Students can download 6th Social Science Term 1 Civics Chapter 1 Understanding Diversity Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Civics Solutions Term 1 Chapter 1 Understanding Diversity
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Understanding Diversity Text Book Back Questions and Answers
A. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
India consists of ……………. states and ……………. Union territories.
(a) 27,9
(b) 29,7
(c) 28,7
(d) 28,9
Answer:
(b) 29,7
Question 2.
India is known as a
(a) Continent
(b) Subcontinent
(c) Island
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Sub continent
![]()
Question 3.
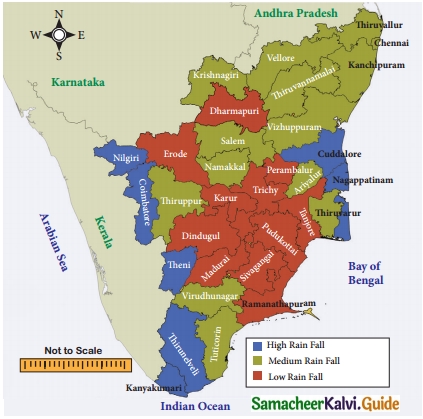
Mawsynram, the land of highest rainfall is located in …………….
(a) Manipur
(b) Sikkim
(c) Nagaland
(d) Meghalaya
Answer:
(d) Meghalaya
Question 4.
Which one of the following religion is not practised in India
(a) Sikhism
(b) Islam
(c) Zoroastrianism
(d) Confucianism
Answer:
(d) Confucianism
Question 5.
Recognised official languages of India, as per VUIth schedule of Indian constitution …………….
(a) 25
(b) 23
(c) 22
(d) 26
Answer:
(c) 2
Question 6.
Onam festival celebrated in
(a) Kerala
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Punjab
(d) Karnataka
Answer:
(a) Kerala
![]()
Question 7.
Mohiniyattam is a classical dance of …………….
(a) Kerala
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Manipur
(d) Karnataka
Answer:
(a) Kerala
Question 8.
Discovery of India’ a book was written by
(a) Rajaji
(b) V.O.C
(c) Nethaji
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Answer:
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Question 9.
The phrase ‘Unity in Diversity’ was coined by …………….
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) Ambedkar
(c) Mahathma Gandhi
(d) Rajaji
Answer:
(a) JawahalalNehru
Question 10.
V.A. Smith called India as __________
(a) Great Democracy
(b) Unique land of diversities
(c) Ethnological museum
(d) Secular nation
Answer:
(c) Ethnological museum
II. Fill in the blanks
- Geographical features and climatic conditions determine the ……………. activities of a region.
- Jaisalmer, the land of lowest rainfall is located in …………….
- Tamil was declared as classical language in the year …………….
- Bihu festival is celebrated in …………….
Answer:
- economic
- Rajasthan
- 2004
- Assam
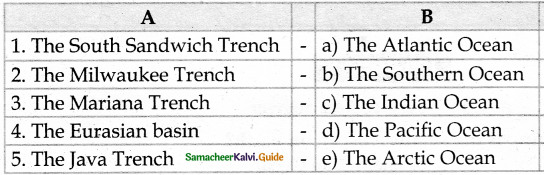
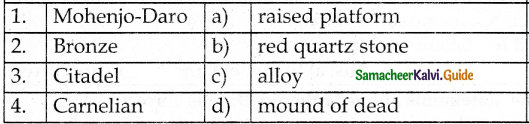
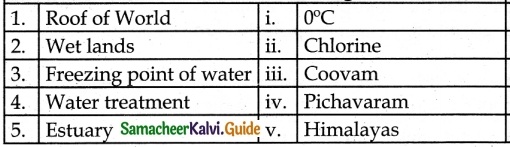
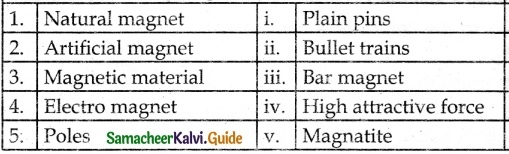
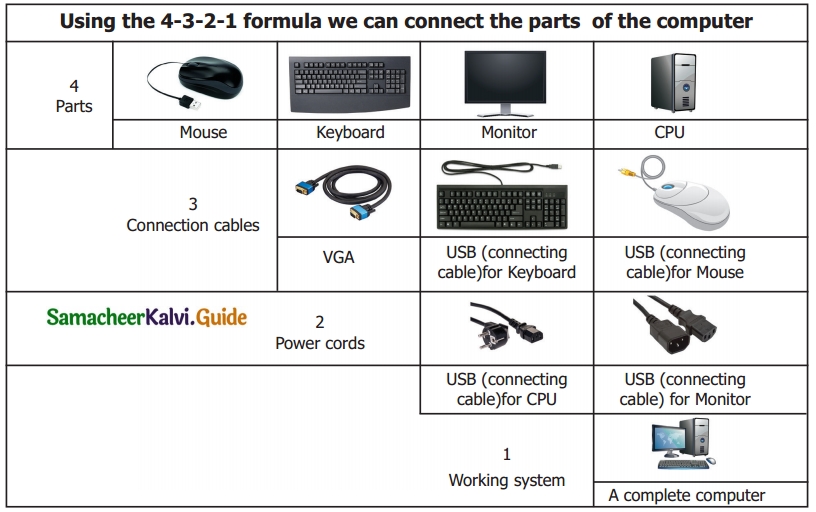
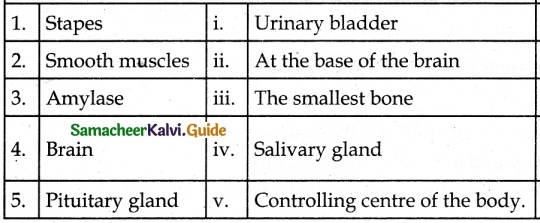
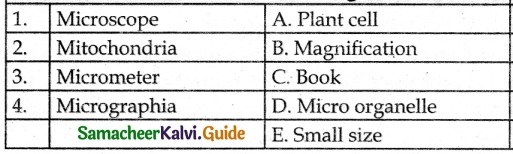
III. Match the following
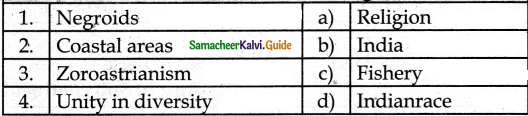
Answer:
1. – d
2. – c
3. – a
4. – b
IV. Answer the following questions
Question 1.
Define diversity.
Answer:
We, the Indians come from different backgrounds, belong to different cultures, worship in different ways. This is known as diversity.
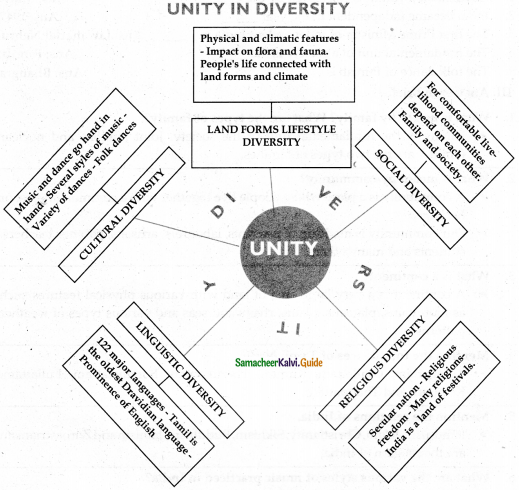
Question 2.
What are the types of diversity?
Answer:
- Landform and lifestyle diversity
- Social diversity
- Religious diversity
- Linguistic diversity
- Cultural diversity
![]()
Question 3.
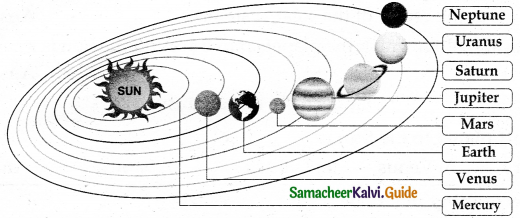
Why is India called a subcontinent?
Answer:
A continent is a very large area of land with various physical features such as mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers and seas, and various types of weather patterns. India has all of them. So India is known as a subcontinent.
Question 4.
Write the names of three major festivals celebrated in India.
Answer:
- Deepavali
- Christmas
- Ramzan
Question 5.
List out some of the classical dances of India,
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu – Bharatanatyam
- Kerala – Kathakali
- Karnataka – Yakshagana
- Odisha – Odissi
- Andhra Pradesh – Kuchipudi
- Manipur – Manipuri
- Assam – Sattriya
Question 6.
Why is India called the land of unity in diversity?
Answer:
Though diversity is visible in every aspect of life in India, we are united by the spirit of patriotism.
V. Answer the following in detail
Question 1.
Explain Linguistic diversity and cultural diversity.
Answer:
Linguistic Diversity:
- According to the census of India 2001, India has 122 major languages and 1599 other languages.
- Four major Indian language families are Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Austroasiatic, and Sino Tibetian. Tamil is the oldest Dravidian language.
- Historically, the Portuguese, the Dutch, the British, the Danish and the French came to India for trade and their occupation of India or some parts of it has left behind a certain impact upon the culture and language of the people.
- In due course, English has emerged as an important language and a medium of instruction in schools and colleges.
- (It is widely used in official communication and daily life.
Cultural Diversity:
- The term ‘culture’ refers to the customs and practices of people, their language, their dress code, cuisine, religion, social habits, music, art, and architecture.
- The culture of a group of people is reflected in their social behaviour and interactions.
- The group identity fostered by social patterns is unique to a group.
- Art and architecture are an integral part of every community.
- It develops as a part of the culture and tradition of a community.
![]()
Question 2.
“‘India is a land of diversity, yet we are all united”. Explain.
Answer:
- Diversity is visible in every aspect of life in India.
- Even then, we are united by the spirit of patriotism.
- Symbols such as the National Flag and National Anthem remind us of our great nation and need to stay united.
- We come together when we celebrate Independence Day, Republic Day and Gandhi Jayanthi every year.
- India has a multi-cultural society.
- India evolved as a single nation through common beliefs, customs, and cultural practices.
- The freedom struggle and the drafting of our constitution stand as ample evidence , to the spirit of unity of India.
VI. Projects and Activities (For Students)
- “The occupation of people depends on the landform of a place” Give some examples.
- Read about a state of your choice and make an album to show the culture and tradition of people who live in that state.
- Collect the pictures to show the and and architecture of Tamilnadu.
VII. HOTS
List out the various festivals celebrated in different states.
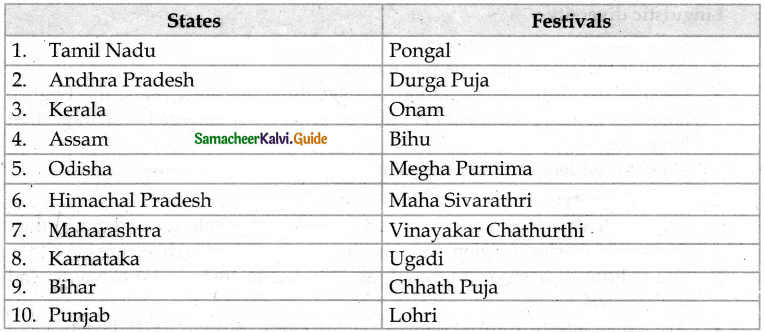
VIII. Life Skill
Suggest measures to bring unity in your school.
- Uniform dress
- Celebrating festivals of all religions.
- Deepavali
- Christmas
- Ramzan
- Pongal
- Conducting community prayers.
- Inter – dining
- Celebration of School Day
- Other extracurricular activities.
- Conducting L.D.S meetings.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Understanding Diversity Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The oldest Dravidian language is …………….
(a) Hindi
(b) Tamil
(c) Sanskrit
(d) Telugu
Answer:
(b) Tamil
Question 2.
Punjab is well-known as for_______ dance.
(a) Bihu
(b) Dandia
(c) Bhangra
(d) Dumhal
Answer:
(c) Bhangra
![]()
Question 3.
Tamil was declared as a classical language in …………….
(a) 2002
(b) 2004
(c) 2012
(d) 2008
Answer:
(b) 2004
II. Fill in the blanks
- Gurunanak Jayanthi is celebrated by the ……………..
- India became independent in the year ……………..
- The first Prime Minister of independent India is ……………..
- The fundamental unit of a society is the ……………..
- The folk dance of Punjab is ……………..
Answer:
- Sikhs
- 1947
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Family
- Bhangra
III. Answer in brief
Question 1.
What is meant by family? What are the types of the family?
Answer:
Family is the fundamental unit of society. Joint families and nuclear families are the two types of families.
Question 2.
Define community.
Answer:
Our community is made up of peasants, labourers, artisans, parents, teachers, students, and many others.
Question 3.
What is a continent?
Answer:
A continent is a very large area of land with various physical features such as mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers and seas and various types of weather patterns.
![]()
Question 4.
Name the religions which flourish in India.
Answer:
Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, Jainism and Zoroastrianism flourish in India.
Question 5.
Mention the religions of India.
Answer:
- Hinduism
- Islam
- Christianity
- Sikhism
- Buddhism
- Jainism and Zoroastrianism are the religion of India.
Question 6.
Mention the people who came to India for trade.
Answer:
The Portuguese, the Dutch, the British, the Danish and the French came to India for trade.
![]()
Question 7.
Mention any four folk dances of India.
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu – Karagattam, Oyillattam, Kummi, Thappattam
- Kerala – Mohiniattam
- Punjab – Bhangra
- Gujarat – Dandia
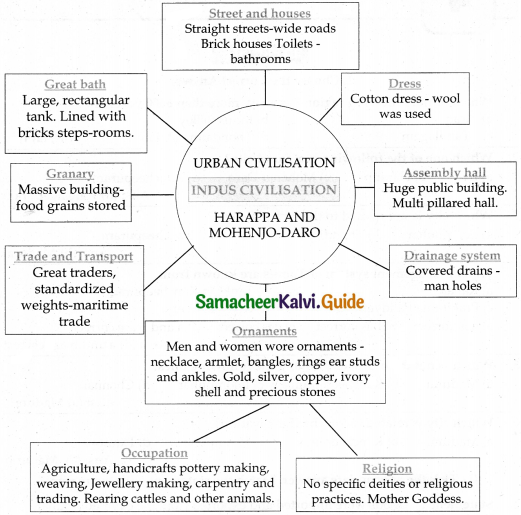
IV. Mind Map