Students can download 6th Science Term 2 Chapter 6 Human Organ Systems Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 6 Human Organ Systems
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Human Organ Systems Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The circulatory system transports these throughout the body
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nutrient
(c) Hormones
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 2.
Main organ of respiration in human body is
(a) Stomach
(b) Spleen
(c) Heart
(d) Lungs
Answer:
(d) Lungs
![]()
Question 3.
Breakdown of food into smaller molecules in our body is known as
(a) Muscle contraction
(b) Respiration
(c) Digestion
(d) Excretion
Answer:
(a) Digestion
II. Fill in the Blanks
- A group of organs together make up an ………. system.
- The part of the skeleton that protects the brain is …………
- The process by which the body removes waste is ………..
- The ………. is the largest sense organ in our body.
- The endocrine glands produce chemical substances called …………
Answer:
- Organ
- Skull
- Excretion
- Skin
- hormones
III. True or False. If False, give the correct answer.
- Blood is produced in the bone marrow.
- All the waste products of the body are excreted through the circulatory system.
- The other name of the food pipe is an alimentary canal.
- Thin tube-like structures which are the component of the circulatory system are called blood vessels.
- The brain, the spinal cord, and nerves form the nervous system.
Answer:
- False – RBC’s are produced in the bone marrow.
- False – All the waste products are transported through the circulatory system.
- False – The other name of the digestive tract is an alimentary canal.
- True
- True
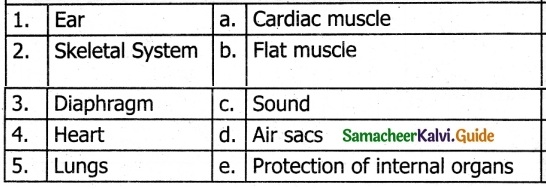
IV. Match the following
Answer:
1. – c
2. – e
3. – b
4. – a
5. – d
![]()
V. Arrange in the correct sequence
Question 1.
Stomach → Large intestine → Oesophagus → Pharynx → Mouth → Small Intestine → Rectum → Anus
Answer:
Mouth → Pharynx → Oesophagus → Stomach → Small intestine → Large intestine → Rectum
Question 2.
Urethra → Ureter → Urinary Bladder → Kidney
Answer:
Kidney → Ureter → Urinary bladder → Urethra
VI. Analogy
- Arteries : Carry blood from the heart:: ……….. : Carry blood to the heart.
- Lungs : Respiratory system :: ……….. : Circulatory system.
- Enzymes : Digestive glands :: ………… : Endocrine glands
Answer:
- Veins
- Heart
- Hormones
VII. Give a Very short answer:
Question 1.
Describe the skeletal system.
Answer:
- The skeletal system consists of bones, cartilages and joints.
- Bones provide a framework for the body.
- Bones along with muscles help in movements such as walking, running, chewing and dancing etc.
Question 2.
Write the functions of epiglottis?
Answer:
- It prevents the entry of food into the windpipe.
- It opens when the air enters the windpipe.
Question 3.
What are the three types of blood vessels?
Answer:
- Arteries
- Veins
- Capillaries
![]()
Question 4.
Define the term “Trachea”
Answer:
- The trachea commonly called “Windpipe” is a tube supported by cartilaginous rings.
- It connects the pharynx and larynx to the lungs.
- Allowing the passage of air.
Question 5.
Write any two functions of the digestive system.
Answer:
- The digestive system is involved in the conversion of complex food substances into simple forms.
- Absorption of digested food.
Question 6.
Name the important parts of the eye?
Three main parts.
Answer:
- Cornea
- Iris
- Pupil
Question 7.
Name the five important sense organs.
Answer:
- Eyes
- Ears
- Nose
- Tongue
- Skin
VIII. Give a short answer:
Question 1.
Write a short note on the rib cage.
Answer:
- The rib cage is made up of 12 pairs of curved, flat rib bones.
- It protects the delicate vital organs such as the heart and lungs.
![]()
Question 2.
