Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 2 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 2 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the questions in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 15 to 28 in Part II are of two marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 29 to 42 in Part III are of five marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 43 to 44 in Part IV are of Eight marks each. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer [14 × 1 = 14]
Question 1.
What is the Battle of Marne remembered for?
(a) Air warfare
(b) Trench warfare
(c) Submarine warfare
(d) Ship warfare
Answer:
(b) Trench warfare
Question 2.
With whom of the following was the Lateran Treaty signed by Italy?
(a) Germany
(b) Russia
(c) Pope
(d) Spain
Answer:
(c) Pope
Question 3.
The United States and European allies formed to resist any Soviet aggression in
Europe.
(a) SEATO
(b) NATO
(c) SENTO
(d) Warsaw Pact
Answer:
(b) NATO
![]()
Question 4.
Find out the militant nationalist from the following.
(a) Dadabhai Naoroji
(b) Justice Govind Ranade
(c) Bipin Chandra Pal
(d) Romesh Chandra
Answer:
(c) Bipin Chandra Pal
Question 5.
When was the first forest Act enacted?
(a) 1858
(b) 1911
(c) 1865
(d) 1936
Answer:
(c) 1865
Question 6.
…………………………. River is known as “Sorrow of Bihar”.
(a) Narmada
(b) Godavari
(c) Kosi
(d) Damodar
Answer:
(c) Kosi
Question 7.
…………………………. helps in quick, ripening of mangoes along the coast of Kerala and Karnataka.
(a) Loo
(b) Nor wester
(c) Mango showers
(d) Jet stream
Answer:
(c) Mango showers
Question 8.
Which crop is called as “Golden fibre” in India?
(a) cotton
(b) Wheat
(c) Jute
(d) Tobacco
Answer:
(c) Jute
Question 9.
Which of the following district is affected by sand dunes to a large extent?
(a) Theni
(b) Madurai
(c) Thanjavur
(d) Ramanathapuram
Answer:
(d) Ramanathapuram
![]()
Question 10.
The transport useful in the inaccessible area is ………………………….
(a) Roadways
(b) Railways
(c) Airways
(d) Waterways
Answer:
(c) Airways
Question 11.
How can the fundamental Rights be suspended?
(a) If the supreme court so desires
(b) If the Prime Minister orders to this effect
(c) If the President orders it during the national emergency
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) If the President orders it during the national emergency
Question 12.
Find the odd one ………………………….
(a) Social welfare
(b) Health care
(c) Diplomacy
(d) Domestic affairs
Answer:
(c) Diplomacy
Question 13.
…………………………. status is one of the indicators of the overall well-being of population and human resources development.
(a) Health
(b) Nutritional
(c) Economic
(d) Wealth
Answer:
(a) Health
![]()
Question 14.
Which one is a trade policy?
(a) irrigation policy
(b) import and export policy
(c) Land-reform policy
(d) Wage policy
Answer:
(b) import and export policy
Part – II
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 28 is compulsory. [10 x 2 = 20]
Question 15.
Write a note on reforms of Ramalinga Adigal.
Answer:
(i) Ramalinga swamigal emphasised the bonds of responsibility and compassion between living beings. He expressed the view that those who lack compassion for suffering of human beings are hard hearted, their wisdom clonded. He showed his compassion and mercy on all living beings including plants.
(ii) He established the Samarasa Vedha Sanmarga Sangam in 1865 and it was renamed in 1872 as ‘Samarasa Suddha Sanmarga Sathya Sangam’ which means ‘Society for pure truth in universal self-hood’. Ramalinga also estabilished a free feeding house for everyone.
Question 16.
Describe the Pearl Harbour incident.
Answer:
(i) Pearl Harbour incident took place in December 1941 when Japan attacked American naval installations in Pearl Harbour, Hawaii, without warning to cripple America’s Pacific fleet. Many battle ships and numerous fighter planes were destroyed.
