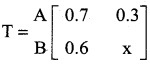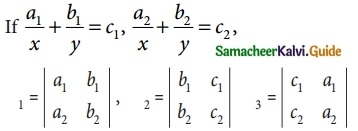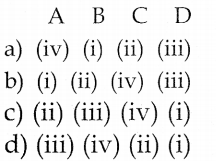Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Integral Calculus I Ex 2.2 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Integral Calculus I Ex 2.2
Question 1.
Integrate the following with respect to x.
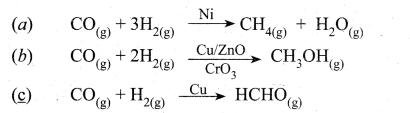
[\(\sqrt { 2x}\) – \(\frac { 1 }{\sqrt { 2x}}\)]²
Solution:
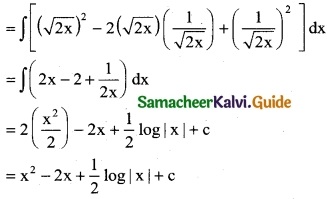
![]()
Question 2.
\(\frac { x^4+x^2+2 }{(x-1)}\)
Solution:
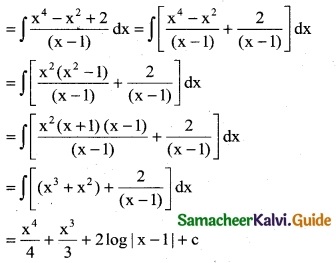
Question 3.
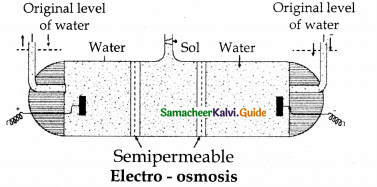
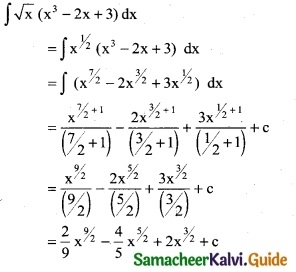
\(\frac { x^3 }{x+2}\)
Solution:
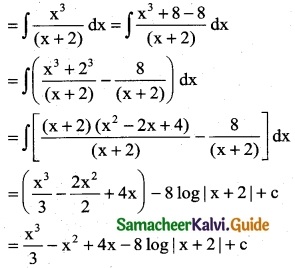
![]()
Question 4.
\(\frac { x^3+3x^2-7x+11 }{x+5}\)
Solution:
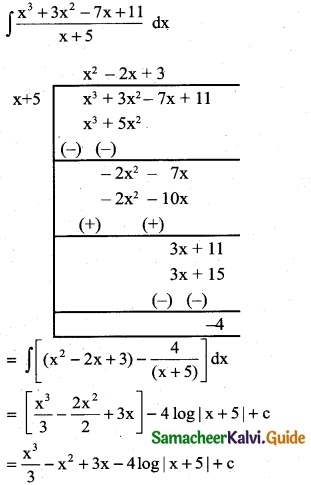
Question 5.
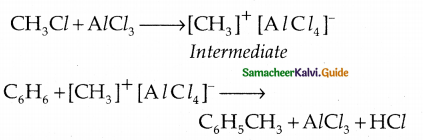
\(\frac { 3x+2 }{(x-2)(x-3)}\)
Solution:
By partial fraction
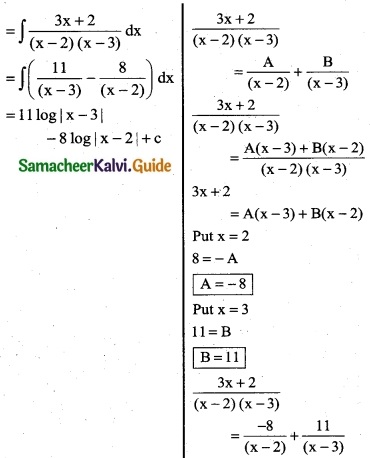
![]()
Question 6.