List out the functions of the human skeleton.
Answer:
- The skeletal system gives shape to the body.
- Bones provide a framework for the body.
- Bones along with muscles help in movements such as walking, running, chewing and dancing, etc.
- It protects the soft internal organs.
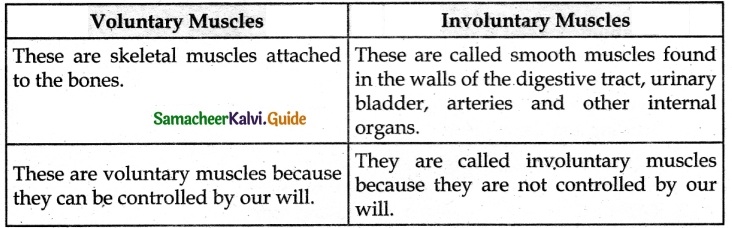
Question 3.
Differentiate between the voluntary muscles and involuntary muscles.
Answer:
IX. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
List out the functions of the Endocrine system and Nervous system.
Answer:
- Endocrine system regulates various functions of the body and maintains the internal environment.
- Endocrine glands produce chemical substances called “Hormones’ which control various activities of the body.
Eg. Growth hormone controls growth, the Adrenalin hormone acts at the time of fear stress, etc.
Functions of the nervous system:
- Sensory input: The conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
- Integration: The interpretation of the sensory signals and the formulation of responses.
- Motor output: The conduction of signals from the brain and spinal card to effectors such as muscle and gland cells.
Question 2.
Label the diagram given below to show the four main parts of the urinary system and answer the following questions.
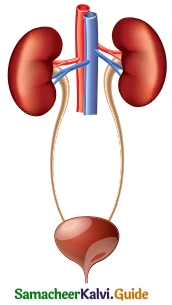
a. Which organ removes extra salts and water from the blood?
b. Where is the urine stored?
c. What is the tube through which urine is excreted out of the body?
d. What are the tubes that transfer urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder called?
Answer:
a. The functional units of the kidney are called Nephrons which filter the blood and form the urine.
b. Urine is stored in the urinary bladder.
c. Urine is expelled out through the urethra.
d. The ureters that transfer urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
![]()
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
What will happen if the diaphragm shows no movement?
Answer:
- The diaphragm is the primary organ of breathing.
- The movement of the diaphragm expands the lungs and creates a vacuum.
- Due to this, the air is sucked in.
- If the diaphragm does not move the lungs do not expand or contract and breathing stops.
- The person will die.
Question 2.
Why is the heart divided into two halves by a thick muscular wall?
Answer:
- The ventricles of the heart have thicker muscular walls than the atria.
- The left ventricle also has a thicker muscular wall than the right ventricle.
- This is due to the higher forces needed to pump blood through the systemic circuit compared to the pulmonary circuit.
Question 3.
Why do we sweat more in summer?
Answer:
- Sweating plays an important health role as it helps to maintain constant body temperature by cooling us down.
- When it is hot and we sweat that moisture evaporates and cools us immediately.
- This is why we sweat more when the summer is very hot.
Question 4.
Why do we hiccup and cough sometimes when we swallow food?
Answer:
Reasons for hiccup and cough :
- Eating too – quickly and swallowing air along with foods.
- Eating too – many fatty or spicy foods in particular.
- Drinking too much-carbonated beverages or alcohol can distend the stomach and irritate the diaphragm which can cause hiccups.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Human Organ Systems Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the right answer:
Question 1.
A newborn baby has ……….. bones.
(a) 206
(b) More than 200
(c) More than 300
(d) 210
Answer:
(c) More than 300
Question 2.
_______ connect bone to muscle.
(a) Skeleton
(b) Tendons
(c) Cartilages
(d) Ligaments
Answer:
(b) Tendons
![]()
Question 3.
The walls of the heart is made up of
(a) Voluntary muscles
(b) Cardiae muscles
(c) Involuntary muscles
(d) Biceps muscle
Answer:
(b) Cardiac muscles
Question 4.
_______ muscles are found in the walls of the digestive tract, urinary bladder arteries, and other internal organs.
(a) Bone
(b) Smooth
(c) Cardiac
(d) triceps
Answer:
(b) Smooth
Question 5.
The bronchi divide further and end in small air sacs called
(a) Cerebrum
(b) Thymus
(c) Alveoli
(d) Pinna
Answer:
(c) Alveoli
II. Fill in the blanks:
- The adult human skeletal system consists of 206 bones and a few ………., ……… and ………..
- The brain is covered by a three-layered tissue covering called………..
- When we are walking, running or climbing the balance of the body is maintained by ………….
- The endocrine gland present in the chest is …………..
- The ………. brings blood containing oxygen and urea from the aorta to the kidneys.
- connects the brain to a different part of the body through nerves.
Answer:
- cartilages, ligaments, and tendons
- meninges
- Ears
- Thymus Gland
- renal artery
- spinal cord
III. Match the Following:
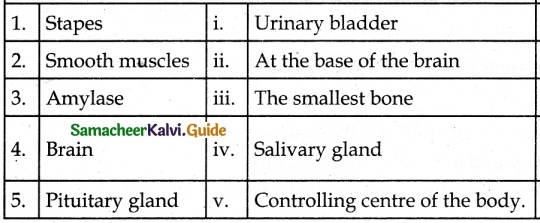
Answer
1. – iii.
2. – i.
3. – iv.
4. – v.
5. – ii.
![]()
IV. Arrange in the correct sequence
Question 1.
Trachea → Bronchi → Pharynx → Lungs → Larynx → Nasal cavity → Nostrils → Bronchiole → Alveolus
Answer:
Nostrils → Nasal cavity → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Bronchi → Bronchiole → Alveolus
Question 2.
Middle ear → Pinna → Outer ear → Inner ear
Answer:
Pinna → Outer ear → Middle ear → Inner ear.
V. Analogy
- Skull: Made up of cranial bones and facial bones :: ………… : Made up of 12 pairs of curved flat rib bones
- Biceps : Bends the arm at the elbow :: ……….. : Straightens the elbow
Answer:
- Ribcage
- Triceps
VI. Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
What are the two major divisions of the skeletal system?
Answer:
The two major divisions of the skeletal system are.
- Axial skeleton
- Appendicular skeleton.
Question 2.
Name the auditory ossicles.
Answer:
- Malleus
- Incus
- Stapes
Question 3.
Which is the longest bone in our body?
Answer:
The thigh bone (femur) is the longest bone.
Question 4.
What is the name of the muscles in the heart?
Answer:
Cardiac muscle.
Question 5.
What is the length of the Alimentary canal?
Answer:
9 metres.
![]()
VII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
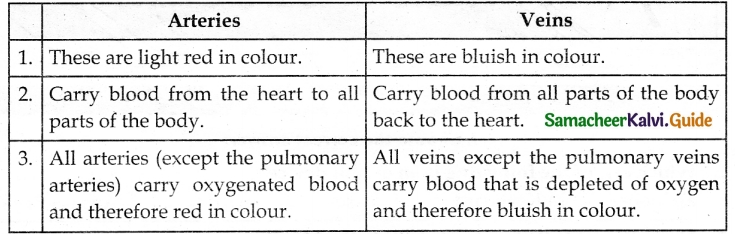
Tabulate the differences between arteries and veins.
Answer:
Arteries:
- Carry blood from the heart to all parts of the body.
- Carry oxygenated blood (Except pulmonary artery).
- They have thick elastic muscular walls.
- Valves are absent.
- Blood flows under high pressure.
Veins:
- Carry blood from all parts of the body back to the heart.
- Carry deoxygenated blood (Except pulmonary vein).
- They have thin non-elastic valves.
- Valves are present to prevent the backward flow of blood.
- Blood flows under low pressure.
Question 2.
Differentiate arteries from a vein and tabulate your answer.
Answer: