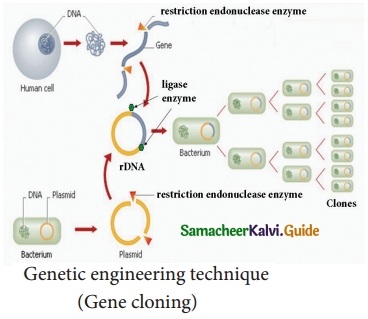
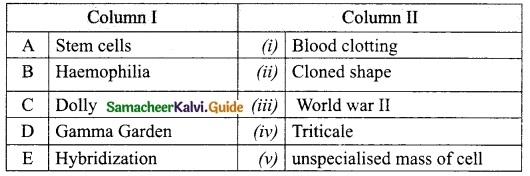
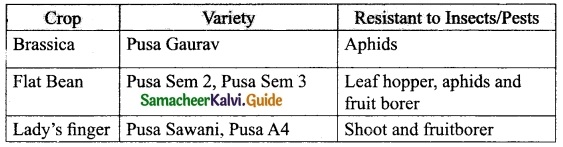
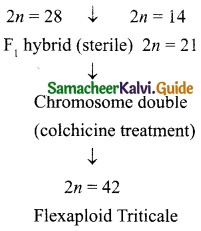
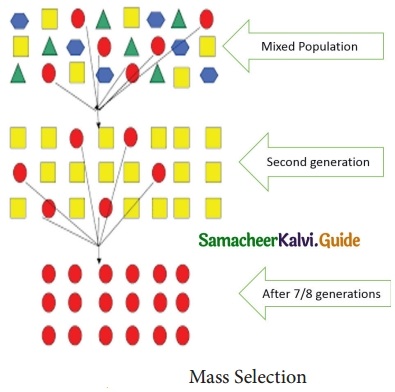
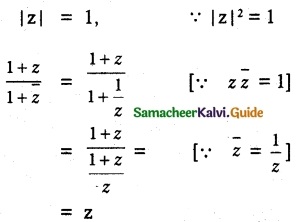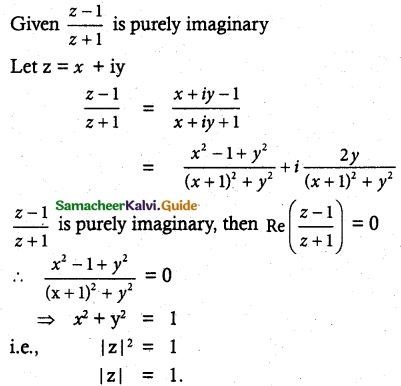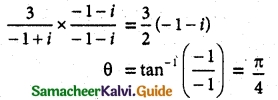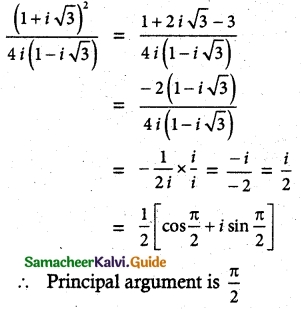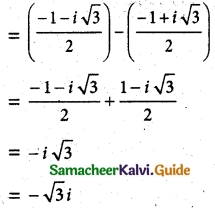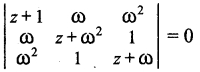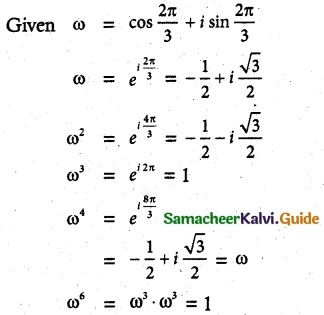Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Complex Numbers Ex 2.8 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Complex Numbers Ex 2.8
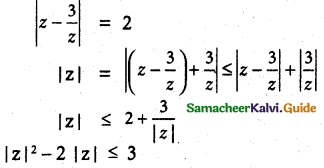
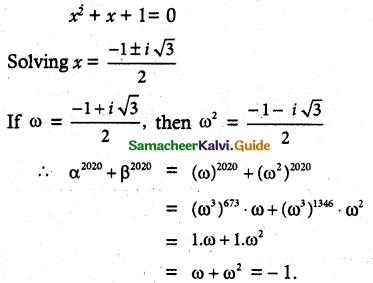
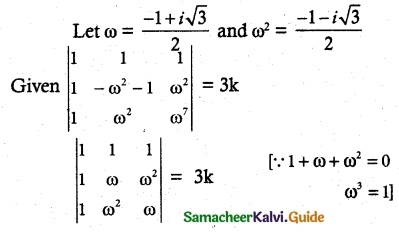
Question 1.
