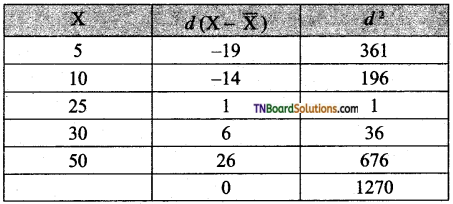
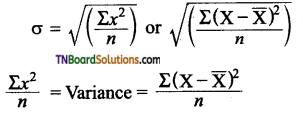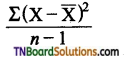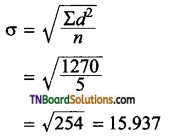Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 4 Principles and Processes of Biotechnology which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 4 Principles and Processes of Biotechnology
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Name the scientists who first produced monoclonal antibodies.
Answer:
- Kohler
- Milstein
Question 2.
Define traditional Biotechnology.
Answer:
Traditional biotechnology is the process developed by our ancestors in the kitchen by using fermentation bacteria. Eg. Idli, Dosa, Curd, Nan, etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Name any two commercial products produced through fermentation technology.
Answer:
- Bread
- Wine
Question 4.
Mention any two single-cell proteins.
Answer:
- Spirulina
- Chlorella
Question 5.
Define conventional recombination.
Answer:
Conventional recombination is a process. which involves the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Question 6.
What is meant by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
Answer:
The polymerase chain reaction is a common laboratory technique used to make a million copies of a particular region of DNA.
Question 7.
What are the basic tools for genetic engineering?
Answer:
The basic tools of genetic engineering include enzymes, vectors, and host organisms.
Question 8.
Define Vectors.
Answer:
Vectors are defined as small DNA molecules capable of self-replication and are used as carriers and transporter of DNA fragments, inserted into them for cloning.
![]()
Question 9.
Define Biopiracy.
Answer:
Biopiracy is defined as the manipulation of intellectual property rights laws by corporations to gain exclusive control over national genetic resources.
Question 10.
What is a plasmid?
Answer:
Plasmids are extrachromosomal, self-replicating ds circular DNA molecules, found in bacterial cells in addition to chromosomal DNA.
Question 11.
Explain Chemical mediated gene transfer.
Answer:
The uptake of DNA into the plant protoplast is induced by some chemicals like polyethylene glycol (PEG) and dextran sulphate. This type of gene transfer is called chemical-mediated gene transfer.
Question 12.
What is an antibiotic gene marker?
Answer:
An antibiotic gene marker is a gene, which is coded for a protein, that provides the cells to resist to a particular antibiotic.
Question 13.
What is meant by ELISA?
Answer:
ELISA otherwise known as Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay is a diagnostic tool for the identification of pathogen species by using antibodies and diagnostic agents.
Question 14.
Define Transfection.
Answer:
Transfection is a technique of introduction of foreign nucleic acids into cells using non-viral methods.
Question 15.
What is a transgenic plant?
Answer:
A transgenic plant is a genetically modified plant, which contains a novel DNA introduced into its genome.
![]()
Question 16.
Name any two genetically modified food.
Answer:
- Bt Brinjal
- Flavrsavr Tomato
Question 17.
Define Biopharming.
Answer:
Biopharming has otherwise known as molecular pharming in which the use of genetically modified transgenic plants to produce pharmaceutical substances.
Question 18.
What is MycOremediation?
Answer:
Mycoremediation is a technique of reducing environmental pollutants using fungi.
Question 19.
What is Composting?
Answer:
Composting is a process in which solid waste is converted into useful manure by the use of microbes or Earthworms.
![]()
Short answer questions
Question 1.
What is a bioreactor?
Answer:
A bioreactor or fermentor is a designed vessel or container for the fermentation process. It provides an optimum environment in which microorganisms or their enzymes interact with a substrate to produce the required product. The environmental conditions like aeration, agitation, temperature, and pH are controlled in the fermentor for optimum production of a product.
Question 2.
Mention any three bioconversion done by fermenting microbes.
