Students get through the TN Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 3 Reproductive Health which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Bio Zoology Important Questions Chapter 3 Reproductive Health
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is amniocentesis?
Answer:
Amniocentesis is a technique used to find out any chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus.
Question 2.
Expand the abbreviation POCSO and PCPNDT.
Answer:
- POCSO – Prevention of Children from Sexual Offences.
- PCPNDT – Preconception and Prenatal Diagnostic Technique.
Question 3.
Define Birth control.
Answer:
Birth control is the voluntary use of contraceptive methods to prevent childbirth, by preventing fertilization of egg or by preventing the implantation of the embryo in the uterus.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the natural contraceptive method?
Answer:
The natural contraceptive method is the procedure to prevent the meeting of sperm with ovum in order to prevent fertilization.
Question 5.
Mention any two chemical barriers used in the contraceptive methods.
Answer:
- Foaming tablets
- Melting suppositories
Question 6.
Explain briefly the hormonal barrier in the contraceptive devices.
Answer:
The hormonal barrier is a contraceptive method, in which the hormonal imbalance prevents the ovaries from releasing ova and thickens the cervical fluid. This keeps the sperm away from the ovum.
Question 7.
What are Non-medicated IUDS?
Answer:
Non-medicated IUDs are intrauterine devices made of plastic or stainless steel.
Eg: the Lippes loop is a double S-Shaped plastic device.
Question 8.
Name any two copper releasing lUDs.
Answer:
- NOVaT
- Multiload 375.
![]()
Question 9.
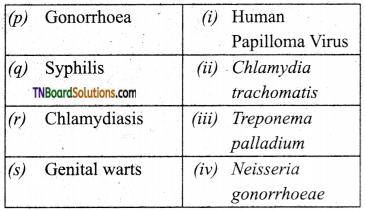
Name any two bacterial sexually transmitted diseases.
Answer:
- Chlamydiosis
- Syphilis
Question 10.
What are the risk factors for cervical cancer? The risk factors for cervical cancer include:
Answer:
- Having sex with multiple unknown partners.
- Prolonged use of contraceptive pills.
Question 11.
Define Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART).
Assisted reproductive technology is a collection of procedures, in which the handling of gametes and/or embryos outside the body to achieve a pregnancy are carried out.
Question 12.
Define Mayer-Rokintansky syndrome.
Answer:
Mayer-Rokintansky syndrome is a condition, in which women do not have a functional uterus.
Question 13.
What is the embryo transfer technique?
Answer:
The embryo transfer technique is the method of transferring an embryo with cells more than the blastomere stage into the uterus.
Question 14.
Define Azoospermia.
Answer:
Azoospermia is defined as the absence of spermatozoa in the ejaculated semen on at least two occasions.
Question 15.
What is Foetoscope?
Answer:
Foetoscope is an instrument used to monitor the heart rate of foetus and other functions during late pregnancy and labor.
![]()
Short answer questions
Question 1.
List the health care programs taken up by the Government of India.
Answer:
- Massive child immunization.
- Supply of nutritional food to pregnant women.
- Implementation of Janani Suraksha Yojana, Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram, RMNCH + A approach (An integrated approach for reproductive, maternal, newborn, child, and adolescent health), Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matriva Abhiyan, etc…
Question 2.
The sex ratio in India has changed from 919 females to every 1000 males. How? Explain.
Answer:
The female foeticide and female infanticide is a manifestation of gender discrimination, in our society, which increases the female foeticide and female infanticide. This leads to the imbalance of sex ratio in our society and to correct this ratio to normal, steps are needed to change the mindset and attitude of people, especially in young adults.
Question 3.
Define lactational amenorrhoea. Explain it as a natural birth control method.
Answer:
Lactational amenorrhoea is defined as the delay in the ovarian cycle due to breastfeeding after childbirth. It serves as a natural, but unreliable form of birth control. During breastfeeding, the sucking of milk by the baby stimulates the pituitary to secrete more prolactin in order to increase milk production. The increased level of prolactin in the blood of the mother may prevent the menstrual cycle by suppressing the release of GnRH (Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone) which in turn suppresses the production of gonadotropin from the pituitary. Thus lactational amenorrhoea indirectly acts as a natural birth control agent.
![]()
Question 4.
Write briefly about oral contraceptives.
Answer:
Oral contraceptives are taken orally in the form of pills, used to prevent ovulation in females. They inhibit the secretion of FSH and LH hormones. The most commonly used birth control pills are combined pills, which contain synthetic progesterone and estrogen hormones. Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow, India developed a nonsteroidal contraceptive pill, called saheli.
Question 5.
Mention the fungal sexually transmitted disease, their causative organisms, and symptoms.
Answer:
Candidiasis: The causative organism is Candida albicans.
Symptoms: It attacks the mouth, throat, intestinal tract, and vagina. It also causes vaginal itching or soreness, abnormal vaginal discharge, and pain during urination.
Trichomoniasis: This disease is due to the fungal infection by Trichomonas vaginalis.
Symptoms: It causes vaginitis, greenish-yellow vaginal discharge, itching, and burning sensation, urethritis, epididymitis, and prostatitis.
Question 6.
What are the causes of infertility in men?
Answer:
- Undescended testes and swollen veins (Varicocoele) in the scrotum,
- The rise of temperature in the scrotum due to tight clothing in men may affect sperm production.
- Underdeveloped testes.
- Males may develop an autoimmune response to their own sperm.
![]()
Question 7.
Name any three procedures followed under assisted reproductive technology.
Answer:
The ART includes:
- Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI)
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Embryo Transfer (ET)
Question 8.
Explain intra-fallopian transfer (GIFT).
Answer:
In this technology, the ovum collected from a donor is transferred into the fallopian tube of the recipient. The transferred eggs are placed with the sperms in the fallopian tube for fertilization. The fertilized egg/zygote moves towards the uterus and gets implanted in the inner lining of the uterus.
Question 9.
What is surrogacy? Explain it briefly.
Answer:
Surrogacy is a method of assisted reproduction or an agreement whereby a woman agrees to carry a pregnancy for another person, who will become the parent of the new born child after birth. The embryos are produced through in vitro fertilization in the lab and are transferred into the uterus of a surrogate mother.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
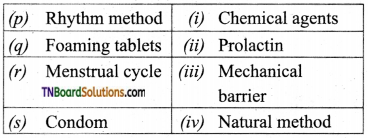
Describe the different natural methods of birth control.
Answer:
The natural method of birth control is used to prevent the meeting of eggs with sperm.
These methods include the Rhythm method (safe period), coitus interruptus, continuous abstinence, and lactational amenorrhoea.
- Rhythm method: In the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs at about the 14th day and the ovum survives for about two days, whereas in the female reproductive tract, the sperms remain alive for about 72 hrs. If the coitus takes place avoiding this time, the fertilization may not take place.
- Continuous abstinence: It is the simplest and most reliable method to avoid pregnancy. In this, it is better not to have coitus for a defined period that facilitates conception.
- Coitus interruptus: It is the oldest family planning method, in which the male partner withdraws his penis before ejaculation, preventing the deposition of semen into the vagina.
- Lactational amenorrhoea: After parturition, the menstrual cycle resume as early as 6-8 weeks. But during breastfeeding, the menstrual cycle is delayed for about six months due to lactational amenorrhoea. During the breastfeeding period, the sucking by the baby stimulates the pituitary to secrete more prolactin hormone in order to increase milk production. This increased concentration of prolactin in the blood suppresses the release of Gonad Stimulating Etormone from the hypothalamus, which in turn prevents the gonadotropin secretion from the pituitary, resulting in the prevention of the menstrual cycle.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Answer:
Intrauterine devices are the materials inserted in the uterus through the vagina by medical experts, in order to prevent pregnancy. It is one of the popular methods of birth control with a success rate of 95 to 99% in India. These devices include
- Copper releasing IUDs
- Hormone releasing IUDs and
- Non-medicated IUDs. IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperm within the uterus and are the ideal contraceptive for women.