(ii) The US declared war on Japan, with Britain and China. This brought together both the Asia Pacific and the European war into one common cause. Most importantly, it brought the United States with its enormous resources into the war as a part of the Allies.
![]()
Question 17.
What was the significance of the Battle of Kalakadu?
Answer:
In the Battle of Kalakadu, Mahfuzkhan’s troops were routed by the huge forces of Puli Thevar.
Question 18.
Write a note on the Khilafat Movement.
Answer:
- After World War I, the Caliph of Turkey, who was considered the head of Muslims all over the world, was given a very harsh treatment. The Khilafat Movement started in support of the Caliph.
- It was led by Maulana Mohamed Ali and Maulana Shaukat Ali, popularly known as the Ali brothers.
- It aimed to restore the prestige and power of the Caliphate. Mahatma Gandhi supported the movement and saw it an opportunity to unite the Hindus and the Muslims.
Question 19.
Define ‘Meteorology’.
Answer:
The branch of science concerned with the processes and phenomena of the atmosphere, especially as a means of forecasting the weather.
Question 20.
Name the types of soil found in India.
Answer:
- Alluvial Soils
- Black soils
- Red soils
- Laterite soils
- Forest and mountain soils
- Arid and desert soils
- Saline and alkaline soils
- Peaty and marshy soils.
Question 21.
Name the important oil producing regions of India.
Answer:
Oil in India is obtained from both from on-shore and off-shore areas.
Western Coast off shore oil fields:
- Mumbai high oil fields
- Gujarat Coast
- Basseim oil field, South of Mumbai high
- Ankleshwar
- Cambay-Luni Region
- Ahemedabad-Kalol Region
- Aliabet oil feild, south of Bhavanagar
Eastern Coast off shore oil fields:
- Brahmaputra valley
- Digboi oil fields
- Nahoratiya oil fields
- Moran-Hugrijan oil fields
- Rudrasagar-Lawa oil fields
- Surrma valley
- Offshore of Andaman and Nicobar, Gulf of Mannar, Baleshwar coast, Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
Question 22.
What is national emergency?
Answer:
National emergency is a situation beyond the ordinary. The President declares this emergency if he is satisfied that India’s security is threatened due to war, external aggression or armed rebellion or if there is an imminent danger or threat.
![]()
Question 23.
Mention the member countries of BRICS.
Answer:
- Brazil
- Russia
- India
- China
- South Africa
Question 24.
Write any five principles of Fair Trade Practices.
Answer:
Five principles of Fair trade practices:
- Creating opportunities for economically disadvantaged producers.
- Transforming and accountability.
- Fair trading practices and payment of fair price.
- Ensuring no child labour and forced labour.
- Respect for the environment.
Question 25.
Define food security according to FAO.
Answer:
The United Nation’s Food and Agriculture Organisation defines food security as follows: “Food security exists when all people, at all times, have physical, social and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food which meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.” (FAO, 2009)
Question 26.
What are the effects of Green Revolution?
Answer:
- It increase the production and cultivation
- It increase the productivity
- Changes in cropping system
- Industrial development
Question 27.
Why is Coimbatore called the Manchester of Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Maximum units are concentrated in and around Coimbatore region. For this region it is known as the “Manchester of South India”. It is known as such because of presence of more than 25,000 small, medium, large scale industries and textile mills.
Question 28.
What was the reason for India to choose the path of Non-Alignment?
Answer:
- The new nations that got independence after the long period of colonial struggle found themselves in a very difficult situation with respect to economic development.
- So it was necessary to align with either of the blocs – United States of America (USA) or United Soviet Socialist Republic (USSR).
- Nehru, India’s first Prime Minister, was opposed to the rivalry of the two superpowers (America and Russia). So he chose the path of Non-Alignment.
Part – III
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 42 is compulsory. [10 x 5 = 50]
Question 29.
