Students get through the TN Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 7 International Economics which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 7 International Economics
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is the Foreign exchange rate?
Answer:
It is a rate at which the currency of one country can be exchanged for the currency of another country.
Question 2.
Write about the equilibrium in the Foreign exchange market.
Answer:
Equilibrium in a free fluctuating foreign exchange market is brought out by the interaction of forces of demand and supply of foreign exchange.
![]()
Question 3.
What is parity value?
Answer:
In a fixed exchange rate system, the value of the currency will be fixed in terms of other currencies or in terms of gold. This value is known as the parity value of the currency.
Question 4.
When is there a deficit in BOT?
Answer:
When the value of exports is less than the value of imports, then there will be a deficit in BOT.
Question 5.
What are the components of BOT?
Answer:
Export of goods and import of goods.
Question 6.
Name four items of the current account of BOT.
Answer:
- Export and import of goods.
- Export and import of services.
- Unilateral transfers.
- Investment income.
Question 7.
Name the two accounts of the BOP account.
Answer:
The current account and the capital account.
Question 8.
What is meant by disequilibrium in BOP?
Answer:
It means that there is either surplus or deficit in a BOP.
![]()
Question 9.
Write the causes for disequilibrium in a BOP.
Answer:
- Large imports due to large-scale development expenditure.
- High domestic prices
- New sources of supply and new substitutes
- Political instability
- Changes in taste, fashion, and preference.
Question 10.
Write various forms of capital account transactions.
Answer:
- Private transactions
- Official transactions
- Direct investment
- Portfolio investment
Question 11.
Define comparative cost advantage.
Answer:
According to Ricardo, “a country can gain from trade when it produces at relatively lower costs. Even when a country enjoys an absolute advantage in both goods; the country would specialize in the production and export of goods of those goods which are relatively more advantageous.”
Question 12.
What is Foreign exchange?
Answer:
Forex is Foreign currencies. It is a mechanism through which payments are effected between two countries having different currency systems.
Question 13.
What do you mean by exchange control?
Answer:
It means that the state intervention in the Forex market. It is a popular method used to influence the BOP position in the country.
Question 14.
What is import control?
Answer:
Imports may be controlled by imposing import duties, restricting imports through import quotas. Licensing and even prohibition of import of certain unimportant products would encourage smuggling.
![]()
Question 15.
What is the meaning of trade?
Answer:
It is expressed as the relationship between export prices and import prices. Term of trade improves when the average price of exports is higher than the average price of imports.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Name the major sectors that benefitted from FDI in India.
Answer:
- Financial sector
- Insurance
- Telecommunication
- Hospitality and tourism
- Pharmaceuticals and
- Software and information technology.
Question 2.
Which are the industrial sectors where FDI is not permitted?
Answer:
- Arms and ammunition
- Atomic energy
- Railways
- Coal and lignite and
- Mining of iron, manganese, etc.
Question 3.
What are the measures to correct BOP disequilibrium?
Answer:
- Depreciation
- Devaluation
- Import control
- Export promotion
- Exchange control
- Production of import substitutes
- Monetary policy
- Capital import
Question 4.
What are the determinates of exchange rates?
Answer:
Differentials in inflation, the differential in interest rates, current account deficit, public debt, terms of trade, political and economic stability, recession, and speculation.
Question 5.
Define (a) NEER, (b) REER and (c) RER.
Answer:
- NEER is the measure of the average relative strength of a given currency without eliminating the effect of price change.
- REER is an effective exchange rate based on real exchange rates instead of nominal rates.
- RER is the exchange rate that is based on constant prices to eliminate the effect of price changes.
Question 6.
Distinguish between BOP and BOT.
Answer:
BOP: It is the difference between nations’ total payment to foreign countries and its receipts from them during a period of time.
BOT: It is the difference between the money value of imports and exports of material goods only. Whereas BOP is the difference between a country’s receipts and payments in Foreign exchange.
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Explain the gains from international trade.
Answer:
The gains from international trade may be categorized under four heads.
(a) Efficient productions: International specialization gives the gains of
- Better utilization of resources.
- The concentration of production of advantageous goods.