(i) Copper releasing IUDs: Copper releasing IUDs are CuT-380A, NovaT, Cae7, CuT 380 Ag, Multiload 375 etc., and they differ from each other by the amount of copper they release as free copper or copper salts into the uterus and prevent sperm motility. They can remain in the uterus for five to ten years.
(ii) Hormone releasing IUDs:
releasing IUDs are progestagen and ING – 20, which are often called as intrauterine systems (IUS). They prevent sperms from entering the cervix by increasing the viscosity of the cervical mucus.
(Hi) Non-medicated IUDs: They are made up of stainless steel or plastic. Double ‘S’ shaped plastic lippes loop is a typical example of a non-medicated IUD.
Question 3.
Describe the method of surgical sterilization.
Answer:
Surgical sterilization methods are permanent birth control methods known as vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females. They block the transport of gametes and prevent fertilization.
(i) Vasectomy: Vasectomy is the male sterilization through a surgical procedure. In this, both the vas deferens are cut and tied through a small incision on the scrotum in order to prevent the entry of sperm into the urethra. Hence the discharge from the penis has no sperms and has no chance of fertilization.
(ii) Tubectomy: The tubectomy is the surgical sterilization in females, in which a small portion of fallopian tubes is cut and tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through the vagina. This prevents the entry of eggs into the uterus as well as fertilization.
![]()
Question 4.
What is cervical cancer? Explain its causes and preventions.
Answer:
Cervical cancer is the abnormal growth of cervical cells or cervical dysplasia, caused by a sexually transmitted virus namely Human Papilloma Virus (HPV).
The Pelvic pain, increased vaginal discharge and abnormal vaginal, bleeding are the symptoms of cervical cancer. Prolonged use of contraceptive pills and having multiple sexual partners are the major risk factors.
Cervical cancer can be diagnosed by a PAP smear (Papanicolaou smear) combined with an HPV test. The stages of cancer can be detected by X-ray, CT scan, MRI and PET scan. Radiotherapy, surgery, and chemotherapy are the options of treatment for cervical cancer.
The precancerous changes in the cervical region can be detected by modem screening techniques and therefore cervical cancer screening can be done for women above 30 years of age once a year. Now vaccination to prevent cervical cancer is available and the HPV vaccination can be given to girls aged between 9-13 years before they attain puberty. Cervical cancer can be prevented by modifications in lifestyle such as having a healthy diet, avoiding tobacco usage, preventing early marriages, practicing monogamy, and regular exercise.
Question 5.
Describe the method of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
Answer:
In vitro fertilization is the procedure in which sperm and eggs are allowed to fertilize outside the body in the laboratory. After fertilization, one or more fertilized eggs are introduced into the uterus of a woman, where they may implant in the wall of the uterus and develop. The excess fertilized eggs can be preserved for future use through cryopreservation. This technique was first used to treat women with blocked, damaged, or absent fallopian tubes. Nowadays this technique is used to treat many cases of infertility. The basic steps involved in IVF treatment include ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization, embryo culture, and embryo transfer.
After 34 to 37 hrs of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) injection, an egg from the ovary is retrieved by minor surgery under anesthesia, using an ultrasound guide. Eggs are prepared by stripping from the surrounding cells. At the same time, sperm preparation is also carried out in special media. For each egg, 10000 – 1,00,000 sperms are needed and the eggs and sperms are brought together for fertilization. The fertilized egg or the zygote is then allowed to divide and form 8 celled blastomere, which is transferred into the uterus for further growth.
The embryo transfer technique is the transfer of an embryo with more than 8 celled blastomere stage into the uterus.
![]()
Choose the correct answers.
