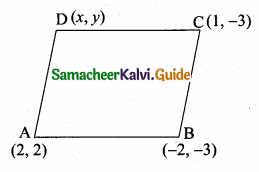
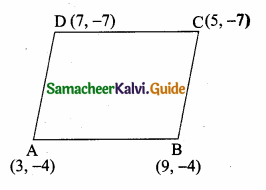
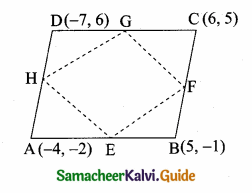
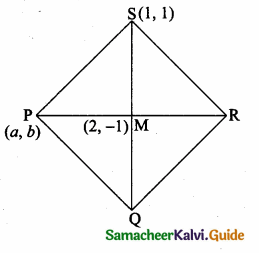
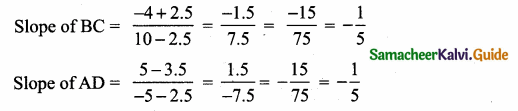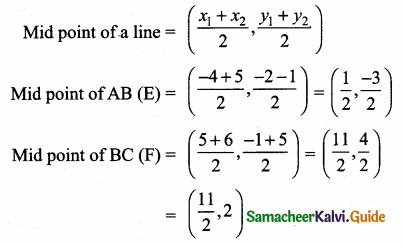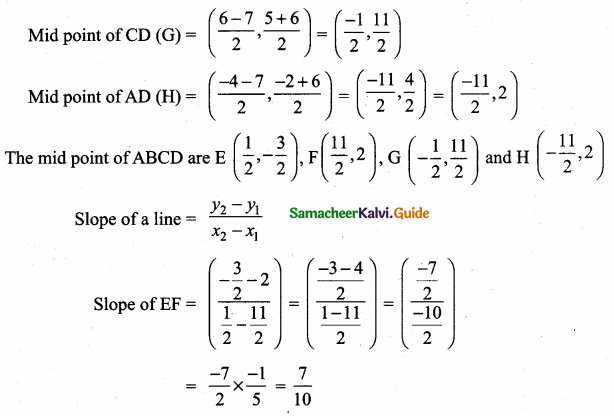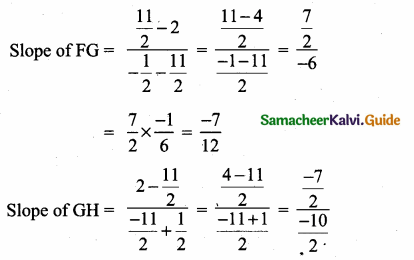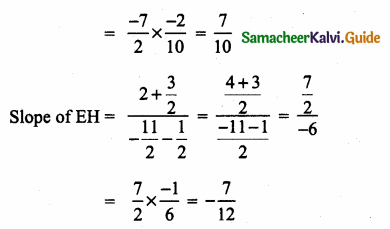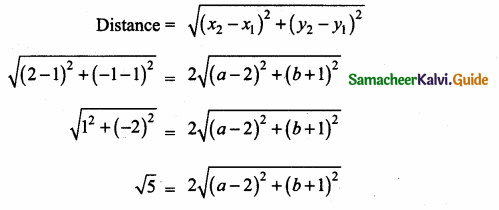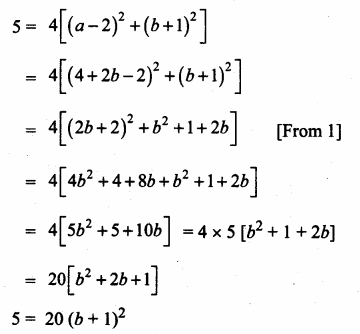Students can download Maths Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.4 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Maths Solutions Term 1 Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.4
Miscellaneous Practise Problems
Question 1.