- Saving in time.
- Perfection of skills in production.
- Improvements in the techniques of production.
- Increased production.
- A higher standard of living in the trading countries.
(b) Equalization of prices between countries: International trade may help to equalize prices in all the trading countries.
- Prices of goods are equalized between the countries.
- The difference in cost of transportation.
- Prices of factors of production are also equalized.
(c) Equitable distribution of scarce materials: It may help the trading countries to have equitable distribution of scarce resources.
(d) General advantages of international trade:
- Availability of a variety of goods for consumption.
- Generation of more employment opportunities.
- Industrialization of backward nations.
- Improvement in the relationship among countries.
- Divisions of labour and specialization.
- Expansions in transport facilities.
![]()
Question 2.
Balance of payment – disequilibrium correction explain, (or) Explain the flow chart of the balance of payment disequilibrium.
Answer:
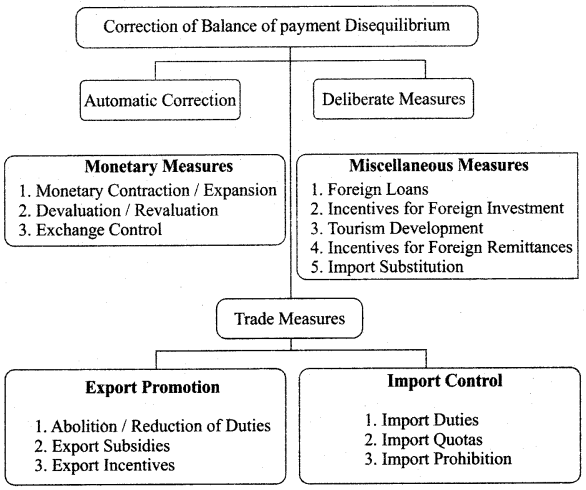
Question 3.
What are the advantages of FDI?
Answer:
- It increases the investment level and in course and employment in the country.
- It facilitates the transfer of technology to the recipient country.
- It brings revenue to the country by tax profits and royalties from concession agreements.
- Expansions, modernization, or development of industries are part of the profit from FDI.
- Through professional management, a managerial revolution is created.
- The export is increased and import is reduced through foreign capital.
- The social returns are greater than the private returns on foreign investment if FDI adds more value to output.
- It helps to increase competition and break domestic monopolies.
- By bringing capital and foreign exchange, FDI may help in filling the earnings gap in order to achieve the goal of national economic development.
- It stimulates domestic enterprises to invest in ancillary industries.
- It also encourages its entrepreneurs to invest.
Question 4.
What are the disadvantages of FDI – Explain.
Answer:
The disadvantages are:
- Private foreign capital tends no flow to the high-profit areas rather than to the priority sectors.
- The technologies brought in by the foreign investor may not be appropriate to the consumption needs.
- Foreign investment has a sometimes unfavorable effect on the balance of payment.
- It sometimes interferes in national politics.
- Foreign investors sometimes engage in unethical trade practices.
- Foreign investment in some cases leads to the destructions or weakening of small and medium enterprises.
- Sometimes foreign investment can result in the dangerous situations of minimizing competitions and creation of monopolies.
- Often there are several costs associated with encouraging foreign investment.
![]()
Activity
Question 1.
Students may be brought to any firm or industry which is involved in foreign trade to make them know the different procedures followed and activities done.
Answer:
- This activity helps to analyze how people are involved in foreign trade.
- Helps to develop a deep understanding of the industry and foreign trade procedures.
- Helps to understand the difference between internal and international trade.
- Helps to know the procedures involved in foreign trade.
- Helps to know about the economy and how foreign trade is practiced in India.
Question 2.
Students may be grouped as countries and directed to have a look at some available goods to be exchanged between them as if they involve in foreign trade.
Answer:
- Helps in interpersonal relationships.
- Helps to take decisions in life.
- Helps to develop a deep understanding of one’s own country and to do a comparison.
- Helps to understand the difference between the barter system and money usage.
- Helps in self-assessment and self-learning.
Multiple choice questions
1. …………. is one of the powerful force of economic integration.