\(\frac { 4x^2+2x+6 }{(x+1)^2(x-3)}\)
Solution:
By partial fraction
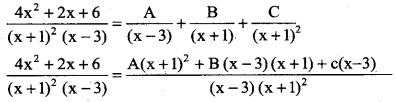
⇒ 4x² + 2x + 6 = A (x + 1)² + B (x – 3) (x + 1) + c (x – 3)
Put x = 3
4(9) + 2(3) + 6 = A(4)²
36 + 6 + 6 = 16A ⇒ A = \(\frac { 48 }{16}\)
A = 3
Put x = -1
4(1) + 2(-1) + 6 = C(-4)
4 – 2 + 6 = -4C ⇒ -4c = 8
C = -2
Put x = 0
6 = A(1) + B(-3) + C(-3)
6 = 3(1) – 3B + (-2) (-3)
6 = 3 – 3B + 6 ⇒ 3B = 3
B = 1
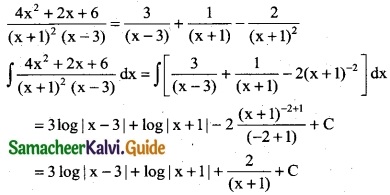
![]()
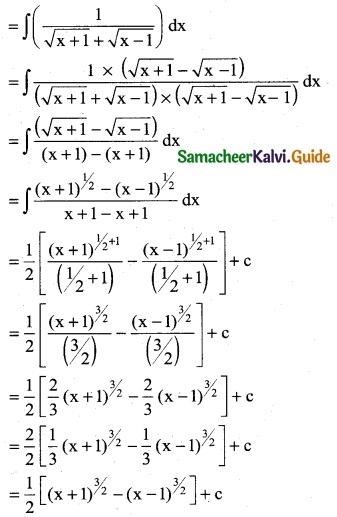
Question 7.
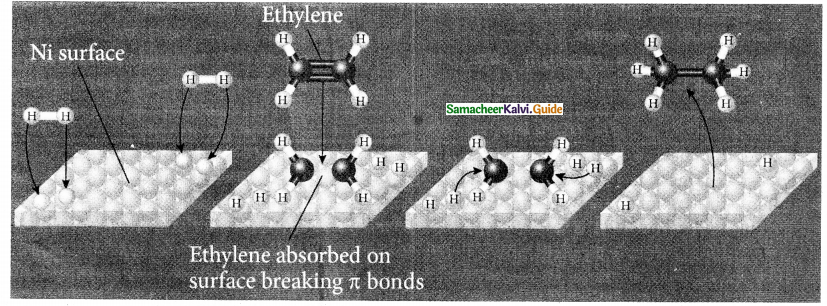
\(\frac { 3x^2-2x+5}{(x-1)(x^2+5)}\)
Solution:
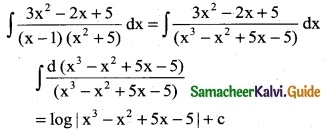
![]()
Question 8.
Given f'(x) = \(\frac { 1 }{x}\) and f (1) = \(\frac { 1 }{π}\), then find f(x)
Solution:
f'(x) = \(\frac { 1 }{x}\)
f(x) = ∫f'(x) dx = ∫\(\frac { 1 }{x}\) dx
f(x) = log|x| + c
f(1) = π/4 ⇒ log|1| + c = π/4.
