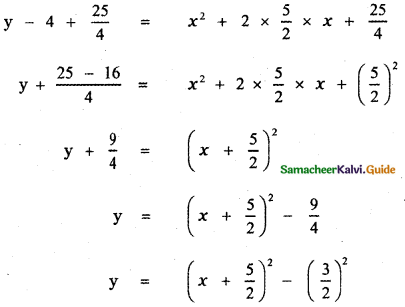Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Basic Algebra Ex 2.4 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Basic Algebra Ex 2.4
Question 1.
Construct a quadratic equation with roots 7 and – 3.
Answer:
The given roots are 7 and -3
Let α = 7 and β = -3
α + β = 7 – 3 = 4
αβ = (7)(-3) = -21
The quadratic equation with roots α and β is x2 – (α + β) x + αβ = 0
So the required quadratic equation is
x2 – (4) x + (-21) = 0
(i.e.,) x2 – 4x – 21 = 0
![]()
Question 2.
A quadratic polynomial has one of its zero 1 + √5 and it satisfies p(1) = 2. Find the quadratic polynomial.
Answer:
Let p(x) = ax2 + bx + c be the required quadratic polynomial.
Given p (1) = 2 , we have
a × 12 + b × 1 + c = 2
a + b + c = 2 ——— (1)
Also given 1 + √5 is a zero of p(x)
∴ a(1 + √5)2 + b (1 + √5) + c = 0
a( 1 + 5 + 2√5) + b (1 + √5) + c = 0
6a + 2a√5 + b + b√5 + c = 0 ——— (2)
If 1 + √5 is zero then 1 – √5 is also a zero of p (x).
∴ a(1 – √5)2 + b (1 – √5) + c = 0
a( 1 – 2√5 + 5) + b (1 – √5) + c = 0
6a – 2a√5 + b – b√5 + c = 0 ——— (3)
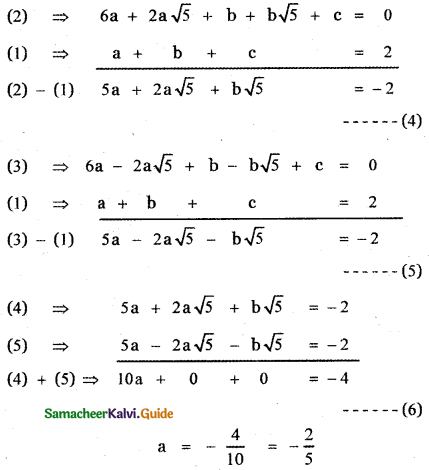
Substituting the value of a in equation (4)
5 × – \(\frac{2}{5}\) + 2 × – \(\frac{2}{5}\) × √5 + b√5 = – 2
– 2 – \(\frac{4}{5}\)√5 + b√5 = – 2
b√5 = – 2 + 2 + \(\frac{4}{5}\) . √5
b√5 = \(\frac{4}{5}\) . √5
b = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Substituting the value of a and b in equation (1), we have
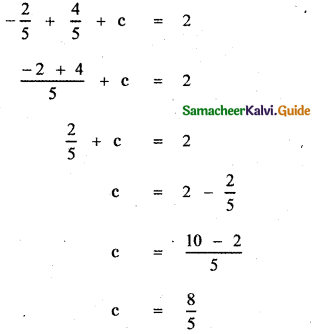
∴ The required quadratic polynomial is
p(x) = \(-\frac{2}{5}\)x2 + \(\frac{4}{5}\)x + \(\frac{8}{5}\)
p(x) = \(-\frac{2}{5}\)(x2 – 2x – 4)
![]()
Question 3.
If α and β are the roots of the quadratic equation x2 + √2x + 3 = 0 form a quadratic polynomial with zeros \(\frac{1}{\alpha}, \frac{1}{\beta}\).
Answer:
Given α and β are the roots of the quadratic polynomial
x2 + √2x + 3 = 0 ——— (1)
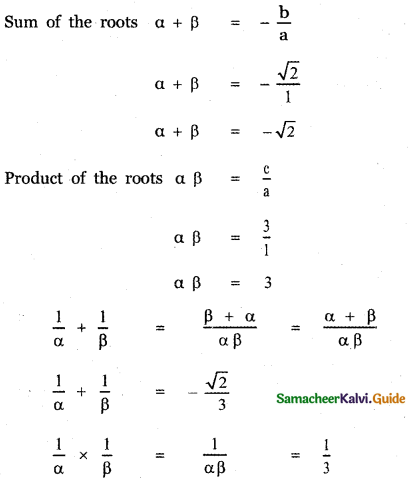
∴ The required quadratic equation whose roots are \(\frac{1}{\alpha}, \frac{1}{\beta}\) is
x2 – (sum of the roots)x + product of the roots = 0
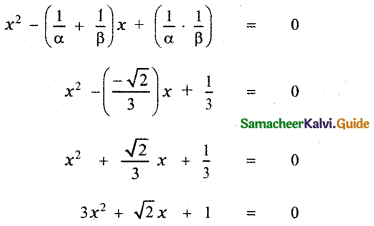
![]()
Question 4.