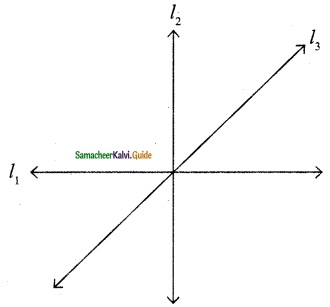
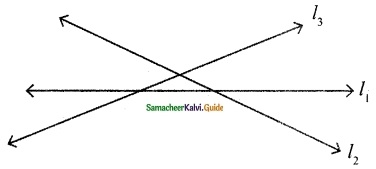
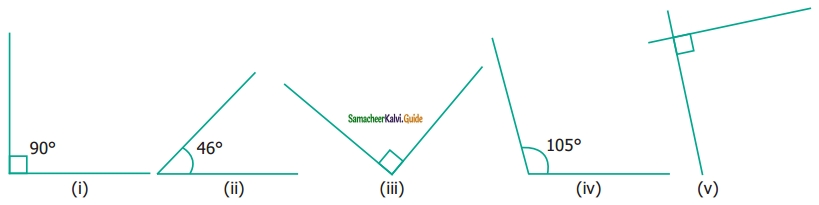
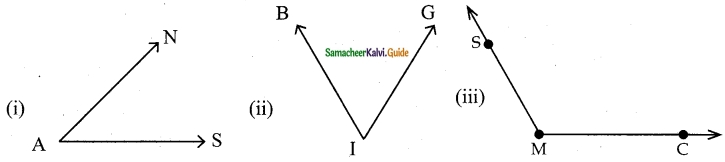
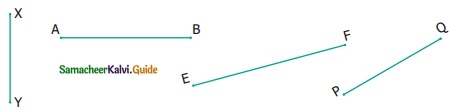
Find the type of lines marked in thick lines (Parallel, intersecting or perpendicular)
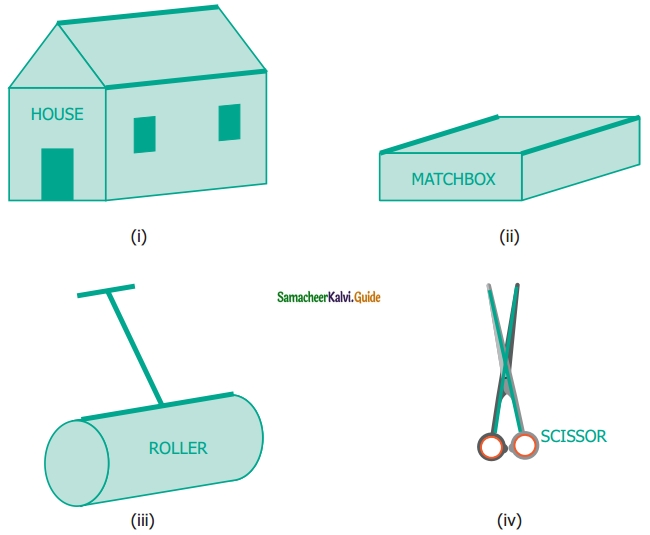
Solution:
(i) Parallel lines
(ii) Parallel lines
(iii) Parallel and Perpendicular lines
(iv) Intersecting lines
![]()
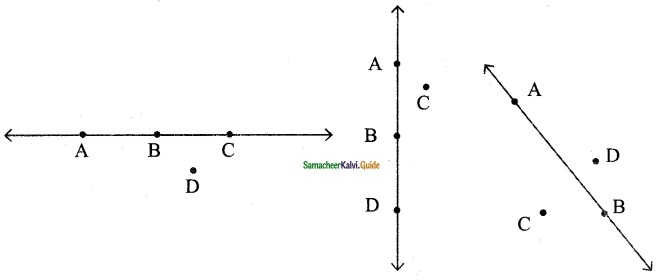
Question 2.
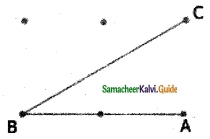
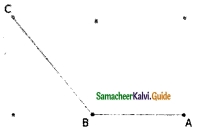
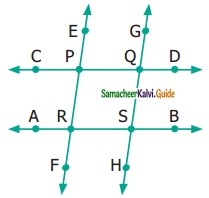
Find the parallel and intersecting line segments in the picture given below.
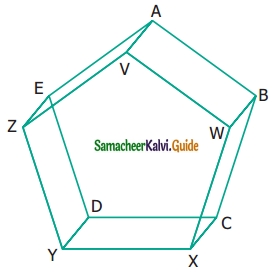
Solution:
(a) Parallel line segments
- \(\overline{\mathrm{YZ}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{DE}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{EA}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{ZV}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{VW}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{WX}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{BC}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{YX}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{DC}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{YD}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{XC}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{XC}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{WB}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{WB}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{VA}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{VA}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{ZE}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{ZE}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{YD}}\)
(b) Intersecting line segments
- DE and ZV
- WX and DC
![]()
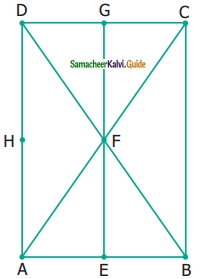
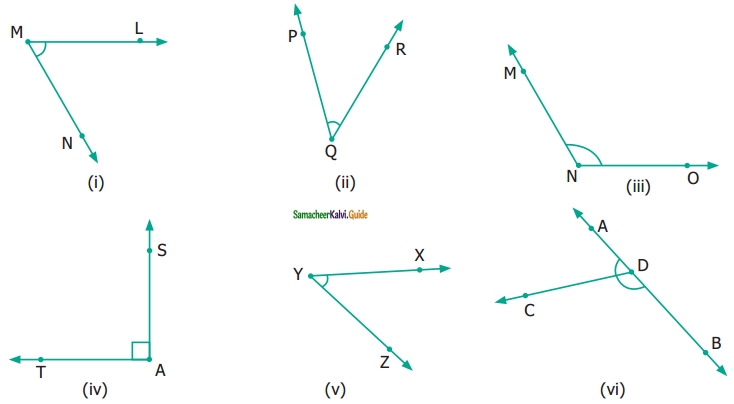
Question 3.
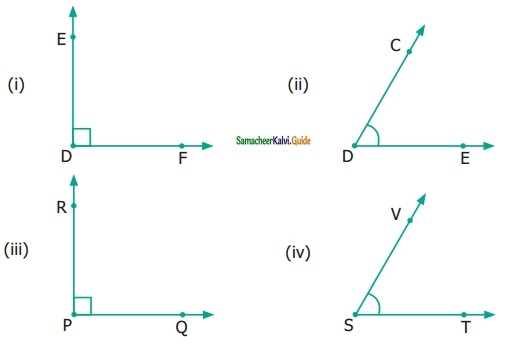
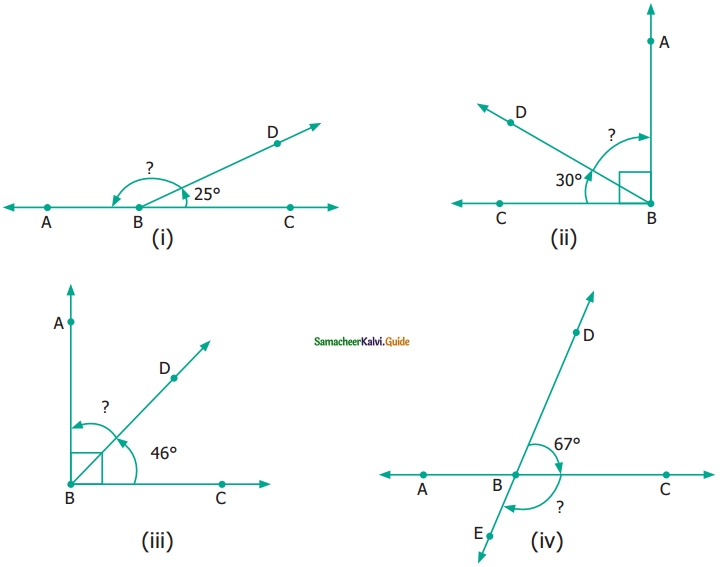
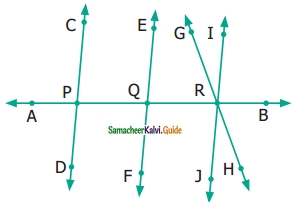
Name the following angles as shown in the figure.
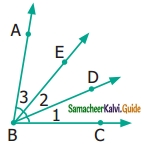
(i) ∠1 =
(ii) ∠2 =
(iii) ∠3 =
(iv) ∠1 + ∠2 =
(v) ∠2 + ∠3 =
(vi) ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 =
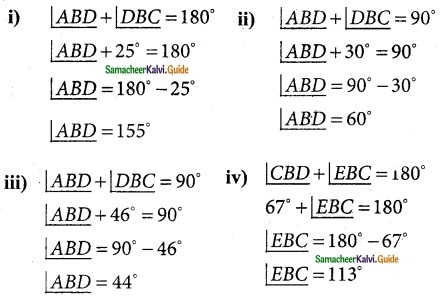
Solution:
(i) ∠1 = ∠DBC or ∠CBD
(ii) ∠2 = ∠DBE or ∠EBD
(iii) ∠3 = ∠ABE or ∠EBA
(iv) ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠EBC or ∠CBE
(v) ∠2 + ∠3 = ∠ABD or ∠DHA
(vi) ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = ∠ABC or ∠B or ∠CBA
![]()
Question 4.
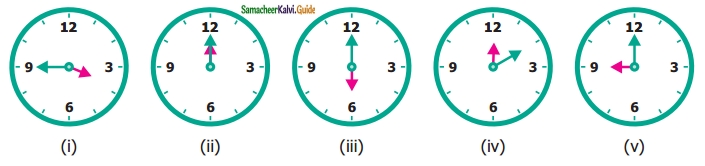
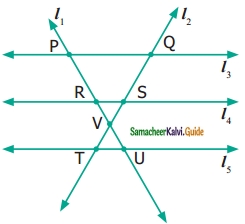
Measure the angles of the given figures using a protractor and identify the type of angle as acute, obtuse, right or straight.
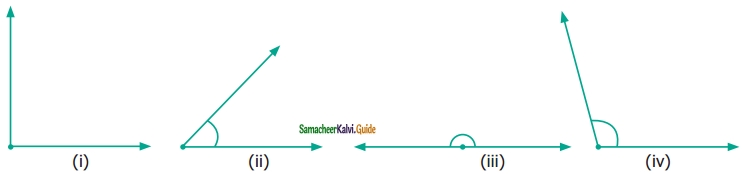
Solution:
(i) right angle
(ii) acute angle
(iii) straight angle
(iv) obtuse angle
![]()
Question 5.
Draw the following angles using the protractor.
(i) 45°
(ii) 120°
(iii) 65°
(iv) 135°
(v) 0°
(vi) 180°
(vii) 38°
(viii) 90°
Solution:
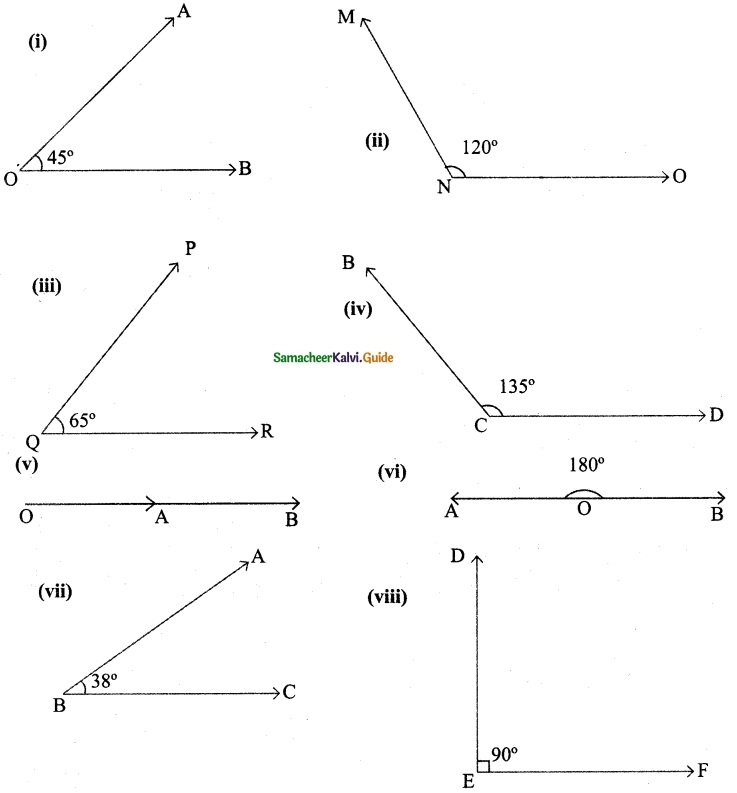
![]()
Question 6.
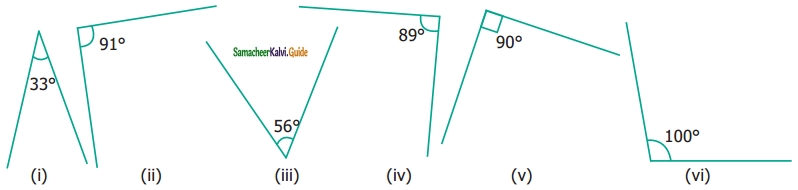
From the figures given below, classify the following pairs of angles into complementary and non-complementary.
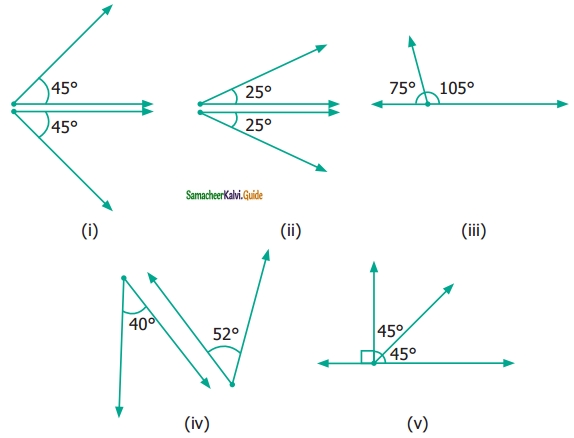
Solution:
We know that the two angles are complementary if they add up to 90°.
Therefore (a) (i) is complementary.
In (v) ∠ABC and ∠CBD are complementary
(b) (ii), (iii), (iv) and (v) are non-complementary
![]()
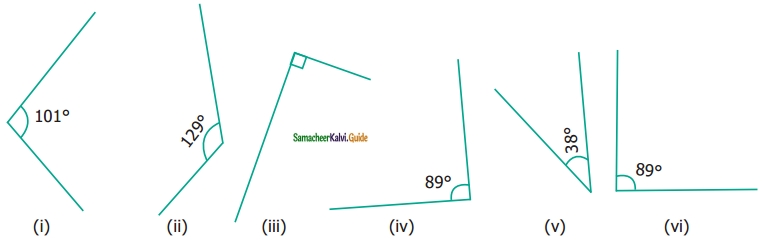
Question 7.
From the figures given below, classify the following pairs of angles into supplementary and non supplementary.
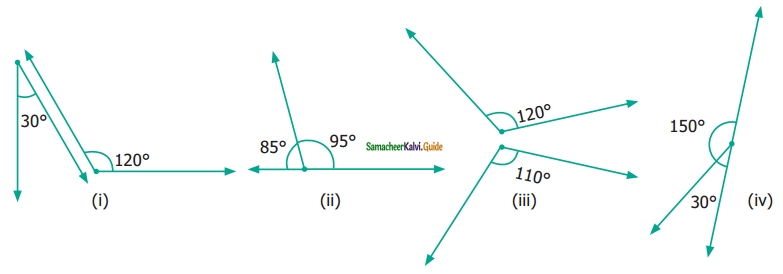
Solution:
Ans: (ii) and (iv) are supplementary angles.
