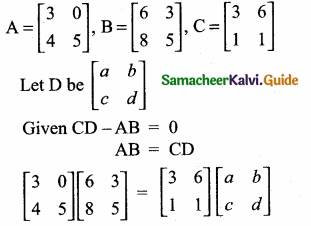
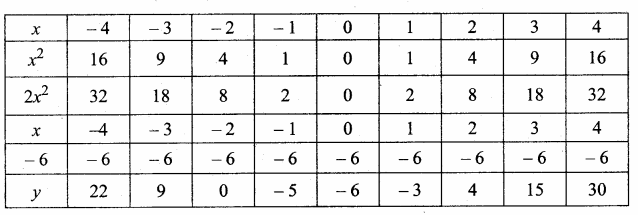
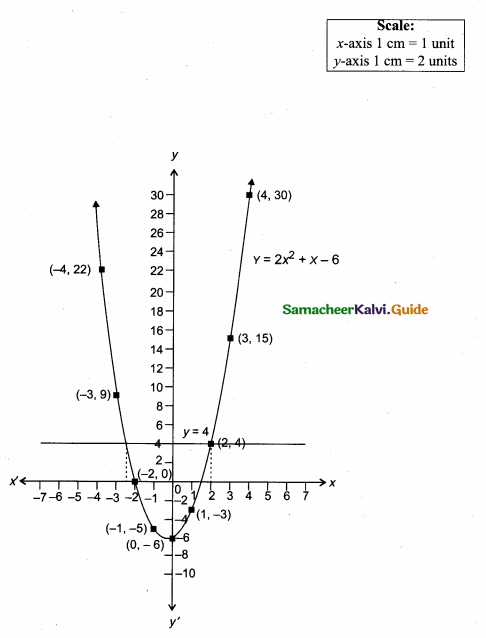
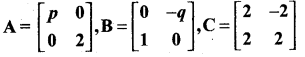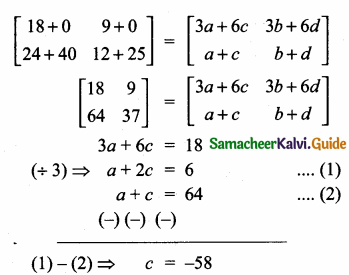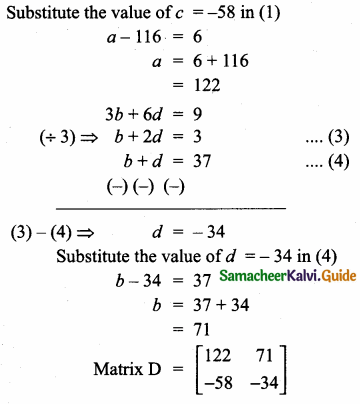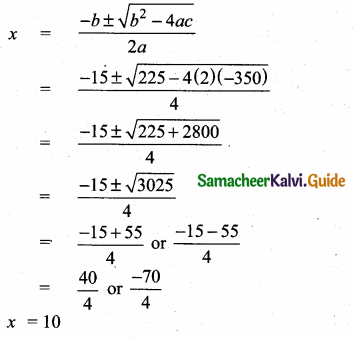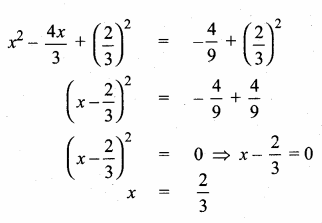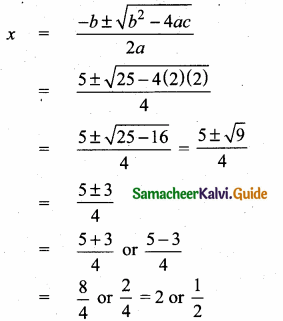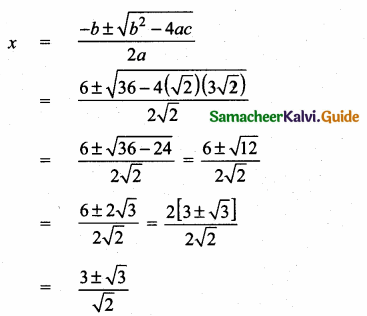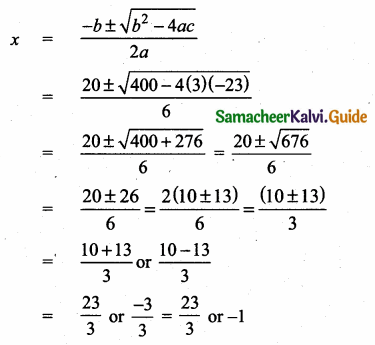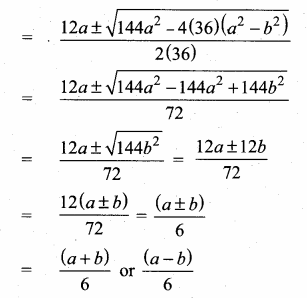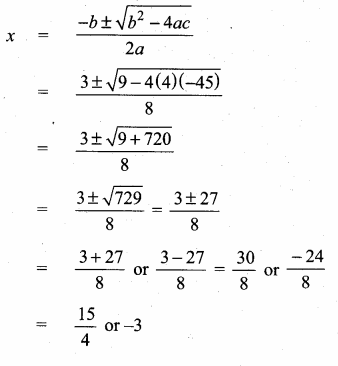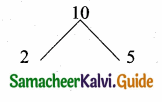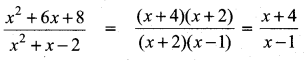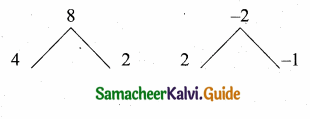Students can download Maths Chapter 4 Geometry Unit Exercise 4 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Geometry Unit Exercise 4
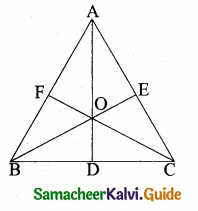
Question 1.
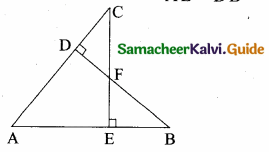
In the figure, if BD ⊥ AC and CE ⊥ AB , prove that
(i) ∆ AEC ~ ∆ADB
(ii) \(\frac { CA }{ AB } \) = \(\frac { CE }{ DB } \)
Solution:
(i) ∠AEC = ∠ADB = 90° ∠A is common By AA – Similarity.
∴ ∆AEC ~ ∆ADB
Since the two triangles are similar
(ii) \(\frac { AE }{ AD } \) = \(\frac { AC }{ AB } \) = \(\frac { EC }{ DB } \)
\(\frac { AC }{ AB } \) = \(\frac { CE }{ DB } \)
![]()
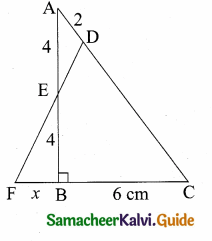
Question 2.