If one root of k (x – 1)2 = 5x – 7 is double the other root, show that k = 2 or – 25
Answer:
The given quadratic equation is
k(x – 1)2 = 5x – 7
k(x2 – 2x + 1) – 5x + 7 = 0
kx2 – 2kx + k – 5x + 7 = 0
kx2 – (2k + 5)x + k + 7 = 0 ———- (1)
Let the roots be α and 2α
Sum of the roots α + 2α = –\(\frac{b}{a}\)
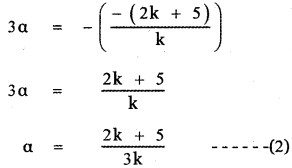
Product of te roots α(2α) = \(\frac{c}{a}\)
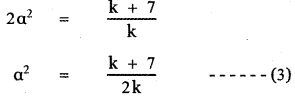
Using equation (2) and (3) we have
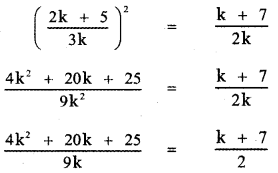
2(4k2 + 20k + 25) = 9k(k + 7)
8k2 + 40k + 50 = 9k2 + 63k
9k2 + 63k – 8k2 – 40k – 50 = 0
k2 + 23k – 50 = 0
k2 + 25k – 2k – 50 = 0
k(k + 25) – 2(k + 25) = 0
(k – 2) (k + 25) = 0
k – 2 = 0 or k + 25 = 0
k = 2 or k = – 25
![]()
Question 5.
If the difference of the roots of the equation 2x2 – (a + 1)x + a – 1 = 0 is equal to their product then prove that a = 2.
Answer:
The given quadratic equation is
2x2 – (a + 1) x + a – 1 = 0 ———– (1)
Let α and β be the roots of the given equation
Given that α – β = αβ —— (2)
Sum of the roots α + β = – \(\frac{b}{a}\)
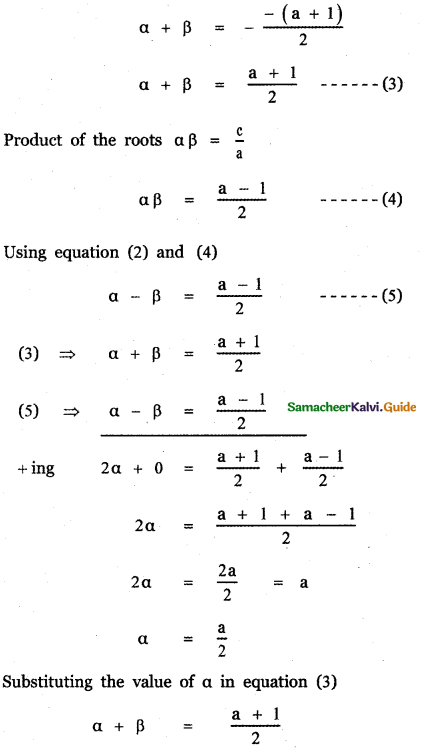
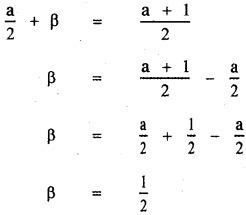
Substituting the values of α and β in equation (2)
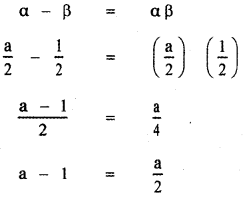
2(a – 1) = a
2a – 2 – a = 0
a – 2 = 0
⇒ a = 2
![]()
Question 6.
Find the condition that one of the roots of ax2 + bx + c may be
(a) negative of the other
(b) thrice the other
(c) reciprocal of the other.
