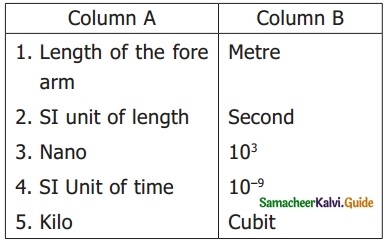
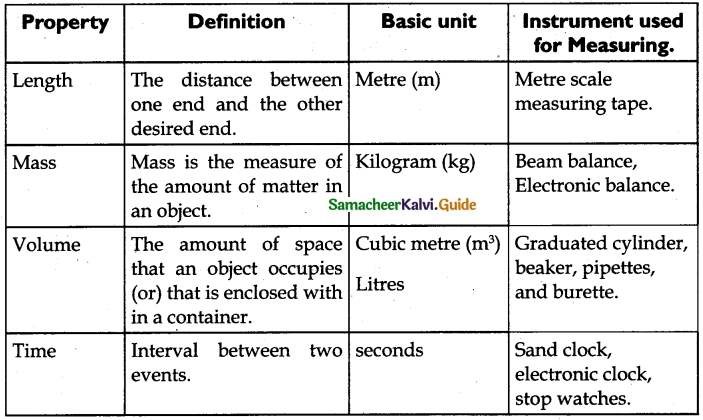
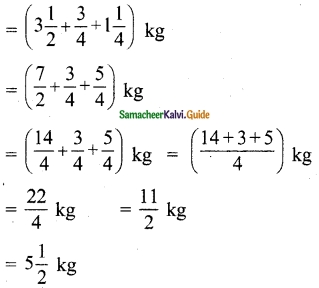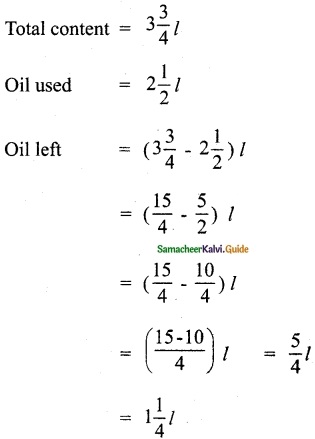Students can download 6th Science Term 2 Chapter 2 Electricity Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 2 Electricity
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Electricity Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy is
(a) fan
(b) solar cell
(c) cell
(d) television
Answer:
(c) cell
Question 2.
Electricity is produced in
(a) transformer
(b) power station
(c) electric wire
(d) television
Answer:
(b) power station
![]()
Question 3.
Choose the symbol for battery
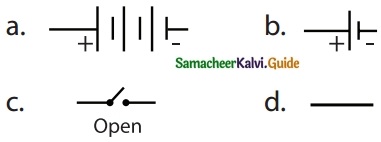
Answer:
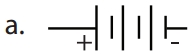
Question 4.
In which among the following circuits does the bulb glow?
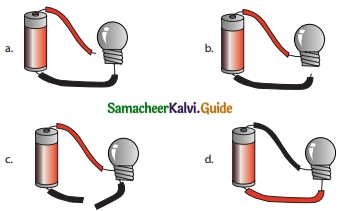
Answer:
Question 5.
_______ is a good conductor
(a) silver
(c) rubber
(b) wood
(d) plastic
Answer:
(a) silver
II. Fill in the Blanks
- ………. are the materials which allow electric current to pass through them.
- Flow of electricity through a closed circuit is …………
- ……… is the device used to close or open an electric circuit.
- The long perpendicular line in the electrical symbol represents its ………… terminal.
- The combination of two or more cells is called a ………..
Answer:
- Conductors
- electric current
- Key
- positive
- battery
III. True or False. If False, give the correct answer.
- In a parallel circuit, the electricity has more than one path.
- To make a battery of two cells, the negative terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the other cell.
- The switch is used to close or open an electric circuit.
- Pure water is a good conductor of electricity.
- Secondary cell can be used only once.
Answer:
- True
- False – The negative terminal of one cell is connected to positive terminal of other cell.
- True
- False – Pure water is an insulator.
- False – Secondary cells can be used many times.
![]()
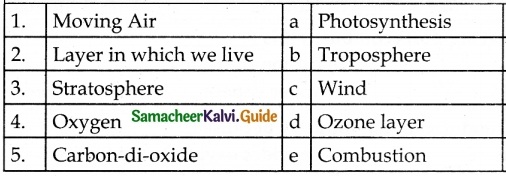
IV. Match the following
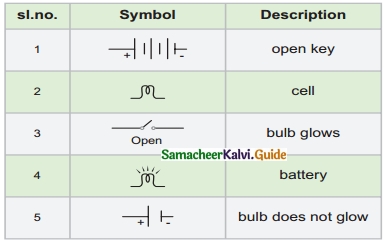
Answer:
1. – Battery
2. – Bulb does not glow
3. – Open key
4. – Bulb glows
5. – Cell
V. Arrange in Sequence
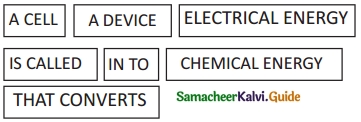
Answer:
A DEVICE THAT CONVERTS CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY IS CALLED A CELL.
