Students get through the TN Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 9 Fiscal Economics which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 9 Fiscal Economics
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
How is public revenue classified?
Answer:
Public revenue can be classified into two types.
- Tax Revenue,
- Non-Tax Revenue
Question 2.
Name the tax revenue sources.
Answer:
They are income tax, corporate tax, sales tax, surcharge tax, and cess.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by escheats?
Answer:
It refers to the claim of the state to the property of persons who die without legal heirs or documentary bills.
Question 4.
What is tax evasion?
Answer:
The burden of direct tax is so heavy that taxpayers always try to evade taxes.
This leads to the generation of black money which is harmful to the economy.
Question 5.
Write the nature of sales tax, VAT, and GST.
Answer:
- Sales tax was multipoint tax with cascading effect.
- VAT was multipoint tax without cascading effect:
- GST is one point tax without cascading effect.
Question 6.
What do you mean by internal public debt?
Answer:
Internal public debt is a loan taken by the Government from the citizens or from different institutions within the country. It only involves the transfer of wealth.
Question 7.
What is the budget?
Answer:
The origin of the word budget is from French which means ‘A small Leather bag’. A budget is an annual financial statement that shows the estimated income and expenditure of the Government for the forthcoming financial years.
![]()
Question 8.
How are Government accounts maintained?
Answer:
They are maintained as
- Consolidate fund,
- Contingency fund and
- Public accounts
Question 9.
Name the accounting committee of the Government.
Answer:
Public accounts committee and the estimates committee.
Question 10.
Name the types of the budget deficit.
Answer:
- Revenue Deficit
- Budget Deficit
- Fiscal Deficit and
- Primary Deficit
Question 11.
Name the local bodies of India.
Answer:
- Village Panchayat
- District Boards or Zila Parished
- Municipalities and
- Municipal Cooperations
Question 12.
Name the source of the village panchayat.
Answer:
- General property tax,
- Tax on land,
- Profession tax and
- Tax on animals and vehicles.
![]()
Question 13.
What do you mean by the fiscal policy?
Answer:
Fiscal policy means the budgetary manipulations affecting the macroeconomic variables – output, employment, saving, investment, etc.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
How does the modern state control monopoly?
Answer:
The concentration of monopoly has to be controlled by Government. So the state intervenes through control of monopolies and restrictive trade practices to curb the concentration of economic power. The Government can play three kinds of roles. They are:
- As per producer of goods and services
- As suppliers of public goods and social goods
- As the regulator of the system
Question 2.
Write a note on GST.
Answer:
- GST is an indirect tax that has replaced many indirect taxes in India. The goods and services taxes was passed in the parliament on 29th March 2017 and it came into effect on 1st July 2017. The GST in India is a comprehensive multi-stage, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition.
- GST has replaced many indirect tax laws.
- GST is one indirect tax for the entire country.
- Under the GST region, the tax will be levied at the final point of sale. In the case of intrastate sales, Central GST and State GST will be charged. Inter-state sales will be chargeable to Integrated GST.
Question 3.
What are the advantages of GST?
Answer:
- GST will remove the cascading effect on the sale of goods and services.
It will directly impact the cost of goods. Since the tax on tax is eliminated in this regime, the cost of goods decreases. - GST is also mainly technologically driven. All activities like registration, return filing, application for a refund, and response to notice need to be done online on the GST portal. This will speed up the process.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the main sources of internal public debt?
Answer:
- Individually purchase Government bonds and securities.
- Banks, both private and public, buy bonds from the Government.
- Non-financial institutions like UTI, LIC, GIC, etc also buy Government bonds.
- A central bank can lend the Government in form of a money supply. The central bank can also issue money to meet the expenditure of the Government.
Question 5.
Balanced budget vs unbalanced budget – explain.
Answer:
Balanced budget: It is a situation in which the estimated revenue of the Government during the year is equal to its anticipated expenditure.
Government’s Estimated Revenue = Government’s Proposed Expenditure.
Unbalanced budget: The Budget in which revenue and expenditure are not equal to each other is known as an unbalanced Budget. It is of two types. They are surplus and deficit budgets.
Question 6.
What is the process in the preparation of the budget?
Answer:
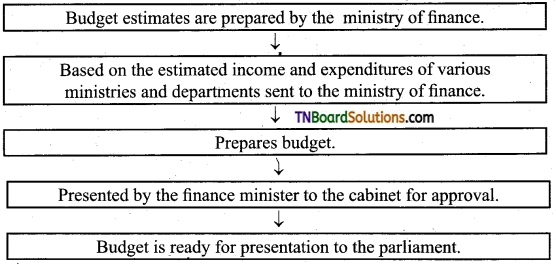
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What are the classifications of public expenditure?
Answer:
I. Classification on the basis of benefit
- Public expenditure benefiting the entire society. Eg: Defence
- Public expenditure conferring a special benefit on certain people and at the same time common benefit on community Eg: Administration of justice.
- Public expenditure directly benefiting a particular group of persons and indirectly the entire society. Eg: Public welfare.
- Public expenditure conferring a special benefit to some individual. Eg: Subsidy.
![]()
II. Classification basis of function
- Protection function: To protect from external invasion and internal disorder. Eg: defense.
- Commercial function: Development of trade and commerce. Eg: transport and communication
- Development function: Public expenditure incurred for the development infrastructure and industry.
Question 2.
Merits of direct taxes – explain.
Answer:
- Equity: Indirect taxes, the rate of tax varies according to the tax base.
Eg: income tax. - Certainty: It can be ensured by direct taxes Eg: income taxpayers know when and what rate he has to pay income tax?
- Elasticity: Direct taxes also satisfy the canon of elasticity. Income tax is income elastic in nature. As income level increases, the tax revenue to the Government also increases automatically.
- Economy: The cost collection of direct taxes is relatively low. The taxpayers pay the tax directly to the state.
Activity
Question 1.
Collect various bills and tabulate different rates of GST for different goods and services.
Answer:
Note: This activity is an eye-opener for the students.
It is the goods and services tax.
- It helps the students to know the method of taxation.
- It helps the students to know how and when it is levied.
- Helps them to identify the rate of taxation on different goods.
- Helps them to realize the importance of taxation.
- Helps them to understand the value of services and the importance of tax payment.
Multiple-choice questions
1. Fiscal economics is also known as:
(a) Public finance
(b) Public expenditure
(c) Increase expenditure
(d) Federal finance
Answer:
(a) Public finance
2. Financial operations of the Government is done by:
(a) Bill of exchange
(b) Cheques
(c) Treasury
(d) RBI
Answer:
(c) Treasury
![]()
3. The term fiscal means in Greek:
(a) Flower
(b) Money
(c) Basket
(d) Tax
Answer:
(c) Basket
4. Main objectives of the public sector are to provide ………… in the economy.
(a) Demand
(b) Social benefit
(c) Supply
(d) Production
Answer:
(b) Social benefit
5. The Government has to administer fiscal policy and monetary policy to achieve ……….. goals.
(a) Micro Economic
(b) Fiscal Economic
(c) Managerial Economic
(d) Macro Economic
Answer:
(d) Macro Economic
6. ………. classified Public expenditure on the basis of functions of Government.
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Ricardo
(c) Marshall
(d) Mill
Answer:
(a) Adam Smith
7. There are more than ………. cities above one million population.
(a) 44
(b) 54
(c) 64
(d) 34
Answer:
(b) 54
![]()
8. According to Dalton the term ……….. has two senses that is wide and narrow.
(a) Public debt
(b) Public expenditure
(c) Public income
(d) Public finance
Answer:
(c) Public income
9. Public revenue can be classified into ……….. types.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer:
(a) 2
10. Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) comes under:
(a) Defence ministry
(b) Ministry of foreign affairs
(c) Ministry of finance
(d) Ministry of health
Answer:
(c) Ministry of finance
11. ………… is paid by a shopkeeper or a retailer.
(a) Excise duty
(b) Sales Tax
(c) Custom duty
(d) Entertainment tax
Answer:
(b) Sales Tax
12. GST is ………. tax.
(a) Road tax
(b) Direct tax
(c) Custom tax
(d) Indirect tax
Answer:
(d) Indirect tax
![]()
13. The GST act was passed in the parliament in the year:
(a) 2016
(b) 2017
(c) 2001
(d) 2018
Answer:
(b) 2017
14. During ………. period private investment is lacking.
(a) Inflation
(b) War
(c) Depression
(d) Business cycle
Answer:
(c) Depression
15. The process of repaying a public debt is called:
(a) Budgetary surplus
(b) Redemption
(c) Capital levy
(d) Conversion
Answer:
(b) Redemption
16. Sinking fund was first introduced in:
(a) Lebanon
(b) the USA
(c) England
(d) India
Answer:
(c) England
![]()
17. Performance budget is also known as:
(a) Union budget
(b) Outcome budget
(c) State budget
(d) Deficit budget.
Answer:
(b) Outcome budget
18. The performance budget was first made in:
(a) London
(b) the USA
(c) USSR
(d) India
Answer:
(b) the USA
Pick the odd one out.
1. Right to print currency involves ………….. of currency.
(a) Creation
(b) Deposit
(c) Distribution
(d) Monitoring
Answer:
(b) Deposit
2. Public finance future investment include:
(a) Building of schools
(b) Banks
(c) Hospitals
(d) Infrastructure
Answer:
(b) Banks
3. It is the duty of the state to make provisions for:
(a) Inflation
(b) Education
(c) Health
(d) Sanitation
Answer:
(a) Inflation
![]()
4. Protection function is to protect the citizen:
(a) defense
(b) police
(c) watchman
(d) court
Answer:
(c) watchman
5. The Government has been providing subsidies on a number of items like:
(a) Fertilisers
(b) Exports
(c) Banks
(d) Education
Answer:
(c) Banks
6. The Government has been tender taking ……….. various development projects is:
(a) Irrigation
(b) Machinery
(c) Human resource
(d) Telecommunication
Answer:
(c) Human resource
7. Fine is imposed on an individual for violation of law example:
(a) Traffic rules
(b) Payment of income tax
(c) Payment after the stipulated time
(d) Illiteracy
Answer:
(d) Illiteracy
8. Non-financial institution is like:
(a) UTI
(b) LIC
(c) Moneylender
(d) GIC
Answer:
(c) Moneylender
![]()
9. The main source of external public debt are:
(a) IMF
(b) IDA
(c) HDFC
(d) ADB
Answer:
(c) HDFC
10. Revenue expenditure includes:
(a) Defence expenditure
(b) Subsidies
(c) Interest payment on debt
(d) Foreign currency
Answer:
(d) Foreign currency