Answer:
The fermenting microbes are capable of producing valuable products, which as follows:
- Conversion of ethanol to acetic acid (Vinegar).
- Conversion of isopropanol to acetone.
- Conversion of sterols to steroids.
Question 3.
Name any three fungi used in the production of SCP?
Answer:
- Agaricus campestris
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast)
- Candida utilize.
Question 4.
Explain the types of restriction enzymes?
Answer:
A restriction enzyme is an enzyme, which is able to cut DNA molecules into fragments at desired sites within the molecule known as restriction sites. They are classified into Exonucleases and Endonucleases based on their mode of action.
- Endonucleases are the enzymes responsible for removing one nucleotide at a time from the end of a DNA molecule.
Eg: Bal 31, Exonuclease III - Endonucleases are enzymes that break the internal phosphodiester bonds within DNA molecules.
Eg: Hind II, EcoRI, Pvul, BamHI, TaqI.
![]()
Question 5.
Give a schematic diagram of Alkaline Phosphate action.
Answer:
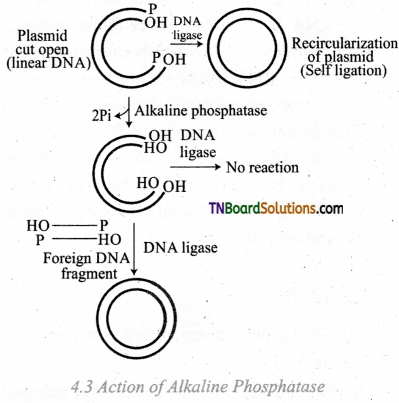
Question 6.
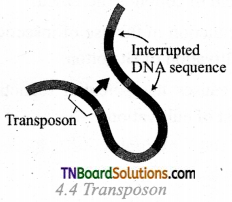
What is meant by the walking gene? Explain it briefly.
Answer:
Walking genes or jumping genes are DNA sequences able to insert themselves at a new location in the genome without having any sequence relationship with the target locus. They are also called transposons, which is well suited in E.coli studies. They are used as genetic tools for the analysis of gene and protein functions, which are responsible for phenotypic expression on the host cell.
Question 7.
Explain briefly about Biolistics.
Answer:
Biolistics is a process in which minute gold or tungsten particles (1-3 pm) are coated with foreign DNA on the surface. These particles coated with DNA are bombarded onto the target tissue or cells using a particle gun or gene gun. The cells or tissue with bombed particles are cultured in a selected medium to regenerate plants from the transformed cell.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the technique of Northern Blot.
Answer:
Alwin et al in 1979 devised this technique, as RNA is not binding cellulose nitrate, the chemical used in Southern blot. In this technique, RNA bands are transferred from the agarose gel into nitrocellulose filter paper. This technique of transfer of RNA from gel to special filter paper is known as Northern. Blotting hybridization. Amino Benzyloxy methyl paper of 540 what man paper is used in Northern Blot.
Question 9.
What are the advantages of Herbicide ” Tolerant crops?
Answer:
- Weed control in agriculture improves crop yields.
- The cultivation of these crops reduces the spray of herbicide.
- It reduces competition between crop plants and weeds.
- The use of low toxicity compound which do not remain active in the soil.
- It helps to conserve soil structure and microbes in the soil.
Question 10.
List the advantages of Bt cotton.
Answer:
- Due to effective control of bollworms, the yield of cotton is increased.
- Reduction in the use of insecticide in the cultivation of Bt cotton.
- It causes a potential reduction in the cost of cultivation.
Question 11.
List the examples of Bioremediation technologies.
Answer:
- Phytoremediation
- Mycoremediation
- Bioventing
- Bioleaching
- Bioaugmentation
- Composting
- Rhizofiltration
- Rhizostimulation
![]()
Question 12.
Distinguish between Rhizofiltration and Rhizostimulation.
Answer:
| Rhizofiltration | Rhizostimulation |
| Rhizofiltration is the uptake of metals or degradation of organic compounds using rhizosphere microorganisms. | Rhizostimulation is a process, in which the stimulation of plant growth by the rhizosphere which provides better growth condition or reduction in toxic material. |
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What is the importance of fermentation technology?
Answer:
Fermentation technology is a kitchen technology developed by our ancestors, using natural fermentation bacteria. It is a metabolic process in which organic molecules such as glucose are converted into alcohols, acids or gases like methane. The conversion takes place in the absence of oxygen or any electron transport chain. In 1856 Lois Pasteur demonstrated fermentation using yeast and this practice is called zymology. Certain types of bacteria and fungi, which thrive without oxygen can also be involved in fermentation.
The process of fermentation is employed in food and beverages industries, which are involved in the conversion of sugar into ethanol to produce alcoholic beverages. The production of CO2 by yeast can be used in the leavening of bread. The production of organic acids can preserve and flavor vegetables and dairy products.
![]()
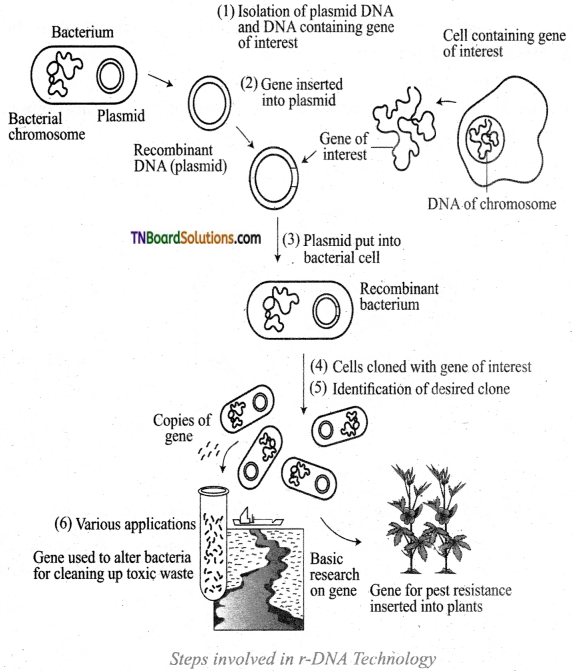
Question 2.
Describe the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer:
The following are the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
- Isolation of a DNA fragment having a gene of interest that needs to be cloned. This DNA fragment is known as an insert.
- The insertion of the DNA fragment into a carrier molecule called the vector produces recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecule. The vector molecule self-replicate within the host cell.
- The transformed host cells that carry the rDNA are selected and allowed to multiply resulting in the multiplication of the rDNA molecule.
- Thus the entire process generates a large amount of rDNA or a large amount of protein expressed by the insert.
- The desired gene is multiplied by the PCR technique if vectors are not involved. The microinjection or shotgun methods are employed to transfer the multiple copies of DNA into the host cell protoplasm.
Question 3.
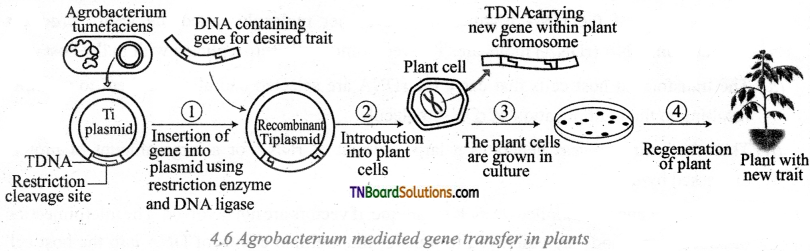
Explain the technique of Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer with a suitable diagram.
Answer:
Vector mediated gene transfer is the indirect type of gene transfer in which a placed vector helps in gene transfer. The T1 plasmid from Agrobacterium tumefacient has been used extensively in vector-based gene transfer. T1 plasmid (Tumor inducing) a portion of which is T-DNA is a large size plasmid. When transferred into to plant genome of the infected cell and cause plant tumors. (Crown gall). This bacterium has the natural ability to transfer the T-DNA region of its plasmid into the plant genome upon infection of cells at the wound site and this is called natural genetic engineering of plants.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the technique of biological hydrogen production by algae with the aid of a suitable diagram.