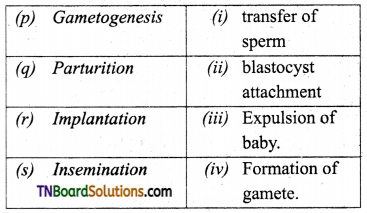
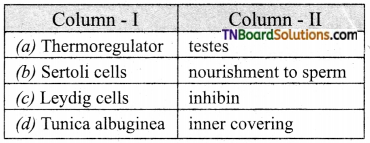
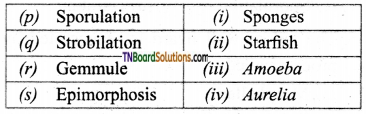
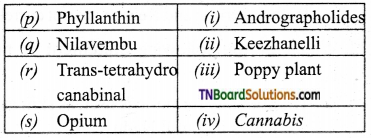
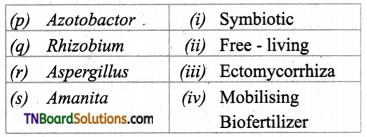
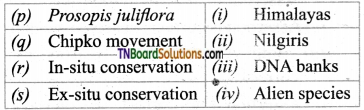
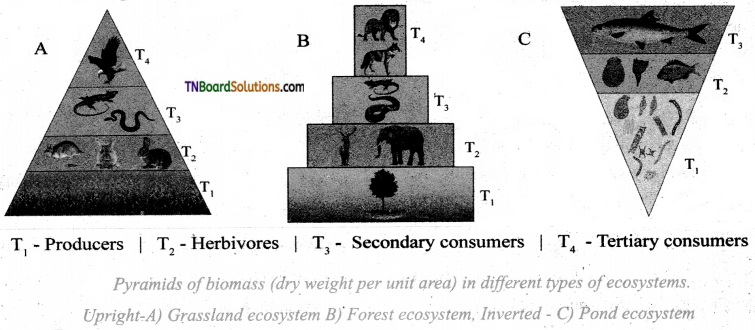
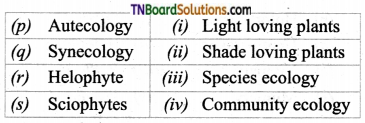
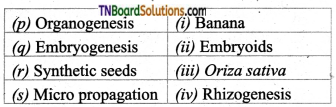
1. Match the following:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(i); (r)-(ii); (s)-(iii)
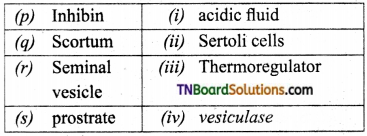
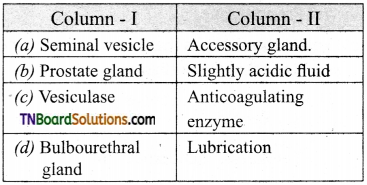
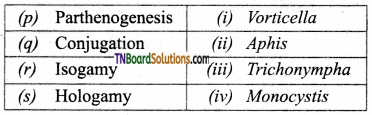
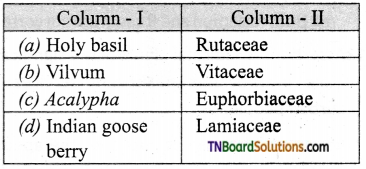
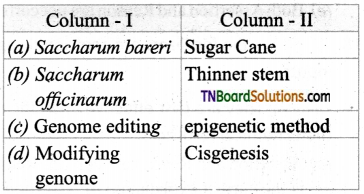
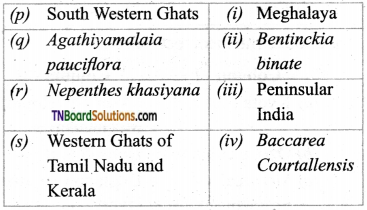
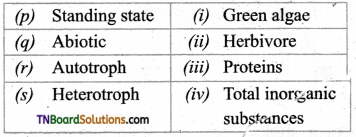
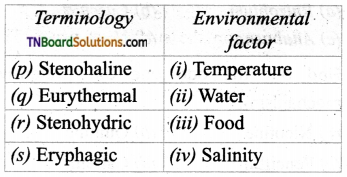
2. Match the following:

(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(d) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
Answer:
(c) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
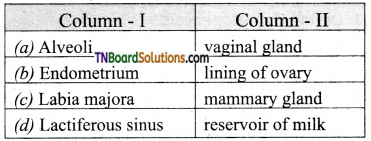
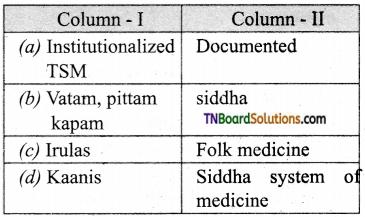
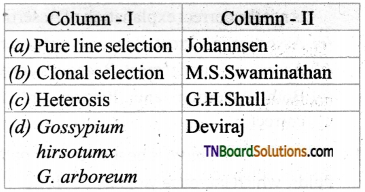