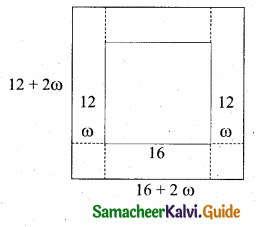
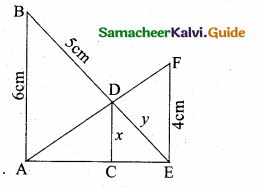
In the given figure AB || CD || EF. If AB = 6 cm, CD = x cm, EF = 4 cm, BD = 5 cm and DE = y cm. Find x and y.
Solution:
In the given diagram ∆AEF and ∆ACD
∠AEF = ∠ACD = 90°
∠A is common
By AA – Similarity.
∴ ∆AEF ~ ∆ACD
\(\frac { AE }{ AC } \) = \(\frac { AF }{ AD } \) = \(\frac { EF }{ CD } \)
\(\frac { AE }{ AC } \) = \(\frac { EF }{ CD } \)
\(\frac { AE }{ AC } \) = \(\frac { 4 }{ x } \)
AC = \(\frac{\mathrm{AE} \times x}{4}\) …..(1)
In ∆EAB and ∆ECD,
∠EAB = ∠ECD = 90°
∠E is common
∆ ECD ~ ∆EAB
\(\frac { EC }{ EA } \) = \(\frac { ED }{ EB } \) = \(\frac { CD }{ AB } \)
\(\frac { EC }{ EA } \) = \(\frac { x }{ 6 } \)
EC = \(\frac{\mathrm{EA} \times x}{6}\) …….(2)
In ∆AEB; CD || AB
By Basic Proportionality Theorem
\(\frac { AB }{ CD } \) = \(\frac { EB }{ ED } \)
\(\frac { 6 }{ x } \) = \(\frac { 5+y }{ y } \)
x = \(\frac { 6y }{ y+5 } \) (EC = x) …….(3)
Add (1) and (2) we get
AC + EC = \(\frac{A E \times x}{4}+\frac{x \times E A}{6}\)
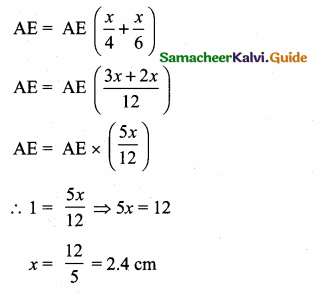 >
>
Substitute the value of x = 2.4 in (3)
2.4 = \(\frac { 6y }{ y+5 } \)
6y = 2.4y + 12
6y – 2.4y = 12 ⇒ 3.6 y = 12
y = \(\frac { 12 }{ 3.6 } \) = \(\frac { 120 }{ 36 } \) = \(\frac { 10 }{ 3 } \) = 3.3 cm
The value of x = \(\frac { 12 }{ 5 } \) (or) 2.4 cm and y = \(\frac { 10 }{ 3 } \) (or) 3.3 cm
![]()
Question 3.
O is any point inside a triangle ABC. The bisector of ∠AOB, ∠BOC and ∠COA meet the sides AB, BC and CA in point D, E and F respectively. Show that AD × BE × CF = DB × EC × FA.
Solution:
In ∆ABC the bisector meets AB at D, BC at E and AC at F.
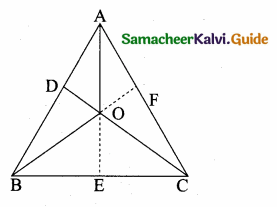
The angle bisector AO, BO and CO intersect at “O”.
By Cevas Theorem
\(\frac { AD }{ DB } \) × \(\frac { BE }{ EC } \) × \(\frac { CF }{ AF } \) = 1
AD × BE × CF = DB × EC × AF
Hence it is proved
![]()
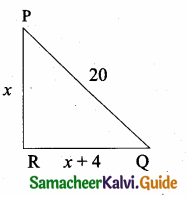
Question 4.
In the figure, ABC is a triangle in which AB = AC. Points D and E are points on the side AB and AC respectively such that AD = AE. Show that the points B, C, E and D lie on a same circle.
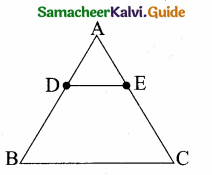
Solution:
∠B = ∠C (Given AB = AC)
AD + DB = AE + EC
BD = EC (Given AD = AE)
DE parallel BC Since AEC is a straight line.
∠AED + ∠CED = 180°
∠CBD + ∠CED = 180°
Similarly of the opposite angles = 180°
∴ BCED is a cyclic quadrilateral
![]()
Question 5.
Two trains leave a railway station at the same time. The first train travels due west and the second train due north. The first train travels at a speed of 20 km/hr and the second train travels at 30 km/hr. After 2 hours, what is the distance between them?
Solution:
A is the position of the 1st train.
B is the position of the 2nd train.
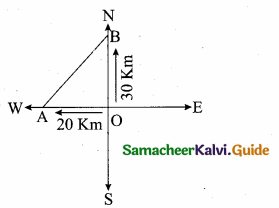
Distance Covered in 2 hours
OA = 2 × 20 = 40 km
OB = 2 × 30 = 60 km
Distance between the train after 2 hours
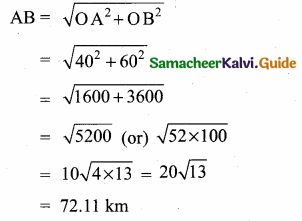
Distance between
the two train = 72.11 km (or) 20\(\sqrt { 13 }\) km
![]()
Question 6.
D is the mid point of side BC and AE ⊥ BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, ED = x, AD = p and AE = h, prove that
(i) b2 = p2 + ax + \(\frac{a^{2}}{4}\)
(ii) c2 = p2 – ax + \(\frac{a^{2}}{4}\)
(iii) a2 + c2 = 2 p2 + \(\frac{a^{2}}{2}\)
Solution:
(i) Given ∠AED = 90°
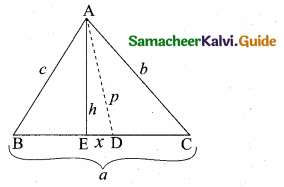
ED = x; DC = \(\frac { a }{ 2 } \)
(D is the mid point of BC)
∴ EC = x + \(\frac { a }{ 2 } \), BE = \(\frac { a }{ 2 } \) – x
∴ In the right ∆ AED
AD2 = AE2 + ED2
p2 = h2 + x2
In the right ∆ AEC,
AC2 = AE2 + EC2
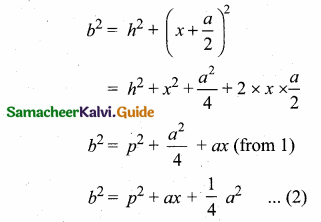
(ii) In the right triangle ABE,
AB2 = AE2 + BE2
c2 = h2 + (\(\frac { a }{ 2 } \) – x)2
c2 = h2 + \(\frac{a^{2}}{4}\) + x2 – ax
c2 = h2 + x2 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) a2 – ax
c2 = p2 – ax + \(\frac{a^{2}}{4}\) (from 1)
(iii) By adding (2) and (3)
b2 + c2 = p2 + ax + \(\frac{a^{2}}{4}\) + p2 – ax + \(\frac{a^{2}}{4}\)
= 2p2 + \(\frac{2a^{2}}{4}\)
= 2p2 + \(\frac{a^{2}}{2}\)
![]()
Question 7.