If to ω ≠ 1 is a cube root of unity, then show that
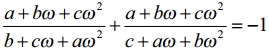
Solution:
L.H.S
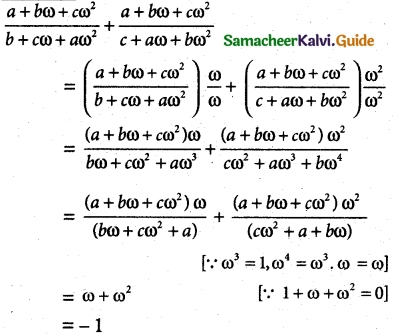
Question 2.
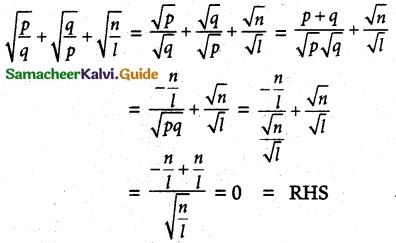
Show that
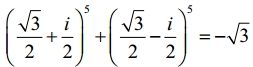
Solution:

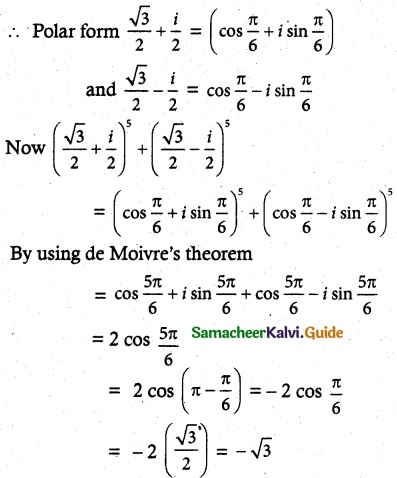
![]()
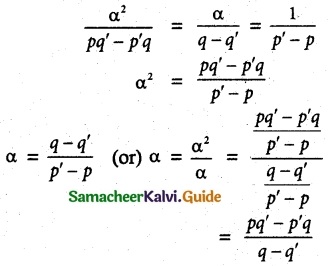
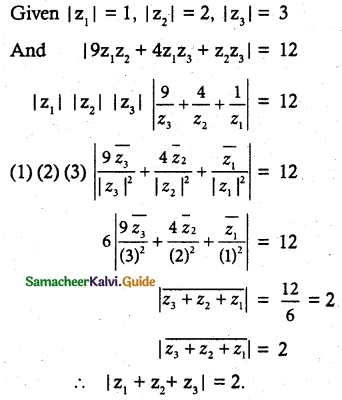
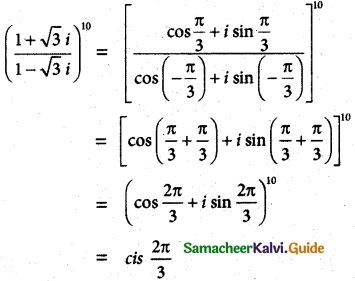
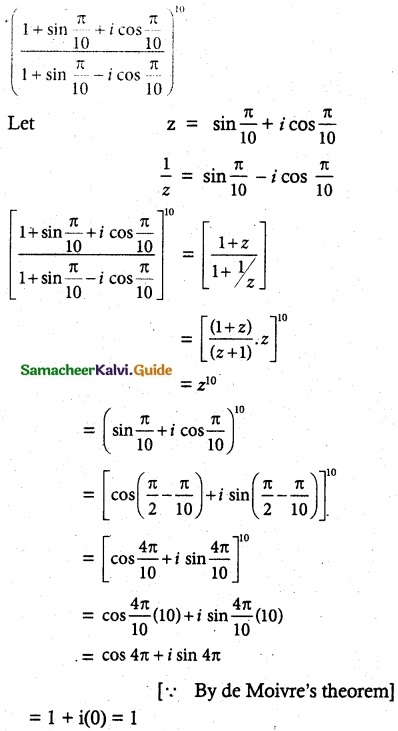
Question 3.
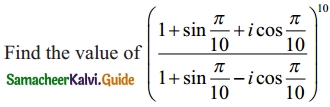
Solution:
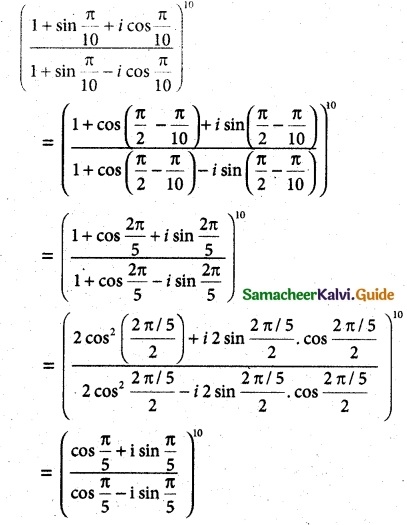
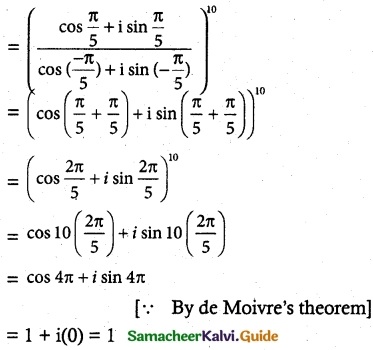
Aliter method:
![]()
Question 4.