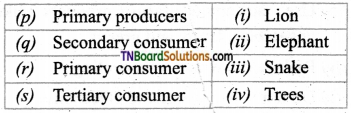
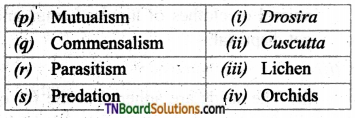
3. Match the following:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
![]()
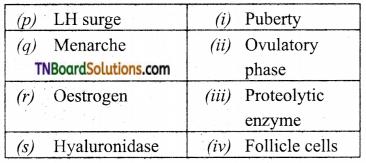
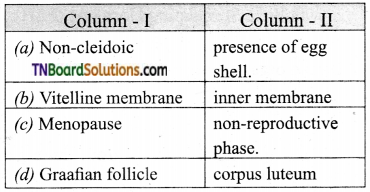
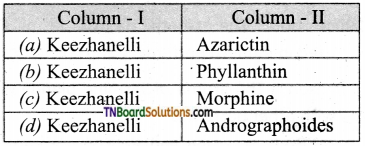
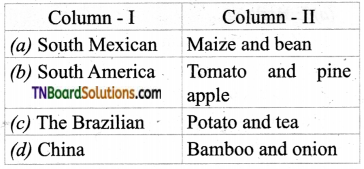
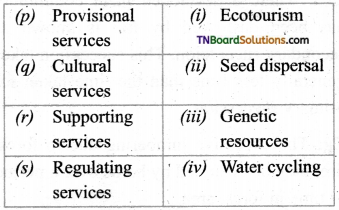
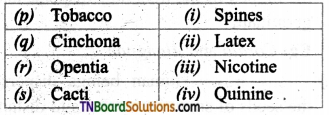
4. Match the following:
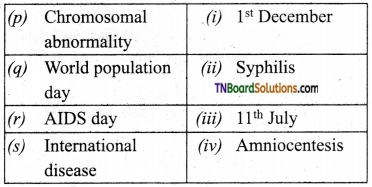
(a) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(ii); (s)-(i)
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
(c) (p)-(ii); (q)-(i); (r)-(iv); (s)-(iii)
(d) (p)-(iii); (q)-(iv); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
Answer:
(b) (p)-(iv); (q)-(iii); (r)-(i); (s)-(ii)
5. In which year Family planning programme was initiated:
(a) 1957
(b) 1962
(c) 1951
(d) 1953
Answer:
(c) 1951
6. An ideal contraceptive should be:
(a) User friendly
(b) Easily available
(c) With least side effect
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
7. When is Justice Verma committe instituted?
(a) 2011
(b) 2016
(c) 2013
(d) 2003
Answer:
(c) 2013
8. W uch of the following is sexually transmitted disease?
(a) Elephantiasis
(b) Hepatitis B
(c) Gonorrhoea
(d) Liver cirrhosis
Answer:
(c) Gonorrhoea
![]()
9. Choose the odd man out:
(a) Gonorrhoea
(b) Chlamydiasis
(c) Candidiasis
(d) Lymphogranuloma venereum
Answer:
(c) Candidiasis
10. Find the odd one out:
(a) Rhythm method
(b) Copper IUD
(c) LNG 20
(d) Condom
Answer:
(a) Rhythm method
11. Indicate the odd one out:
(a) Ultra sound scanning
(b) Amniocentesis
(c) Foetoscope
(d) Mammogram
Answer:
(d) Mammogram
12. Choose the odd one out:
(a) Continuous abstinence
(b) Melting suppositories
(c) Coitus interruptus
(d) Lactational Amenorrhoea
Answer:
(b) Melting suppositories
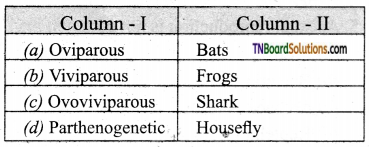
13. Choose the correct pair:
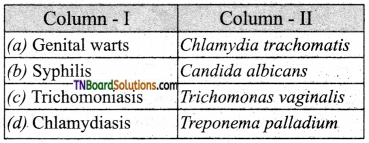
Answer:
(c)
![]()
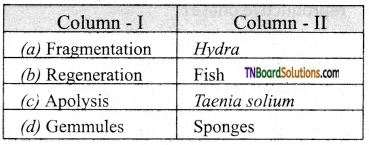
14. Indicate the incorrect pair:
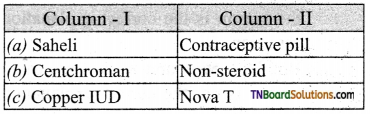

Answer:
(d)
15. Choose the correct pair:
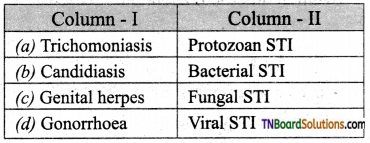
Answer:
(a)
16. Choose the incorrect pair:
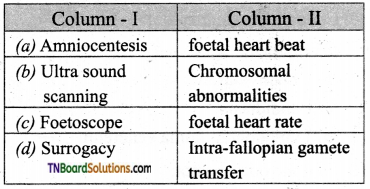
Answer:
(c)
17. Assertion: Creating awareness and providing medical assistance to people can build a healthy society.
Reason: Introducing sex education in schools provides information about adolescence among school children.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is true.
(d) Assertion is true, Reason is false
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
![]()
18. Assertion: Increased health facilities and better living conditions have enhanced longivity.
Reason: Because they have reduced the mortality due to disease and other living conditions.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is true.
(d) Assertion is true, Reason is false
(e) Both assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
19. Assertion: Oral pills are used to prevent ovulation by inhibiting the secretion of FSH and LH hormones.
Reason: It contains synthetic Gonad Stimulating Hormones.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is true.
(d) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(d) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
20. Assertion: Cervical cancer is caused by a sexually transmitted HIV virus.
Reason: The risk factors for cervical cancer include having sex with multiple unknown partners and prolonged use of contraceptive pills.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is true.
(d) Assertion is true, Reason is false.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is false, Reason is true.
![]()
21. Which of the following statement is true?
(a) The sexually transmitted disease, syphilis is caused by a bacteria called Clamidia trachomatis.
(b) Syphilis is caused by a virus.
(c) Syphilis is due to fungal infection.
(d) All the above are not correct.
Answer:
(d) All the above are not correct.
22. Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Diaphragms are made up of rubber.
(b) Diaphragms are one of the natural birth control methods.
(c) Saheli is a contraceptive pill developed by Central Drug Research Institute, Lucknow.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Diaphragms are one of the natural birth control methods.
23. Indicate the correct statement:
(a) Amniocentesis is a prenatal technique used to detect any chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus.
(b) Amniocentesis is used to measure heart rate of foetus in the uterus.
(c) Amniocentesis is used to measure the kidney function in foetus.
(d) Amniocentesis is used to measure blood flow from mother to foetus.
Answer:
(a) Amniocentesis is a prenatal technique used to detect any chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus.
![]()
24. Which of the following statement is wrong?
(a) Ovulation occurs at about 14th day of normal menstrual cycle.
(b) The ovum survives for about 2 days.
(c) Sperm remains alive for about 48 hrs in the female reproductive tract.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Sperm remains alive for about 48 hrs in the female reproductive tract.