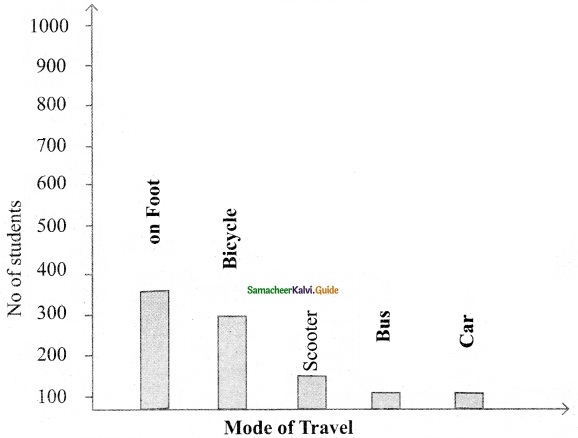
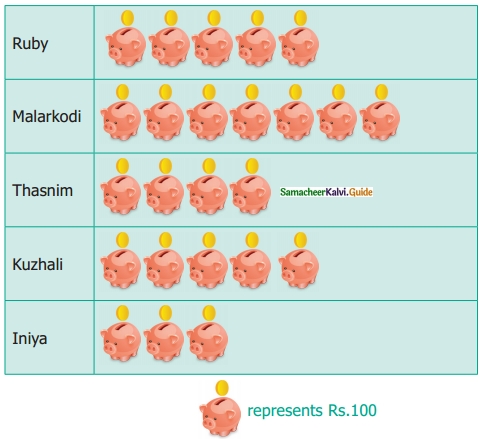
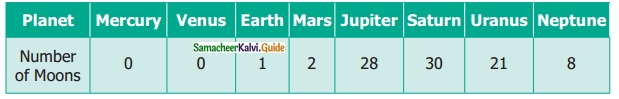
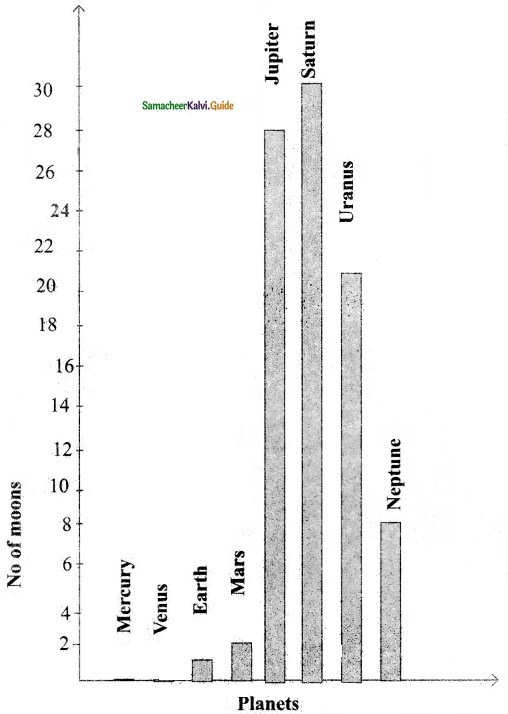
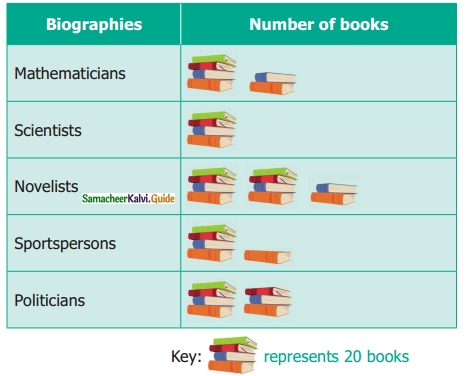
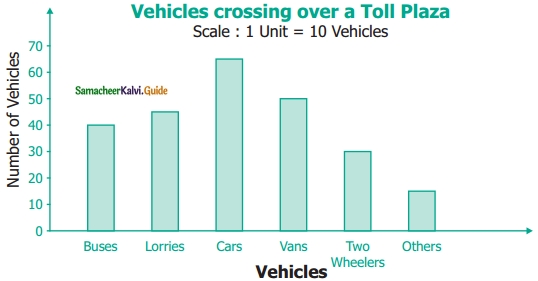
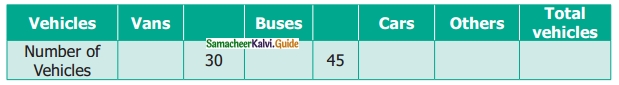
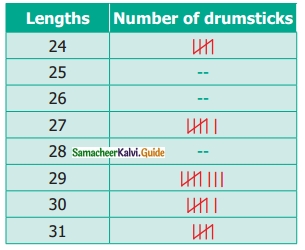
Students can download 6th Science Term 3 Chapter 1 Magnetism Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 1 Magnetism
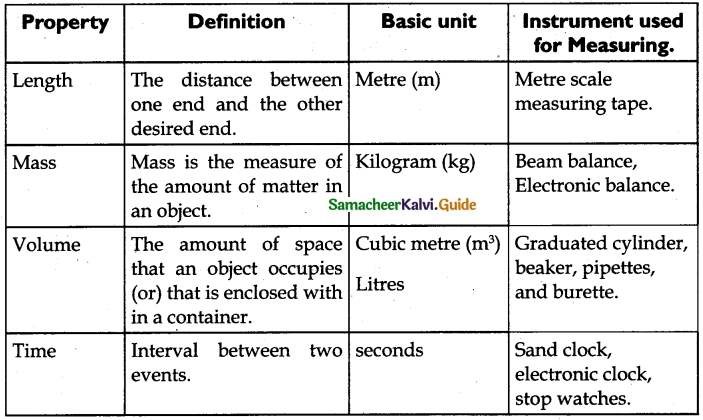
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Magnetism Text Book Back Questions and Answers
1. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
An object that is attracted by a magnet.