Fill in the blanks
(i) …………………………. was the headquarters of the Council of Europe.
(ii) …………………………. is the highest peak in the southern most part of the Eastern Ghats.
(iii) …………………………. is the instrument for implementing foreign policy of a state.
(iv) …………………………. is an important indicator of nutrition deficiency.
(v) Sathanur dam is constructed across the river ………………………….
Answers
(i) Strasbourg
(ii) Solaikaradu
(iii) Diplomacy
(iv) Underweight
(v) Thenpennai.
![]()
Question 30.
Match the following:

Answer

Question 31.
Match the following:

Answer

Question 32.
(a) Distinguish between
(i) Western Coastal Plains and Eastern Coastal Plains
(ii) Marine Fishing and Inland Fishing
Answer:
(a) (i) Western Coastal Plains and Eastern Coastal Plains:
Western Coastal Plains :
- It lies between the Western Ghats and Arabian Sea.
- It is a narrow plain, which stretches from Gujarat to Kerala with an average width of 50 – 80 Km.
- This plain is drained by less rivers like Narmada and Tapti forming estuaries.
- It consists of three sections. The northern part of the coast is called the Konkan (Mumbai – Goa), the
- Central stretch is called the Kannad plain while the southern stretch is referred to as the Malabar coast.
Eastern Coastal Plains:
- It lies between the Eastern Ghats and Bay of Bengal Sea.
- They are wide and level plains with an average width of 80 – 100 Km.
- This plain is drained by more rivers forming deltas like Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri.
- It consists of two sections. In the northern part, it is referred to as the Northern Circar, while the southern part is known as the Coromandal coast.
- Lake Chilka is an important feature along the eastern coast.
(ii) Marine Fishing and Inland Fishing:
Marine Fishing :
- It includes coastal off-shore and deep sea fisheries mainly on the continent shelf.
- Kerala leads in the marine fish production in India.
Inland Fishing :
- Rivers, lakes, canals, reservoirs, ponds, tanks etc.
- Andhra Pradesh is the leading producer in India.
(b) Give reason: Western Coastal plain is narrow.
Answer:
- It lies between the Western Ghats and Arabian Sea.
- It is a narrow plain, which stretches from Gujarat to Kerala with an average width of 50-80 km.
- It is mainly characterised by sandy beaches, coastal sand dunes, mud flats, lagoons, estuary, laterite platforms and residual hills.
Question 33.
Attempt an essay on the rise and fall of Adolf Hitler.
Hitler was great orator. He swayed the people by his impassioned speeches, promising a return to the glorious military past of Germany. He founded the National Socialist Party, known as ‘the Nazis’.
He came to power in 1933 and ruled Germany till 1945, with a small group of fanatic followers. He rearmed Germany. He made huge expenditure on the recruitment of armed forces and the manufacture of armaments and machinery for the army, navy and air force. Soon the economic condition of Germany got strengthened and the problem of unemployment came to an end. In 1938, Hitler invaded Austria and Czechoslovakia.
Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia was German-speaking, and Hitler’s claim was that the German-speaking people should be united in one nation. Though Hitler gave an assurance in the Munich Pact that Germany would not attack any other country, but this was broken immediately. In 1939, he invaded Czechoslovakia.
Poland was attacked next, and this was the final act which resulted in declaration of war by Britain and France against Germany. In June 1940, Italy joined Germany, and in September 1940, Japan also joined the Axis Powers.
The German army followed a tactic of ‘lightning strike’ to storm into various countries and overrun them. In June 1941, German army invaded Russia and remained successful in the initial years. But ultimately got defeated due to the resistance by Soviet army, and the fierce Russian winter.
In the Battle of Alamein 1942, the Allied forces counter-attacked and defeated the German and Italian forces in North Africa. The German army was chased across the desert, out of North Africa. The war continued till Hitler’s suicide in April 1945.
![]()
Question 34.
