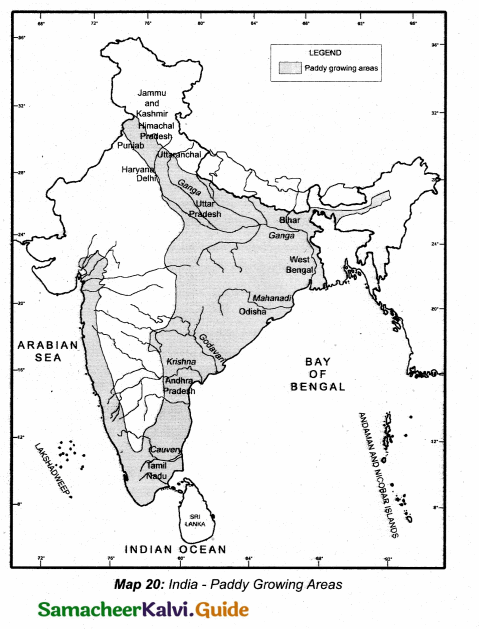
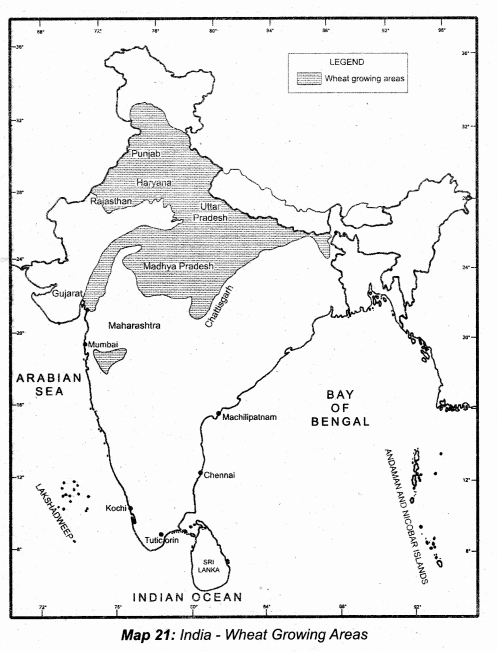
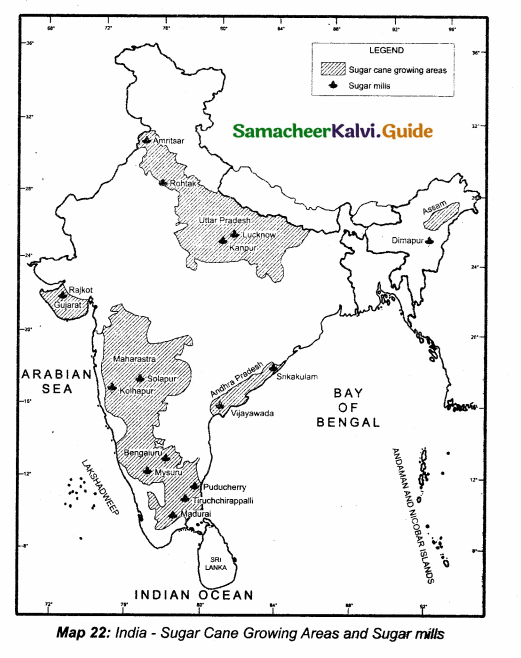
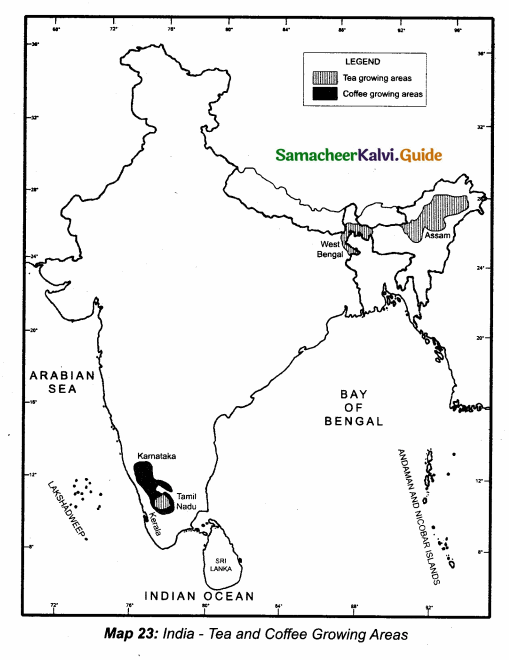
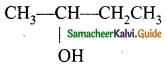
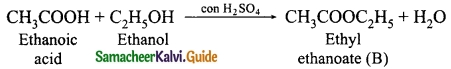
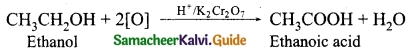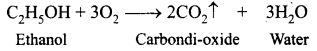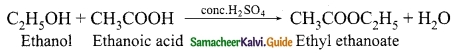Students can download 10th Science Chapter 10 Types of Chemical Reactions Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 10 Types of Chemical Reactions
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Types of Chemical Reactions Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1
H2(g) + Cl29(g) → 2HCl(g)
(a) Decomposition Reaction
(b) Combination Reaction
(c) Single Displacement Reaction
(d) Double Displacement Reaction
Answer:
(a) Decomposition Reaction
Question 2.
Photolysis is a decomposition reaction caused by ______.
(a) heat
(b) electricity
(c) light
(d) mechanical energy
Answer:.
(c) light
Hint:
\(2 \mathrm{AgBr}_{(\mathrm{s})} \stackrel{\mathrm{Light}}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{Ag}_{(\mathrm{s})}+\mathrm{Br}_{2(\mathrm{g})}\)
![]()
Question 3.
A reaction between carbon and oxygen is represented by C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + Heat. In which of the type(s), the above reaction can be classified?
(i) Combination Reaction
(ii) Combustion Reaction
(iii) Decomposition Reaction
(iv) Irreversible Reaction
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Question 4.
The chemical equation \(\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{BaCl}_{2(\mathrm{aq})} \rightarrow \mathrm{BaSO}_{4(\mathrm{s})} \downarrow+2 \mathrm{NaCl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}\) represents which of the following types of reaction?
(a) Neutralisation
(b) Combustion
(c) Precipitation
(d) Single displacement.
Answer:
(c) Precipitation
Hint: This reaction involves the precipitation of white BaSO4 by mixing of Na2SO4 (aq) and BaCl2 (aq). Hence it belongs to precipitation reaction.
Question 5.
Which of the following statements are correct about a chemical equilibrium?
(i) It is dynamic in nature
(ii) The rate of the forward and backward reactions are equal at equilibrium
(iii) Irreversible reactions do not attain chemical equilibrium
(iv) The concentration of reactants and products may be different
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Question 6.
A single displacement reaction is represented by \(\mathrm{X}_{(\mathrm{s})}+2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(\mathrm{aq})} \rightarrow \mathrm{XCl}_{2(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{H}_{2(\mathrm{g})}\). the following(s) could be X?
(i) Zn
(ii) Ag
(iii) Cu
(iv) Mg.
Choose the best pair.
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) iii and iv
(d) i and iv.
Answer:
(d) i and iv.
Hint:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2.
Question 7.
Which of the following is not an “element + element → compound” type reaction?
(a) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
(b) 2K(s) + Br2(l) → 2KBr(s)
(c) 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g)
(d) 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
Answer:
(c) 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g)
Question 8.
Which of the following represents a precipitation reaction?
(a) A(s) + B(s) → C(s) + D(s)
(b) A(s) + B(aq) → C(aq) + D(l)
(c) A(aq) + B(aq) → C(s) + D(aq)
(d) A(aq) + B(s) → C(aq) + D(l)
Answer:
(c) A(aq) + B(aq) → C(s) + D(aq)
Question 9.
The pH of a solution is 3. Its [OH–] concentration is ______.
(a) 1 × 10-3 M
(b) 3 M
(c) 1 × 10-11 M
(d) 11 M.
Answer:
(c) 1 × 10-11 M
Hint: pH = 3
It means [H+] = 10-3
[H+] [OH–] = 10-14
[10-3] [OH–] = 10-14
[OH–] = 10-11
Question 10.
Powdered CaCO3 reacts more rapidly than flaky CaCO3 because of :
(a) large surface area
(b) high pressure
(c) high concentration
(d) high temperature
Answer:
(a) large surface area
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. A reaction between an acid and a base is called ………..
2. When zinc metal is placed in hydrochloric acid, ………. gas is evolved.
3. The equilibrium attained during the meiting of ice is known as ………..
4. The pH of a fruit juice is 5.6. If you add slaked lime to this juice, its pH ……….
5. The value of ionic product of water at 25 °C is ………..
6. The normal pH of human blood is …………
7. Electrolysis is type of ……….. reaction.
8. The number of products formed in a synthesis reaction is ………..
9. Chemical volcano is an example for ……….. type of reaction.
10. The ion formed by dissolution of H+ in water is called …………
Answer:
1. neutralization
2. H2
3. physical equilibrium
4. increases to ‘7’
5. 1 × 10-14 mol² dm-6
6. 7.4
7. decomposition
8. 1
9. decomposition
10. hydronium ion
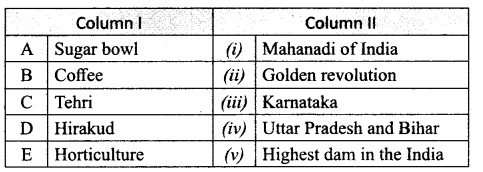
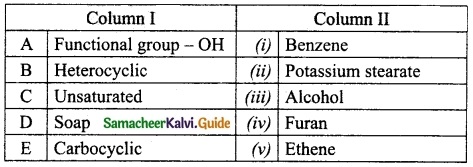
III. Match the following:
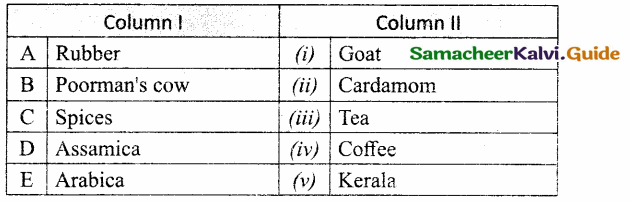
Question 1.
Identify the types of reaction:
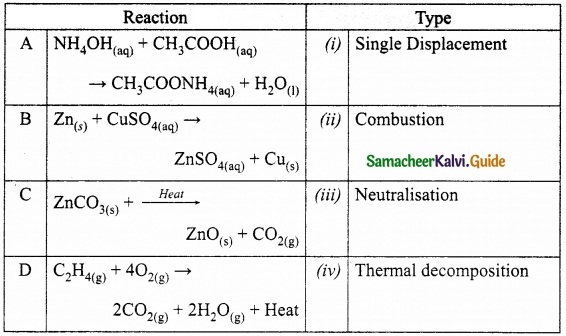
Answer:
A. (iii)
B. (i)
C. (iv)
D. (ii)
IV. True or False: (If false give the correct statement)
- Silver metal can replace hydrogen gas from nitric acid.
- The pH of rain water containing dissolved gases like SO3, CO2, NO2 will be less than 7.
- At the equilibrium of a reversible reaction, the concentration of the reactants and the products will be equal.
- Periodical removal of one of the products of a reversible reaction increases the yield.
- On dipping a pH paper in a solution, it turns into yellow. Then the solution is basic.
Answer:
- False – Silver cannot displace H2 from HNO3 acid, since it is placed below hydrogen in the activity series.
- True
- False – At equilibrium the concentration of the reactants and products do not change it remains constant, but the concentration of the reactants and the products will not be equal.
- True
- False – The solution is neutral if the solution is basic it will be green in colour.
V. Short answer questions:
Question 1.
When an aqueous solution of potassium chloride is added to an aqueous solution of silver nitrate, a white precipitate is formed. Give the chemical equation of this reaction.
Answer:
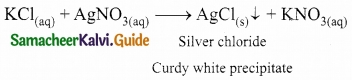
Question 2.
Why does the reaction rate of a reaction increase in raising the temperature?
Answer:
On increasing temperature heat is supplied to the reactant. This energy breaks more bonds and thus speed up the chemical reaction. Foods kept at room temperature spoils faster than that kept in the refrigerator.
Question 3.
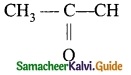
Define combination reaction. Give one example for an exothermic combination reaction.
Answer:
A combination reaction is a reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a compound.
Eg: C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + heat
![]()
Question 4.
Differentiate reversible and irreversible reactions.
Answer:

VI. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
What are called thermolysis reactions?
Answer:
Thermal decomposition reactions are called ‘thermolysis’ reaction. In this type of reaction, the reactant is decomposed by applying heat. There are two types of thermolysis reactions. They are:
(i) Compound to element / element decomposition:
A compound is decomposed into two elements.
Eg:
![]()
(ii) Compound to compound / compound decomposition:
A compound is decomposed into two compounds.
Eg:
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the types of double displacement reactions with examples.
Answer:
There are two major classes of double displacement reactions. They are,
(i) Precipitation Reactions: When aqueous solutions of two compounds are mixed, if they react to form an insoluble compound and a soluble compound, then it is called precipitation reaction.
\(\mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_{3}\right)_{2(\mathrm{aq})}+2 \mathrm{KI}_{(\mathrm{aq})} \rightarrow \mathrm{PbI}_{2(\mathrm{s})} \downarrow+2 \mathrm{KNO}_{3(\mathrm{aq})}\)
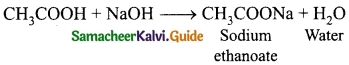
(ii) Neutralisation Reactions: Another type of displacement reaction in which the acid reacts with the base to form a salt and water. It is called ‘neutralisation reaction’ as both acid and base neutralize each other.
\(\mathrm{NaOH}_{(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{HCl}_{(\mathrm{aq})} \rightarrow \mathrm{NaCl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{l})}\).
Question 3.
Explain the factors influencing the rate of a reaction.
Answer:
Important factors that affect rate of a reaction are:
- Nature of the reactants
- Concentration of the reactants
- Temperature
- Catalyst
- Pressure
- Surface area of the reactants
1. Nature of the reactants : The reaction of sodium with hydrochloric acid is faster than that with acetic acid, because Hydrochloric acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid and thus more reactive. So, the nature of the reactants influence the reaction rate.
2Na(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2(g) (fast)
2Na(s) + 2CH3COOH(aq) → 2CH3COONa(aq) + H2(g) (slow)
2. Concentration of the reactants : Changing the amount of the reactants also increases the reaction rate. More the concentration, more particles per volume exist in it and hence faster the reaction. Granulated zinc reacts faster with 2M hydrochloric acid than 1M hydrochloric acid.
3. Temperature : Most of the reactions go faster at higher temperature. Because adding heat to the reactants provides energy to break more bonds and thus speed up the reaction. Calcium carbonate reacts slowly with hydrochloric acid at room temperature. When the reaction mixture is heated the reaction rate increases.
4. Pressure : If the reactants are gases, increasing their pressure increases the reaction rate. This is because, on increasing the pressure the reacting particles come closer and collide frequently.
5. Catalyst : A catalyst is a substance which increases the reaction rate without being consumed in the reaction. In certain reactions, adding a substance as catalyst speeds up the reaction. For example, on heating potassium chlorate, it decomposes into potassium chloride and oxygen gas, but at a slower rate. If manganese dioxide is added, it increases the reaction rate.
6. Surface area of the reactants : Powdered calcium carbonate reacts more readily with hydrochloric acid than marble chips. Because, powdering of the reactants increases the surface area and more energy is available on collision of the reactant particles. Thus, the reaction rate is increased.
![]()
Question 4.
How does pH play an important role in everyday life?
Answer:
- The pH of blood is almost 7.4. Any increase or decrease in this value leads to diseases
- Citrus fruits require slightly alkaline soil, while rice requires acidic soil and sugarcane requires neutral soil.
- If the pH of rainwater becomes less than 7, it becomes acid rain which is harmful in day-to-day life.
- pH changes cause tooth decay.
- During indigestion, the stomach produces too much acid and this causes pain and irritation.
Question 5.
What is chemical equilibrium? What are its characteristics?
Answer:
Chemical equilibrium is a state of a reversible chemical reaction where the,
Rate of forward reaction = Rate of backward reaction.
No change in the amount of the reactants and products takes place.
Characteristics of equilibrium:
- In a chemical equilibrium, the rates of the forward and backward reactions are equal.
- The observable properties such as pressure, concentration, colour, density, viscosity etc., of the system remain unchanged with time.
- The chemical equilibrium is a dynamic equilibrium, because both the forward and backward reactions continue to occur even though it appears static externally.
- In physical equilibrium, the volume of all the phases remain constant.
VII. HOT Questions:
Question 1.
A solid compound ‘A’ decomposes on heating into ‘B’ and a gas ‘C’ On passing the gas ‘C’ through water, it becomes acidic. Identify A, B and C.
Answer:
A – CaCO3, solid compound
‘A’ decomposes on heating into ‘B’ and a gas ‘C’.
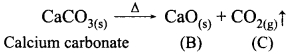
On passing the gas CO2 through water, it becomes acidic.
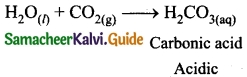
A – CaCO3, Calcium carbonate
B – CaO, Calcium oxide
C – CO2, Carbondioxide gas
![]()
Question 2.
Can a nickel spatula be used to stir copper sulphate solution? Justify your answer.
Answer:
No, nickel spatula cannot be used to stir the copper sulphate solution. Actually, on the basis of activity series, nickel is more reactive than copper, so nickel will displace copper from its solution and copper will be deposited on nickel spatula.
VIII. Solve the following problems:
Question 1.
Lemon juice has a pH 2, what is the concentration of H+ ions?
Answer:
pH = – log [H+]
[H+] = antilog of [-pH]
= antilog [-2]
[H+] = 10-2 M
[OR]
PH = – log [H+]
[H+] = 10-pH
[H+] = 10-2M
Question 2.
Calculate the pH of 1.0 × 10-4 molar solution of HNO3.
Answer:
pH = – log [H+]
HNO3 → H+ + NO3–
pH = -log [1 × 10-4]
= -(-4)log10 10 = 4
pH = 4
Question 3.
What is the pH of 1.0 x 10-5 molar solution of KOH?
Answer:
KOH → K+ + OH–
pOH = -log[OH–]
= -log [1 × 10-5]
pOH = 5
pH + pOH = 14
∴ pH of KOH = 14 – 5 = 9
pH = 9
Question 4.
Laundry detergent has a pH 8.5, What is the concentration of H+ ions?
Answer:
pH = 8.5
pH = – log [H+]
[H+] = 10-pH
[H+] = 10-8.5
[H+] = 3.16 × 10-9 M
Question 5.
The hydroxide ion concentration of a solution is 1 × 10-11M. What is the pH of the solution?
Answer:
[OH–] = 1 × 10-11 M
pOH = – log[OH–]
= – log[1 × 10-11]
= -log101 – log1010-11
= -(-11) log1010 = 11
pOH = 11
pH + pOH = 14
pH = 14 – 11
pH = 3
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Types of Chemical Reactions Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The unit of rate of a reaction is:
(a) dm³/mol
(b) dm-3
(c) mol dm-3
(d) mol
Answer:
(c) mol dm-3
Question 2.
As the molecule is dissociated by the absorption of heat it is otherwise called as ______.
(a) Thermolysis
(b) Photolysis
(c) Electrolysis
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Thermolysis
Question 3.
The chemical formula of marble is:
(a) CaCO3
(b) MgCO3
(c) Na2CO3
(d) PbCO3
Answer:
(a) CaCO3
Question 4.
As the decomposition is caused by light, this kind of reaction is called ______.
(a) Thermolysis
(b) Photolysis
(c) Electrolysis
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Photolysis
Question 5.
Fluorine will displace the following halide ion from the solution:
(a) chloride
(b) bromide
(c) iodide
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 6.
The decomposition of AgBr into grey coloured silver metal is an example of ……… reaction.
(a) compound to element/element
(b) compound to compound/compound
(c) combination
(d) neutralization
Answer:
(a) compound to element/element
Question 7.
The Metathesis reaction among the following is:
(a) C3H8(g) +5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O + heat
(b) Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
(c) HNO3(aq) + NH4OH(aq) → NH4NO3(aq) + H2O(l)
![]()
Answer:
(c) HNO3(aq) + NH4OH(aq) → NH4NO3(aq) + H2O(l)
Question 8.
KI and Pb(NO3)2 solutions are mixed to give a precipitate. What is the colour of the precipitate?
(a) White
(b) Brown
(c) Red
(d) Yellow.
Answer:
(d) Yellow
![]()
Question 9.
The pH of rain water is approximately:
(a) 7
(b) 8
(c) 4
(d) 14
Answer:
(a) 7
Question 10.
Most of the reactions go faster at ______.
(a) low temperature
(b) moderate temperature
(c) 0°C
(d) high temperature.
Answer:
(d) high temperature
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. A chemical equation provides information on the ……….. of the substances and the reaction condition.
2. The symbol ‘aq’ in a chemical equation represent the physical state of the substance as ……….
3. 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) represent the combination reaction between a ……… and ……
4. After white washing with a solution of slaked lime a thin layer of ……….. is formed.
5. Reactions in which heat is absorbed is called ……….. reactions.
6. Electrolytic refining of copper is based on ……….. reaction.
7. When 10-6 mole of a monobasic strong acid is dissolved in water, the pH of the solution is ………..
8. When pH of a solution is 2, the [H+] in mol/L is ……….
9. Combustion of coal is an example of ………. reaction.
10. [ ] represents the concentration of either the reactant or product in ……….
Answer:
1. physical state
2. aqueous solution
3. metal, non-metal
4. CaCO3
5. endothermic
6. electrolytic decomposition
7. 6
8. 1 × 10-2
9. irreversible
10. mol/Lit
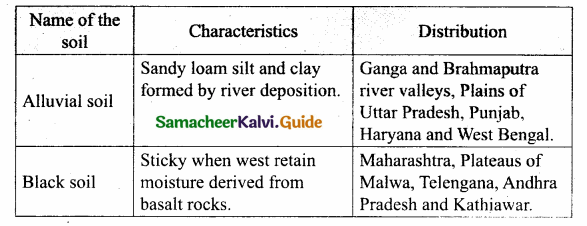
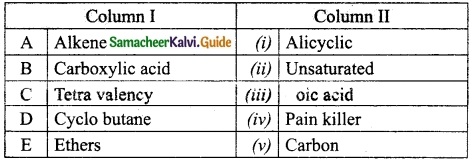
III. Match the following.
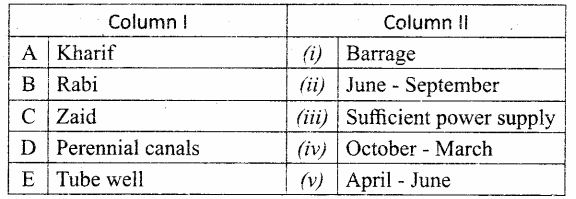
Question 1.
Match the following table:
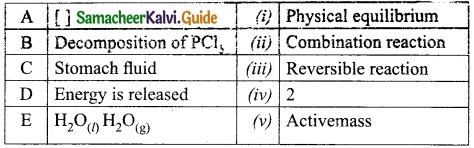
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (iii)
C. (iv)
D. (ii)
E. (i)
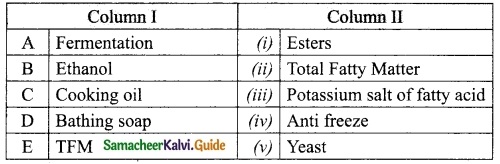
Question 2.
Match the following table:
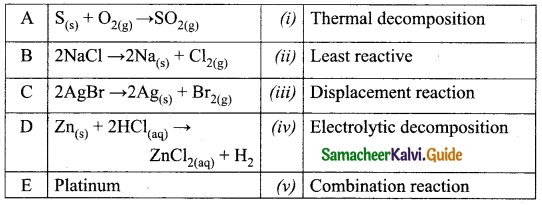
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (iv)
C. (i)
D. (iii)
E. (ii)
![]()
Question 3.
Match the following table:
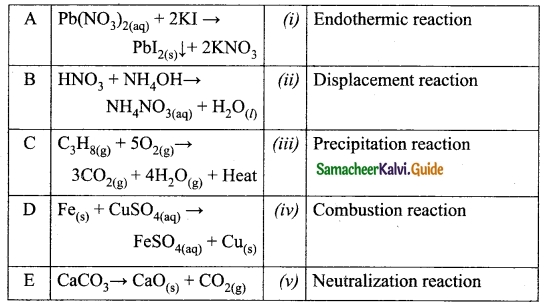
Answer:
A. (iii)
B. (v)
C. (iv)
D. (ii)
E. (i)
Question 4.
Match the following table:
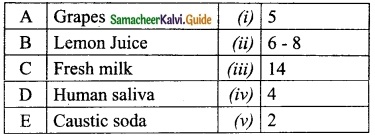
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (v)
C. (i)
D. (ii)
E. (iii)
IV. True or False: (if false give the correct statement)
- Formation of calcium silicate from silica and calcium oxide is a combination reaction.
- Most of the combination reactions are endothermic in nature.
- Decomposition of mercuric oxide into mercury and O2 is an example of . photolysis.
- Chlorine can displace fluoride ion from its aqueous solution.
- Magnesium is more reactive than iron.
Answer:
- True
- False – Most of the combination reactions are exothermic in nature.
- False – Decomposition of mercuric oxide into mercury and O2 is an example of thermolysis.
- False – Chlorine is less reactive than Fluorine, so it cannot displace fluoride ion from its aqueous solution.
- True
V. Short answer questions:
Question 1.
Write a note on double displacement reaction with an example.
Answer:
When two compounds react, if their ions are interchanged, then the reaction is called double displacement reaction.
Eg: NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O
Question 2.
Identify the wrong statements and correct them.
- Sodium benzoate is used in food preservative.
- Nitric acid is not used as fertilizer in agriculture.
- Sulphuric acid is called the king of chemicals.
- The pH of acid is greater than 7.
- Acetic acid is used in aerated drinks.
Answer:
- Correct statement.
- Wrong statement. Nitric acid is used as a fertilizer in agriculture.
- Correct statement.
- Wrong statement. The pH of the acid is lesser than 7.
- Wrong statement. Carbonic acid is used in aerated drinks.
Question 3.
Why a combustion reaction may be called as an exothermic oxidation?
Answer:
In a combustion reaction heat is evolved, it is an exothermic reaction. As oxygen is added, it is also an oxidation. So, combustion may be called as an exothermic oxidation.
![]()
Question 4.
Take two conical flasks. Label them as I and II. Take a small amount of copper sulphate solution in the first conical flask. Take a small amount of granulated zinc in the second conical flask. Allow the copper sulphate solution to react with the zinc.
- Name the type of reaction.
- Say whether the metal zinc is more reactive or less reactive.
- Write a complete and balanced reaction.
- Say whether this change is reversible or irreversible.
Answer:
- The reaction taken place is displacement reaction.
- Metal zinc is more reactive.
- Balanced chemical equation.
\(\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{s})}+\mathrm{CuSO}_{4(\mathrm{aq})} \rightarrow \mathrm{ZnSO}_{4(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{s})} \downarrow\) - This change is an irreversible change.
Question 5.
What is an irreversible reaction? Give an example.
Answer:
The reaction that cannot be reversed is called irreversible reaction. The irreversible reactions are unidirectional, i.e., they take place only in the forward direction. Consider the combustion of coal into carbon dioxide and water.
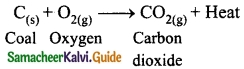
Question 6.
Define the rate of a reaction.
Answer:
“Rate of a reaction is the change in the amount or concentration of any one of the reactants or products per unit time”.
Consider the following reaction,
A → B
The rate of this reaction is given by
Rate = –\(\frac{d[A]}{dt}\) = +\(\frac{d[B]}{dt}\)
Where,
[A] – Concentration of A
[B] – Concentration of B
The negative sign indicates the decrease in the concentration of A with time. The positive sign indicates the increase in the concentration of B with time.
Question 7.
What is meant by combination reaction? Give an example.
Answer:
A reaction in which a single product is formed from two or more reactants is known combination reaction.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO.
Question 8.
What is a catalyst?
Answer:
A catalyst is a substance which increases the reaction rate without being consumed in the reaction.
Question 9.
Define Displacement reaction. Give an example.
Answer:
The reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound is called displacement reaction.
\(\mathrm{Pb}+\mathrm{CuCl}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbCl}_{2}+\mathrm{Cu} \downarrow\)
Lead displaces copper from copper chloride solution.
Question 10.
When a aerated soft drink bottle is kept open it will go flat. Why?
Answer:
(i) In the sealed aerated soft drink bottle, the dissolved CO2, in the form of carbonic acid and gaseous CO2 are in equilibrium.
(ii) When we open the bottle the gaseous CO2 will escape and the dissolved CO2 begins to undissolve to the gas phase to maintain the equilibrium. So when we keep the bottle open for a long time it will go flat with all the dissolved CO2 gone.
Question 11.
Can copper displace zinc or lead from their salt solutions?
Answer:
No, copper cannot displace zinc or lead from their salt solutions. Because copper is less reactive than zinc and lead.
Question 12.
What is called as acid rain?
Answer:
The pH of rain water is approximately ‘7’ but when the air is polluted with oxides of S and N, they get dissolved in the rain water and make its pH less than 7, then it is called acid rain.
Question 13.
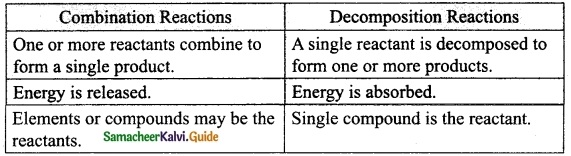
Write the differences between combination and decomposition reaction.
Answer:
![]()
VI. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Two acids ‘A’ and ‘B’ were kept in beakers. Acid ‘A’ undergoes partial dissociation in water, whereas acid ‘B’ undergoes complete dissociation in water.
- Of the two acids ‘A’ and ‘B’ which is weak acid and which is strong acid?
- What is a weak acid?
- What is a strong acid?
- Give one example of each.
Answer:
- Of the two acids ‘A’ and ‘B’, ‘A’ is a weak acid and ‘B’ is a strong acid.
- A weak acid is the one which ionises partially when dissolved in water.
- A strong acid is the one which ionises completely when dissolved in water.
- Weak acid – Acetic acid(CH3COOH)
Strong acid – Sulphuric acid (H2SO4).
Question 2.
Sodium hydroxide and HCl acid react as shown in this equation
NaOH(aq)4 + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O
(i) Which type of chemical reaction is this?
Answer:
Neutralization reaction
(ii) The reaction is exothermic. Explain what that means?
Answer:
When heat is evolved during a chemical reaction it is called exothermic.
(iii) Differentiate exothermic and endothermic reaction.
Answer:
Exothermic :
- Heat is evolved.
- Temperature increases.
Endothermic :
- Heat is absorbed.
- Temperature decreases.
(iv) What happens to the temperature of the solution as the chemicals react?
Answer:
Temperature of the solution increases.
Question 3.
Take two conical flasks. Label them as I and II. Take a small amount of CuSO4 in the I conical flask and small amount of granulated Zinc in the II conical flask. Allow the CuSO4 solution to react with Zinc.
(i) Name the type of reaction.
Answer:
Displacement reaction.
(ii) Say whether the metal Zn is more reactive or less reactive.
Answer:
Zinc is more reactive than Copper.
(iii) Write the complete and balanced reaction.
Answer:
Zn(s)+ CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)↓
(iv) Say whether this change is reversible or irreversible
Answer:
Irreversible.
Question 4.
Suggest a reason for each observation given below.
- In fireworks, powdered magnesium is used rather than magnesium ribbon.
- Zinc and dilute H2SO4 react much more quickly when a few drops of copper sulphate solutions are added.
- The reaction between magnesium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid speeds up when some concentrated HCl is added.
Answer:
- In fireworks, powdered magnesium is used because it has more surface area than magnesium ribbon. Because of more surface area, powdered magnesium reacts faster than magnesium ribbon.
- Zinc and dilute H2SO4 react much more quickly when a few drops of copper sulphate solution is added. Copper sulphate acts as a catalyst which increases the rate of the reaction.
- When the concentration of the reactants increases, the rate of the reaction also increases. So the reaction between magnesium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid speeds up by the addition of some concentrated HCl.
![]()
VII. Hot Questions:
Question 1.
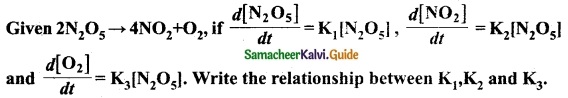
Answer:
According to the rate Law for the reaction.
2N2O5 → 4NO2 + O2
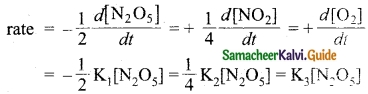
2K1 = K2 = 4K3 [neglecting negative and positive signs]
Question 2.
When solutions of silver nitrate and potassium bromide are mixed, a pale yellow precipitate is formed.
The ionic equation for the reaction is Ag+ + Br– → AgBr
- (a) What is the name of the pale yellow precipitate?
(b) Is it soluble or insoluble? - Is the formation of silver bromide precipitate, a result of redox reaction or not? Justify your answer.
- What is this type of reaction called?
Answer:
- (a) The pale yellow precipitate is silver bromide.
(b) Silver bromide is sparingly soluble. - Yes, the formation of silver bromide precipitate is due to redox reaction. Ag+ gains electron (reduction) and Br– loses electron (oxidation). So it is a redox reaction.
- This reaction is a double displacement reaction.
VIII. Numericals:
Question 1.
The hydrogen ion concentration of a fruit juice is 3.3 × 10-2M. What is the pH of the juice? Is it acidic or basic?
Answer:
[H+] = 3.3 × 10-2 M
Formula:
pH = -log[H+]
pH = -log[3.3 × 10-2]
= -[log 3.3 + log 10-2]
= -[0.5185 – 2 log1010]
= -0.5185 + 2 log1010 [log1010 = 1]
= -0.5185 + 2
pH = 1.4815
Since pH is less than 7, the solution is acidic.
Question 2.
If a solution has a pH of 7.41, determine its H+ concentration.
Answer:
pH = 7.41
Formula:
[H+] = antilog[-pH]
= antilog[-7.41] = 10-7.41
= 3.89 × 10-8M
![]()
Question 3.
The pH of a solution is 5.5 at 25°C. Calculate its [OH–].
Answer:
pH = 5.5
Since pH + pOH = 14
pOH = 14 – pH
= 14 – 5.5 = 8.5
[OH–] = 10-pOH
= 10-8.5
= 3.16 × 10-9M
(OR)
[OH–] = antilog[-8.5]
= 3.16 × 10-9M
[OH–] = 3.16 × 10-9M
Question 4.
Calculate the pH of 0.001 M HCl solution.
Answer:
Since HCl is a strong acid, it dissociates
HCl → H+ + Cl–
[H+] = [HCl] = 0.001 M
[H+] = 1 × 10-3M
pH = -log[H+]
= -log[1 × 10-3]
pH = 3
Question 5.
The hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is 1 × 10-8M.
(i) What is the pH of the solution?
Answer:
pH = -log[1 × 10-8]
pH = 8
(ii) What is the pOH of the solution?
Answer:
pOH = 14 – 8
= 6
(iii) Is the given solution acidic or basic?
Answer:
Acidic
Question 6.
Calculate the pH of 0.02 M Ba(OH)2, Ba(OH)2 solution is a strong electrolyte.
Answer:
[Ba(OH)2] = 0.02 M
Ba(OH)2 → Ba2+ + 2OH–
[OH–] = 2[Ba(OH)2]
= 2 × 0.02 = 0.04 M
pOH = – log[0.04]
= -log[4 × 10-2]
= -[log 4 + log 10-2]
= -[0.6020 – 2 log 10]
pOH = -0.6020 + 2 × 1
= 1.398
pH = 14 – 1.398
= 12.602