VI. Give Very Short Answers
Question 1.
In the given circuit diagram, which of the given switches) should be closed. So that only the bulb A glows.
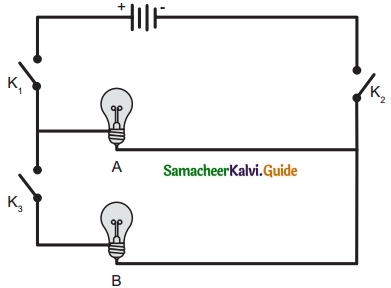
Answer:
K1 and K2 should be connected to glow bulb A in the circuit
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : It is very easy for our body to receive electric shock.
Reason (R) : Human body is a good conductor of electricity.
a. Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
b. A is correct, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
c. A is wrong but R is correct.
d. Both A and R are correct and R is not the correct explanation for A.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
Question 3.
Can you produce electricity from a lemon?
Answer:
- We can produce electricity from the lemon.
- Take lemon as an electrolyte, copper plate as positive terminal, and small hairpin as the negative terminal. This setup will work as a cell.
- If we connect the electric bulb with it bulb will glow.
Question 4.
Identify the conductor from the following figures.

Answer:
Metallic chain is a conductor.
![]()
Question 5.
What type of circuit is there in a torchlight?
Answer:
Simple circuit system is used in a torchlight.
Question 6.
Circle the odd one out. Give a reason for your choice.
Answer:
Switch, Bulb, Battery, Generator.
Generator is the source of electricity. Others are parts of a circuit.
VII. Give Short Answers:
Question 1.
Draw the circuit diagram for the series connection.
Answer:
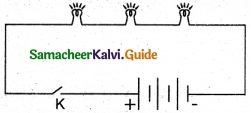
Question 2.
Can the cell used in the clock give us an electric shock? Justify your answer.
Answer:
- The cell used in the clock will not give us an electric shock because the voltage of that cell is very low nearly 1.5 v.
- So it will not affect our body.
Question 3.
Silver is a good conductor but it is not preferred for making electric wires. Why?
Answer:
- Silver is a costly metal.
- So economically we can not use it in electric wires.
VIII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
What is the source of electricity? Explain the various power stations in India.
Answer:
- In thermal power stations, thermal energy is generated by burning coal, diesel, or gas to produce steam.
- Steam is used to rotate the turbine to generate electricity.
- Here heat energy is converted into electric energy.
Hydel power stations:
- In hydel power stations, the turbine is made to rotate by the flow of water from dams.
- Here kinetic energy is converted into electric energy.
Atomic power station:
- Here nuclear energy is used to boil water
- The steam thus produced is used to rotate the turbine, as a result, electricity is produced.
- Here nuclear energy is converted into mechanical energy.
Windmills:
- In windmills, wind energy is used to rotate turbines to produce electricity.
- Here kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy.
![]()
Question 2.
Tabulate the different components of an electric circuit and their respective symbols.
Answer:
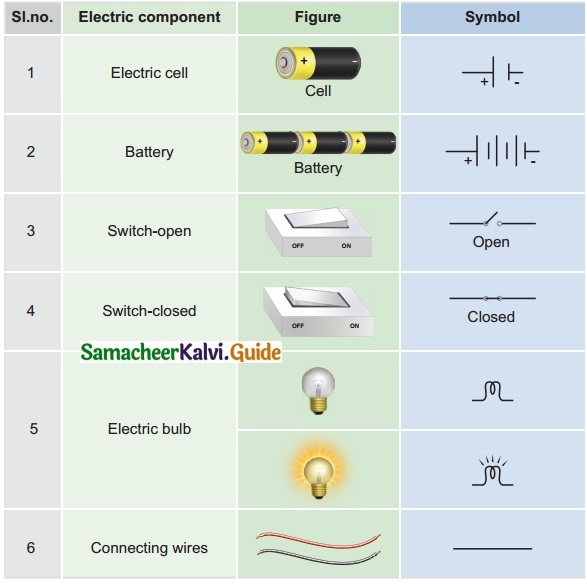
Question 3.
Write short notes on conductors and insulators.
Answer:
Conductors:
The rate of flow of electric charges in a circuit is called electric current. The materials which allow electric charges to pass through them are called conductors.
Examples: Copper, iron, aluminum, impure water, earth, etc.,
Iniulaton (Non-Conductors):
The materials which do not allow electric charges to pass through them are called insulators or non-conductors.
Examples: plastic, glass, wood, rubber, china clay, ebonite, etc.
IX. Questions Based on Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
Rahul wants to make an electric circuit. He has a bulb, two wires, a safety pin, and a piece of copper. He does not have any electric cell or battery. Suddenly he gets some idea. He uses lemon instead of a battery and makes a circuit. Will the bulb glow?
Answer:
1. Yes, the bulb will glow.
2. Insert a piece of copper on one side of lemon, safety pin on another side. This system will work as a battery.
3. Copper rod – Positive terminal
Safety pin – Negative terminal, Lemon – Electrolyte
4. Connect the connecting wire in both the terminals and finally connect to the bulb.
5. The current produced is passed through the circuit and the bulb will glow.
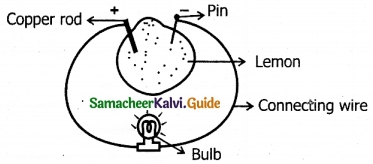
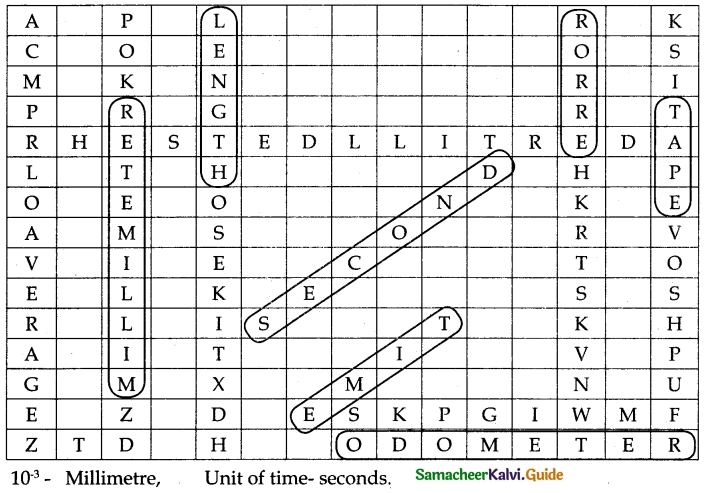
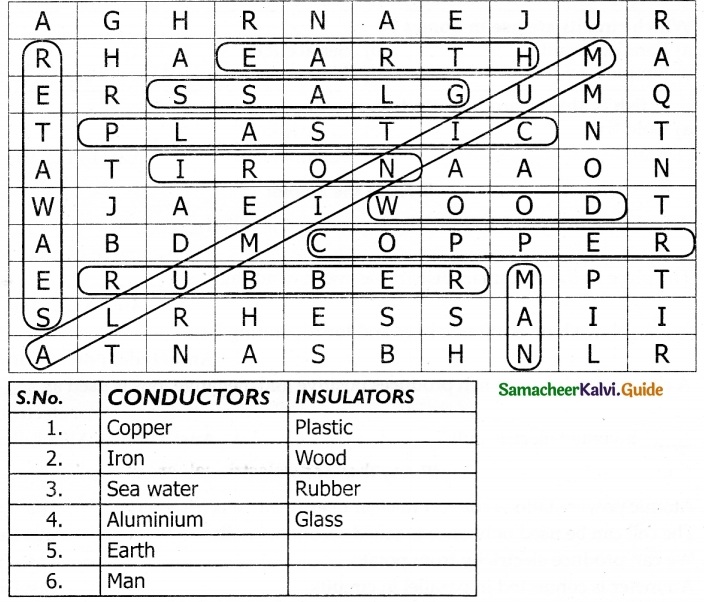
X. Search ten words in the given word grid and classify them as conductors and insulators
Question 1.
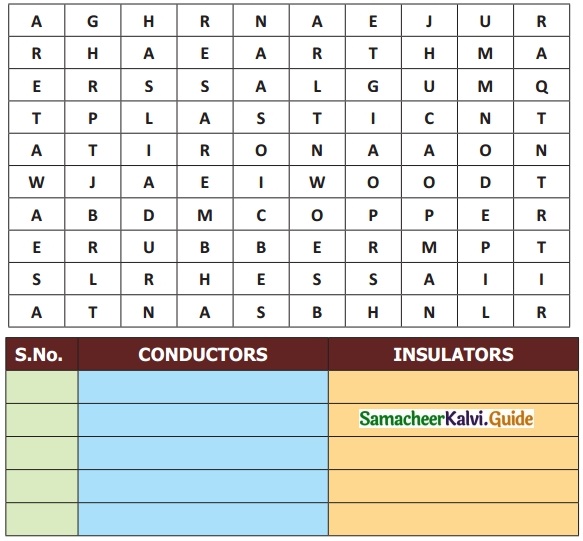
Answer:
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Electricity Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the right answer:
Question 1.
Here heat energy is converted into electric energy
(a) Thermal power station
(b) Atomic power station
(c) Hydel power station
(d) Windmills
Answer:
(a) Thermal power station
Question 2.
In atomic power station, ________ is used to rotate the turbine.
(a) water
(b) steam
(c) Air
(d) diesel
Answer:
(b) steam
Question 3.
Which one of the following is using secondary using cells?
(a) Hand watch
(b) Robo toy
(c) Laptop
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Laptop
Question 4.
If two or more ________ are connected in series in a circuit, then it is called a series circuit.
(a) keys
(b) cells
(c) connecting wires
(d) bulbs
Answer:
(d) bulbs
Question 5.
……….. fish is able to produce an electric current.
(a) Goldfish
(b) Electric Eel
(c) Katla
(d) Salamon fish
Answer:
(b) Electric Eel
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
- Any device from which electricity is produced is called ………..
- The place in Kanyakumari district that has more windmills is ………..
- ……….. have long economic lives and low operating cost.
- A chemical solution that produces positive and negative ions is used as ………….
- ……….. invented the electric bulb.
Answer:
- Source of electricity
- Aralvaimozhi
- Hydel power stations
- electrolyte
- Thomas Alva Edison
III. Say True of False.
- Atomic power stations convert nuclear energy into electric energy.
- The cell can be used only once is called secondary cells.
- We can produce electricity from potatoes.
- An ammeter is connected in parallel in circuits.
- The voltage of the torchlight battery is 1.5 v.
Answer:
- True
- False
- 3. True
- False
- True
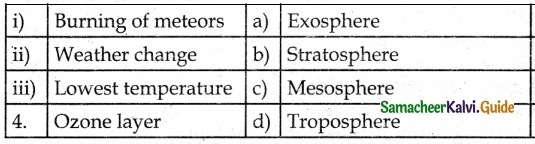
IV. Match the Following:
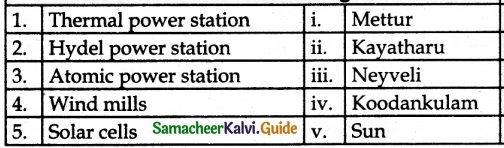
Answer:
1. – iii
2. – i
3. – iv
4. – ii
5. – v
V. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Experiments with electricity should only be performed with torch or radio batteries.
Reason (R) : Household electric supply will have high voltage and dangerous
a. Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
b. A is correct, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
c. A is wrong but R is correct.
d. Both A and R are correct and R is not the correct explanation
Answer:
a. Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Primary cells can not be recharged, they can be used only once.
Reason (R) : In vehicles, we use primary cells.
a. Both A and R are correct and R is the correct reason for A.
b. A is true but R is not correct.
c. Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct reason for A
d. A is not correct but R is correct
Answer:
b. A is true but R is not correct
![]()
VI. Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
What are the places in which atomic power stations located in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
- Kalpakkam, Kanchipuram district.
- Koodankulam, Tirunelveli district.
Question 2.
List out the parts required to make an electric circuit
Answer:
A key, connecting wires, dry cell or battery, and electric bulb.
Question 3.
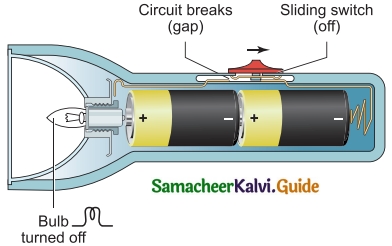
How to connect the cells in torchlight to glow bulbs?
Answer:
1. Connect the positive terminal of one cell with the negative terminal of another cell.
2. The bulb will glow.
Question 4.
How electric current is produced in Thermal power stations?
Answer:
The thermal energy generated by burning coal is used to produced steam. The steam thus produced is used to rotate the turbine. While the turbine rotates, the coil of wire kept between the electromagnet rotates. Due to electromagnetic induction, electricity is produced.
Question 5.
What is meant by a battery or collection of cells?
Answer:
Two or more cells are combined together to make a battery or collection of cells.
VII. Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What is a cell? Explain the types of cells.
Answer:
A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy is called a cell. Cells are classified, in two types. They are-
- Primary cells,
- Secondary cells.
1. Primary cells:
- They can not be recharged.
- They can be used only once.
- They are small in size.
- Eg. Cells used in clocks, watches, and toys, etc.
2. Secondary cells:
- A cell that can be recharged many times is called secondary cells.
- Depending upon usage size may vary.
- Eg. Secondary cells are used in mobile phones, laptops, emergency lamps, and vehicle batteries.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the safety measures to safeguard a person from electric shock?
Answer:
Safety measures to safeguard a person from electric shock:
- Switch off the power supply.
- Remove the connection from the switch.
- Push him away using non-conducting materials.
- Give him first aid and take him to the nearest health centre.