If 2cos α = x + \(\frac{1}{x}\) and 2 cos β = y + \(\frac{1}{x}\), show that
(i) \(\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}=2 \cos (\alpha-\beta)\)
Solution:
Given 2 cos α = x + \(\frac{1}{x}\) and cos β = y + \(\frac{1}{y}\)
simplifying x² – 2x cos α + 1 = 0
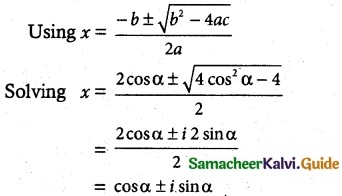
if x = cos α + i sin α, then \(\frac{1}{x}\) = cos α – i sin α
similarly y = cos β + i sin β and \(\frac{1}{y}\) = cos β – i sin β
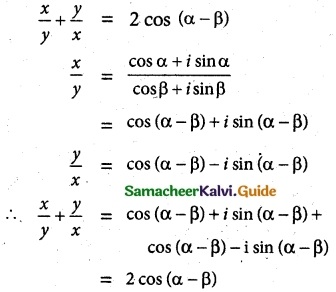
Hence proved
(ii) xy = (cos α + i sin α)(cos β + i sin β )
Solution:
xy = (cos α + i sin α) (cos β + i sin β)
= cos (α + β) + i sin (α + β)
[∵ arg (z1z2) = arg z1 + arg z2
\(\frac{1}{xy}\) = cos (α + β) – i sin (α + β)
∴ xy – \(\frac{1}{xy}\) = cos (α + β) + i sin (α + β) – cos (α + β) + i sin (α + β)
= 2i sin (α + β)
Hence proved
(iii) \(\frac{x^{m}}{y^{n}}-\frac{y^{n}}{x^{m}}\) = 2 i sin (mα – nβ)
Solution:
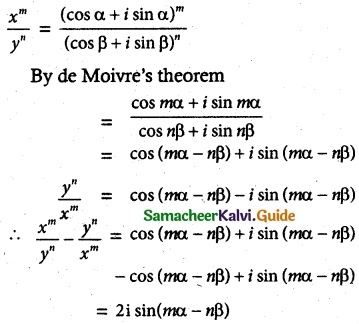
Hence Proved
![]()
(iv) xm yn + \(\frac { 1 }{ x^m y^n }\) = 2 cos(mα – nβ)
Solution:
= (cos mα + sin mα) (cos nβ + i sin nβ)
= cos (mα + nβ) + i sin (mα + nβ)
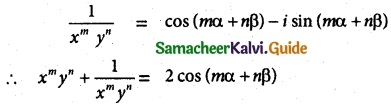
Hence proved
Question 5.
Solve the equation z³ + 27 = 0.
Solution:
z³ + 27 = 0
z³ = – 27 = 27 (-1)
= 27 [cos(π + 2kπ) + i sin(π + 2kπ)], k ∈ z
∴ z = (27)1/3[cos (2k + 1)π + i sin (2k+1)π]1/3 k ∈ z
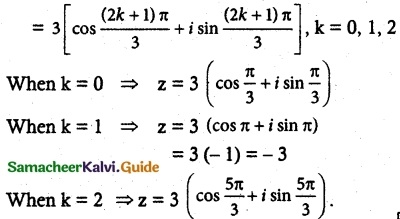
![]()
Question 6.
If ω ≠ 1 is a cube root of unity, show that the roots of the equation (z – 1)³ + 8 = 0 are -1, 1 – 2ω, 1 – 2ω².
Solution:
Given ω ≠ 1 is a active root of unity
(z – 1)³ + 8 = 0
(z- 1)³ = -8
z – 1 = (-8)1/3 (1)1/3
= (-2) (1, ω, ω²)
z – 1 = (-2, -2ω, -2ω²)
= z – 1 = -2
z = -2 + 1 = -1
z – 1 = -2ω
z = 1 – 2ω
z – 1 = -2ω²
z = 1 – 2ω²
![]()
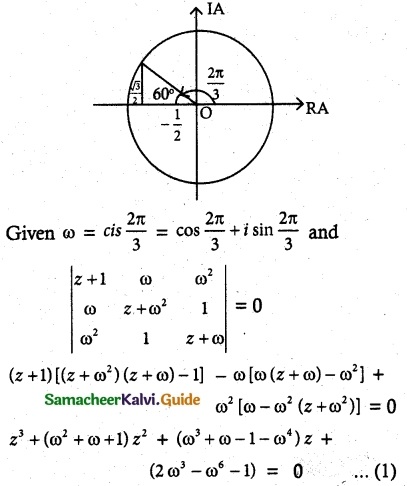
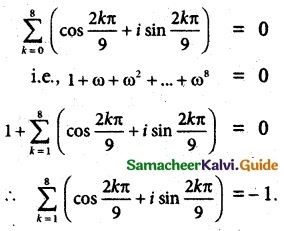
Question 7.
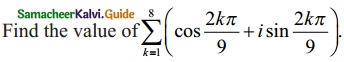
Solution:
\(\sum_{k=1}^{8}\) (cos \(\frac { 2kπ }{ 9 }\) + i sin \(\frac { 2kπ }{ 9 }\))
The sum all nth root of unity is
1 + ω + ω² + …….. + ωn-1 = 0
From the given polar from , it is clear that the complex number is 1 + i0 (unity)
Question 8.
If ω ≠ 1 is a cube root of unity, show that
(i) (1 – ω + ω²)6 + (1 + ω – ω²)6 = 128.
Solution:
ω is a cube root of unity ω3 = 1; 1 + ω + ω2 = 0
(1 – ω + ω2)6 + (1 + ω – ω2)6
= (-ω – ω)6 + (-ω2 – ω2)6
= (-2ω)6 + (-2ω2)6
= (-2)6(ω6 + ω12)
= (64)(1 + 1)
= 128
![]()
(ii) (1 + ω) (1 + ω²) (1 + ω4) (1 + ω8)….. (1 + ω2n) = 1
Solution:
(1 + ω)(1 + ω2)(1 + ω4)(1 + ω8) …… (1 + ω2n)
= (1 + ω)(1 + ω2)(1 + ω4)(1 + ω8) ……. 2n factors
= (-ω2)(-ω)(-ω2)(-ω) …… 2n factors
= ω3. ω3
= 1
Hence proved.
Question 9.
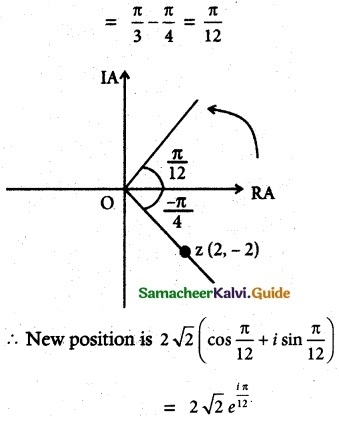
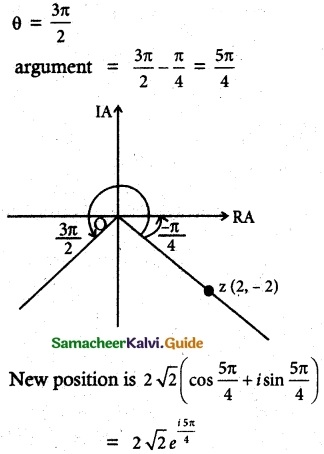
If z = 2 – 2i, find the rotation of z by θ radians in the counterclockwise direction about the origin when
Solution:
Let 2 – 2i
Modules = |z| = \(\sqrt{2^2+2^2}\) = 2√2
Argument θ = tan-1(\(\frac{-2}{2}\)) = tan-1(-1) = –\(\frac{π}{4}\)
(i) when ‘z’ is rotated in the counter clockwise direction about the origin when θ = \(\frac{π}{3}\) i.,e argument of new position
(ii) θ = \(\frac{2π}{3}\)
Solution:
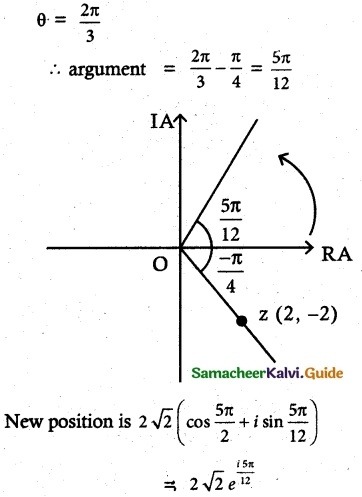
![]()
(iii) θ = \(\frac{3π}{3}\)
Solution:
![]()