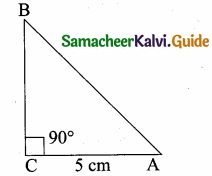
AB2 = AC2 + BC2
AB2 = 52 + 52
(It is an isosceles triangle)
AB = \(\sqrt { 50 }\) = \(\sqrt{25 \times 2}\)
AB = 5 \(\sqrt { 2 }\)
![]()
Question 4.
In a given figure ST || QR, PS = 2 cm and SQ = 3 cm. Then the ratio of the area of ∆PQR to the area of ∆PST is …………….
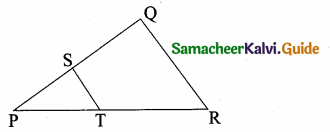
(1) 25 : 4
(2) 25 : 7
(3) 25 : 11
(4) 25 : 13
Answer:
(1) 25 : 4
Hint. Area of ∆PQR : Area of ∆PST
\(\frac{\text { Area of } \Delta \mathrm{PQR}}{\text { Area of } \Delta \mathrm{PST}}=\frac{\mathrm{PQ}^{2}}{\mathrm{PS}^{2}}=\frac{5^{2}}{2^{2}}=\frac{25}{4}\)
Area of ∆PQR : Area of ∆PST = 25 : 4
Question 5.
The perimeters of two similar triangles ∆ABC and ∆PQR are 36 cm and 24 cm respectively. If PQ =10 cm, then the length of AB is ………….
(1) 6 \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) cm
(2) \(\frac{10 \sqrt{6}}{3}\)
(3) 66 \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) cm
(4) 15 cm
Answer:
(4) 15 cm
Hint:
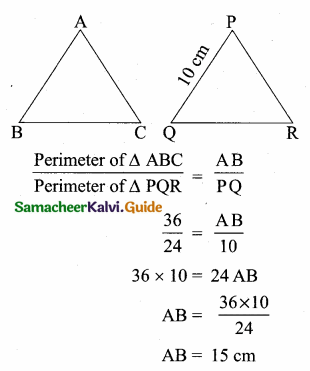
![]()
Question 6.
If in ∆ABC, DE || BC. AB = 3.6 cm, AC = 2.4 cm and AD = 2.1 cm then the length of AE is ………..
(1) 1.4 cm
(2) 1.8 cm
(3) 1.2 cm
(4) 1.05 cm
Answer:
(1) 1.4 cm
Hint:
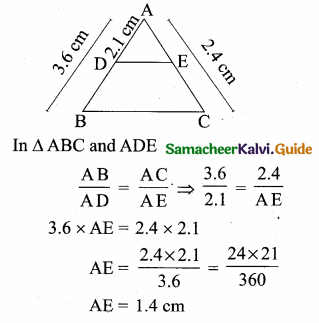
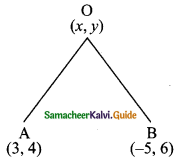
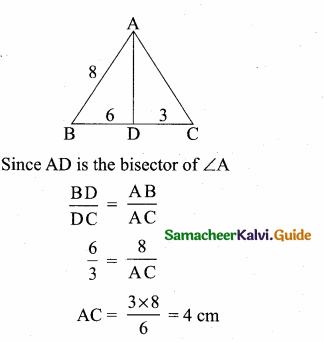
Question 7.
In a ∆ABC, AD is the bisector of ∠BAC. If AB = 8 cm, BD = 6 cm and DC = 3 cm.
The length of the side AC is ………….
(1) 6 cm
(2) 4 cm
(3) 3 cm
(4) 8 cm
Answer:
(2) 4 cm
Hint:
![]()
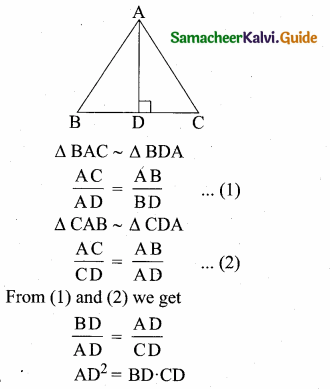
Question 8.
In the adjacent figure ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC then ………..
