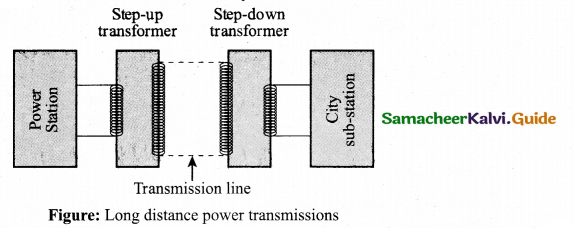
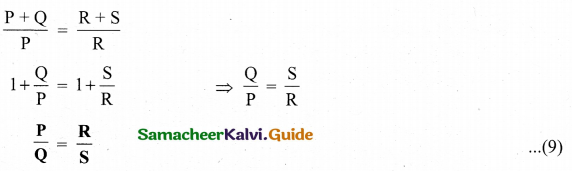Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Physics Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Physics Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 12th Physics Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 15 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four
alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 16 to 24 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered
in about one or two sentences. - Question numbers 25 to 33 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered
in about three to five short sentences. - Question numbers 34 to 38 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered
in detaiL Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Max Marks: 70
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [15 x 1 = 15]
Question 1.
Which charge configuration produces a uniform electric field?
(a) point charge
(b) infinite uniform line charge
(c) uniformly charged infinite plane
(d) uniformly charged spherical shell
Answer:
(c) uniformly charged infinite plane
Question 2.
The work done in carrying a charge Q, once round a circle of radius R with a charge Q2 at the centre is ………….
(a) \(\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1} \mathrm{Q}_{2}}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{R}^{2}}\)
(b) Zero
(c) \(\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{1} \mathrm{Q}_{2}}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{R}} \)
(d) infinite
Answer:
(b) Zero
Hint: The electric field is conservative. Therefore, no work is done in moving a charge around a closed path in a electric field.
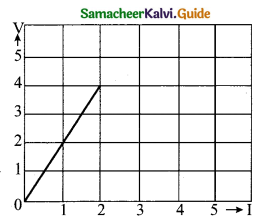
Question 3.
The internal resistance of a 2.1 V cell which gives a current of 0.2 A through a resistance of 10 Ω is……………………..
(a) 0.2 Ω
(b) 0.5 Ω
(c) 0.8 Ω
(d) 1.0 Ω
Answer:
(b) 0.5 Ω
![]()
Question 4.
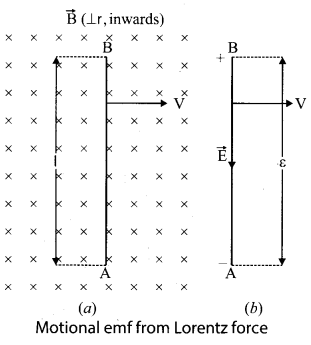
An electron moves straight inside a charged parallel plate capacitor of uniform charge density σ. The time taken by the electron to cross the parallel plate capacitor when the plates of the capacitor are kept under constant magnetic field of induction \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}\) is ……….
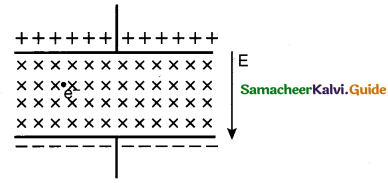

Answer:
(d)
Question 5.
In a series resonant RLC circuit, the voltage across 100Ω resistor is 40 V. The resonant frequency co is 250 rad/s. If the value of C is 4 pF, then the voltage across L is……………….
(a) 600 V
(b) 4000 V
(c) 400 V
(d) IV
Answer:
(c) 400 V
Question 6.
During the propagation of electromagnetic waves in a medium:
(a) electric energy density is double of the magnetic energy density
(b) electric energy density is half of the magnetic energy density
(c) electric energy density is equal to the magnetic energy density
(d) both electric and magnetic energy densities are zero
Answer:
(c) electric energy density is equal to the magnetic energy density
![]()
Question 7.
First diffraction minimum due to a single slit of width 1.0 x 10-5 cm is at 30°. Then wavelength of light used is, …………………
(a) 400 Å
(b) 500 Å
(c) 600 Å
(d) 700 Å
Answer:
(b) 500 Å
Hint. For diffraction minima, d sin θ = nλ
\(\lambda=\frac{d \sin \theta}{n}=\frac{1 \times 10^{-5} \times 10^{-2} \times \sin 30^{\circ}}{1}=0.5 \times 10^{-7}\)
λ = 500 Å
Question 8.
The sky would appear red instead of blue if
(a) atmospheric particles scatter blue light more than red light
(b) atmospheric particles scatter all colours equally
(c) atmospheric particle scatter red light more than blue light
(d) the sun was much hotter
Answer:
(c) atmospheric particle scatter red light more than blue light
Question 9.
Kinetic energy of emitted electron depends upon
(a) frequency
(b) intensity
(c) nature of atmosphere surrounding the electron
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) frequency
Hint: Kinetic energy of emitted electron depends on the frequency of incident radiation.
Question 10.
The ratio between the first three orbits of hydrogen atom is…………….