(a) BOP
(b) BOT
(c) Trade
(d) FDI
Answer:
(c) Trade
2. International trade refers to exchange of goods and services between countries.
(a) Two or more
(b) Four
(c) Five
(d) Three
Answer:
(a) Two or more
![]()
3. …………… in 1776 developed the theory of absolute cost advantage.
(a) Alfred Marshall
(b) Adam Smith
(c) David Ricardo
(d) J.S. Mill
Answer:
(b) Adam Smith
4. The modern theory of international trade was developed by economist Eli Heckscher.
(a) German
(b) French
(c) Sweedish
(d) American
Answer:
(c) Sweedish
5. If for a given quantity of export, more quantity of import can be consumed by a country, then one can say that terms of trade are:
(a) Correct
(b) Favourable
(c) Not correct
(d) Unfavourable
Answer:
(b) Favourable
6. The income terms of trade was given by in 1948.
(a) Adam Smith
(b) J.S.Mill
(c) G.S.Dorrance
(d) Ricardo
Answer:
(c) G.S.Dorrance
7. ………….. has devised another concept called the single factoral terms of trade.
(a) Viner
(b) G.S. Dorrance
(c) Ricardo
(d) Marshall
Answer:
(a) Viner
![]()
8. Gross barter terms of trade was an improvement over:
(a) Balance of trade
(b) Balance of payment
(c) Net terms of trade
(d) Factoral terms of trade
Answer:
(c) Net terms of trade
9. BOP and BOT are two different concepts in the subject of:
(a) Internal Trade
(b) External Trade
(c) International Trade
(d) Home Trade
Answer:
(c) International Trade
10. Export and imports of commodities are also known as:
(a) Invisible trade
(b) Direct trade
(c) Visible trade
(d) Indirect trade
Answer:
(c) Visible trade
11. BOP is to be favourable that is:
(a) R/P > 1
(b) R/P < 1 (c) R/Q > 1
(d) R/Q < 1 Answer: (a) R/P > 1
12. World trade shrinks during:
(a) Equilibrium
(c) Inflation
(b) Disequilibrium
(d) Depression
Answer:
(d) Depression
13. Structural disequilibrium is called in ………… economics.
(a) Traditional
(b) Developing
(c) Underdeveloped
(d) Capitalistic
Answer:
(b) Developing
![]()
14. Deficit in the balance of payment of developing countries is caused by:
(a) Veblen effect
(b) Demonstration effect
(c) Giffen effect
(d) Income effect
Answer:
(b) Demonstration effect
15. When the market forces of demand and supply are allowed to play freely ……….. will be restored.
(a) Demand
(b) Supply
(c) Market
(d) Equilibrium
Answer:
(d) Equilibrium
16. ……… is responsible for high imports and how exports.
(a) High domestic price level
(b) High domestic income level
(c) High domestic supply level
(d) High domestic exchange level
Answer:
(a) High domestic price level
17. …………. means a deliberate reduction of the official rate
(a) Inflation
(b) Deflation
(c) Devaluation
(d) Price discrimination
Answer:
(c) Devaluation
18. Exchange control means the state intervention in the:
(a) FOREX market
(b) Capital market
(c) Monopoly market
(d) Perfect market
Answer:
(a) FOREX market
19. ……….. is a method employed to influence the BOP in a country.
(a) Credit control
(b) Exchange control
(c) Money control
(d) Devaluation
Answer:
(b) Exchange control
![]()
20. …………… refers to foreign currencies.
(a) FOREX
(b) USD
(c) GNP
(d) NDP
Answer:
(a) FOREX
21. Inflation and exchange rates are ………. related.
(a) Positively
(b) Negatively
(c) Directly
(d) Inversely
Answer:
(d) Inversely
22. RBI can influence both inflation and exchange rates by manipulating:
(a) Rate of income
(b) Rate of supply
(c) Interest rate
(d) Rate of demand
Answer:
(c) Interest rate
23. Excess demands for foreign currency ………. a country’s exchange rate.
(a) Lowers
(b) Increases
(c) Equalises
(d) Spoils
Answer:
(a) Lowers
![]()
24. ……….. is part of the capital account of the BOP.
(a) FII
(b) FDI
(c) CRR
(d) FPI
Answer:
(d) FPI
25. Foreign investment takes the form of:
(a) Indirect investment
(b) Direct investment
(c) Induced investment
(d) Capital investment
Answer:
(b) Direct investment
26. Balance of payments of a country is a statement that records:
(a) Sources of foreign exchange
(b) Uses of foreign exchange
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
27. The categories of transactions that are included in the current account of BOP are:
(a) Exports and imports of goods
(b) (a) + exports and imports of services
(c) (b) + income from and to abroad
(d) (c) + Transfers from and to abroad
Answer:
(d) (c) + Transfers from and to abroad
28. Balance of trade equal:
(a) Exports less imports
(b) Exports of goods less import of goods
(c) Exports of services less import of services
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Exports of goods less import of goods
![]()
29. The categories of transactions that are included in the capital account of BOP are:
(a) Investments from and to abroad
(b) Borrowings and lendings from and to abroad
(c) Changes in foreign exchange reserves
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
30. The measurement of the balance of payments deficit is based on:
(a) Autonomous transactions
(b) Accounting transactions
(c) Current account transactions
(d) Capital account transactions
Answer:
(a) Autonomous transactions
Pick the odd one out.
1. International economics consists of not only trade in goods and services but also:
(a) Capital flows
(b) Demand
(c) BOP
(d) Rate of exchange
Answer:
(b) Demand
2. The financial institutions like:
(a) IMF
(b) IBRD
(c) ICICI
(d) Moneylender
Answer:
(d) Moneylender
3. Internal trade is also known as:
(a) Domestic trade
(b) Home trade
(c) Foreign trade
(d) Intra – regional trade
Answer:
(c) Foreign trade
![]()
4. Comparative cost theory was refined by:
(a) J.S.Mill
(b) Marshall
(c) Taussing
(d) Adam Smith
Answer:
(d) Adam Smith
5. The principle items shown on the credit side are:
(a) Transfer receipts in the forms of gifts
(b) FDI
(c) Borrowing from abroad
(d) Balance of trade
Answer:
(d) Balance of trade
6. The principle items on the debit side include imports of goods and services and:
(a) Transfer payment to foreigners
(b) Lending to foreign countries
(c) Gold from foreign countries
(d) Deficit payment
Answer:
(d) Deficit payment
7. The official reserve assets of a country include its:
(a) Gold stock
(b) SDR
(c) convertible foreign currencies
(d) Balance of trade
Answer:
(d) Balance of trade
8. Types of BOP disequilibrium are:
(a) Cyclical disequilibrium
(b) Secular disequilibrium
(c) Structural disequilibrium
(d) Development disequilibrium
Answer:
(d) Development disequilibrium
![]()
9. The less developed countries in the early stage of development depend on developed countries for:
(a) Import of commodities
(b) Demand of commodities
(c) Capital and technology
(d) Export potential is low
Answer:
(b) Demand of commodities
10. Under free exchange the automatic adjustments of BOP can take place through changes in the variables like :
(a) Price
(b) Interest
(c) Income
(d) Supply
Answer:
(d) Supply
11. The deliberate measures may be broadly grouped into:
(a) Monetary measures
(b) Trade measures
(c) Export measures
(d) Miscellaneous measures
Answer:
(c) Export measures
12. FDI is helpful to accelerate economic growth by development programmes like:
(a) Capital goods
(b) Raw materials
(c) Rural development
(d) Others inputs
Answer:
(c) Rural development
![]()
13. Fll is an investment in:
(a) Insurance companies
(b) Pension funds
(c) Bill of exchange
(d) Pension funds
Answer:
(c) Bill of exchange
14. FDI has been advantages in terms of:
(a) Improved technology
(b) Education
(c) Access to markets
(d) Free flow of capital
Answer:
(b) Education
15. FDI Firms in India have started investing in countries like:
(a) Nepal
(b) Tamilnadu
(c) Uganda
(d) Ethopia.
Answer:
(b) Tamilnadu