a. wooden piece
b. plain pins
c. eraser
d. a piece of paper
Answer:
b. Plain pins
Question 2.
People who made mariner’s compass for the first time.
(a) Indians
(b) Europeans
(c) Chinese
(d) Egyptians
Answer:
(c) Chinese
Question 3.
A freely suspended magnet always comes to rest in the direction
a. North-east
b. South-west
c. East-west
d. North-south
Answer:
d. North-South
![]()
Question 4.
Magnets lose their properties when they are
(a) used
(b) stored
(c) hit with a hammer
(d) cleaned
Answer:
(c) hit with a hammer
Question 5.
Mariner’s compass is used to find the
a. speed
b. displacement
c. direction
d. motion.
Answer:
c. direction
II. Fill in the Blanks
- Artificial magnets are made in different shapes such as ……….., ………… and ………..
- The Materials which are attracted towards the magnet are called ………..
- Paper is not a ……….. material.
- In olden days, sailors used to find direction by suspending a piece of ………..
- A magnet always has ………. poles.
Answer:
- Oval shape, Disc Shape, cylindrical shape
- magnetic materials
- magnetic
- lodestone
- Two
III. True or False. If False, give the correct answer.
- A cylindrical magnet has only one pole.
- Similar poles of a magnet repel each other.
- Maximum iron filings stick in the middle of a bar magnet when it is brought near them.
- A compass can be used to find East-West direction at any place.
- Rubber is a magnetic material.
Answer:
- False – A cylindrical magnet has two poles.
- True
- False – Maximum iron fillings stick in the poles of a bar magnet when it is brought near them.
- False – A. compass can be used to find north-south direction at any place.
- False – Rubber is a non-magnetic material.
![]()
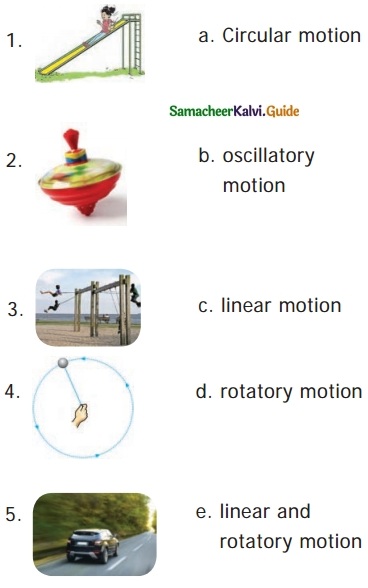
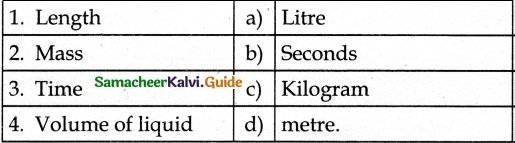
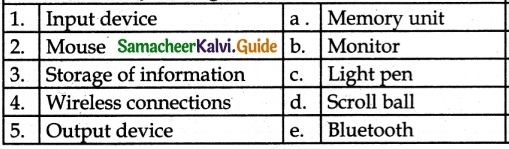
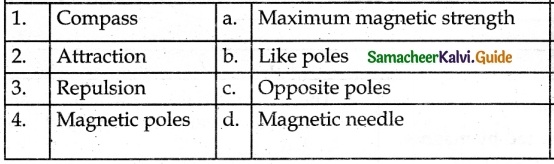
IV. Match the following
Answer:
1. – d
2. – c
3. – b
4. – a
V. Circle the odd ones and give reasons
Question 1.