Answer:
Photobiological splitting of H2O is the technique used in the biological production of Hydrogen using algae. The algae, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii releases oxygen in normal photosynthesis. When it is deprived of sulfur, it switches to the production of hydrogen during photosynthesis and the electrons are transported to ferredoxins [F]- hydrogenase enzymes combine them into the production of hydrogen gas.
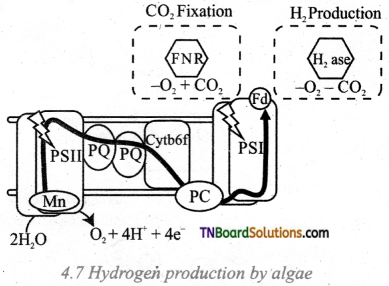
Question 5.
Bring out the differences between blotting techniques.
Answer:
There are three types of blotting techniques and the differences are tabulated below:
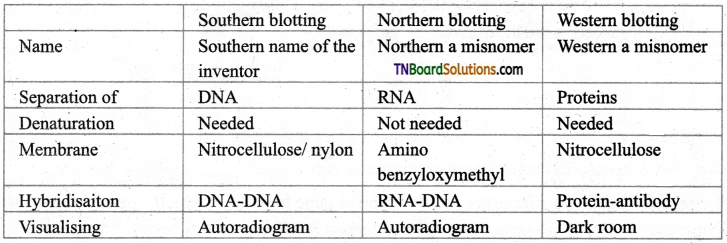
Question 6.
Draw the schematic diagram of steps involved in the Southern blotting technique.
Answer:
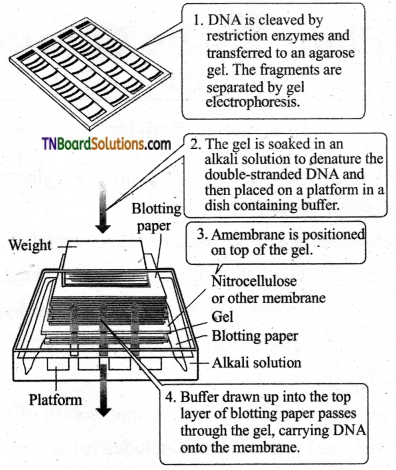
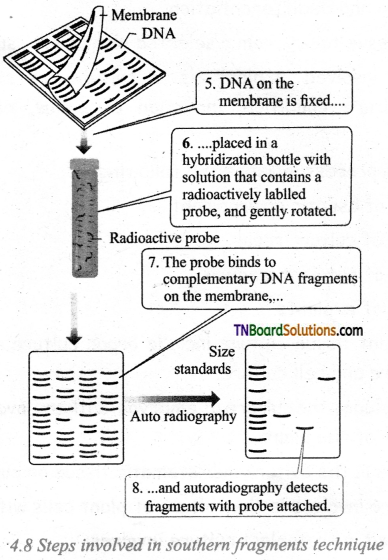
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
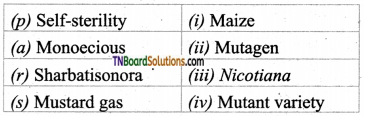
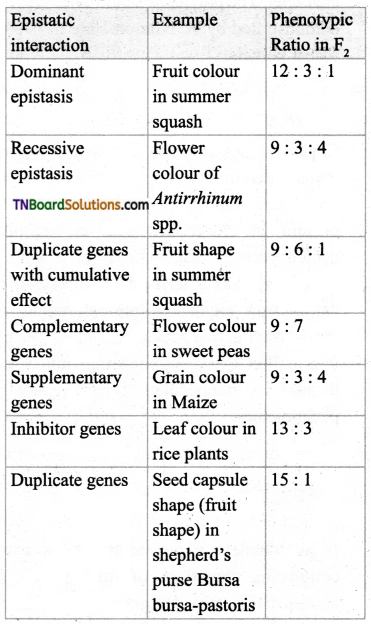
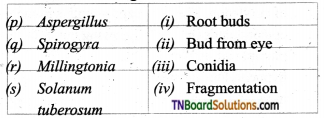
1. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(iii); (s)-(a)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
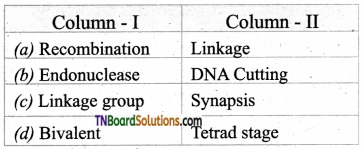
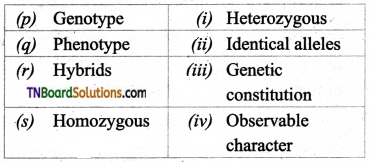
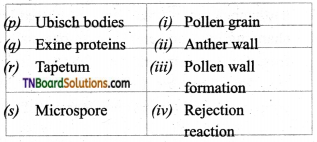
2. Match the following:
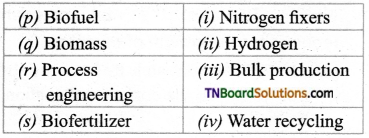
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(ii); (q)-(in); (r)-(iv); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(ii); (q)-(in); (r)-(iv); (s)-(i)
3. Match the following: (Products of Biotechnology)


(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
![]()
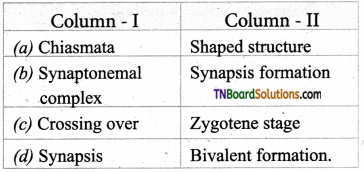
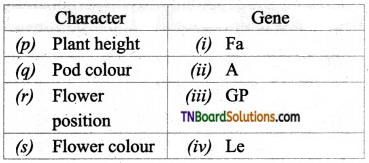
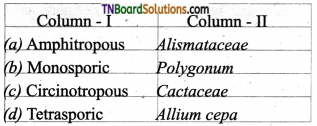
4. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(iii); (r)-(iv); (s)-(i)
Answer:
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(iii); (r)-(iv); (s)-(i)
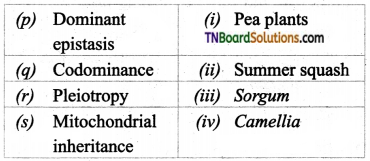
5. Match the following:
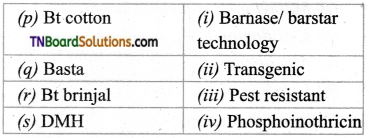
(a) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
6. Curd forming is a process of:
(a) Biodegradation
(b) Fermentation
(c) Sterilization
(d) Bioremediation
Answer:
(b) Fermentation
7. The technique of gene transfer using a pulse high voltage is known as:
(a) Liposome mediated transfer
(b) Electromagnetic transfer
(c) Electrophoration
(d) Biolistic
Answer:
(c) Electrophoration
8. The chemical used in southern blotting is:
(a) B galactoside
(b) Nitrophenol
(c) Nitrocellulose
(d) Benzyloxymethyl
Answer:
(c) Nitrocellulose
![]()
9. Bt Brinjal is produced by inserting a crystal protein gene from:
(a) Bacillus hyphae
(b) Streptomyces hygroscopic
(c) Streptomyces grises
(d) Bacillus thuringiensis
Answer:
(d) Bacillus thuringiensis
10. Addition of selected microbes to speed up degradation process called:
(a) Bioleaching
(b) Bioaugmentation
(c) Biofilteration
(d) Bioventing
Answer:
(b) Bioaugmentation
11. Choose the odd man out:
(a) Ethanol
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Vitamins
(d) Citric acid
Answer:
(c) Vitamins
12. Indicate the odd one out:
(a) Fermentation
(b) r-DNA technology
(c) Bioconversion
(d) SCP production
Answer:
(b) r-DNA technology
13. Find out the odd one:
(a) Methylophilus methylotropus
(b) Cellulomonas
(c) Alcaligenes
(d) Candida utilis
Answer:
(d) Candida utilis
![]()
14. Choose the odd one:
(a) Hind III
(b) CoIEl
(c) EcoRI
(d) BamHI
Answer:
(b) CoIEl
15. Indicate the odd one:
(a) Micro injection
(b) Electroporation
(c) Biolistic
(d) Western blot
Answer:
(d) Western blot
16. Chooose the correct pair.
(a) Streptomyces grises – Tetracycline
(b) Streptomyces nodosus – Amphotericin-B
(c) Streptomyces aureofacins – Penicillin
(d) Penicillin chryosogenum – Streptomycin
Answer:
(b) Streptomyces nodosus – Amphotericin-B
17. Find out the incorrect pair.
(a) Genetic Engineering – r-DNA technology
(b) Restriction Enzyme – Endonuclease
(c) DNA ligase – Clevage enzyme
(d) Vector – Plasmid
Answer:
(c) DNA ligase – Clevage enzyme
18. Indicate the correct pair:
(a) Ti plasmid – Agrobacterhim tumifaciens
(b) Walking gene – Expression vector
(c) Gene transfer – Nitrocellulose
(d) Liposome – artificial glycolipid vesicle
Answer:
(a) Ti plasmid – Agrobacterhim tumifaciens
19. Choose the incorrect pair:
(a) Bt cotton – GM food
(b) Basta – Herbicide tolerant
(c) Bt Brinjal – Delhi university
(d) DMH-II – Transgenic mustard
Answer:
(c) Bt Brinjal – Delhi university
20. Indicate the correct pair:
(a) Phytoremediation – use of algae
(b) Mycoremediation – use of Fungi
(c) Bioventing – use of plants
(d) Bioleaching – use of earthworm
Answer:
(b) Mycoremediation – use of Fungi
![]()
21. Assertion: Traditional Biotechnology is the kitchen technology by using fermenting bacteria.
Reason There is no scientific validation of these kitchen technologies.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
22. Assertion: Secondary metabolites are those i which are required for the vital life process of microbes.
Reason: They are the vital compounds required for the growth of microbes.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is not correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
23. Assertion: The single-cell protein forms an important source of food.
Reason: Because they contain protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
![]()
24. Assertion (A): The restriction enzymes are called as molecular scissors.
Reason (R): They cleave the DNA molecules into fragments at specific recognition sites.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
25. Assertion (A): Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable and bioactive thermoplastic.
Reason (R): It is an aliphatic polyester derived from renewable resources.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true. But Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
26. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Liposomes are the artificial lipoprotein vesicles vised for gene transfer.
(b) Liposomes are the artificial glycoprotein vesicles used for gene transfer.
(c) Liposomes are the artificial phospholipid vesicles used for gene transfer.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Liposomes are the artificial phospholipid vesicles used for gene transfer.
27. Choose the incorrect statement.
(a) The bacterium Strepfpmyces nodosus produces the antibiotic Amphotericin-B.
Ethanol is the primary metabolite produced by microorganisms.
(c) Vitamins are the secondary metabolites.
(d) All the above statements are not correct.
Answer:
(d) All the above statements are not correct.
![]()
28. Indicate the correct statement:
(a) Humulin is the first pharmaceutical product of rDNA technology for human use.
(b) The first transgenic animal, Dolly was developed by rDNA technology.
(c) First crop plant genome was sequenced in wheat.
(d) Sir Robert G.Edwards grew stem cells in the laboratory.
Answer:
(a) Humulin is the first pharmaceutical product of rDNA technology for human use.
29. Which of the following statement is wrong:
(a) Enzymes are biosensors in the processing industry.
(b) Biomass is the bulk production of single-cell organisms.
(c) Process engineering is the tool of biotechnology used for effluent treatment.
(d) All the above statements are wrong.
Answer:
(d) All the above statements are wrong.
30. Choose the correct statement.
(a) Composting is the process of recycling solid waste by microbes.
(b) Composting is the process of recycling solid waste by plants.
(c) Bioleaching is the use of plants to recover metal pollutants.
(d) Rhizofiltration is the process of water purification.
Answer:
(a) Composting is the process of recycling solid waste by microbes.