Answer:
The given quadratic equation is
ax2 + bx + c = 0 ——- (1)
Let α and β be the roots of the equation (1) then
Sum of the roots α + β = ——- (2)
Product of the roots αβ = ——- (3)
(a) Given one root is the negative of the other
β = – α
(2) ⇒ α + (-α) = – \(\frac{b}{a}\)
0 = – \(\frac{b}{a}\)
⇒ b = 0
(3) ⇒ α(-α) = \(\frac{c}{a}\)
– α2 = \(\frac{c}{a}\)
Hence the required condition is b = 0
(b) Given that one root is thrice the other
β = 3α
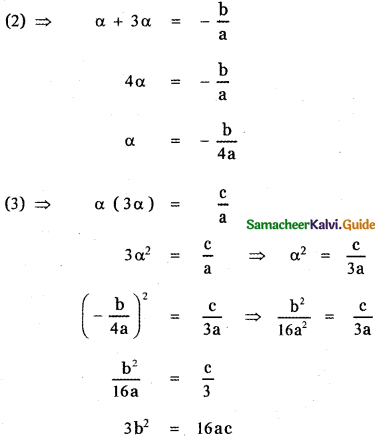
When is the required condition?
(c) One root is reciprocal of the other
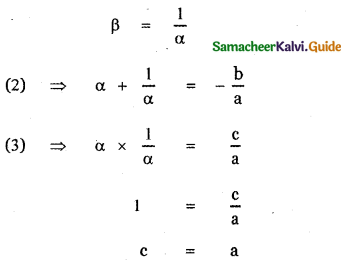
When is the required condition?
![]()
Question 7.
If the equations x2 – ax + b = 0 and x2 – ex + f = 0 have one root in common and if the second equation has equal roots then prove that ae = 2(b + f).
Answer:
The given quadratic equations are
x2 – ax + b = 0 ———- (1)
x2 – ex + f = 0 ——— (2)
Let α be the common root of the given quadratic equations (1) and (2)
Let α, β be the roots of x2 – ax + b = 0
Sum of the roots α + β = \(-\left(-\frac{a}{1}\right)\)
α + β = a ———- (3)
Product of the roots αβ = \(\frac{b}{1}\)
αβ = b ——– (4)
Given that the second equation has equal roots.
∴ The roots of the second equation are a, a
Sum of the roots α + α = \(-\left(-\frac{e}{1}\right)\)
2α = e ——— (5)
Product of the roots α.α = \(\frac{f}{1}\)
α2 = f ———- (6)
ae = (α + β)2α (Multiplying equations (3) and (5))
ae = 2α2 + 2αβ
ae= 2 (f) + 2b From equations (4) and (6)
ae= 2(f + b) Hence proved.
![]()
Question 8.
Discuss the nature of roots of
(i) – x2 + 3x + 1 = 0
(ii) 4x2 – x – 2 = 0
(iii) 9x2 + 5x = 0.
Answer:
(i) -x2 + 3x + 1 = 0
⇒ comparing with ax2 + bx + c = 0
∆ = b2 – 4ac = (3)2 – 4(1)(-1) = 9 + 4 = 13 > 0
⇒ The roots are real and distinct
(ii) 4x2 – x – 2 = 0
a = 4, b = -1, c = -2
∆ = b2 – 4ac = (-1)2 – 4(4)(-2) = 1 + 32 = 33 >0
⇒ The roots are real and distinct
(iii) 9x2 + 5x = 0
a = 9, b = 5, c = 0
∆ = b2 – 4ac = 52 – 4(9)(0) = 25 > 0
⇒ The roots are real and distinct
![]()
Question 9.
Without sketching the graphs, find whether the graphs of the following functions will intersect the x-axis and if so in how many points.
(i) y = x2 + x + 2
(ii) y = x2 – 3x – 7
(iii) y = x2 + 6x + 9
Answer:
(i) y = x2 + x + 2
y = x2 + x + 2 ——— (1)
Compare this equation with the equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0
we have a = 1 , b = 1, c = 2
b2 – 4ac = 12 – 4 × 1 × 2 = 1 – 8
b2 – 4ac = – 7 < 0
Since the discriminant is negative the quadratic equation has no real roots and therfore the graph does not meet x-axis.
(ii) y = x2 – 3x – 7
y = x2 – 3x – 7 ——— (2)
Compare this equation with the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
we have a = 1 , b = – 3 , c = – 1
b2 – 4ac = (-3)2 – 4(1)(-1)
= 9 + 4
b2 – 4ac = 13 > 0
Since the discriminant is positive the quadratic equation has real and distinct roots and therefore the graph intersect the x – axis at two different points,
(iii) y = x2 + 6x + 9
y = x2 + 6x + 9 ——— (3)
Compare this equation with the equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0
we have a = 1 , b = 6, c = 9
b2 – 4ac = 62 – 4 × 1 × 9
= 36 – 36 =0
Since the discriminant is zero the quadratic equation has real and equal roots and therefore the graph touches the x-axis at one point.
![]()
Question 10.
Write f(x) = x2 + 5x + 4 in completed square form.
Answer:
The given quadratic equation is
f(x) = x2 + 5x + 4
Let y = x2 + 5x + 4
y – 4 = x2 + 5x