A man whose eye-level is 2 m above the ground wishes to find the height of a tree. He places a mirror horizontally on the ground 20 m from the tree and finds that if he stands at a point C which is 4 m from the mirror B, he can see the reflection of the top of the tree. How height is the tree?
Solution:
Let the height of the tree AD be “h”.
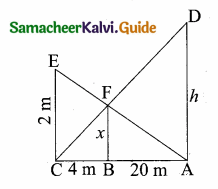
In ∆ ACD and ∆ BCF,
∠A = ∠B = 90°
∠C is common
∆ ACD ~ ∆ BCF by AA similarity
\(\frac { AD }{ BF } \) = \(\frac { AC }{ BC } \)
\(\frac { h }{ x } \) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 2 } \) = 6
h = 6x ………(1)
In ∆ ACE and ∆ ABF,
∠C = ∠B = 90°
∠A is common
∴ ∆ ACE ~ ∆ ABF
\(\frac { CE }{ BF } \) = \(\frac { AC }{ AB } \)
\(\frac { 2 }{ x } \) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 20 } \)
24x = 20 × 2
x = \(\frac{20 \times 2}{24}=\frac{5 \times 2}{6}=\frac{10}{6}\)
x = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \)
Substitute the value of x in (1)
h = 6 × \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \) = 10 m
∴ Height of the tree is 10 m
![]()
Question 8.
An emu which is 8 ft tail is standing at the foot of a pillar which is 30 ft high. It walks away from the pillar. The shadow of the emu falls beyond emu. What is the relation between the length of the shadow and the distance from the emu to the pillar?
Solution:
Let the shadow of the emu AE be “x” and BE be “y” ED || BC
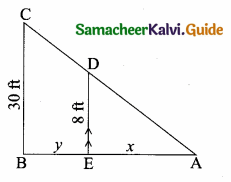
By basic proportionality theorem
\(\frac { AE }{ AB } \) = \(\frac { ED }{ BC } \)
\(\frac { x }{ x+y } \) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 30 } \)
30x = 8x + 8y
22x – 8y = 0
(÷ by 2) 11x – 4y = 0
11x = 4y
x = \(\frac { 4 }{ 11 } \) × y
x = \(\frac { 4 }{ 11 } \) × distance from the pillar to emu
Length of = \(\frac { 4 }{ 11 } \) × distance from the shadow the pillar to emu
![]()
Question 9.
Two circles intersect at A and B. From a point P on one of the circles lines PAC and PBD are drawn intersecting the second circle at C and D. Prove that CD is parallel to the tangent at P.
Solution:
Proof:
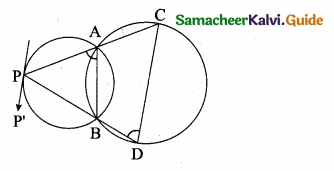
A and B are the points intersecting the circles. Join AB.
∠P’PB = ∠PAB (alternate segment theorem)