⇒ 0 + c = π/4
∴ c = π/4
∴ Required f (x) = log |x| + π/4
![]()

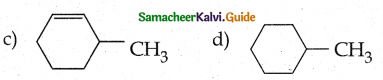
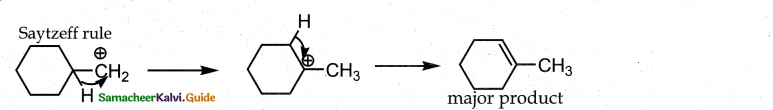
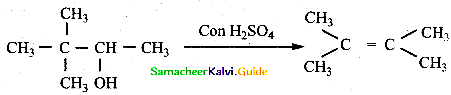
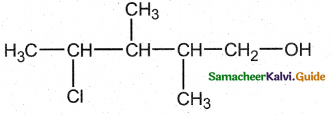
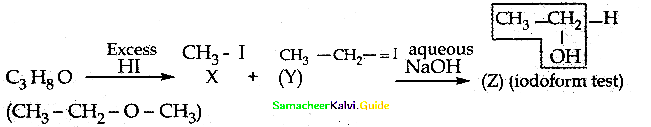
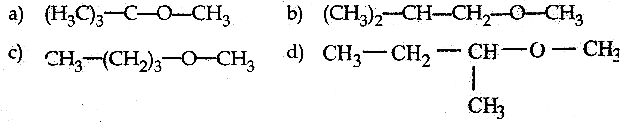
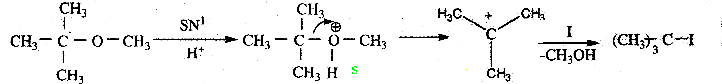
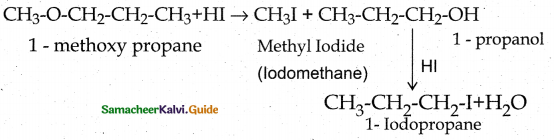
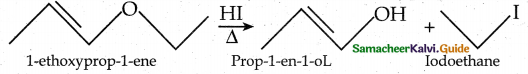
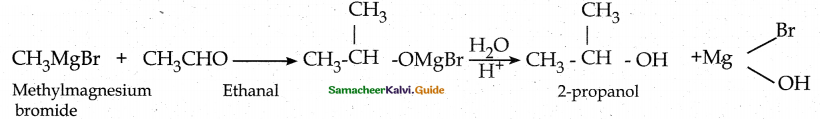
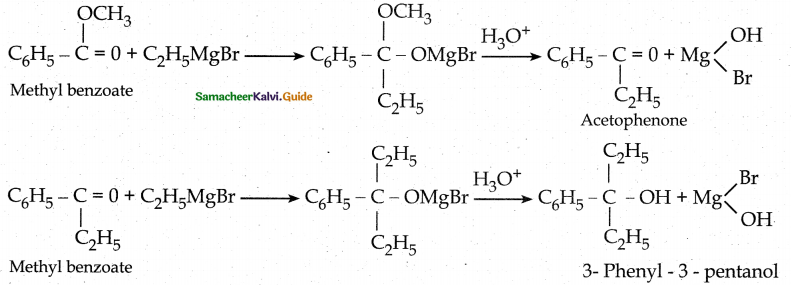
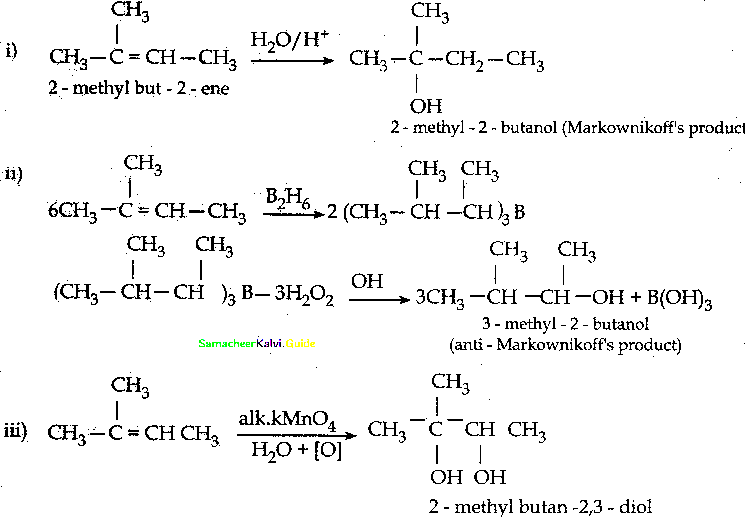
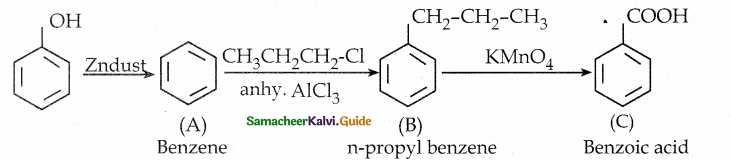
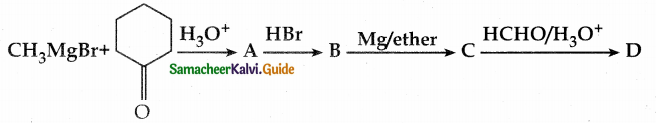
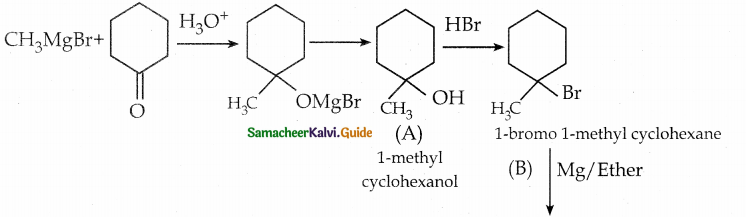
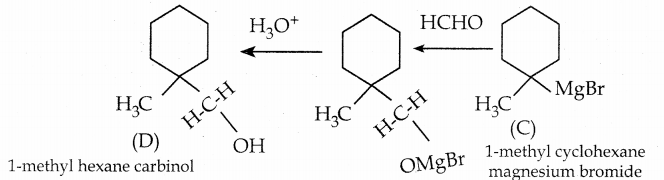


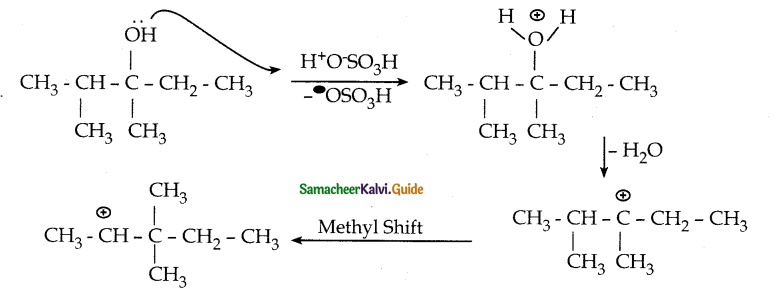
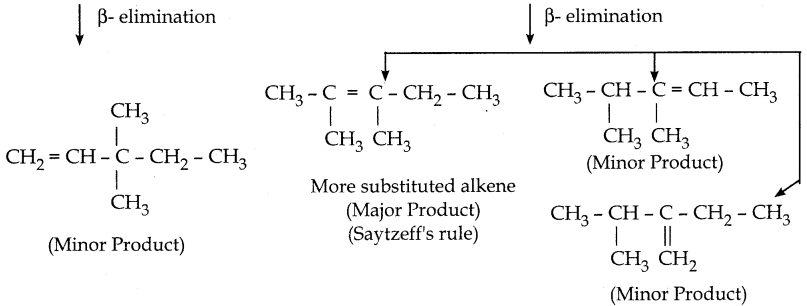
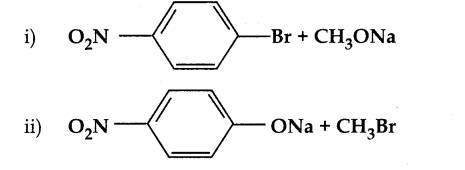
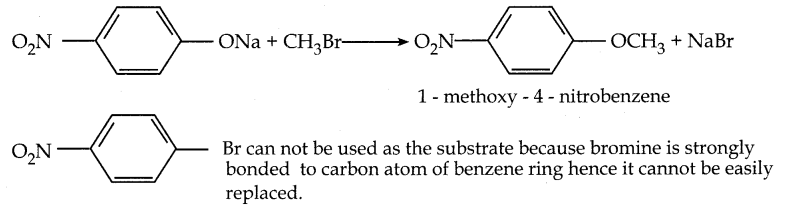
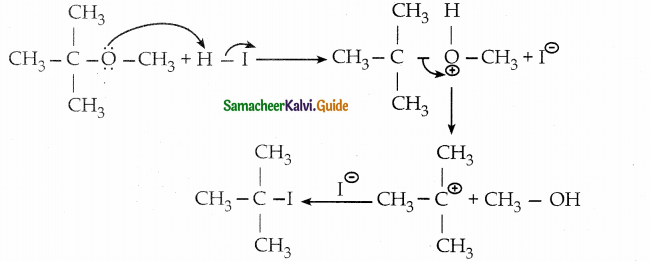
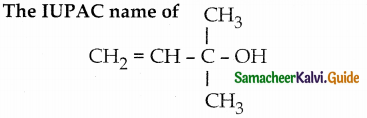

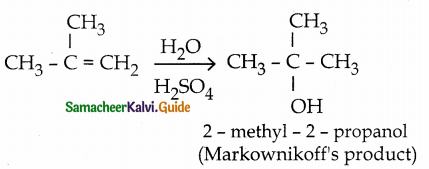
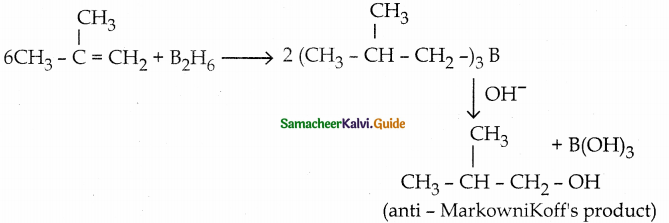

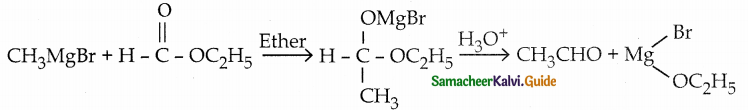
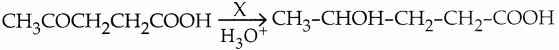
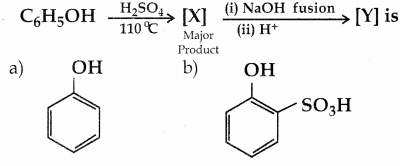
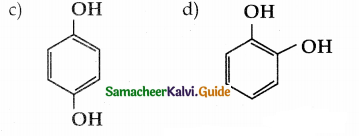
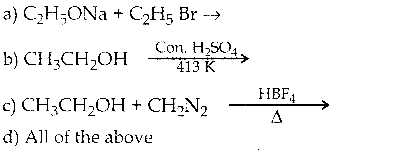
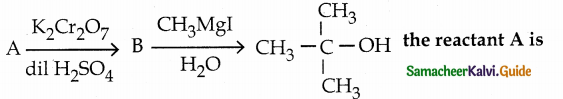
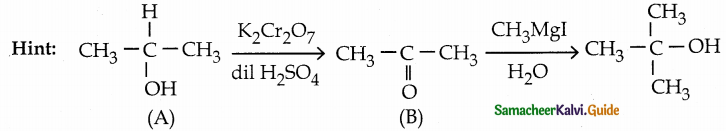
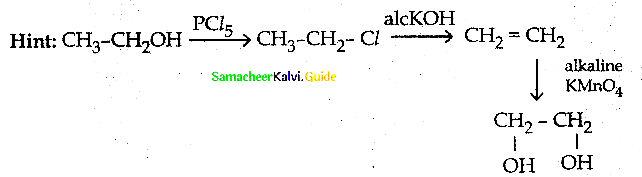

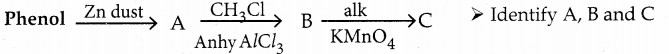
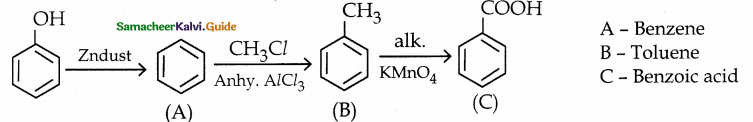
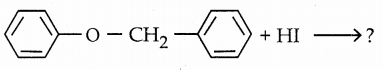
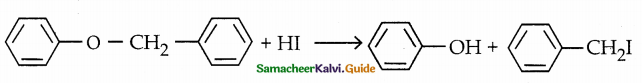
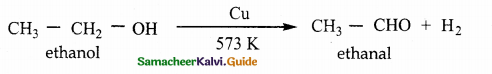
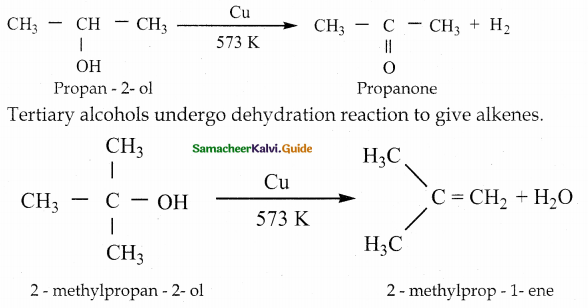
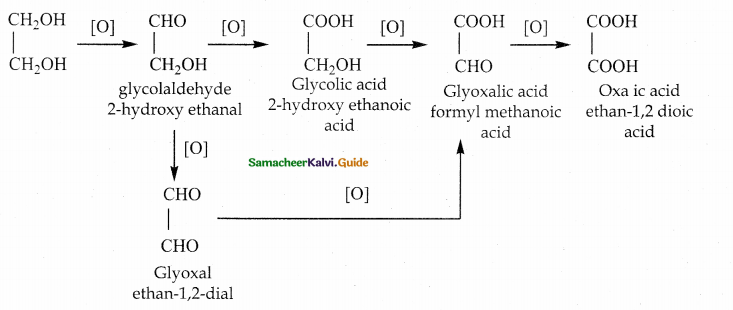
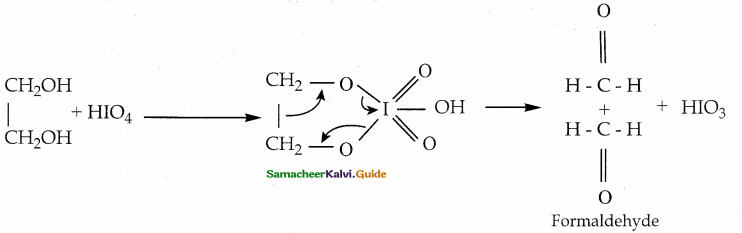

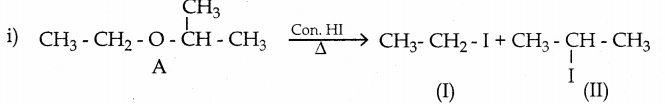
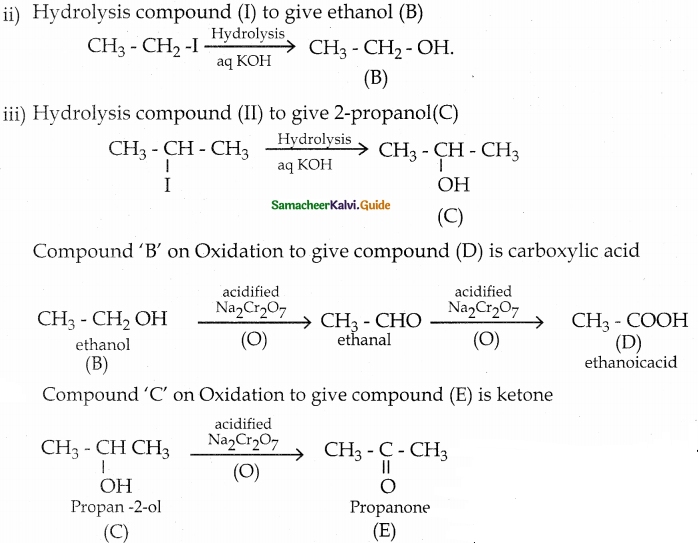
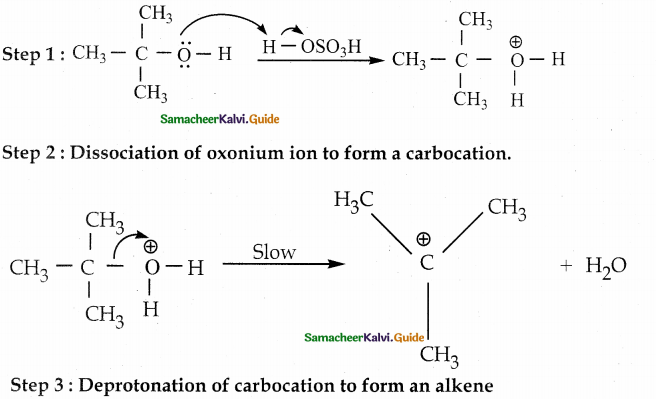
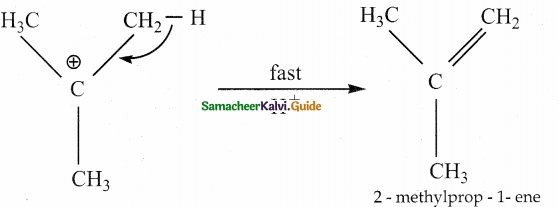

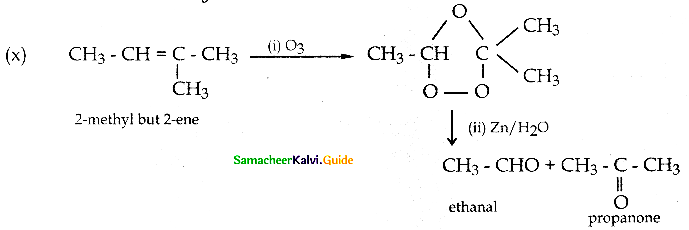
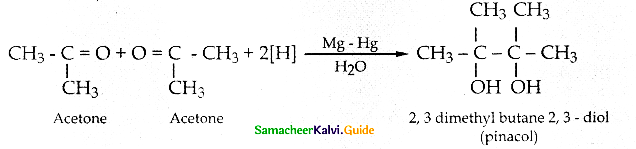

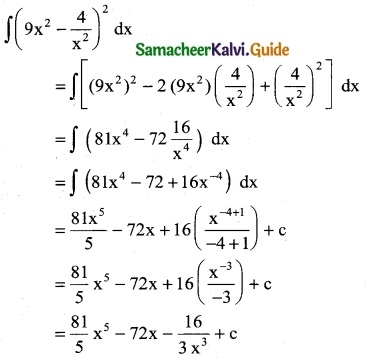
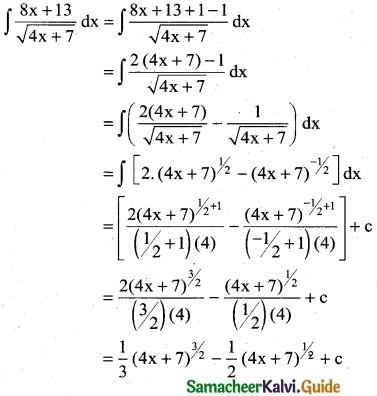
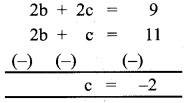
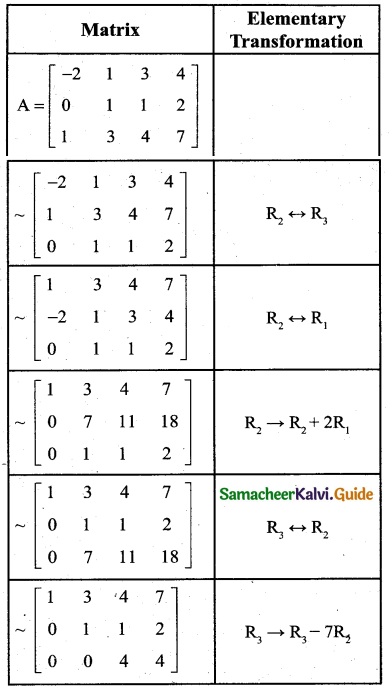
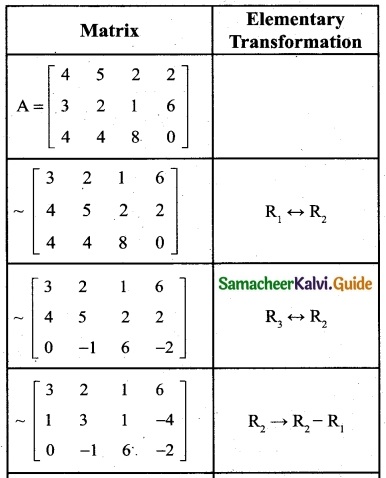
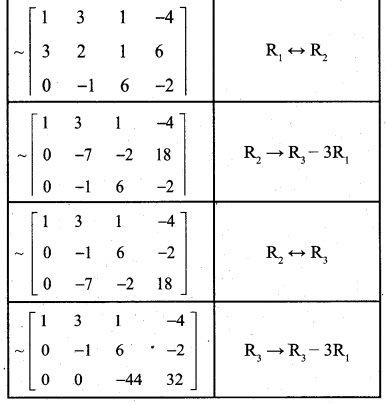
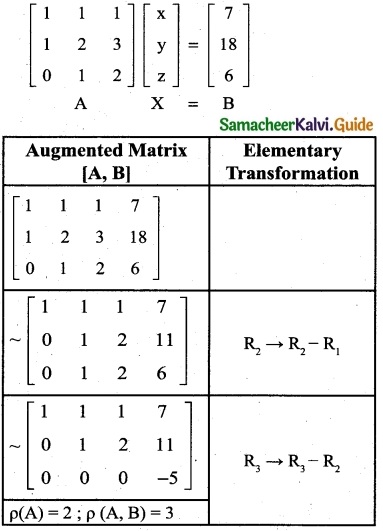
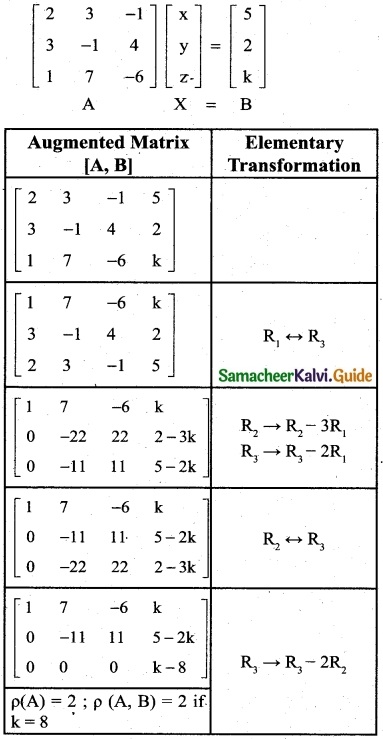
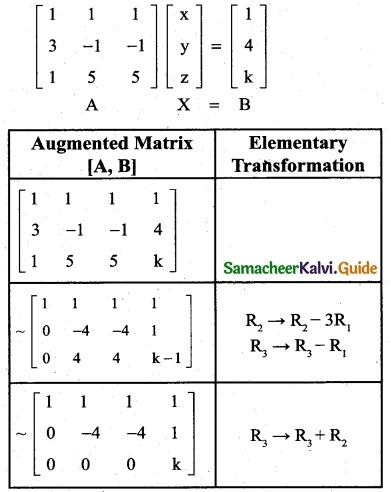
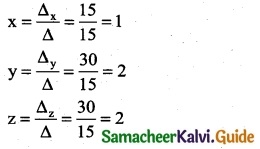
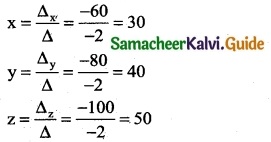
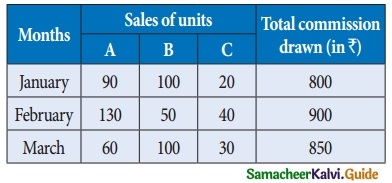
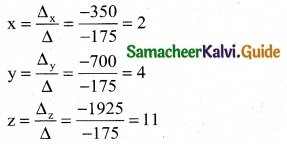
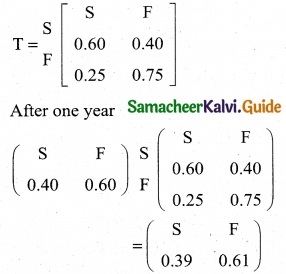



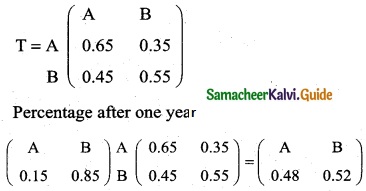
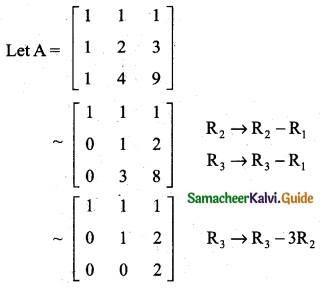
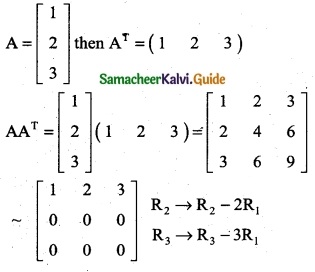
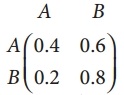 is a transition probability matrix, then at equilibriuium A is equal to
is a transition probability matrix, then at equilibriuium A is equal to

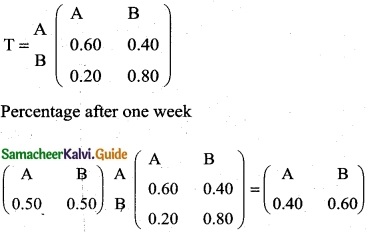
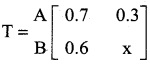 is a transition probability matrix, then the value of x is
is a transition probability matrix, then the value of x is