Iron, nail, pins, rubber tube, needle
Answer:
Iron, nail, pins, ![]() needle
needle
Rubber tube is a non-magnetic substance.
Question 2.
Lift, escalator, electromagnetic train, electric bulb
Answer:
Lift, escalator, electromagnetic train, ![]()
Electromagnet is not used in an electric bulb.
Question 3.
Attraction, repulsion, pointing direction, illumination
Answer:
Attraction, repulsion, pointing direction, ![]()
Illumination is not a magnetic property.
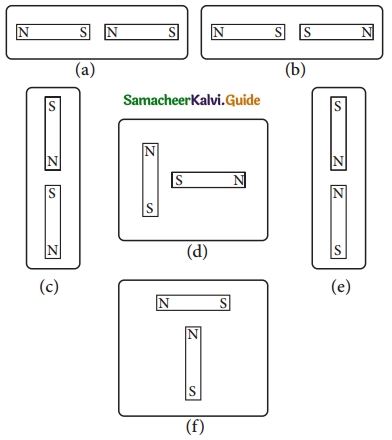
VI. The following diagrams show two magnets near one another. Use the words, ‘Attract, Repel,Turn around’ to describe what happens in each case:
Answer:
(a) Attract. Opposite poles S – N attracts each other.
(b) Repel. Like poles S – S repel each other.
(c) Attract. Opposite poles N – S attract each other.
(d) Turn around.
(e) Repel. Like poles N – N repel each other.
(f) Turn around.
![]()
VII. Write down the names of substances.
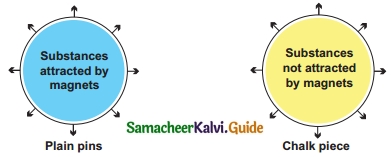
Answer:
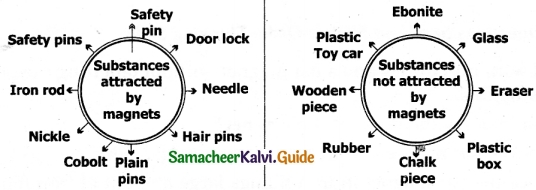
VIII. Give Short Answer
Question 1.
Explain the attraction and repulsion between magnetic poles.
Answer:
- Like poles (N – N, S – S) repel each other.
- Unlike poles (N – S, S – N) attract each other.
Question 2.
A student who checked some magnets in the school laboratory found out that their magnetic force is worn out. Give three reasons for that?
Answer:
Magnets lose their properties if they are heated or dropped from a height or hit with a hammer.
IX. Answer in detail
Question 1.
You are provided with an iron needle. How will you magnetize it?
Answer:
- Place the iron needle on the table.
- Take a bar magnet and place one of its poles near one edge of the iron needle.
- Rub from one end to another without changing the direction of the pole of the magnet.
- Repeat the process 30 to 40 times. The needle will be magnetized.
- If it will not attract pin or iron fillings continue the same process for some more time.
![]()
Question 2.
How does electromagnetic train work?
Answer:
- Electromagnets are used in electromagnetic trains.
- Electromagnets are magnetised when current flows through them. When the direction of the current is changed, poles will be changed.
- Magnets are attached at the bottom of the train and rail tracks.
- The train is lifted from track up to 10 cm height by the property of the same poles repel each other.
- By using attraction and repulsion at the same time between the magnets in tracks and bottom of train move forward.
- The magnets are controlled by electricity.
- There is no friction. So the train can easily attain a speed of 300 km/ h.
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
You are provided with iron filings and a bar magnet without labelling the poles of the magnet. Using this ……….
a. How will you identify the poles of the magnet?
Answer:
- When we place the bar magnet in iron fillings a large number of iron fillings stick on the two ends of the bar magnet. These ends are poles of the magnet.
- Poles will attract more iron filings. Because poles have high magnetic strength.
b. Which part of the bar magnet attracts more iron filings? Why?
Answer:
The more iron filings are attracted by the poles of the magnet because the poles have more concentrated magnetic power.
Question 2.
Two bar magnets are given in figure A and B. By the property of attraction, identify the North pole and the South pole in the bar magnet (B)
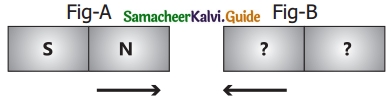
Answer:
Opposite poles attract each other. The second pole of magnet A is N (north pole). So magnet B has S – N poles. Then only they will attract.

![]()
Question 3.
Take a glass of water with a few pins inside. How will you take out the pins without dipping your hands into the water?
Answer:
- Take a bar magnet.
- Tie it in a thread.
- Dip the tied magnet into the glass of water.
- The pins are attracted by the magnet.
- Now take out the magnet from the glass of water.
- Collect the pins from the magnet.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Magnetism Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the right answer:
Question 1.
Which is not attracted by a magnet?
(a) Iron
(b) Cobolt
(c) Nickel
(d) Rubber
Answer:
(d) Rubber
Question 2.
Among the following which one is a magnetic substance?
(a) Nickel
(b) Sodium
(c) Oxygen
(d) Potassium
Answer:
(a) Nickel
![]()
Question 3.
Who invented leading stone?
(a) Indians
(b) Europians
(c) Chinese
(d) Americans
Answer:
(c) Chinese
Question 4.
Magnets lose their properties if they are _______
(a) dipped in water
(b) dipped in oil
(c) heated
(d) in freezer
Answer:
(c) heated
Question 5.
The maximum speed of electromagnetic train is
(a) 380 km/hr
(b) 600 km/h
(c) 480 km/h
(d) 690 km/h
Answer:
(b) 600 km/h
II. Fill in the blanks:
- Magnets are used to find directions. So they are called as ………..
- ……….. is the ore with attracting property.
- Ever silver spoon is a ……….. material.
- ……….. is used to seperate iron from wastages.
- The attractive force of magnet is high near …………
Answer:
- leading stem
- Magnetite
- non-magnetic
- electromagnet
- Poles
III. Match the Following:
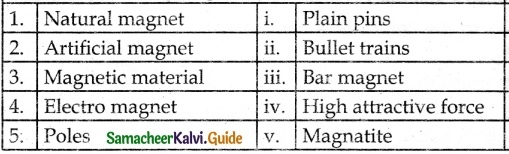
Answer:
1. – v.
2. – iii.
3. – i.
4. – ii.
5. – iv.
![]()
IV. Very Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What are artificial magnets?
Answer:
Man-made magnets are called artificial magnets.
(Eg.) bar-magnets, horseshoe magnets.
Question 2.
What are the different types of artificial magnets?
Answer:
- Bar-magnet, Horseshoe magnet, Ring magnet and Needle magnet are generally used artificial magnets.
- Oval-shape, Disc shape and cylindrical shape magnets are also available.
Question 3.
What are magnetic substances?
Answer:
Substances which are attracted by magnets are called magnetic substances. (Eg.) Iron, Cobolt, Nickel
Question 4.
What are non-magnetic substances?
Answer:
Substances which are not attracted by magnets are called non-magnetic substances. (Eg.) Paper, Plastic etc.
Question 5.
What are the uses of magnets?
Answer:
- We use various equipment with magnets in day to day life.
- We use magnets in speakers, small electric motors, some door locks, bags, some toys, compass, pencil boxes, phone covers, pin holders and magnetic crane.
V. Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What are the storage methods of magnets?
Answer:
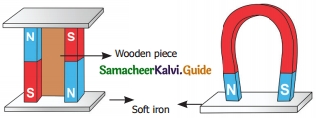
- Improper storage can also cause magnets to lose their properties.
- To keep them safe, bar magnets should be kept in pairs with their unlike poles on the same side.
- They must be seperated by a piece of wood and two pieces of soft iron should be placed across their ends.
- For a horse shoe magnet a single piece of soft iron can be used as a magnetic keeper across the poles.
![]()
Question 2.
How to find directions with a magnet?
Answer:
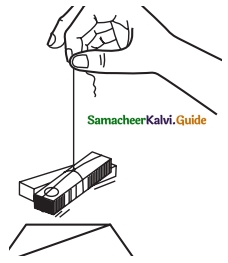
- Tie a piece of thread to the centre of a bar magnet and suspend it freely.
- Note the direction in which the magnet stops.
- Draw a line on a cardboard sheet along the direction in which the bar magnet stops, (ie., a line parallel to the bar magnet)
- Turn the magnet gently and let it come to stop again.
- Repeat it three or four times. The magnet always comes to rest in north-south direction.
VI. Questions based on higher-order thinking skills:
Question 1.
When iron needle is rubbed with bar magnet the needle get magnetized. But rubber piece is rubbed with magnet it will not get magnetized. Why?
Answer:
Because rubber is a non-magnetic substance.
Question 2.
What will happen when we place magnets near cell phone, computer and DVD?
Answer:
- Magnets will lose their property.
- These objects also will get affected.
![]()