Students can download Maths Chapter 2 Numbers and Sequences Ex 2.9 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Numbers and Sequences Ex 2.9
Question 1.
Find the sum of the following series
(i) 1 + 2 + 3 + …….. + 60
(ii) 3 + 6 + 9 + …….. +96
(iii) 51 + 52 + 53 + …….. + 92
(iv) 1 + 4 + 9 + 16 + …….. + 225
(v) 62 + 72 + 82 + …….. + 212
(vi) 103 + 113 + 123 + …….. + 203
(vii) 1 + 3 + 5 + …… + 71
Solution:
(i) 1 + 2 + 3 + …….. + 60 = \(\frac{60 \times 61}{2}\)
[Using \(\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\) formula]
= 1830
(ii) 3 + 6 + 9 + …….. + 96 = 3(1 + 2 + 3 + ……… + 32)
= \(\frac{3 \times 32 \times 33}{2}\)
= 1584
(iii) 51 + 52 + 53 + …….. + 92 = (1 + 2 + 3 + ……. + 92) – (1 + 2 + 3 + …… + 50)
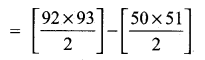
= 4278 – 1275
= 3003
(iv) 1 + 4 + 9 + 16 + …….. + 225 = 12 + 22 + 32 + 42 + ………… + 152
\(\frac{15 \times 16 \times 31}{6}\)
[using \(\frac{n(n+1)(2 n+1)}{6}\)] formula
= 1240
(v) 62 + 72 + 82 + …….. + 212 = 1 + 22 + 32 + 42 + ………… + 212 – (1 + 22 + ………… + 52)
= \(\frac{21 \times 22 \times 43}{6}\) – \(\frac{5 \times 6 \times 11}{6}\)
= 3311 – 55
= 3256
(vi) 103 = 113 + 123 + …….. + 203 = 13 + 23+ 33 + ………… + 203 – (13 + 23 + 33 + …………. + 93)
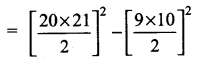
[Using (\(\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\))2 formula]
= 2102 – 452 = 44100 – 2025
= 42075
(vii) 1 + 3 + 5+ … + 71
Here a = 1; d = 3 – 1 = 2; l = 71
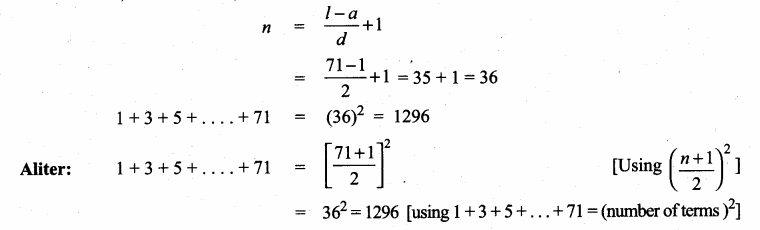
![]()
Question 2.
If 1 + 2 + 3 + …. + k = 325 , then find 13 + 23 + 33 + …………. + k3
Answer:
1 + 2 + 3 + …. + k = 325
\(\frac{k(k+1)}{2}\) = 325 ……(1)
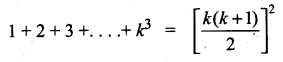
= 3252 (From 1)
= 105625
Question 3.
If 13 + 23 + 33 + ………… + K3 = 44100 then find 1 + 2 + 3 + ……. + k
Answer:
13 + 23 + 33 + ………….. + k3 = 44100
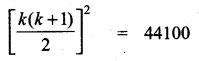
\(\frac{k(k+1)}{2}\) = \(\sqrt { 44100 }\) = 210
1 + 2 + 3 + …… + k = \(\frac{k(k+1)}{2}\)
= 210
Question 4.
How many terms of the series 13 + 23 + 33 + …………… should be taken to get the sum 14400?
Answer:
13 + 23 + 33 + ……. + n3 = 14400
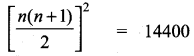
\(\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\) = \(\sqrt { 14400 }\)
\(\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\) = 120 ⇒ n2 + n = 240
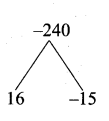
n2 + n – 240 = 0
(n + 16) (n – 15) = 0
(n + 16) = 0 or (n – 15) = 0
n = -16 or n = 15 (Negative will be omitted)
∴ The number of terms taken is 15
![]()
Question 5.
The sum of the squares of the first n natural numbers is 285, while the sum of their cubes is 2025. Find the value of n.
Answer:
12 + 22 + 32 + …. + n2 = 285
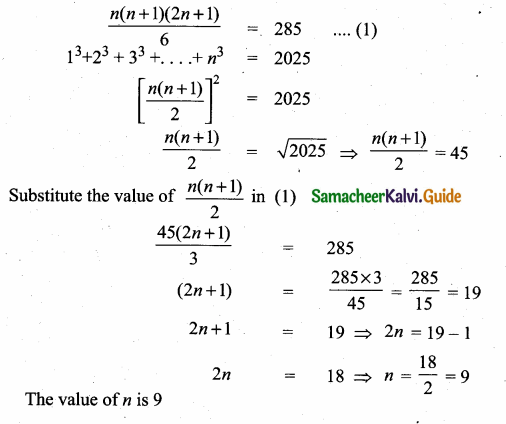
Question 6.
Rekha has 15 square colour papers of sizes 10 cm, 11 cm, 12 cm, …, 24 cm. How much area can be decorated with these colour papers?
Answer:
Area of 15 square colour papers
= 102 + 112 + 122 + …. + 242
= (12 + 22 + 32 + …. + 242) – (12 + 22 + 92)
= \(\frac{24 \times 25 \times 49}{6}-\frac{9 \times 10 \times 19}{6}\)
= 4 × 25 × 49 – 3 × 5 × 19
= 4900 – 285
= 4615
Area can be decorated is 4615 cm2
![]()
Question 7.
Find the sum of the series (23 – 1)+(43 – 33) + (63 – 153) + …….. to
(i) n terms
(ii) 8 terms
Answer:
Sum of the series = (23 – 1) + (43 – 33) + (63 – 153) + …. n terms
= 23 + 43 + 63 + …. n terms – (13 + 33 + 53 + …. n terms) …….(1)
23 + 43 + 63 + …. n = ∑(23 + 43 + 63 + ….(2n)3]
∑ 23 (13 + 23 + 33 + …. n3)
= 8 (\(\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\))2
= 2[n (n + 1)]2
13 + 33 + 53 + ……….(2n – 1)3 [sum of first 2n cubes – sum of first n even cubes]
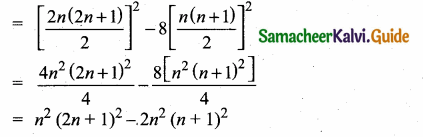
Substituting (2) and (3) in (1)
Sum of the series = 2n2 (n + 1)2 – n2 (2n + 1)2 + 2n2(n + 1)2
= 4n2 (n + 1)2 – n2 (2n + 1)2
= n2 [(4(n + 1)2 – (2n + 1)2]
= n2 [4n2 + 4 + 8n – 4n2 – 1 – 4n]
= n2 [4n + 3]
= 4n3 + 3n2
(ii) when n = 8 = 4(8)3 + 3(8)2
= 4(512) + 3(64)
= 2240