(a) 1:2:3
(b) 2:4:6
(c) 1:4:9
(d) 1:3:5
Answer:
(c) 1:4:9
Hint :
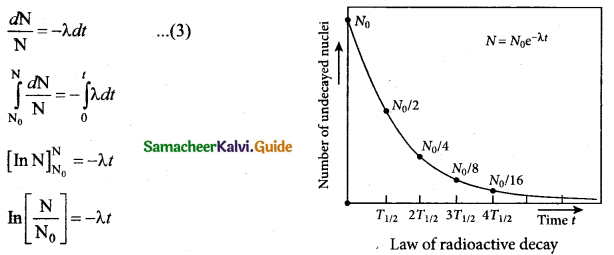
En = \(\frac{-13.6 \times z^{2}}{n^{2}}\)
n = 1; E1 =- 13.6 eV/ atom
n = 2; E2 = – 3.4 eV/ atom
n = 3; E3 = -1.51 eV/atom ’
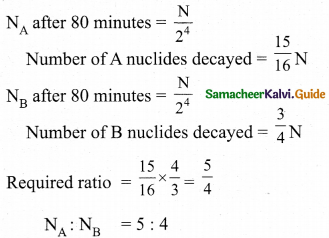
The ratio of three orbits E1 : E2 : E3 = 13.6 : 3.4 : 1.51 = 1 : 4 : 9
![]()
Question 11.
Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom did not explain fully
(a) diameter of H-atom
(b) emission spectra
(c) ionisation energy
(d) the fine structure of even hydrogen spectrum
Answer:
(d) the fine structure of even hydrogen spectrum
Hint: Bohr theory could not explain the five structure of hydrogen spectrum.
Question 12.
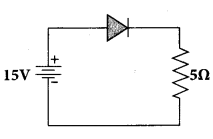
If a half-wave rectified voltage is fed to a load resistor, which part of a cycle the load current will flow?
(a) 0° – 90°
(b) 90° – 180°
(c) 0° – 180°
(d) 0° – 360°
Answer:
(c) 0° – 180°
Question 13.
Diamond is very hard because ……………..
(a) it is covalent solid
(b) it has large cohesive energy
(c) high melting point
(d) insoluble in all solvents
Answer:
(b) it has large cohesive energy
Question 14.
The internationally accepted frequency deviation for the purpose of FM broadcasts.
(a) 75 kHz
(b) 68 kHz
(c) 80 kHz
(d) 70 kHz
Answer:
(a) 75 kHz
![]()
Question 15.
The blue print for making ultra durable synthetic material is mimicked from
(a) Lotus leaf
(b) Morpho butterfly
(c) Parrot fish
(d) Peacock feather
Answer:
(c) Parrot fish
Part – II
Answer any six questions in which Q. No 17 is compulsory. [6 x 2 = 12]
Question 16.
Define ‘electric flux’.
Answer:
The number of electric field lines crossing a given area kept normal to the electric field lines is called electric flux. Its unit is N m2 C-1. Electric flux is a scalar quantity.
Question 17.
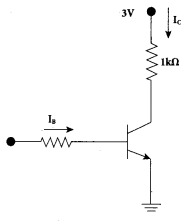
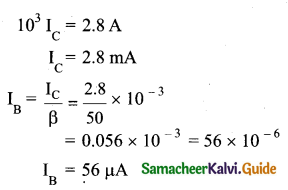
Determine the number of electrons flowing per second through a conductor, when a current of 32 A flows through it.
Answer:
I = 32A, t= 1 s
Charge of an electron, e = 1.6 x 10-19 C
The number of electrons flowing per second, n =?
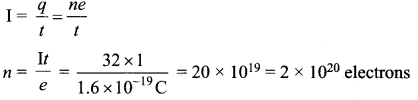
Question 18.
Define magnetic flux.
Answer:
The number of magnetic field lines crossing per unit area is called magnetic flux φB
\(\phi_{\mathrm{B}}=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}} \cdot\overrightarrow{\mathrm{A}}=\mathrm{B} \mathrm{A} \cos \theta=\mathrm{B} \perp \mathrm{A}\)
Question 19.
Give any one definition of power factor.
Answer:
The power factor is defined as the ratio of true power to the apparent power of an a.c. circuit.
It is equal to the cosine of the phase angle between current and voltage in the a.c. circuit.
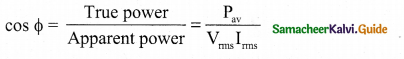
![]()
Question 20.
State the laws of reflection.
Answer:
- The incident ray, reflected ray and normal to the reflecting surface all are coplanar (ie. lie in the same plane).
- The angle of incidence i is equal to the angle of reflection r. i = r
Question 21.
Why do metals have a large number of free electrons?
Answer:
In metals, the electrons in the outer most shells are loosely bound to the nucleus. Even at room temperature, there are a large number of free electrons which are moving inside the metal in a random manner.
Question 22.
The radius of the 5th orbit of hydrogen atom is 13.25 A. Calculate the wavelength of the electron in the 5th orbit.
Answer:
2πr = nλ
2 x 3.14 x 13.25 Å = 5 x λ
.’. λ = 16.64 Å
Question 23.
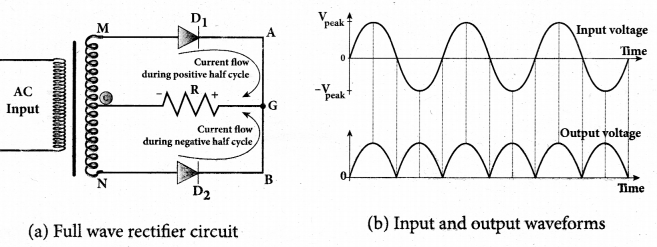
Draw the output waveform of a full wave rectifier.
Answer:
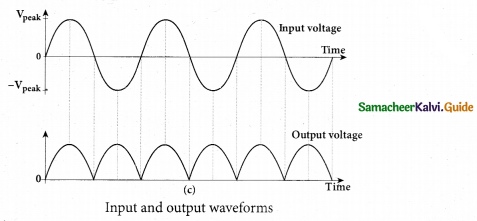
Question 24.
Explain centre frequency or resting frequency in frequency modulation.
Answer:
When the frequency of the baseband signal is zero (no input signal), there is no change in the frequency of the carrier wave. It is at its normal frequency and is called as centre frequency or resting frequency.
Part – III
Answer any six questions in which Q.No. 28 is compulsory. [6 x 3 = 18]
Question 25.
What is corona discharge?
Answer:
The electric field near the edge is very high and it ionizes the surrounding air. The positive ions are repelled at the sharp edge and negative ions are attracted towards the sharper edge.
This reduces the total charge of the conductor near the sharp edge. This is called action at points or corona discharge.
![]()
Question 26.
What is electric power and electric energy?
Answer:
Electric power: It is the rate at which an electric appliance converts electric energy into other forms of energy. Or, it is the rate at which work is done by a source of emf in maintaining an electric current through a circuit.
\({ P }=\frac { { W } }{ t } ={ VI }={ I }^{ 2 }{ R }=\frac { { V }^{ 2 } }{ { R } } \)
Electric energy: It is the total workdone in maintaining an electric current in an electric circuit for a given time.
W = Vt = VIr joule = I2R? joule.
Question 27.
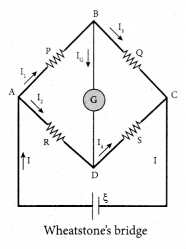
A bar magnet having a magnetic moment \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{M}}\) is cut into four pieces i.e., first cut in two pieces along the axis of the magnet and each piece is further cut into two pieces. Compute the magnetic moment of each piece.
Answer:
Consider a bar magnet of magnetic moment \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{M}}\). When a bar magnet first cut in two pieces along the axis, their magnetic moment is \(\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{M}}}{2}\)
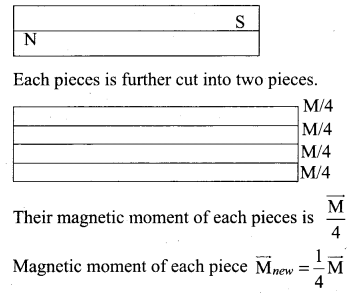
Question 28.
The current in an inductive circuit is given by 0.3 sin (200t – 40°) A. Write the equation for the voltage across it if the inductance is 40 mH.
Answer:
L = 40 x 10-3H; i = 0.1 sin (200 t – 40°); XL = ωL = 200 x 40 x 10-3 = 8 Ω
Vm = Im XL = 0.3 x 8 = 2.4 V
In an inductive circuit, the voltage leads the current by 90° Therefore,
υ = Vm sin (ωt + 90°)
υ = 2.4 sin (200f – 40°+ 90°)
υ = 2.4 sin (200f +50°)volt
![]()
Question 29.
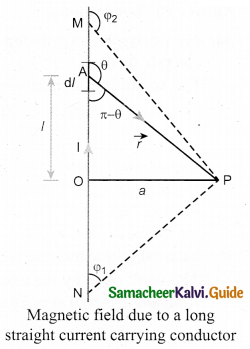
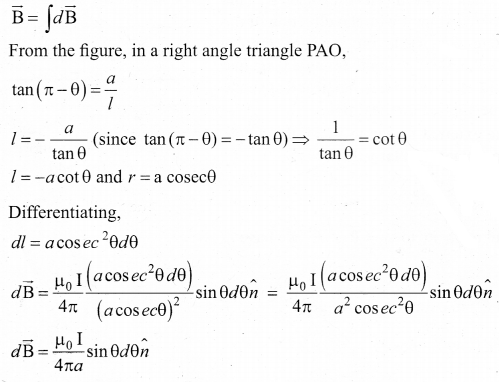
Writedown the integral form of modified Ampere’s circuital law.
Answer:
This law relates the magnetic field around any closed path to the conduction current and displacement current through that path.
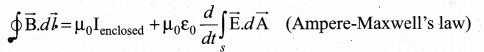
Question 30.
Two light sources have intensity of light as Io. What is the resultant intensity at a point where the two light waves have a phase difference of π/3?
Answer:
Let the intensities be Io
The resultant intensity is, I = 4 Io cos2 (φ/2)
Resultant intensity when, ϕ = π/ 3, is I = 4I0 cos2 (π / 6) I
= 4I0(√3 / 2)2 =3I0
Question 31.
Write the properties of cathode rays.
Answer:
- Cathode rays possess energy and momentum and travel in a straight line with high speed of the order of 107m s-1
- It can be deflected by application of electric and magnetic fields.
- When the cathode rays are allowed to fall on matter, they produce heat.
- They affect the photographic plates and also produce fluorescence when they fall on certain crystals and minerals.
- When the cathode rays fall on a material of high atomic weight, x-rays are produced.
- Cathode rays ionize the gas through which they pass.
- The speed of cathode rays is up \(\left( \frac { 1 }{ 10 } \right) ^{ th }\) of the speed of light.
Question 32.
Distinguish between wireline and wireless communication.
Answer:
| Wireline communication | Wireless communication |
| It is a point-to-point communication. | It is a broadcast mode communication. |
| It uses mediums like wires, cable and optical fibres. | It uses free space as a communication medium. |
| These systems cannot be used for long distance transmission as they are connected. | These systems can be used for long distance transmission. |
| Ex. telephone, intercom and cable TV. | Ex. mobile, radio or TV broadcasting and satellite communication. |
![]()
Question 33.
What is the difference between Nano materials and Bulk materials?
Answer:
- The solids are made up of particles. Each of the particle has a definite number of atoms, which might differ from material to material. If the particle of a solid is of size less than 100 nm, it is said to be a ‘nano solid’.
- When the particle size exceeds 100 nm, it is a ‘bulk solid’. It is to be noted that nano and bulk solids may be of the same chemical composition.
- For example, ZnO can be both in bulk and nano form.
- Though chemical composition is the; same, nano form of the material shows strikingly different properties when compared to its bulk counterpart.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [5 x 5 = 25]
Question 34.
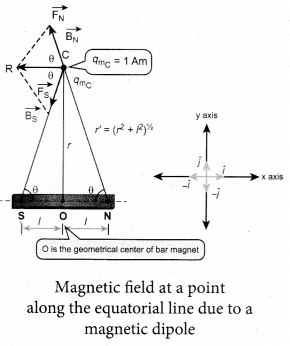
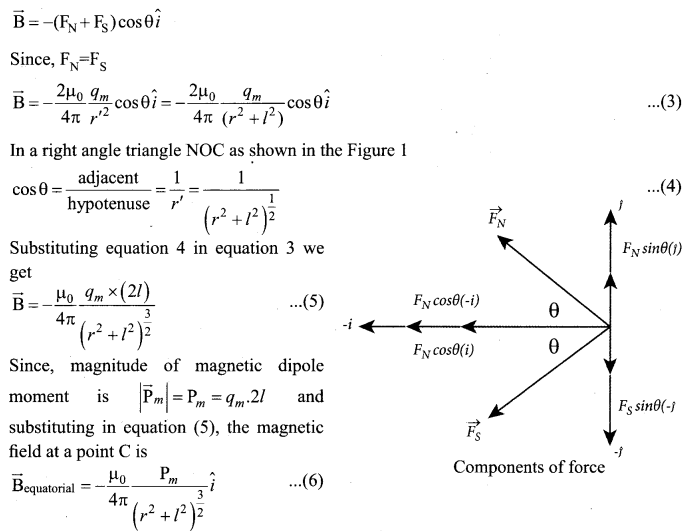
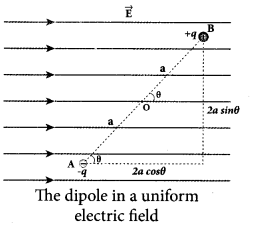
(a) Calculate the electric field due to a dipole on its equatorial plane.
Answer:
Electric field due to an electric dipole at a point on the equatorial plane. Consider a point C at a distance r from the midpoint O of the dipole on the equatorial plane as shown in Figure.
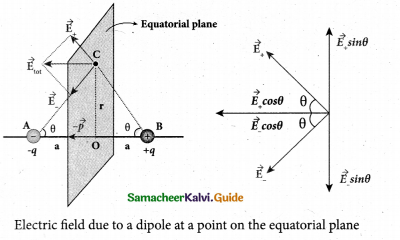
Since the point C is equidistant from +q and -q, the magnitude of the electric fields of +q and -q are the same. The direction of \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{+}\) is along BC \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{-} \) and the direction of E is along CA. \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{+} \) and \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{-} \) and E are resolved into two components; one component parallel to the dipole axis and the other perpendicular to it. The perpendicular components \(\left|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{+}\right| \sin \theta \) and \(\left|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{-}\right| \sin \theta \) are oppositely directed and cancel each other. The magnitude of the total electric field at point C is the sum of the parallel components of E+ and E and its direction is \(\overrightarrow { { E } } _{ + }\quad and\quad \overrightarrow { { E } } _{ – }\) and its direction is along \(-\hat{p}\)
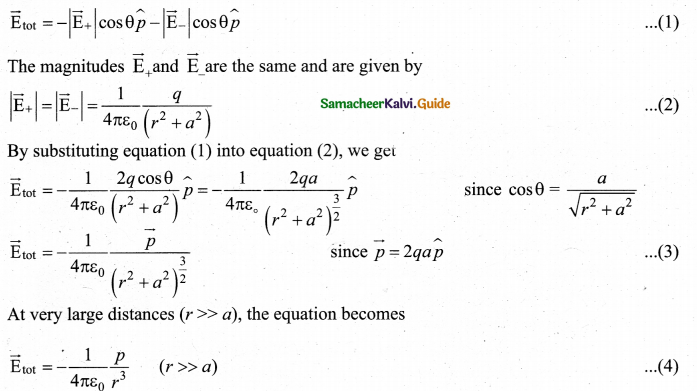
(b) How the emf of two cells are compared using potentiometer?
Answer:
Comparison of emf of two cells with a potentiometer: To compare the emf of two cells, the circuit connections are made as shown in figure. Potentiometer wire CD is connected to a battery Bf and a key K in series. This is the primary circuit. The end C of the wire is connected to the terminal M of a DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw) switch and the other terminal N is connected to a jockey through a galvanometer G and a high resistance HR. The cells whose emf ξ1 and ξ2 and to be compared are connected to the terminals M1, N1 and M2, N2, of the DPDT switch. The positive terminals of Bf ξ1 and ξ2 should be connected to the same end C.
The DPDT switch is pressed towards M1, N1 so that cell ξ1, is included in the secondary circuit and the balancing length l1, is found by adjusting the jockey for zero deflection. Then the second cells ξ2, is included in the circuit and the balancing length l2, is determined. Let r be the resistance per unit length of the potentiometer wire and I be the current flowing through the wire.
we have
ξ1 = Irl1 ……………….. (1)
ξ2 = Irl2 ……………….. (2)
By dividing equation (1) by (2)
\(\frac{\xi_{1}}{\xi_{2}}=\frac{l_{1}}{l_{2}}\)
By including a rheostat (Rh) in the primary circuit, the experiment can be repeated several times by changing the current flowing through it.
![]()
Question 35.
(a) Discuss the working of cyclotron in detail.
Answer:
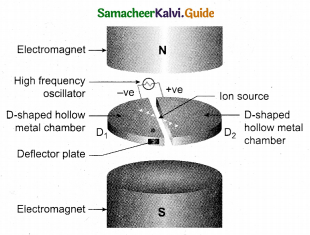
Cyclotron : Cyclotron is a device used accelerate the charged particles to gain large kinetic energy. It is also called as high energy accelerator. It was invented by Lawrence and Livingston in 1934.
Principle : When a charged particle moves normal to the magnetic field, it experiences magnetic Lorentz force.
Construction : The particles are allowed to move in between two semicircular metal containers called Dees (hollow D – shaped objects). Dees are enclosed in an evacuated chamber and it is kept in a region with uniform magnetic field controlled by an electromagnet. The direction of magnetic field is normal to the plane of the are enclosed in an evacuated chamber and it is kept in a region with uniform magnetic field controlled by an electromagnet. The direction of magnetic field is normal to the plane of the Dees. The two Dees are kept separated with a gap and the source S (which ejects the particle to be accelerated) is placed at the center in the gap between the Dees. Dees are connected to high frequency alternating potential difference.
Working: Let us assume that the ion ejected from source S is positively charged. As soon as ion is ejected, it is accelerated towards a Dee (say, Dee – 1) which has negative potential at that time. Since the magnetic field is normal to the plane of the Dees, the ion undergoes circular path. After one semi-circular path in Dee-1, the ion reaches the gap between Dees. At this time, the polarities of the Dees are reversed so that the ion is now accelerated towards Dee-2 with a greater velocity. For this circular motion, the centripetal force of the charged particle q is provided by Lorentz force.
![]()
\(\frac { mv^{ 2 } }{ r } =qv{ B }\Rightarrow r=\frac { m }{ q{ B } } v\Rightarrow r\propto v\)
From the equation, the increase in velocity increases the radius of circular path. This process continues and hence the particle undergoes spiral path of increasing radius. Once it reaches near the Very important condition in cyclotron operation is the resonance condition. It happens when the frequency { at which the positive ion circulates in the magnetic field must be equal to the constant frequency of the electrical oscillator fosc From equation
\(f_{\text {osc }}=\frac{q \mathrm{B}}{2 \pi m} \Rightarrow \mathrm{T}=\frac{1}{f_{\text {osc }}}\)
The time Period of oscillation is \(\mathrm{T}=\frac{2 \pi m}{q \mathrm{B}}\)
The kinetic energy of the charged particle is \(\mathrm{KE}=\frac{1}{2} m v^{2}=\frac{q^{2} \mathrm{B}^{2} r^{2}}{2 m}\)
Limitations of cyclotron
- the speed of the ion is limited
- electron cannot be accelerated
- uncharged particles cannot be accelerated
[OR]
(b) Give the uses of Foucault current.
Answer:
Though the production of eddy current is undesirable in some cases, it is useful in some other cases. A few of them are
(1) Induction stove : Induction stove is used to cook the food quickly and safely with less energy consumption. Below the cooking zone, there is a tightly wound coil of insulated wire. The cooking pan made of suitable material, is placed over the cooking zone. When the stove is switched on, an alternating current flowing in the coil produces high frequency alternating magnetic field which induces very strong eddy currents in the cooking pan. The eddy currents in the pan produce so much of heat due to Joule heating which is used to cook the food.
(2) Eddy current brake : This eddy current braking system is generally used in high speed trains and roller coasters. Strong electromagnets are fixed just above the rails. To stop the train, electromagnets are switched on. The magnetic field of these magnets induces eddy currents in the rails which oppose or resist the movement of the train. This is Eddy current linear brake.
In some cases, the circular disc, connected to the wheel of the train through a common shaft, is made to rotate in between the poles of an electromagnet. When there is a relative motion between the disc and the magnet, eddy currents are induced in the disc which stop the train. This is Eddy current circular brake.
![]()
(3) Eddy current testing : It is one of the simple non-destructive testing methods to find defects like surface cracks and air bubbles present in a specimen. A coil of insulated wire is given an alternating electric current so that it produces an alternating magnetic field. When this coil is brought near the test surface, eddy current is induced in the test surface. The presence of defects causes the change in phase and amplitude of the eddy current that can be detected by some other means. In this way, the defects present in the specimen are identified.
(4) Electro magnetic damping : The armature of the galvanometer coil is wound on a soft iron cylinder. Once the armature is deflected, the relative motion between the soft iron cylinder and the radial magnetic field induces eddy current in the cylinder. The damping force due to the flow of eddy current brings the armature to rest immediately and then galvanometer shows a steady deflection. This is called electromagnetic damping.
Question 36.
(a) Write down the properties of electromagnetic waves.
Answer:
Properties of electromagnetic waves:
- Electromagnetic waves are produced by any accelerated charge.
- Electromagnetic waves do not require any medium for propagation. So electromagnetic wave is a non-mechanical wave.
- Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. This means that the oscillating electric field vector, oscillating magnetic field vector and propagation vector (gives direction of propagation) are mutually perpendicular to each other.
- Electromagnetic waves travel with speed which is equal to the speed of light in vacuum
or free space, \(c=\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { \varepsilon _{ 0 }\mu _{ 0 } } } =3\times 10^{ 8 }{ ms }^{ -1 }\) - The speed of electromagnetic wave is less than speed in free space or vacuum, that is, v < c. In a medium of refractive index,
[OR]
(b) Explain the Young’s double slit experimental setup and obtain the equation for path difference.
Answer:
Experimental setup
Wavefronts from S1 and S2 spread out and overlapping takes place to the right side of double slit. When a screen is placed at a distance of about 1 meter from the slits, alternate bright and dark fringes which are equally spaced appear on the screen. These are called interference fringes or bands.
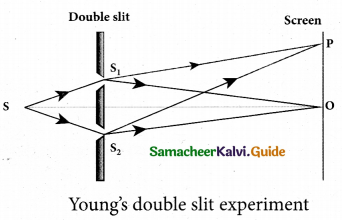
S1 and S2 travel equal distances and arrive in-phase. These two waves constructively interfere and bright fringe is observed at O. This is called central bright fringe.
The fringes disappear and there is uniform illumination on the screen when one of the slits is covered. This shows clearly that the bands are due to interference.
![]()
Equation for path difference
Let d be the distance between the double slits S1 and S2 which act as coherent sources of wavelength λ. A screen is placed parallel to the double slit at a distance D from it. The mid-point of S1 and S2 is C and the midpoint of the screen O is equidistant from S1 and S2. P is any point at a distance y from O.
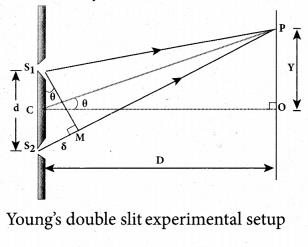
The waves from S1 and S2 meet at P either inphase or out-of-phase depending upon the path difference between the two waves. The path difference S between the light waves from S1 and S2 to the point P is, δ = S2P and S1P
A perpendicular is dropped from the point S1, to the line S2P at M to find the path difference more precisely.
δ = S2P – MP = S2M
The angular position of the point P from C is θ. ∠OCP = θ.
From the geometry, the angles ∠OCP and ∠S2S1 M are equal.
∠OCP = ∠S2S1 M = θ
In right angle triangle ΔS1S2M, the path difference, S2M = d sin θ
δ = d sin θ
If the angle θ is small, sin θ ≈ tan θ ≈ θ From the right angle triangle ΔOCP, tan θ = y/D. The path difference, δ =dy/D
Question 37.
(a) Give the construction and working of photo emissive cell.
Answer:
Photo emissive cell:
Its working depends on the electron emission from a metal cathode due to irradiation of light or other radiations.
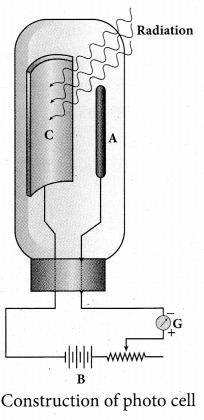
- It consists of an evacuated glass or quartz bulb in which two metallic electrodes – that is, a cathode and an anode are fixed.
- The cathode C is semi-cylindrical in shape and is coated with a photo sensitive material. The anode A is a thin rod or wire kept along the axis of the semi-cylindrical cathode.
- A potential difference is applied between the anode and the cathode through a galvanometer G.
Working:
- When cathode is illuminated, electrons are emitted from it. These electrons are attracted by anode and hence a current is produced which is measured by the galvanometer
- For a given cathode, the magnitude of
the current depends on the intensity to incident radiation and
the potential difference between anode and cathode.
![]()
[OR]
Question 37.
(b) Explain the J.J. Thomson experiment to determine the specific charge of electron.
Answer:
In 1887, J. J. Thomson made remarkable improvement in the scope of study of gases in discharge tubes. In the presence of electric and magnetic fields, the cathode rays are deflected. By the variation of electric and magnetic fields, mass normalized charge or the specific charge (charge per unit mass) of the cathode rays is measured.
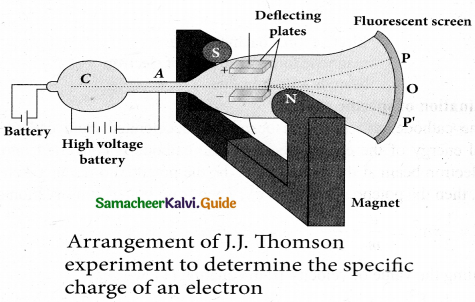
A highly evacuated discharge tube is used and cathode rays (electron beam) produced at cathode are attracted towards anode disc A. Anode disc is made with pin hole in order to allow only a narrow beam of cathode rays. These cathode rays are now allowed to pass through the parallel metal plates, maintained at high voltage. Further, this gas discharge tube is kept in between pole pieces of magnet such that both electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other. When the cathode rays strike the screen, they produce scintillation and hence bright spot is observed. This is achieved by coating the screen with zinc sulphide.
(i) Determination of velocity of cathode rays
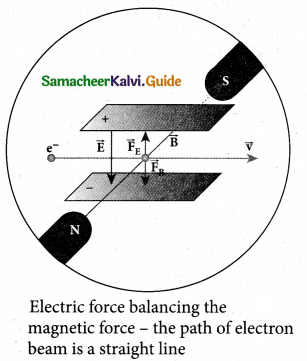
For a fixed electric field between the plates, the magnetic field is adjusted such that the cathode rays (electron beam) strike at the original position O. This means that the magnitude of electric force is balanced by the magnitude of force due to magnetic field. Let e be the charge of the cathode rays, then eE = eBv
\(v=\frac{E}{B}\) …………….. (1)
(ii) Determination of specific charge
Since the cathode rays (electron beam) are accelerated from cathode to anode, the potential energy of the electron beam at the cathode is converted into kinetic energy of the electron beam at the anode. Let V be the potential difference between anode and cathode, then the potential energy is eV. Then from law of conservation of energy,
\(e \mathrm{V}=\frac{1}{2} m v^{2} \Rightarrow \frac{e}{m}=\frac{v^{2}}{2 \mathrm{V}}\)
Substituting the value of velocity from equation (1) , we get
\(\frac{e}{m}=\frac{1}{2 \mathrm{V}} \frac{\mathrm{E}^{2}}{\mathrm{B}^{2}}\) ………..(2)
Substituting the value of E ,B and V, the specific charge vam be determined as
\(\frac{e}{m}=1.7 \times 10^{11} \mathrm{Ckg}^{-1}\)
![]()
(iii) Deflection of charge only due to uniform electric field
When the magnetic field is turned off, the deflection is only due to electric field. The
deflection in vertical direction is due to the electric force.
Fe = eE ………………….. (3)
Let m be the mass of the electron and by applying Newton’s second law of motion,
acceleration of the electron is
\(a_{e}=\frac{1}{m} \mathrm{F}_{e}\) ………………… (4)
Substituting equation (4) in equation (3),
\(a_{e}=\frac{1}{m} e E=\frac{e}{m} E\)
Let y be the deviation produced from original position on the screen. Let the initial upward velocity of cathode ray be μ = 0 before entering the parallel electric plates. Let l be the time taken by the cathode rays to travel in electric field. Let l be the length of one of the plates, then the time taken is
\(t=\frac{l}{v}\) …………(5)
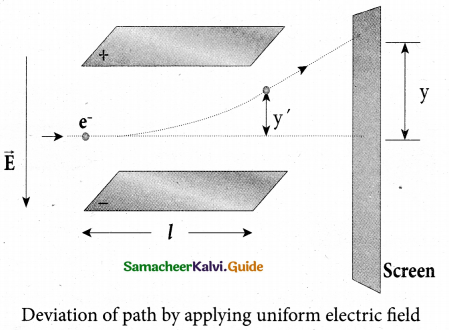
Hence, the deflection y’ of cathod rays is( note : u = 0 and \(a_{e}=\frac{e}{m} \mathrm{E}\))
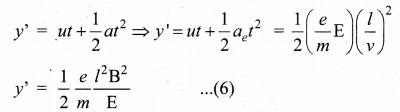
Therefore, the deflection y on the screen is
y α y’ ⇒ y = Cy’
where C is proportionality constant which depends on the geometry of the discharge tube and substituting y’ value in equation (6), we get
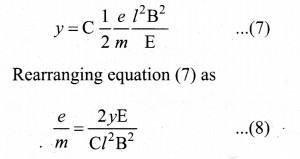
Substituting the values on RHS, the value of specific charge is calculated as
e/m = 1.7 x 1011Ckg-1
Question 38.
(a) What is an LED? Give the principle of operation with a diagram.
Answer:
Light Emitting Diode (LED): LED is a p-n junction diode which emits visible or invisible light when it is forward biased. Since, electrical energy is converted into light energy, this process is also called electroluminescence. The cross-sectional view of a commercial LED is shown in figure (b). It consists of a p-layer, n-layer and a substrate. A transparent window is used to allow light to travel in the desired direction. An external resistance in series with the biasing source is required to limit the forward current through the LED. In addition, it has two leads; anode and cathode.
When the p-n junction is forward biased, the conduction band electrons on n-side and valence band holes on p-side diffuse across the junction. When they cross the junction, they become excess minority carriers (electrons in p-side and holes in n-side). These excess minority carriers recombine with oppositely charged majority carriers in the respective regions, i.e. the. electrons in the conduction band recombine with holes in the valence band as shown in the figure (c). During recombination process, energy is released in the form of light (radiative) or heat (non-radiative). For radiative recombination, a photon of energy hv is emitted. For non- radiative recombination, energy is liberated in the form of heat.
The colour of the light is determined by the energy band gap of the material. Therefore, LEDs are available in a wide range of colours such as blue (SiC), green (AlGaP) and red (GaAsP). Now a days, LED which emits white light (GalnN) is also available.
![]()
[OR]
(b) Give the applications of ICT in mining and agriculture sectors.
Answer:
(i) Agriculture
The implementation of information and communication technology (ICT) in agriculture sector enhances the productivity, improves the living standards of farmers and overcomes the Challenges and risk factors.
- ICT is widely used in increasing food productivity and farm management.
- It helps to optimize the use of water, seeds and fertilizers etc.
- Sophisticated technologies that include robots, temperature and moisture sensors, aerial images, and GPS technology can be used.
- Geographic information systems are extensively used in farming to decide the suitable place for the species to be planted.
(ii) Mining
- ICT in mining improves operational efficiency, remote monitoring and disaster locating system.
- Information and communication technology provides audio-visual warning to the trapped underground miners.
- It helps to connect remote sites.











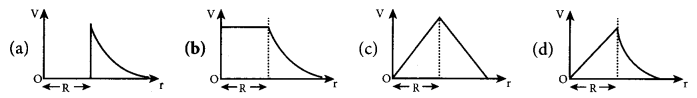
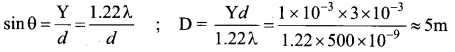
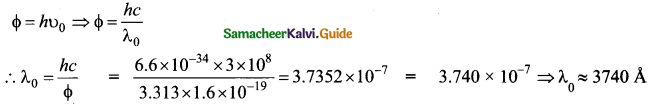
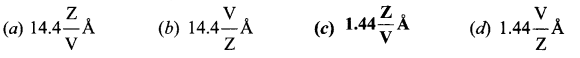
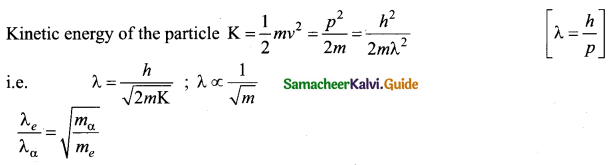
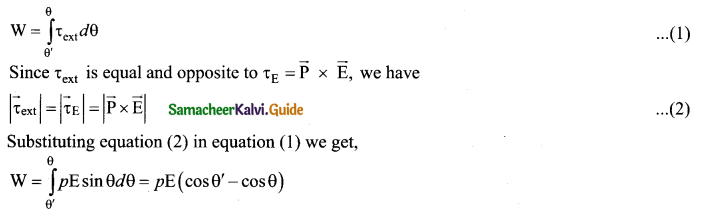
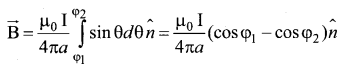
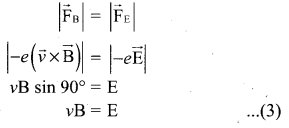
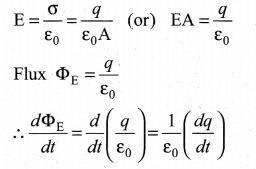
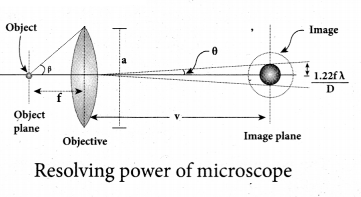
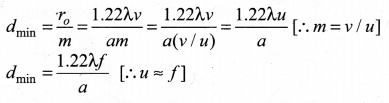
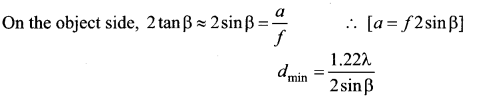
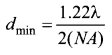
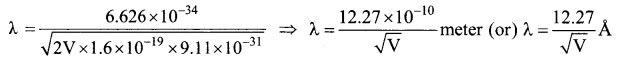
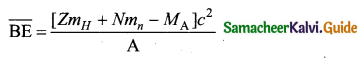






















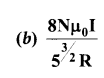
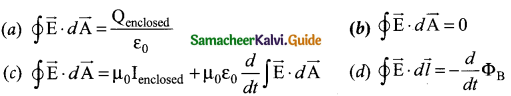


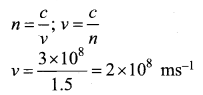
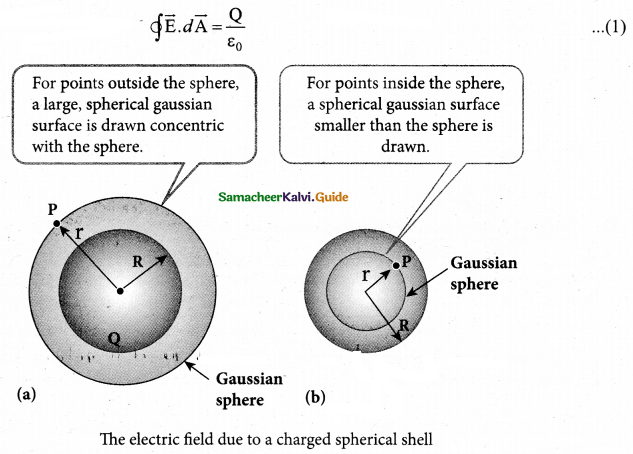
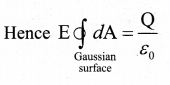
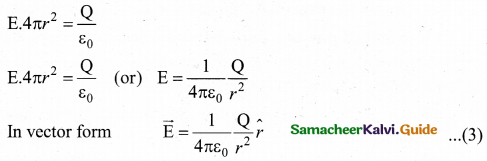
 = total area of Gaussian surface = 4πr2 Substituting this value in equation (2)
= total area of Gaussian surface = 4πr2 Substituting this value in equation (2)