∠PAB + ∠BAC = 180° …(1)
(PAC is a straight line)
∠BAC + ∠BDC = 180° …(2)
ABDC is a cyclic quadrilateral.
From (1) and (2) we get
∠P’PB = ∠PAB = ∠BDC
P’P and DC are straight lines.
PD is a transversal alternate angles are equal.
∴ P’P || DC.
![]()
Question 10.
Let ABC be a triangle and D, E, F are points on the respective sides AB, BC, AC (or their extensions).
Let AD : DB = 5 : 3, BE : EC = 3 : 2 and AC = 21. Find the length of the line segment CF.
Solution:
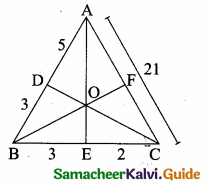
\(\frac { AD }{ DB } \) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \); \(\frac { BE }{ EC } \) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \); AC = 21
By Ceva’s theorem
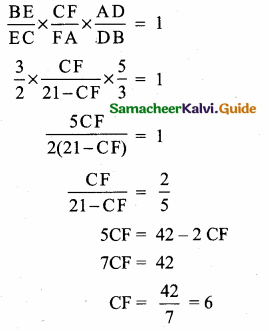
Length of the line segment CF = 6 units
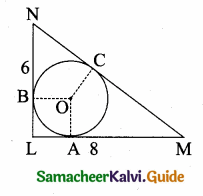
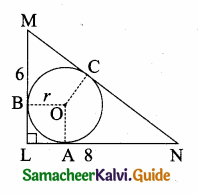
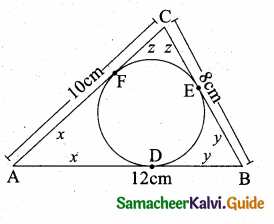
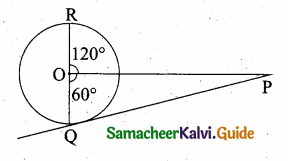
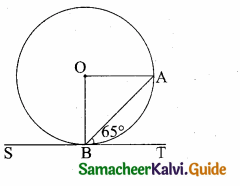
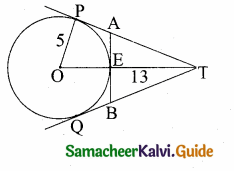
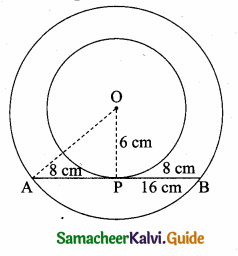
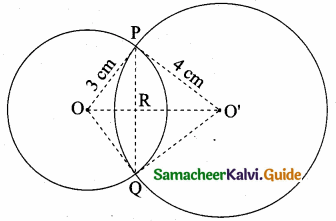
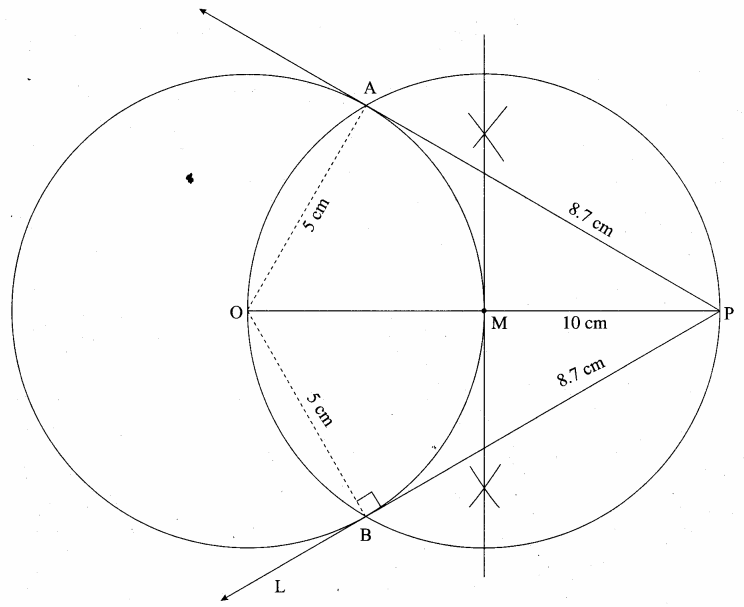
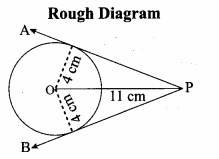
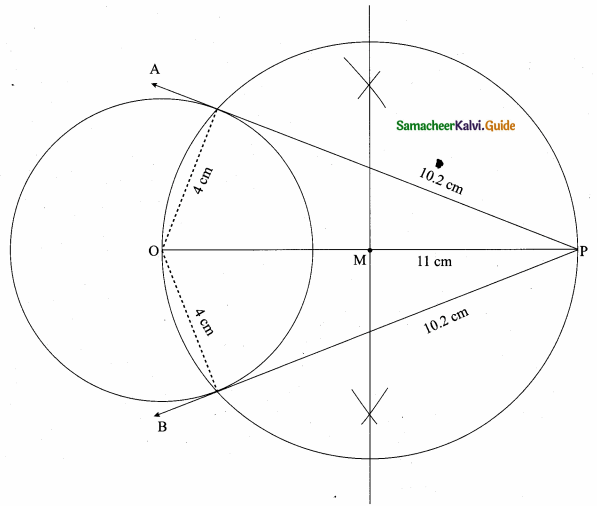
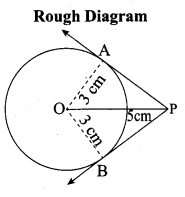
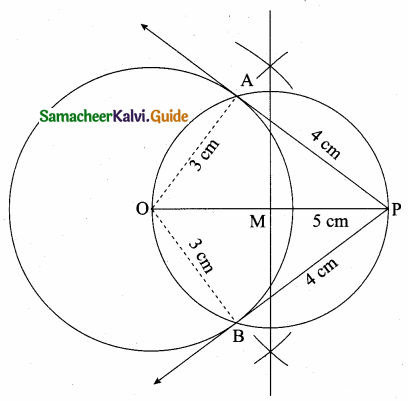
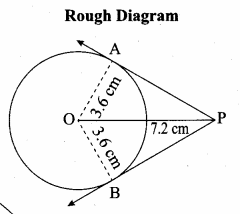
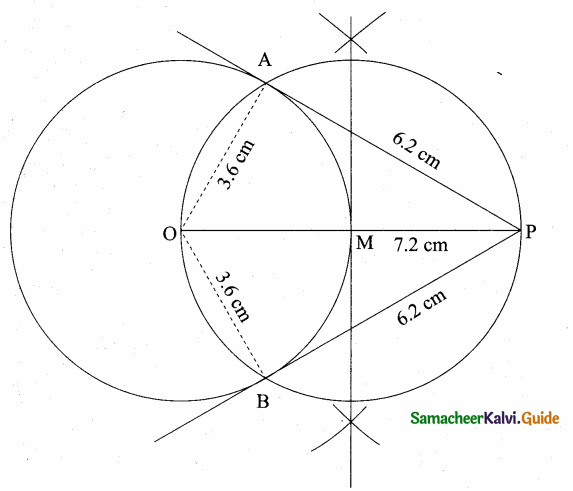
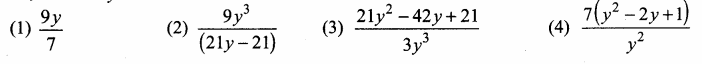
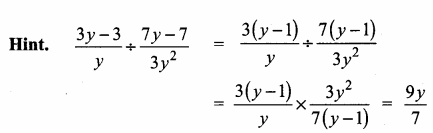
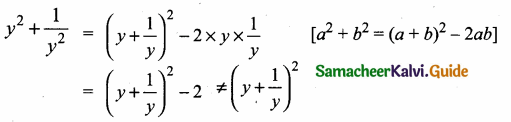

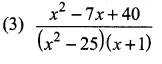
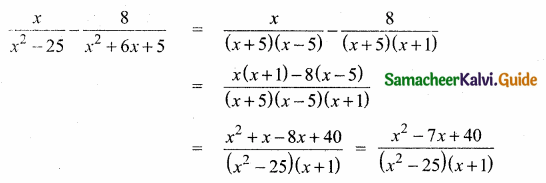


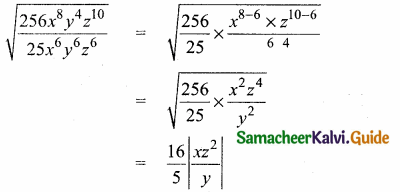
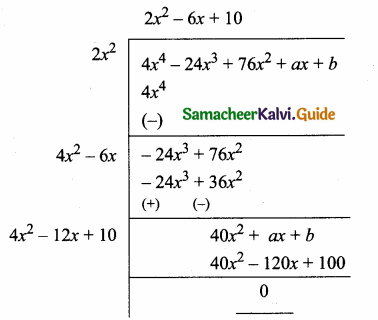
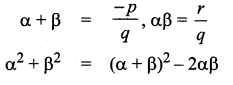
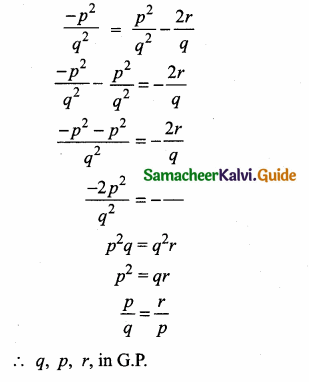
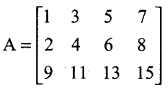
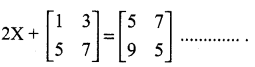


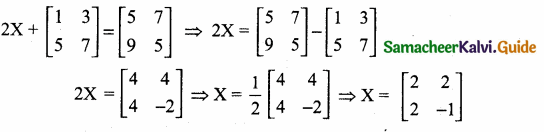
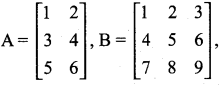
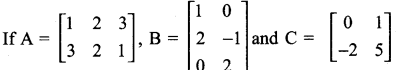
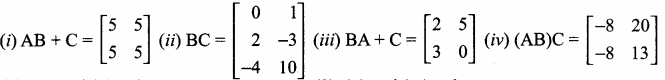
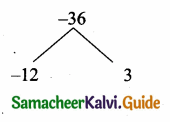
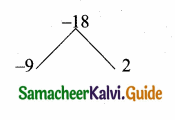
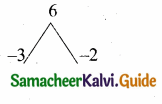
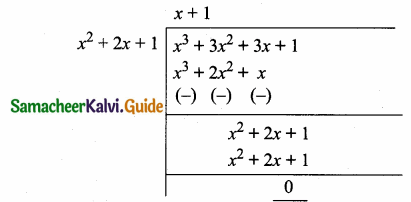
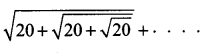 is ……….
is ……….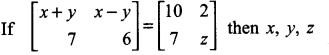
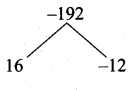
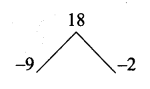
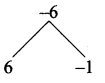
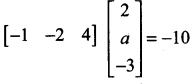 then the value of “a” is ………….
then the value of “a” is ………….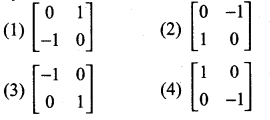

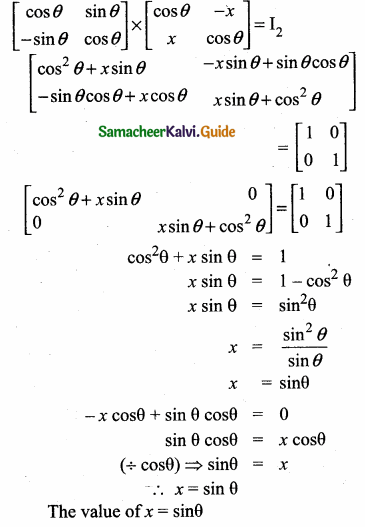
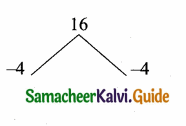
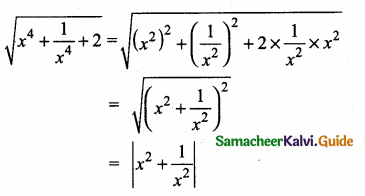
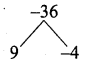
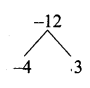
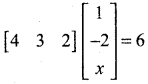 then “x” is ……………..
then “x” is ……………..
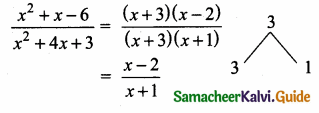
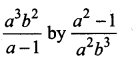
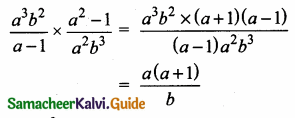
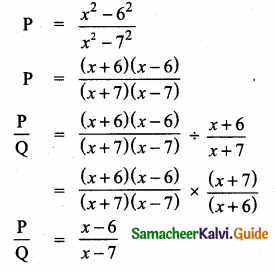
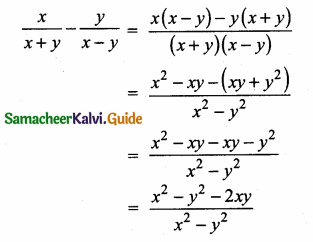
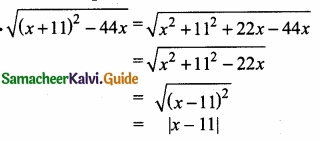
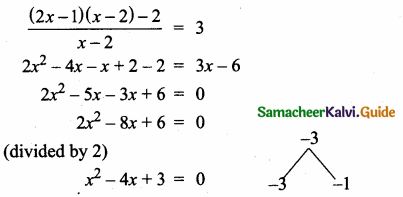
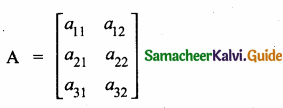
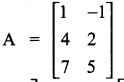
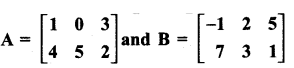
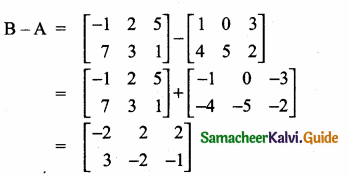
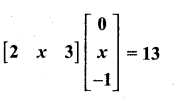
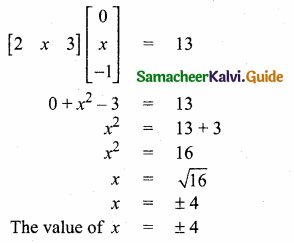
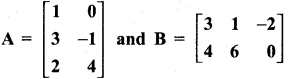
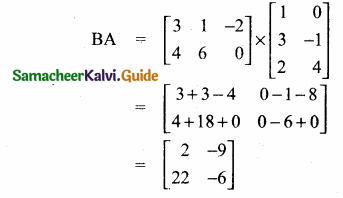

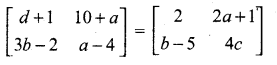
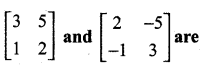
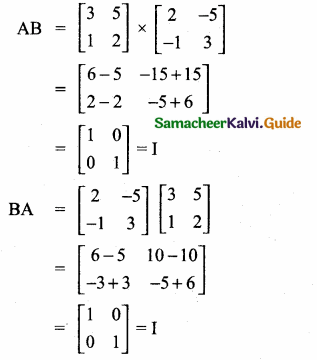
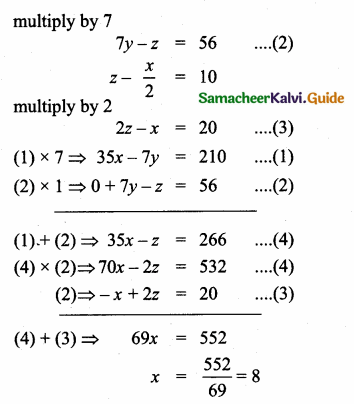
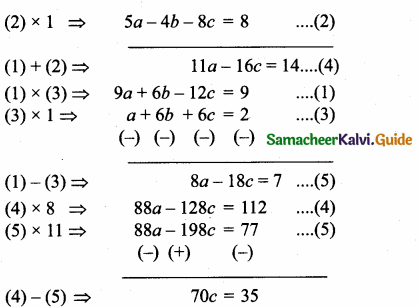
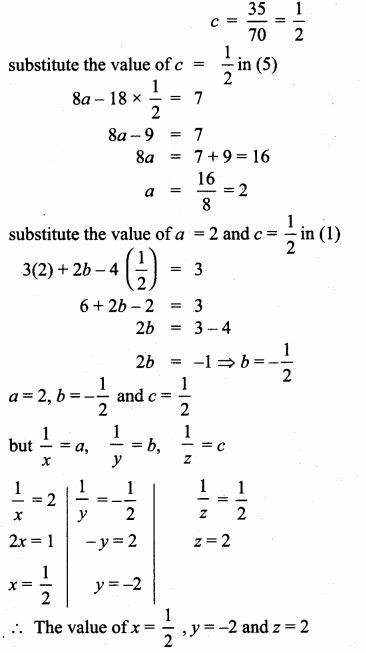
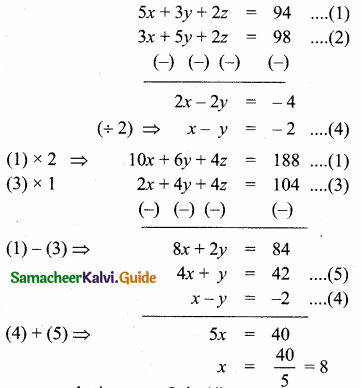
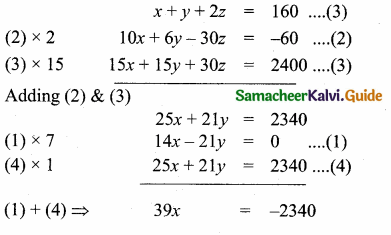
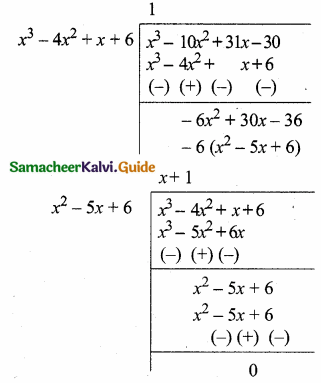
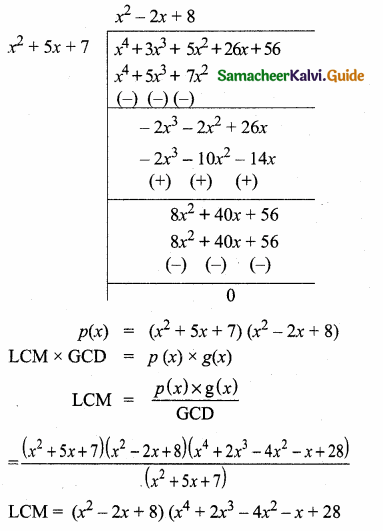
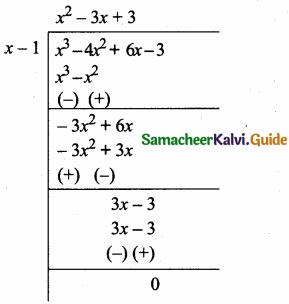
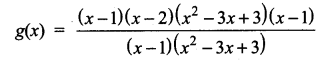
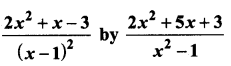
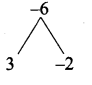
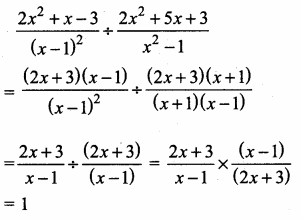
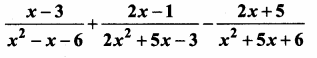
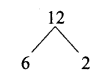
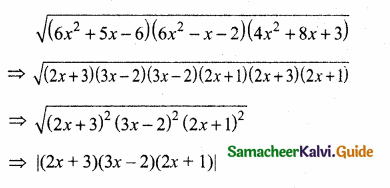
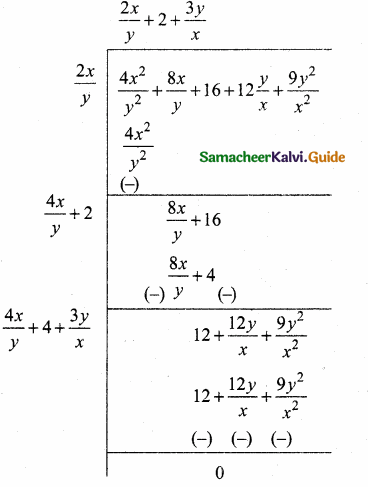
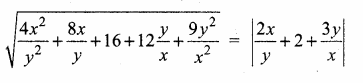

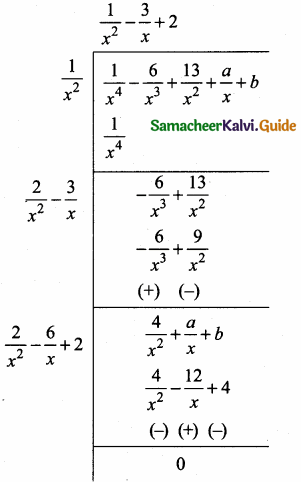
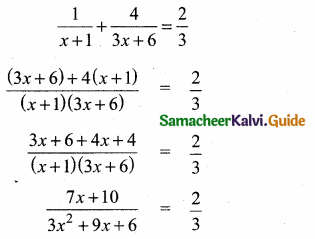
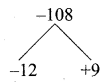
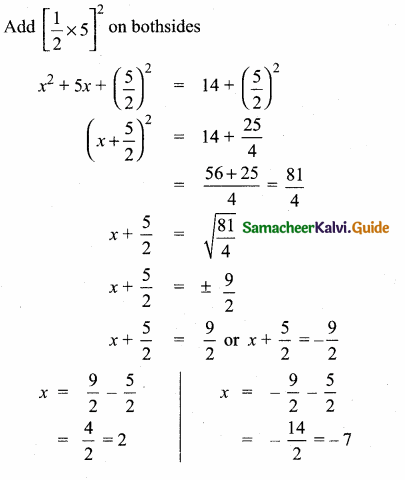
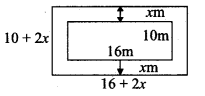
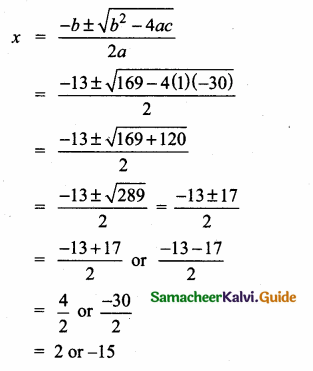
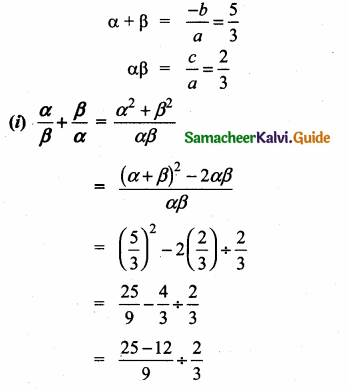
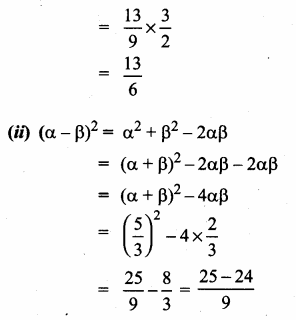
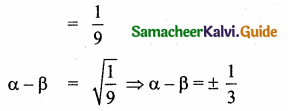
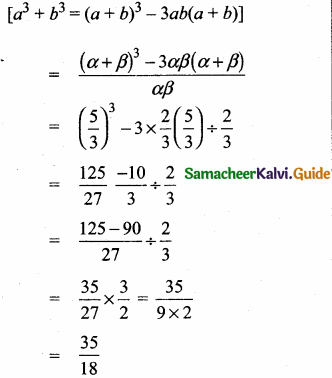
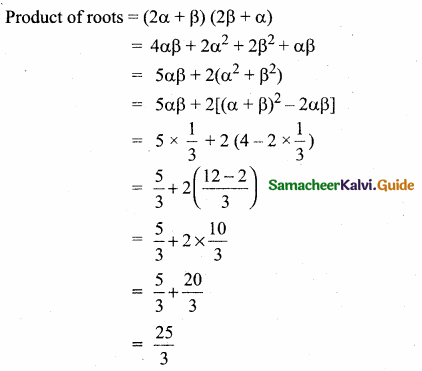
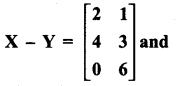
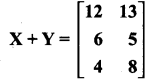
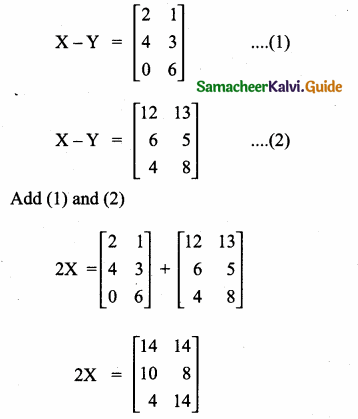
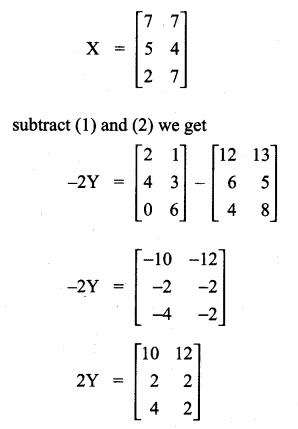
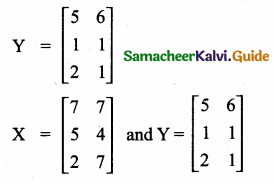
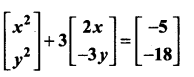
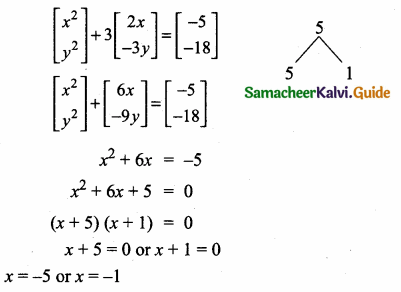
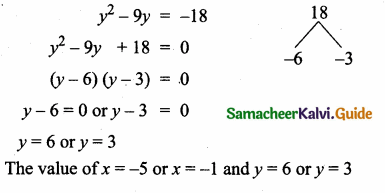
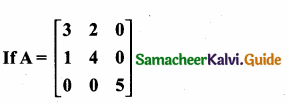
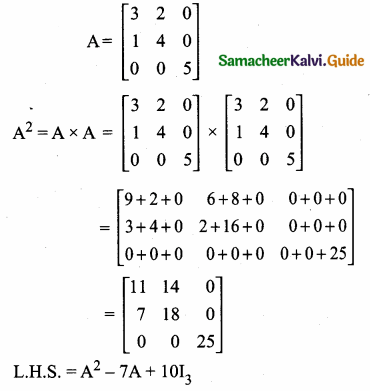
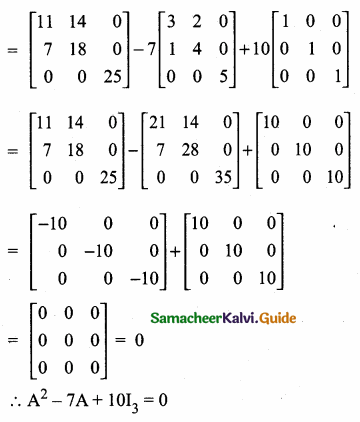
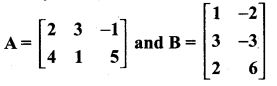
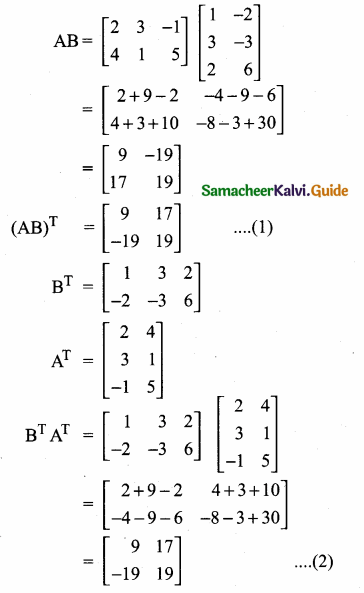
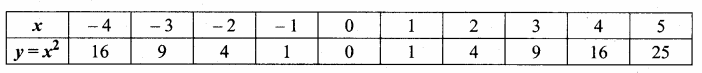
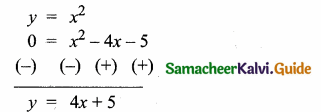
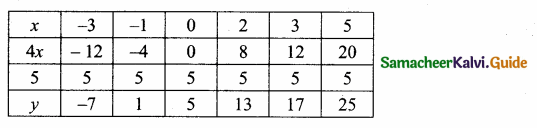
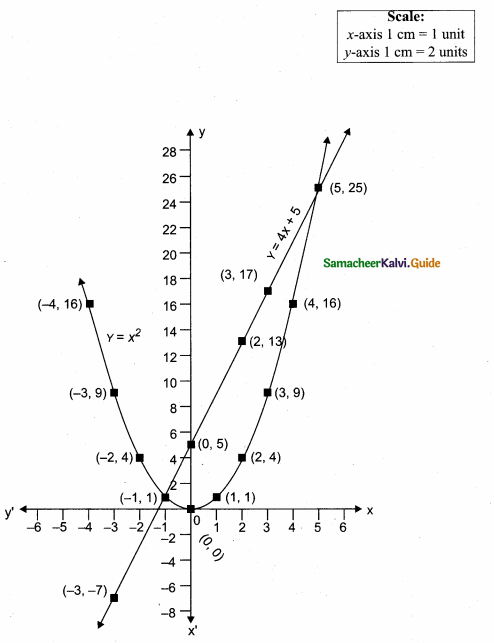
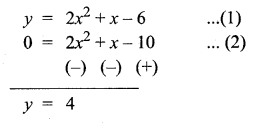
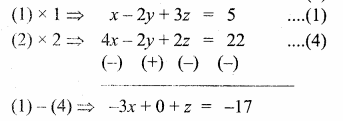
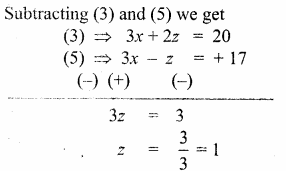
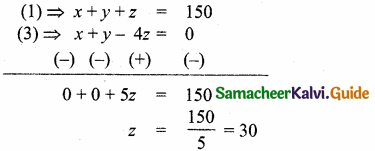
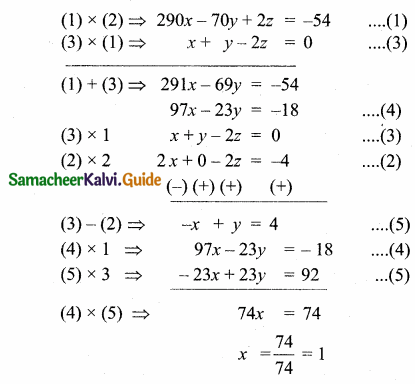
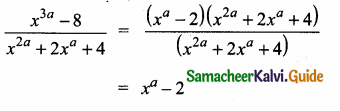
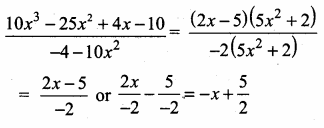
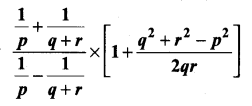
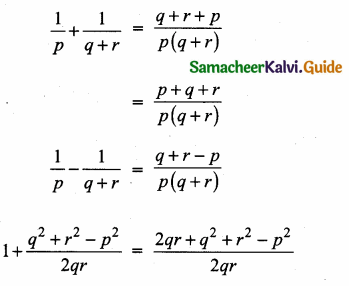
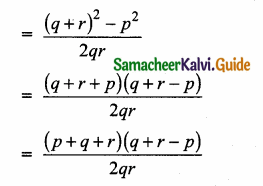
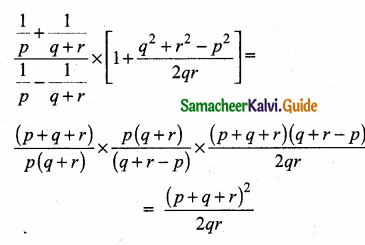
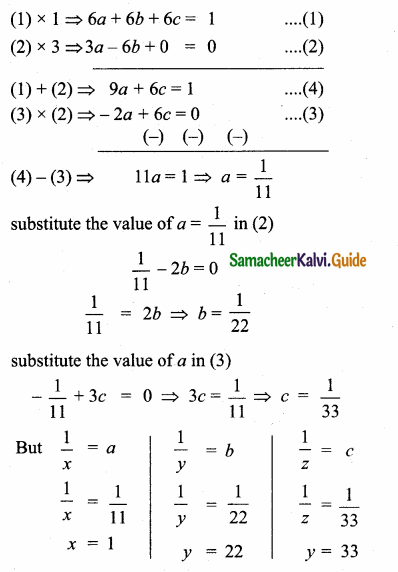
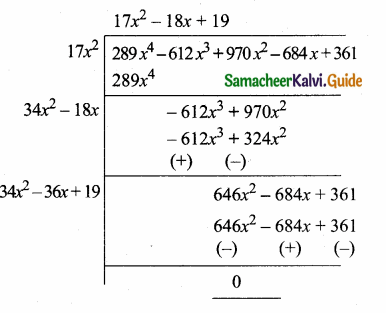
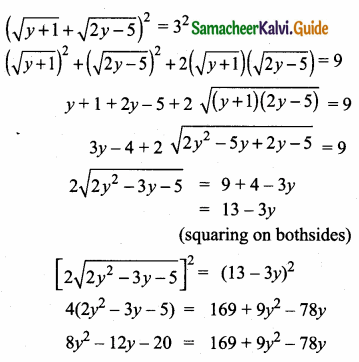
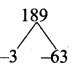
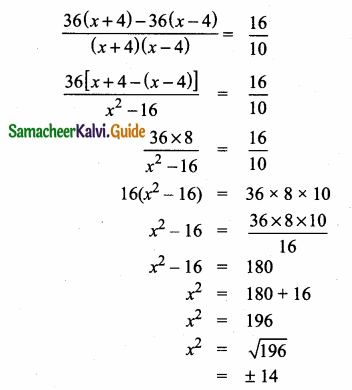
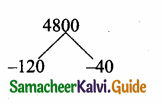
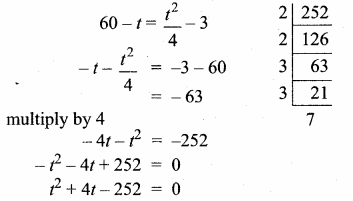
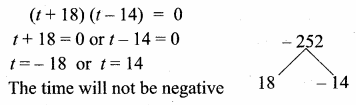
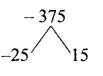
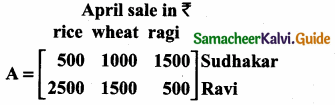
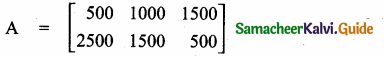

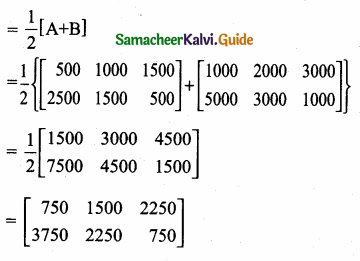
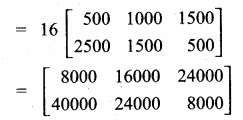
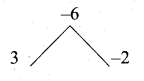
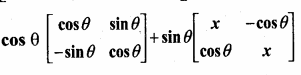 = I2, find x.
= I2, find x.