Discuss the reasons behind the partition of India.
While the Indian National Congress was calling for Britain to quit India, in 1943, the Muslim League passed a resolution demanding the British to divide and quit. There were several reasons for the separate Muslim homeland in the sub-continent:
- As colonizers, the British had followed a divide-and-rule policy in India. In the census they categorized people according to religion and viewed and treated them as separate from each other.
- The British based their knowledge of the people of India on religious texts and the intrinsic differences they found in them, instead of examining how people of different religions coexisted.
- As soon as the Muslim League was formed, Muslims were placed on a separate electorate.
Thus, the separateness of Muslims in India was built into the Indian electoral process. - There was also an ideological divide between the Muslims and the Hindus of India. While there were strong feelings of nationalism in India, by the late 19th century there were also communal conflicts and movements in the country that were based on religious identities rather than class or regional ones.
- Both Hindu Mahasabha and Muslim League claimed that the interests of the Hindus and Muslims were different and hostile to each other.
- The British policy of divide and rule, through measures such as Partition of Bengal, Communal Award, had encouraged the vested interests out to exploit the religious differences.
Question 35.
State the types of soil in India and explain the characteristics and distribution of soil.
Answer:
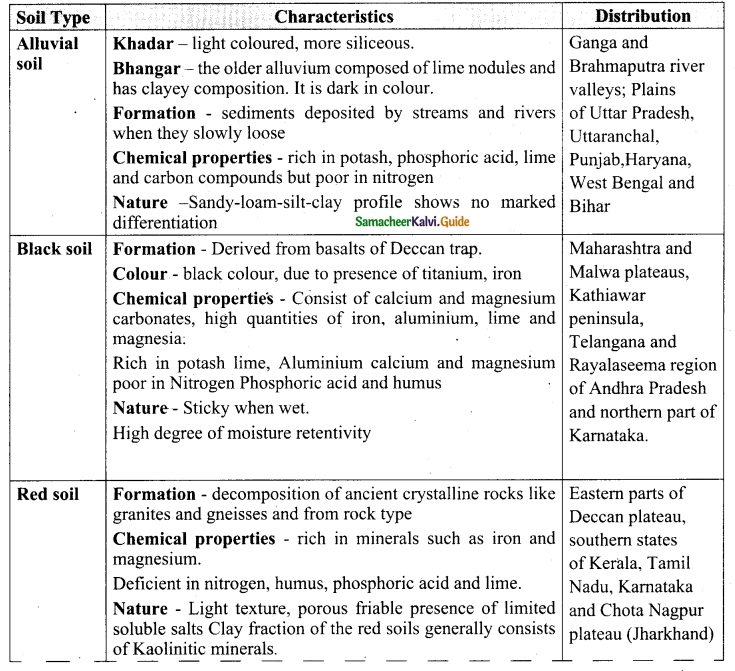
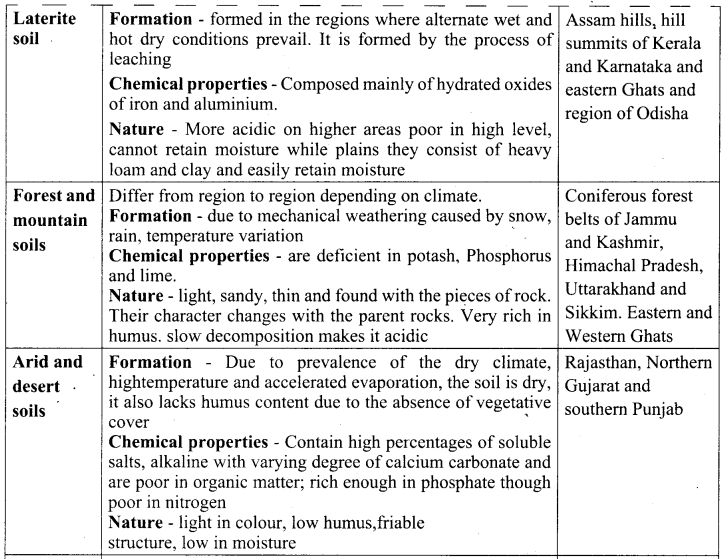

Question 36.
Describe the nature of the plateau region of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- Plateau of Tamil Nadu are located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats.
- It is roughly triangular in shape and covers an area of about 60,000 sq. km. .
- Its height increases from east to west. Its height ranges between 150 and 600 m.
- This plateau is broader in the north and very narrow in the south and it has many subdivisions.
- Bharamahal plateau is a part of the Mysore plateau situated in the northwestern part of Tamil Nadu. Dharmapuri and Krishnagiri districts are located in this region.
- Coimbatore plateau lies between the Nilgiris and Dharmapuri districts. Its height varies from 150 to 450 metres. Moyar river separates this plateau from the Mysore plateau.
- Rivers like Bhavani, Noyyal and Amaravathi, which originate from Western Ghats form Valleys in the region. Many intermontane plateaus are found in the region of the Nilgiris. Sigur plateau is one such plateau.
- Madurai plateau found in madurai district extends up to the foothills of the Western Ghats. Vaigai and Thamirabarani basins are located in the zone.
![]()
Question 37.
Point out the fundamental Rights.
The Fundamental Rights are enshrined in Part III of the Constitution from Articles 12 to 35. There are six Fundamental Rights –
- Right to Equality It provides equality before law. It prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. It abolishes untouchability.
- Right to Freedom It provides freedom of speech and expression, assembly, association, movement, residence and profession.
- Right against Exploitation It prohibits trafficking in human beings and forced labour. It also prohibits employment of children in factories, etc.
- Right to religion It gives freedom of conscience and free profession practice and propagations of religion. ,
- Cultural and Educational rights It gives protection of language, script and culture of minorities. It also gives minorities the right to establish and administer educational institutions.
- Right to Constitutional Remedies It allows individuals to seek redressal for the violation of their Fundamental Rights.
Question 38.
Make a list on basic concepts followed by India to maintain friendly relations with its neighbours.
Answer:
- Indian foreign policy has always regarded the concept of neighbourhood as one of widening concentric circles, around the central axis of historical and cultural commonalties.
- India gives political and diplomatic priority to her immediate neighbours and the Indian Ocean Island states such as Maldives. ,
- India provides neighbours with support as needed in this form of resources equipment and training.
Question 39.
Explain various terms associated with measuring of national income.
Answer:
Various terms associated with measuring of national income.
(i) Gross National Product or GNP is the total value of goods and services produced and income received in a year by domestic residents of a country. It excludes profits earned from capital invested abroad.
(ii) Gross Domestic Product or GDP is the total value of output of goods and services produced by the factors of production within the geographical boundaries of the country.
(iii) Net National Product or NNP refers to gross national product, i.e., the total market value of all final goods and services produced by the factors of productions of a country or other polity during a given time period, minus depreciation.
(iv) Net Domestic Product or NDP is a part of Gross Domestic Product. It is obtained from the Gross Domestic Product by deducting the Quantum of the wear and tear expenses (depreciation).
NDP = GDP – Depreciation
(v) Per .Capita Income or PCI is an indicator to show the living standard of people in a country.
It is obtained by dividing the National Income by the population of a country.
National Income
Per Capita Income = \(\frac{\text { National Income }}{\text { Population }}\)
(vi) Personal Income or PI is the total money income received by individuals and households of a country from all possible services before direct taxes. Personal income can be expressed as follows:
PI = NI Corporate Income Taxes – Undistributed Corporate Profits – Social Security Contributions + Transfer payment.
(vii) Disposable Income or DI means actual income which can be spent on consumption by individuals and families. It can be expressed as DPI = PI – Direct Taxes.
Question 40.
Write in detail about the types of policies adopted by the Tamil Nadu government to industrialise?
Industrial Policy of Tamil Nadu:
Tamil Nadu enjoys growth and has excellent infrastructure. A straggly established cluster and political stability are the major advantages. The state government has a pro-active industrial policy and is very encouraging when it comes to SEZs.
Important industrial policies:
- Tamil Nadu Industrial Policy – 2014
- Implementation of Industrial Policy – 2015
- Tamilnadu State Environmental Policy – 2014
- Tamilnadu SEZs Policy -2013
- Tamilnadu Automobiles and Auto Parts Policy – 2014 (/) Tamilnadu Biotechnology Policies – 2014
Question 41.
Draw a time line for the following:
live important events between 1922-1943
Answer:

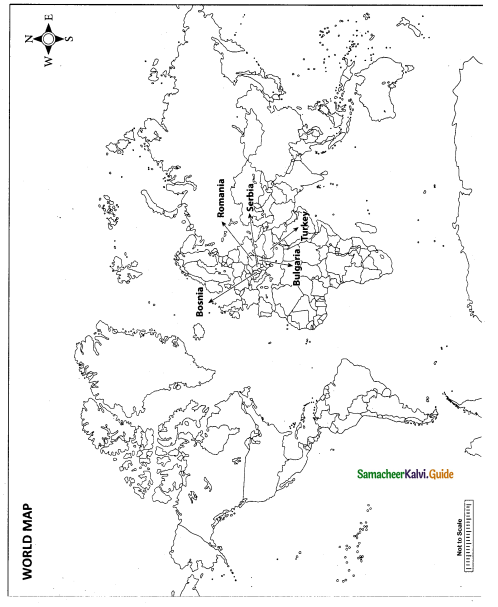
Question 42.
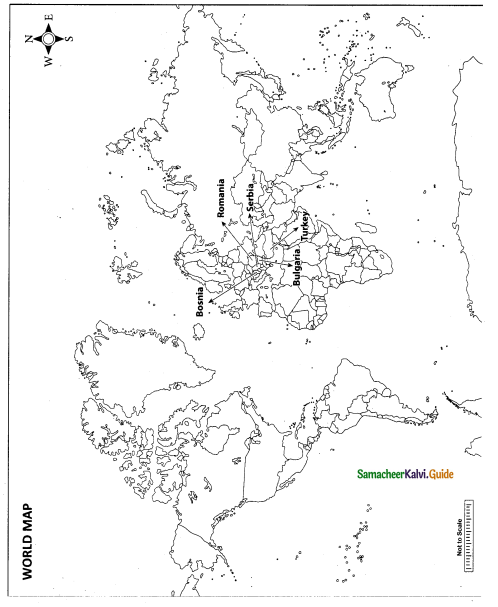
Mark the following places on the world map.
(i) Bosnia
(ii) Romania
(iii) Serbia
(iv) Bulgaria
(v) Turkey
Part – IV
Answer both questions. [2 x 8 = 16]
Question 43.
(a) Balkan Wars
(i) Why was Balkan league formed?
(ii) What was the outcome of the first Balkan war?
(iii) Who were defeated in this war?
(iv) What was the name of the Treaty signed at the end of this second Balkan war?
Answer:
(a) Balkan Wars
(i) Balkan League was formed to attack and defeat Turkish forces in the first Balkan War in 1912-13.
(ii) The new state of Albania was created and the other Balkan states divided up Macedonia between them. Turkey was reduced to the area around Constantinople.
(iii) The Turkish forces were defeated in the first Balkan War.
(iv) The name of the Treaty signed at the end of the second Balkan War was the Treaty of Bucharest.
(b) Deccan Riots
(i) When and where did the first recorded incident of rioting against the moneylenders in the Deccan appear?
(ii) What was the right given to moneylenders under a new law of the British?
(iii) What did it result in?