(i), and (iii) non-supplementary angles.
Question 8.
From the figure
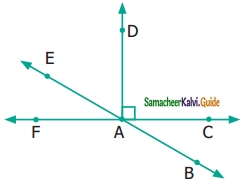
(i) name a pair of complementary angles.
(ii) name a pair of supplementary angles.
Solution:
(i) ∠FAE; ∠EAD
(ii) ∠FAD; ∠DAC
∠BAC; ∠CAE
∠FAB; ∠BAC
∠FAB; ∠FAE
![]()
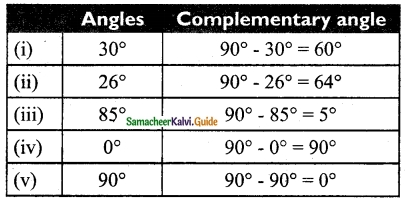
Question 9.
Find the complementary angle of
(i) 30°
(ii) 26°
(iii) 85°
(iv) 0°
(v) 90°
Solution:
Question 10.
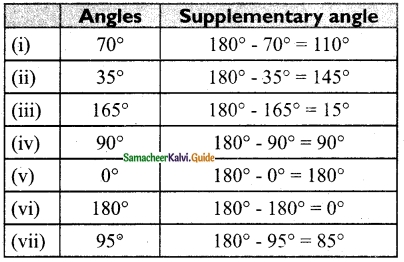
Find the supplementary angle of
(i) 70°
(ii) 35°
(iii) 165°
(iv) 90°
(v) 0°
(vi) 180°
(vii) 95°
Solution:
![]()
Challenging Problems
Question 11.
Think and write an object having
(i) Parallel lines (1) ……….. (2) ………. (3) ………..
(ii) Perpendicular lines (1) ……… (2) ……… (3) ………..
(iii) Intersecting lines (1) ……….. (2) ………. (3) ……….
Solution:
(i) Legs of the table, railway tracks, edges of the scale
(ii) Adjacent sides of a Board, Crossbars of windows, Adjacent sides of the textbook
(iii) Crossbars of windows, Ladder, blades of a scissor.
Question 12.
Which angle is equal to twice its complement.
Solution:
Let the angle be x
According to the problem, x = 2 × (90 – x)
x = 180 – 2x
x + 2x = 180
3x = 180
x = \(\frac{180}{3}\)
x = 60
∴ The angle is 60°
![]()
Question 13.
Which angle is equal to two-thirds of its supplement.
Solution:
Let the angle be x
According to the problem,
x = \(\frac{2}{3}\) × (180° – x)
3x = 2(180 – x)
3x = 360 – 2x
3x + 2x = 360°
5x = 360°
x = \(\frac{360°}{5}\)
x = 72°
∴ The angle is 72°
Question 14.
Given two angles are supplementary and one angle is 20° more than the other. Find the two angles.
Solution:
Let the angles be x and x + 20°
According to the problem,
x + x + 20 = 180°
2x + 20° = 180°
2x = 180° – 20°
2x = 160°
x = \(\frac{160°}{2}\)
x = 80°
x + 20 = 80° + 20°
= 100°
∴ The two angles are 80° and 100°
![]()
Question 15.
Two complementary angles are in ratio 7 : 2. Find the angles.
Solution:
Let the angles be 7x, 2x
According to the problem,
7x + 2x = 90
9x = 90
x = \(\frac{90}{9}\)
x = 10
7x = 7 × 10
= 70
2x = 2 × 10
= 20
∴ Two angles are 70° and 20°
Question 16.
Two supplementary angles are in ratio 5 : 4. Find the angles.
Solution:
Total of two supplementary angles = 180°
Given they are in the ratio 5 : 4
Dividing total angles to 5 + 4 = 9 equal parts.
One angle \(=\frac{5}{9} \times 180=100^{\circ}\)
Another angle \(=\frac{4}{9} \times 180=80^{\circ}\)
Two angles are 100° and 80°.
![]()