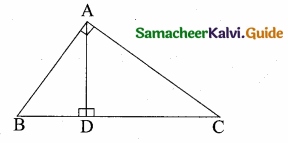
(1) BD.CD = BC2
(2) AB.AC = BC2
(3) BD.CD = AD2
(4) AB.AC = AD2
Answer:
(3) BD CD = AD2
Hint:
![]()
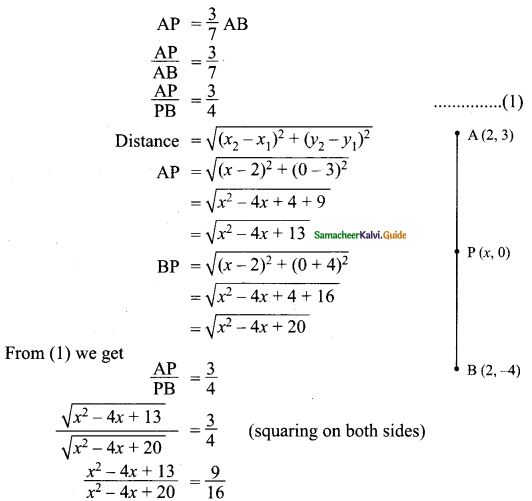
Question 9.
Two poles of heights 6 m and 11m stand vertically on a plane ground. If the distance between their feet is 12 m, what is the distance between their tops?
(1) 13 m
(2) 14 m
(3) 15 m
(4) 12.8 m
Answer:
(1) 13 m
Hint:
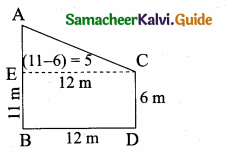
AC2 (Distance between the two tops)
= AE2 + EC2
= 52 + 122
= 25 + 144= 169
AC = \(\sqrt { 169 }\) = 13 cm
![]()
Question 10.
In the given figure, PR = 26 cm, QR = 24 cm, ∠PAQ = 90°, PA = 6 cm and QA = 8 cm. Find ∠PQR.
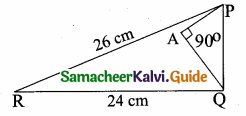
(1) 80°
(2) 85°
(3) 75°
(4) 90°
Answer:
(4) 90°
Hint.
PR = 26 cm, QR = 24 cm, ∠PAQ = 90°
In the ∆PQR,
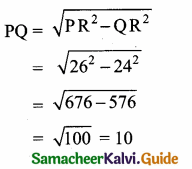
In the right ∆ APQ
PQ2 = PA2 + AQ2
= 62 + 82
= 36 + 64 = 100
PQ = \(\sqrt { 100 }\) = 10
∆ PQR is a right angled triangle at Q. Since
PR2 = PQ2 + QR2
∠PQR = 90°
Question 11.
A tangent is perpendicular to the radius at the
(1) centre
(2) point of contact
(3) infinity
(4) chord
Solution:
(2) point of contact
![]()
Question 12.
How many tangents can be drawn to the circle from an exterior point?
(1) one
(2) two
(3) infinite
(4) zero
Answer:
(2) two
Question 13.
The two tangents from an external points P to a circle with centre at O are PA and PB.
If ∠APB = 70° then the value of ∠AOB is ……….
(1) 100°
(2) 110°
(3) 120°
(4) 130°
Answer:
(2) 110°
Hint.
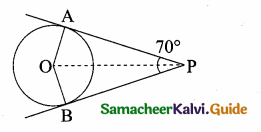
∠OAP = 90°
∠APO = 35°
∠AOP = 180 – (90 + 35)
= 180 – 125 = 55
∠AOB = 2 × 55 = 110°
![]()
Question 14.
In figure CP and CQ are tangents to a circle with centre at 0. ARB is another tangent touching the circle at R. If CP = 11 cm and BC = 7 cm, then the length of BR is …….
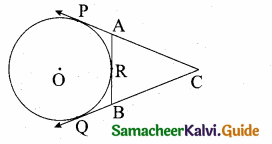
(1) 6 cm
(2) 5 cm
(3) 8 cm
(4) 4 cm
Answer:
(4) 4 cm
Hint.
BQ = BR = 4 cm (tangent of the circle)
PC = QC = 11 cm (tangent of the circle)
QC = 11 cm
QB + BC = 11
QB + 7 = 11
QB = 11 – 7 = 4 cm
BR = BQ = 4 cm
![]()
Question 15.
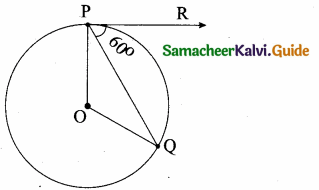
In figure if PR is tangent to the circle at P and O is the centre of the circle, then ∠POQ is ………….
(1) 120°
(2) 100°
(3) 110°
(4) 90°
Answer:
(1) 120°
Hint.
Since PR is tangent of the circle.
∠QPR = 90°
∠OPQ = 90° – 60° = 30°
∠OQB = 30°
In ∆OPQ
∠P + ∠Q + ∠O = 180°
30 + 30° + ∠O = 180°
(OP and OQ are equal radius)
∠O = 180° – 60° = 120°
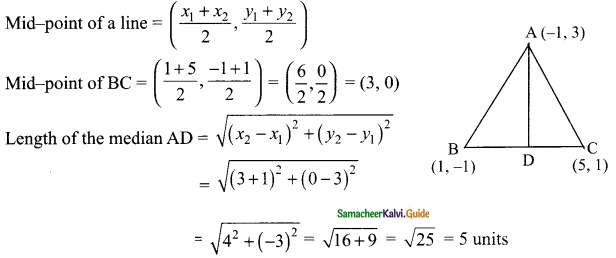
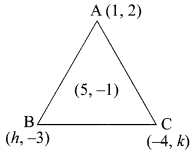
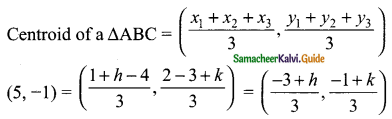
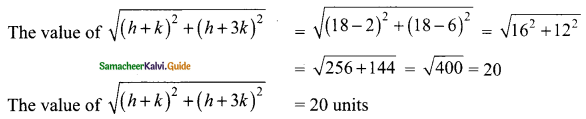

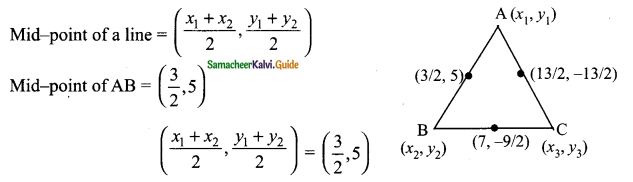
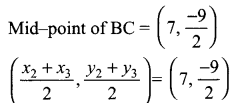
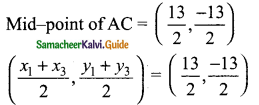
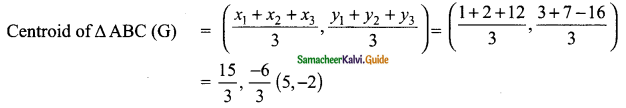
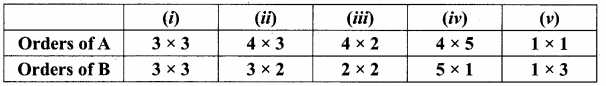
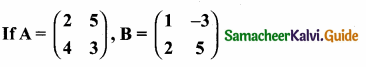
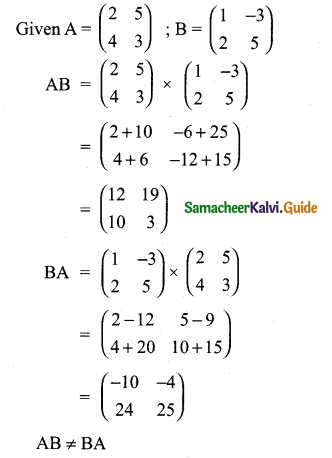
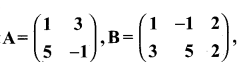
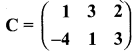
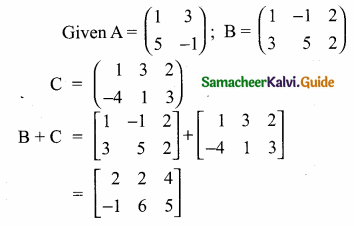
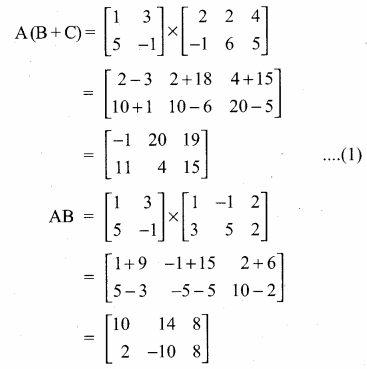
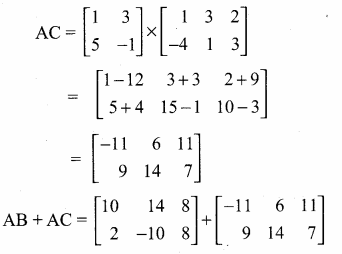
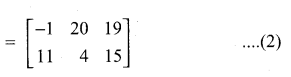
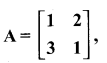
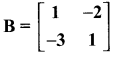
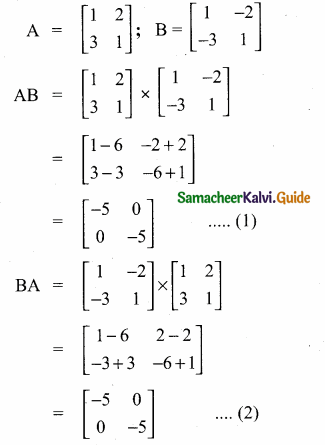
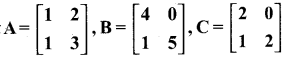
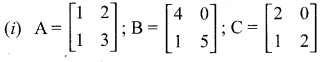
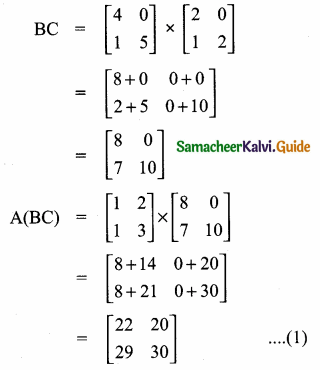
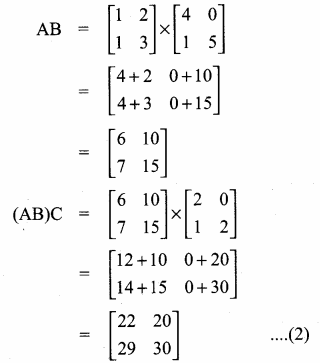
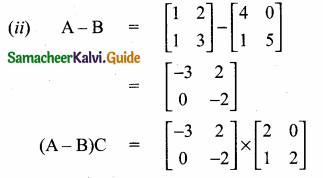
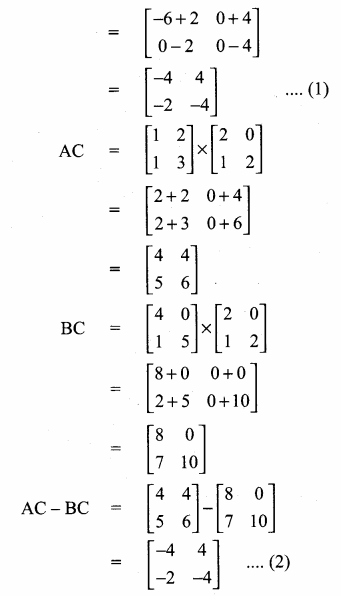
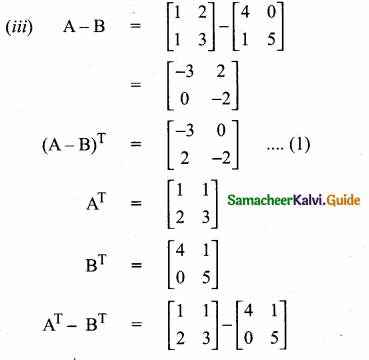
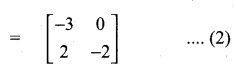
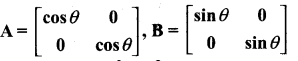
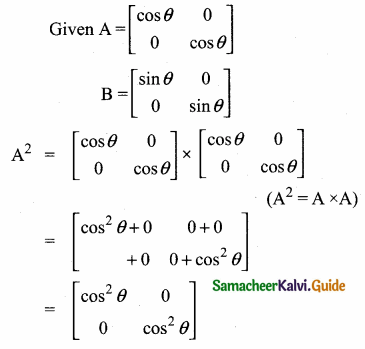
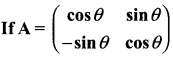
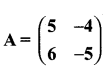
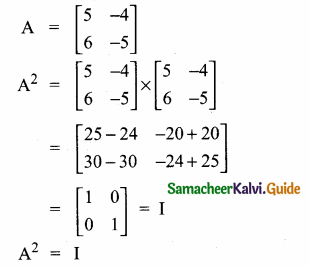
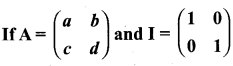
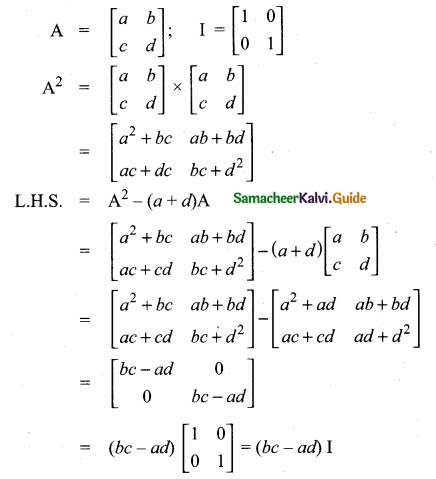
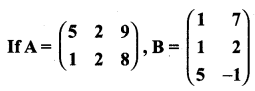
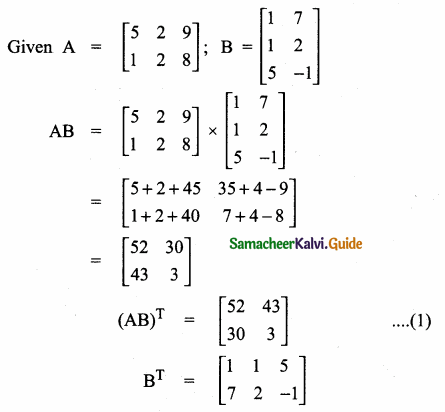
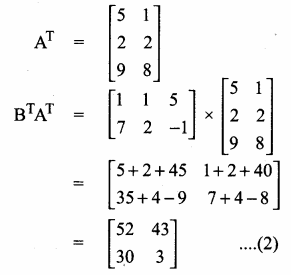
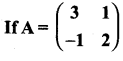
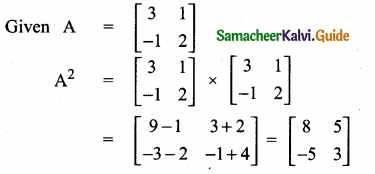
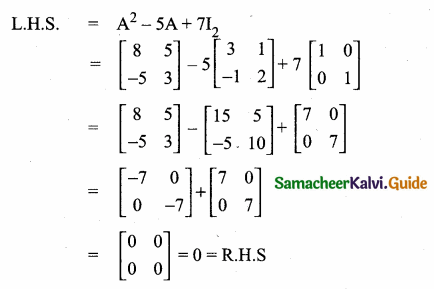
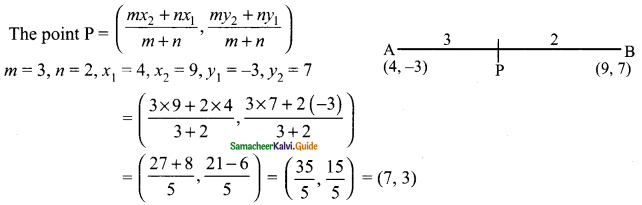
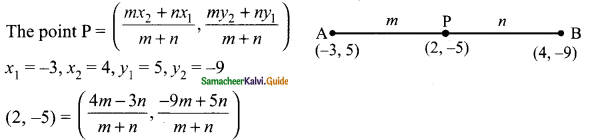
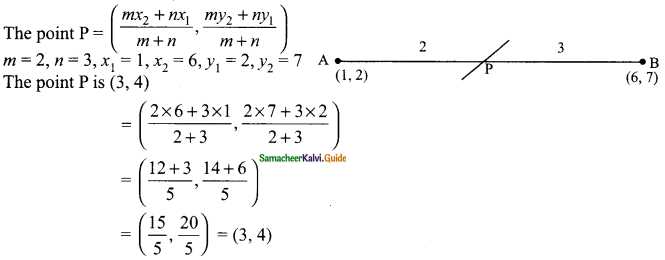
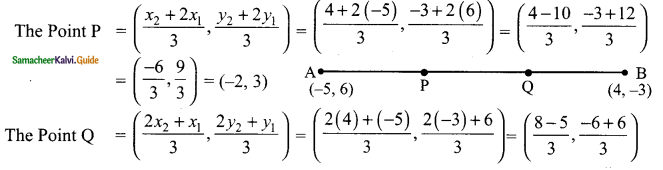
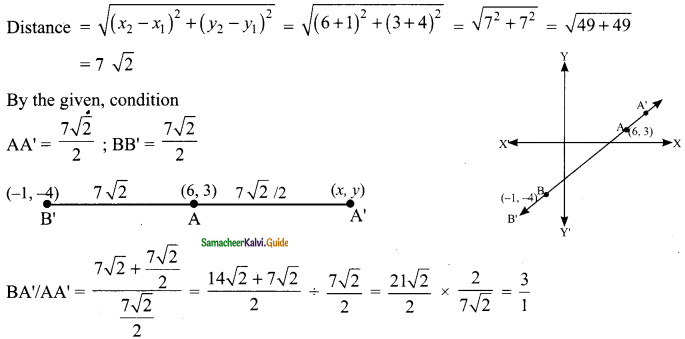
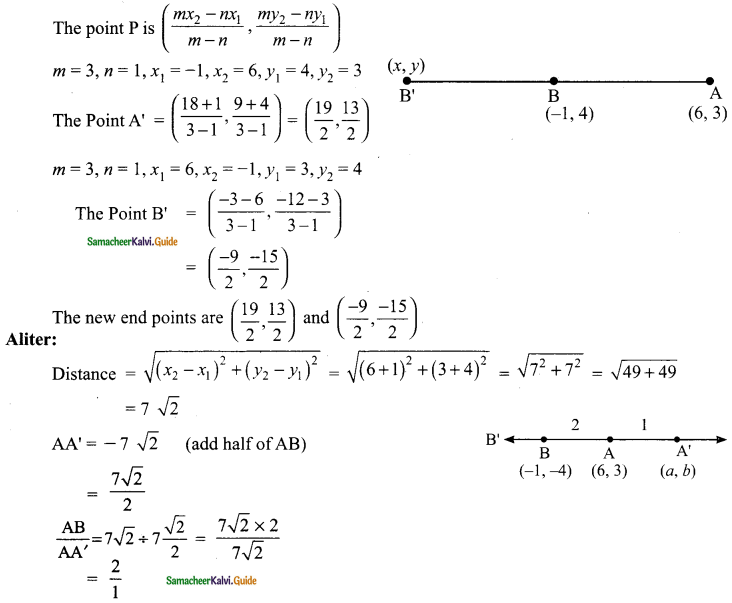
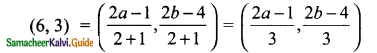
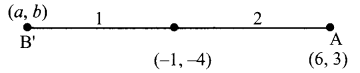
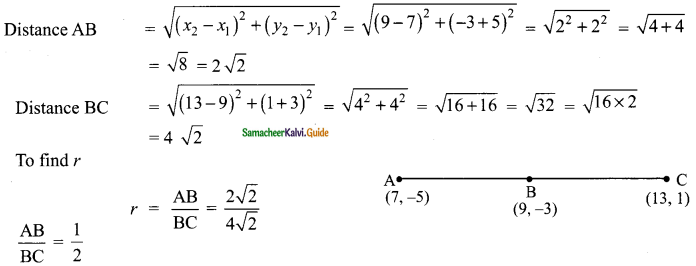
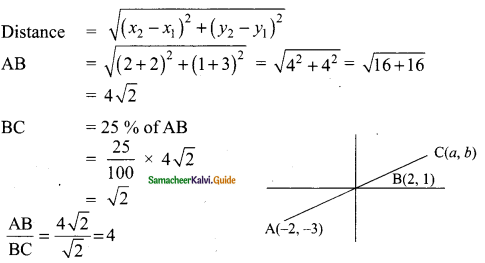
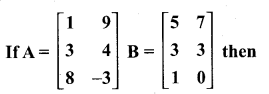
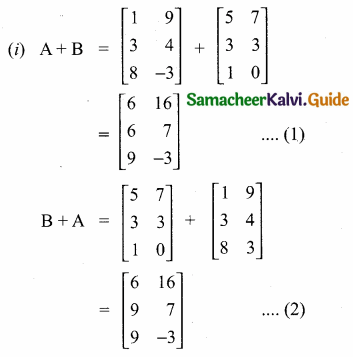
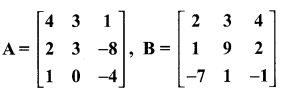
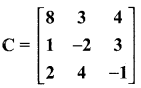 then verify that
then verify that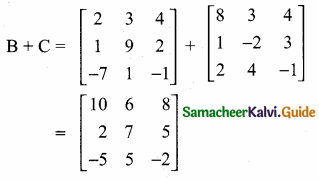
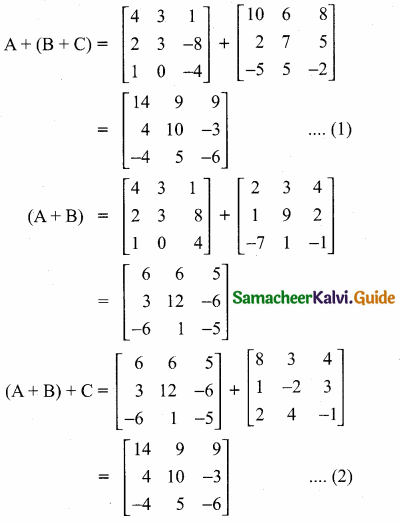
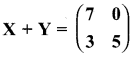 and
and 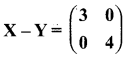
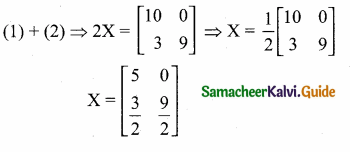
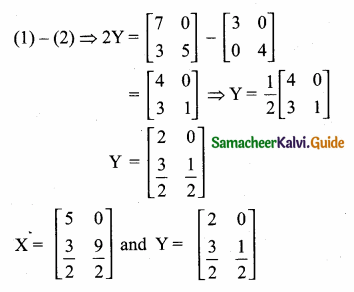
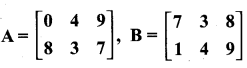
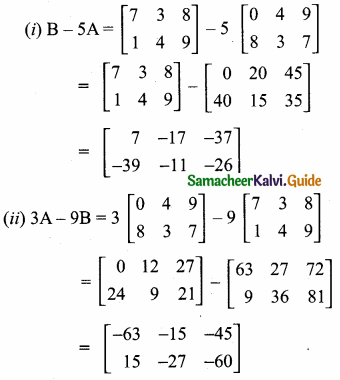
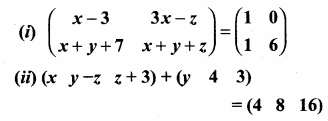
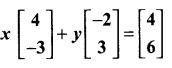
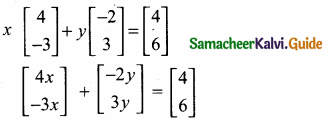
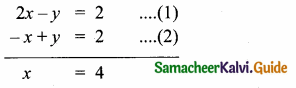
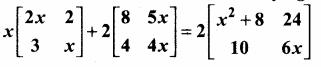
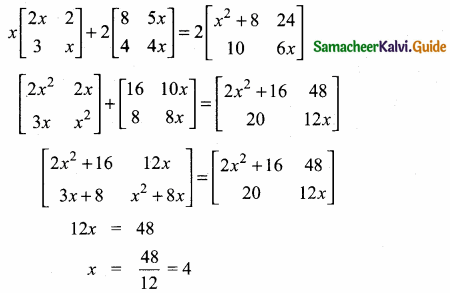
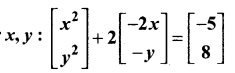
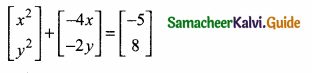
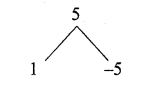
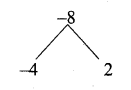
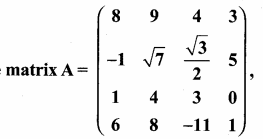
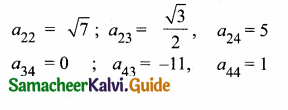

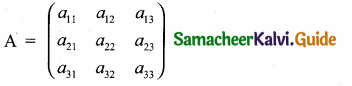
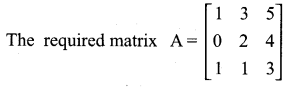
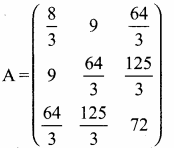
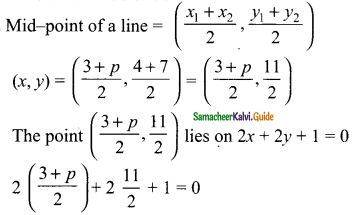
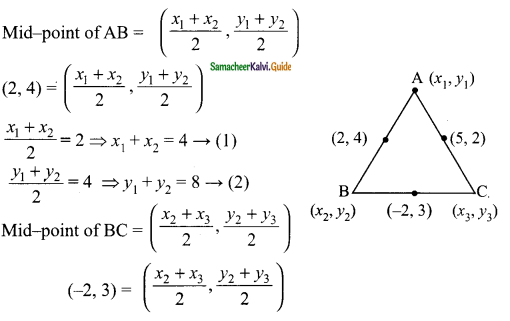
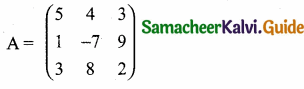 then find the tranpose of A.
then find the tranpose of A.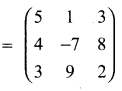
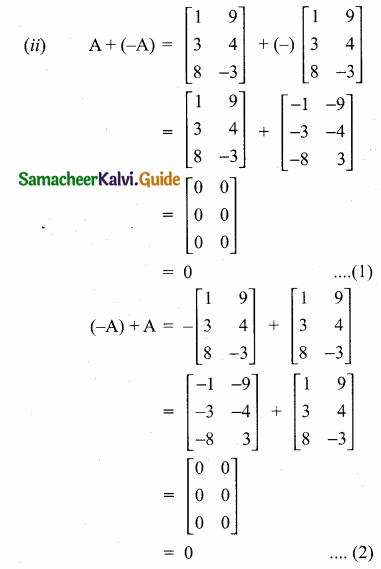
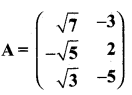 then find the tranpose of – A
then find the tranpose of – A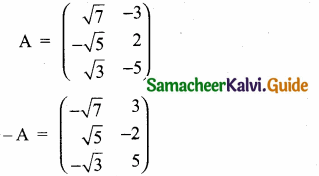
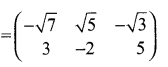
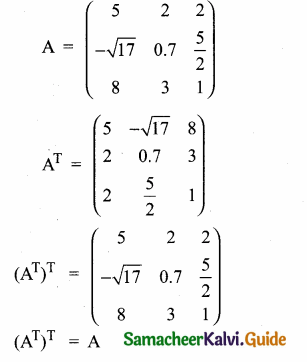
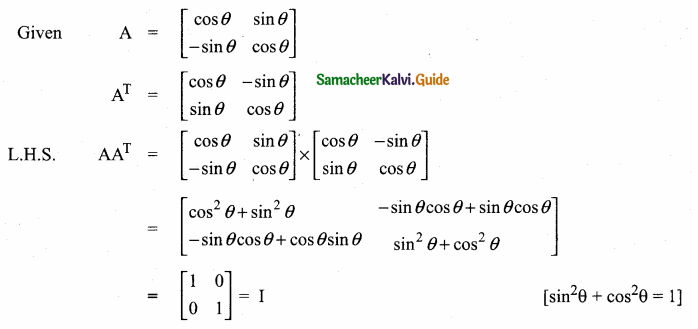
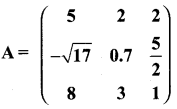 then verify (AT)T = A
then verify (AT)T = A