(iv) Against whom was the violence directed in the Deccan riots.
Answer:
(b) Deccan Riots
(i) The first recorded incident of rioting against the moneylenders in the Deccan appeared in May 1875, in Supa, a village near Poona.
(ii) Under a new law, the British moneylenders were allowed to attach the mortgaged land of the defaulters and auction it off.
(iii) It resulted in transfer of lands from the cultivators to the non-cultivating classes.
(iv) The violence was directed mostly at the Gujarat moneylenders.
[OR]
(c) Early Nationalist Movement in Tamil Nadu
(i) What were the objectives of Madras Native Association?
(ii) What led to the emergence of nationalist press in Tamil Nadu?
(iii) What were the demands of Madras Mahajana Sabha?
(iv) Who were the early nationalist leaders in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
(c) Early Nationalist Movement in Tamil Nadu
(i) The objective of Madras Native Association was to promote the interests of its members and reduction of taxes. It also protested against the government’s support to missionary activities.
(ii) The entire press opposed the appointment of the first South Indian judge of the Madras High Court in 1878. This led to a need of a nationalist press to express the Indian perspective. The Hindu was started in 1878 and soon became a vehicle for nationalist propaganda.
(iii) The demands of Madras Mahajana Sabha were to conduct civil services examinations simultaneously in England and India, abolition of India Council in London, reduction of taxes, and reduction of civil and military expenditure.
(iv) Some early nationalists in Tamil Nadu were: V.S. Srinivasa Sastri, P.S. Sivasamy Iyer, V. Krishnasamy Iyer, T.R. Venkatrama Sastri, G.A. Natesan, T.M. Madhava Rao and S. Subramania Iyer.
(d) Labour Movement in Tamil Nadu
(i) Highlight the factors that caused the birth of Trade Union Movement in Madras.
(ii) Identify the three prominent persons associated with the Madras Labour Union.
(iii) Where was the first conference of All India Trade Union Congress held?
(iv) Who organized the first ever celebration of May Day in Madras and which year?
Answer:
(d) Labour Movement in Tamil Nadu
(i) The factors that caused the birth of Trade Union Movement in Madras are,
- Retrenchment of workers at the end of the First World War.
- Nationalists’ support to the cause of labour.
(ii) Three prominent persons associated with the Madras Labour Union are B.R Walia, M. Singaravelar and Thiru.Vi. Kalyanasundaram.
(iii) The first All India Trade Union Conference was held in Bombay.
(iv) M. Singaravelar organised the first ever celebration of May Day in Madras in 1923.
![]()
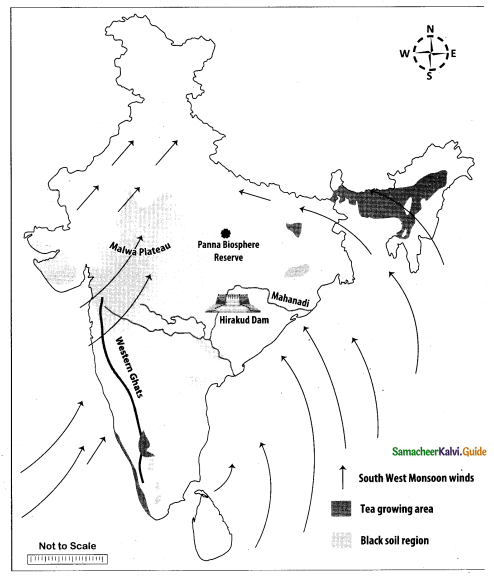
Question 44.
Mark the following places on the given outline map of India.
(i) Western Ghats
(ii) Mahanadi
(iii) Malwa Plateau
(iv) Panna biosphere reserve
(v) Southwest Monsoon
(vi) Black soil region
(vii) Tea growing area
(viii) Hirakud Dam
Answer:
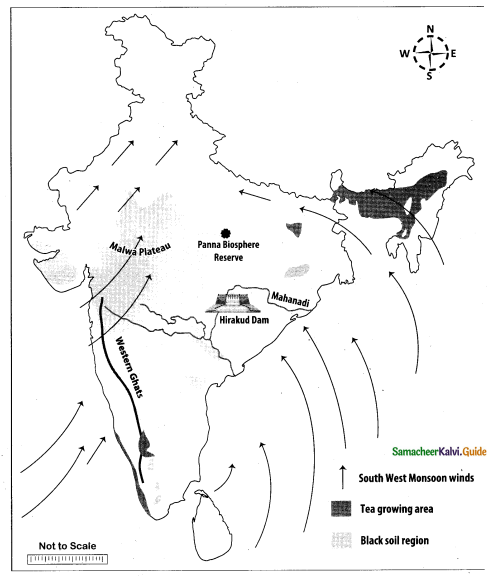
[OR]
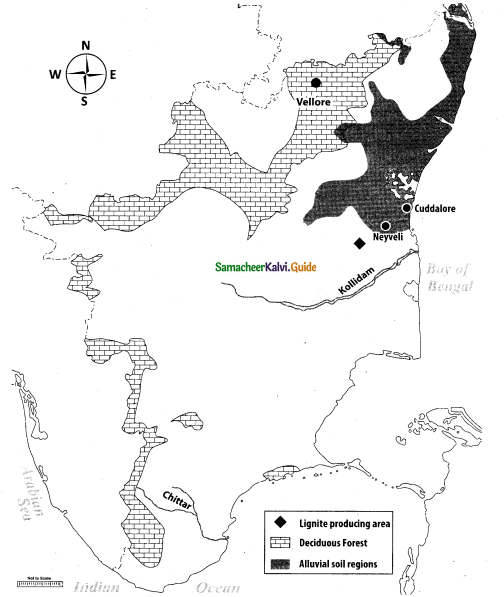
Mark the following places on the given outline map of Tamil Nadu:
(i) One Lignite producing area
(ii) Neyveli
(iii) Kollidam
(iv) Decidious forest area
(v) Alluvial soil region
(vi) Cuddalore
(vii) Vellore
(viii) River Chittar
Answer:
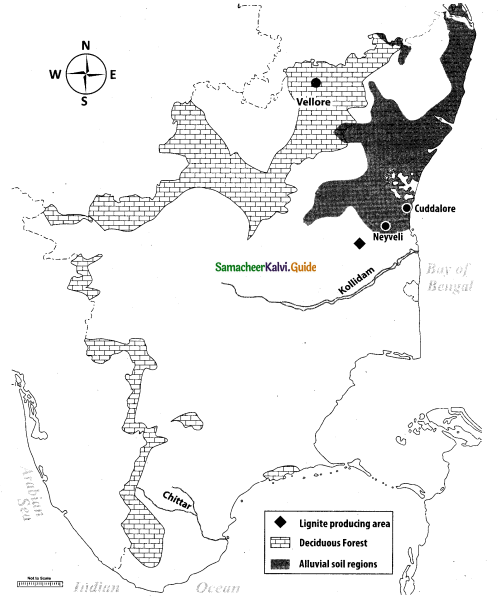
Map for Q. 42
(i) Bosnia
(ii) Romania
(iii) Serbia
(iv) Bulgaria
(v) Turkey
Answer:
Map for Q. 44
(i) Western Ghats
(ii) Mahanadi
(iii) Malwa Plateau
(iv) Panna biosphere reserve
(v) Southwest Monsoon
(vi) Black soil region
(vii) Tea growing area
(viii) Hirakud Dam
Answer:
Map for Q.44
(j) One Lignite producing area
(ii) Neyveli
(iii) Kollidam
(iv) Decidious forest area
(v) Alluvial soil regions
(vi) Cuddalore
(vii) Vellore
(viii) River Chittar
Answer: