Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Guide Pdf Chapter 14 Marketing and Marketing Mix Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions 14 Marketing and Marketing Mix
12th Commerce Guide Marketing and Marketing Mix Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Correct Answer.
Question 1.
The initial stage of Marketing system is ……………
a) Monopoly system
b) Exchange to money
c) Barter system
d) Self producing
Answer:
c) Barter system
Question 2.
Who is supreme in the market?
a) Customer
b) Seller
c) Wholesaler
d) Retailer
Answer:
a) Customer
![]()
Question 3.
In the following variables which one is not the variable of the marketing mix?
a) Place the variable
b) Product variable
c) Program variable
d) Price variable
Answer:
c) Program variable
Question 4.
Marketing mix means a marketing program that is offered by a firm to its target ………………… to earn profits through the satisfaction of their wants.
a) Wholesaler
b) Retailer
c) Consumer
d) Seller
Answer:
c) Consumer
![]()
Question 5.
Which one is the example of an Intangible product?
a) Education
b) Mobiles
c) Garments
d) Vehicles
Answer:
a) Education
II. Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
What is Marketing?
Answer:
Marketing is one of the business functions that all activities that take place in relation to markets for actualise potential exchanges for the purpose of satisfying human needs and wants.
Question 2.
Define marketing mix.
Answer:
“Marketing mix is a pack of four sets of variables namely product variable, price variable, promotion variable, and place variable”
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by Grading?
Answer:
Grading means the classification of standardized products into certain well-defined classes.
Question 4.
Define product.
Answer:
“A product is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use to consumption that might satisfy a want or a need” – PHILIP KOTLER
![]()
III. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
What are the objectives of marketing?
Answer:
Baker and Anshen say, “The end of all the marketing activities is the satisfaction of human wants”. The following are the objectives of marketing:
- Intelligent and capable application of modem marketing policies.
- To develop the marketing field.
- To develop guiding policies and their implementation for a good result.
Question 2.
What is need for market and explain the concept of marketing?
Answer:
Market is needed for the following:
- To the movement of goods from the manufacturer to the consumer.
- To increase the standard of living of the people.
- To increase the national income
- To increase employment opportunities.
Concept of marketing:
What I can sell?
- Make what you can sell, but do not try to sell what you can make Shall I first create products?
- No, first create a consumer, then create products.
Shall I love my products?
No, love your customers not the products.
Who is supreme in the market?
Customer is supreme or king.
Who will shape my decision?
Customers’ preferences shape your decisions.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the factors affecting the Price of the Product? COMMO
Answer:
Factors affecting Price of product/service:
(a) Internal Factors:
- Marketing Objectives
- Marketing Mix Strategy
- Organizational considerations
- Costs
- Organization Objectives
(b) External Factors:
- The market after demand
- Competition
- Customers
- Suppliers
- Legal factors
- Regulatory factors..
Question 4.
What do you mean by marketing mix? Describe any two elements.
Answer:
- Marketing mix means a marketing programme that is offered by a firm to its target consumers to earn profits through the satisfaction of their wants.
- It is a mixture of four ingredients namely 4Ps.
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion.
- Product
- “Product” is the main element of marketing.
- Without a product, there can be no marketing.
- Price is the value of a product expressed in monetary terms.
- t is the amount charged for the product.
![]()
IV. Long Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Discuss the evolution of marketing.
Answer:
Barter system:
Before the invention of money, goods were exchanged for goods.
Production orientation:
- Producers more cared about the mass production of goods for the purpose of profit.
- They cared very little about the customers.
Sales orientation:
- The stage witnessed a major change in all the spheres of economic life.
- Sales become the dominant factor, neglect the consumer needs and satisfaction.
Marketing orientation:
Customer’s importance was realized, but only as a means of disposing of goods aggressive advertising is used to compete for the stiff competition.
Consumer orientation:
Under this stage only such products are brought forward to the market which are capable of satisfying the tastes, preferences and expectations of consumer satisfaction.
Management orientation:
It assumes a managerial role to co-ordinate the business activities with the objective of planning, promoting and services to the present and potential consumers.
Question 2.
Why marketing is important to society and individual firms? Explain.
Answer:
To the Society:
- Marketing is a connecting link between the consumers and the producers
- Helps in increasing the living standard of people.
- Helps in increasing the nation’s income.
- Helps to increase employment opportunities.
- II creates a modern cultivator.
- Reduction in the cost of marketing is a direct benefit to society.
- It includes all activities in the creation of Form, place, time, and possession utilities.
To the individual firms:
- It generates revenue [profit] to the firm.
- It helps the development of business and creates employment opportunities for people.
- It provides information to the top management for taking an overall decision on production
- Marketing and innovation are two basic functions of all business, the world is dynamic.
![]()
Question 3.
Narrate the elements of the marketing mix.
Answer:
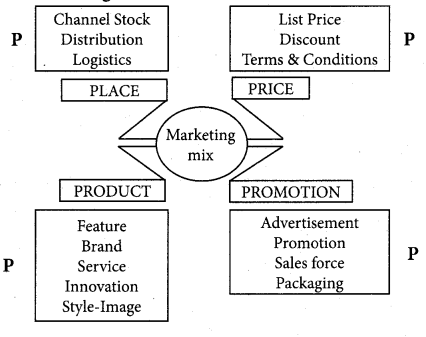
Marketing mix means a marketing programme that is offered by a firm for the satisfaction of human wants. There are four elements of the marketing mix:
- Product: A Product is the main element of marketing. Without a product, there can be no marketing.
- Price: Price is the value of a product expressed in monetary terms. It is the amount charged for the product.
- Place (Physical Distribution): An excellent quality product, with a good price, will be waste, if it is not transferred from the production place to the consumption place.
- Promotion: An excellent product with a competitive price cannot achieve a desired success and acceptance in the market, with special features are conveyed to the consumers.
![]()
12th Commerce Guide Marketing and Marketing Mix Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Correct Answer.
Question 1.
…………………………………….. Creates place utility.
a) Transport
b) Warehouse
c) Bank
d) Insurance
Answer:
a) Transport
Question 2.
Warehouse creates …………………………… utility.
a) Form
b) Place
c) Time
d) Possession
Answer:
c) Time
![]()
Question 3.
Before the invention of money, goods were exchanged for goods known as …………..
a) Trade
b) Commerce
c) Business
d) Barter
Answer:
d) Barter
Question 4.
Pick the odd one out:
a) Grading
b) Branding
c) Packing
d) Warehousing
Answer:
d) Warehousing
![]()
Question 5.
Pick the odd one out:
a) Price
b) Promotion
c) Place
d) Power
Answer:
d) Power
Question 6.
Choose the correct statement
i. Transport creates place utility.
ii. Were house creates time utility.
iii. Storage creates from utility
a) (i) and (ii) correct
b) (ii) and (iii) correct
c) All are correct
d) (i) and (ii) correct (iii) incorrect
Answer:
d) (i) and (ii) correct (iii) incorrect
![]()
Question 7.
Which one is not the correct method?
a) Promotion – Advertisement
b) Branding – Name
c) Packaging – Wrapping
d) Grading – Value
Answer:
d) Grading – value
Question 8.
Which of the following elements is the related marketing mix?
a) Place
b) production
c) consumption
d) trade
Answer:
a) place
![]()
II. Match The Following
Question 1.
Match list-1 with list-2
|
List-1 |
List-2 |
| (i) Branding | 1. Movement of goods |
| (ii) Pricing | 2. Preservation of goods |
| (iii) Storage | 3. Sum of the values |
| (iv) Transportation | 4. Symbol |

Answer:
a) (i) 4, (ii) 3, (iii) 2, (iv) 1
Question 2.
Match list-1 with list-2
|
List-1 |
List-2 |
| i. Price | 1. Advertisement |
| ii. Product | 2. Terms and condition |
| iii. Place | 3. Distribution |
| iv. Promotion | 4. Innovation |

Answer:
a) (i) 2, (ii) 4, (iii) 3, (iv) 1
![]()
III. Assertion and Reason.
Question 1.
Assertion [A]: Movement of goods from the place of production to the place of consumption by means of transport
Reason [R]: It creates place utility,
a) (A) is false (R) is true
b)(A) is true (R) is true
c) (A) is false (R) is false
d) (A) is true (R) is false
Answer:
b) (A) is True (R) is True
Question 2.
Assertion [ A]: Product is the main element of marketing.
Reason [R]: There can be no market without a product.
a) Both (A) and (R) are correct
b) Both (A) and (R) are incorrect
c) (A) is correct
d) (R) is correct
Answer:
a) Both (A) and (B) is correct
![]()
IV. Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Define marketing.
Answer:
“Marketing is concerned with the people and the activities involved in the flow of goods and services from the producer to the consumer”. -AMERICAN MARKETING ASSOCIATION.
Question 2.
What are the functions of exchange? BAS
Answer:
- Buying
- Assembling
- Selling
Question 3.
Give the traditional marketing mix. 4Ps
Answer:
- Price
- Product
- Place
- Promotion
![]()
Question 4.
Give the modern marketing mix. 4Ps
Answer:
- People
- Performance
- Programme
- Process
Question 5.
What are the functions of marketing? G.B. GILES.
Answer:
- Market research
- Planning
- Product development
- Promotion
- Distribution
- Service offer sales
![]()
Question 6.
What are the functions of marketing? CLARK AND CLARK.
Answer:
- Functions of exchange
- Functions of physical supply
- Facilitating functions.
Question 7.
Define price.
Answer:
“Price is the amount of money charged for a product or service or the sum of the values that consumers exchange for the benefits of having or using the product or service”. – PHILIP KOTLER
![]()
Question 8.
Give any two internal factors affecting the price of product/service. COMMO
Answer:
- Costs
- Organizational objectives
- Marketing objectives
- Marketing mix strategy
- Organizational consideration
V. Long Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Explain the functions of physical supply.
Answer:
Transportation:
- Transport means carrying goods and services from one place to another. [Goods- men.]
- It creates place utility by moving goods from the places when they are available in plenty to places where they are needed.
- Types of transport – land, water, and air.
Storage:
- Generally, there is a time gap between production and consumption of goods.
- It involves the holding and preservation of goods from the time of production to the time of consumption.
Warehousing:
It creates time utility by storing the goods throughout the year and releasing them as and when they are needed.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the facilitating functions of marketing?
Answer:
- Financing: Long term – medium term and short term financing.
- Risk bearing: Time – place – competition – human and political risks.
- Grading: It means the classification of the standardized product into certain well-defined classes.
- Branding: It means giving a name or symbol to a product to differentiate it from a competitive product
- Packing: It means wrapping and crating of goods before distribution.
- Pricing: Price must be determined only to offer to take all the relevant factors into consideration.
![]()
Question 3.
What is marketing?
Answer:
- Marketing is one of the business functions that all activities that take place in relation to markets for actualizing potential exchanges [from the producer to the consumer] for the purpose of satisfying human needs and wants.
- Selling is basically concerned with putting the goods into the hands of the buyers for a price.
- But marketing is much wider than selling.
- It is an evolution rather than revolutionary.
- Marketing is what a marketer does. It is not clear to understand the meaning.
- It is one of the oldest professions in the world.
- The traditional objective of marketing had been to make the goods available at places where they are needed.
- This idea was later on changed by shifting the emphasis from exchange to satisfaction of human wants.
- Marketing must first find out what customers want and then plan a product to satisfy the wants.
Question 4.
State to advantages of warehousing.
Answer:
Storage:
- There is a time gap between production [supply] and consumption [demand].
- During the time gap, the goods may be damaged or destroyed or perished.
- For that goods need storage or warehouse.
- It creates time utility.
Equalization of demand and supply:
- It equalizes the demand and supply of goods.
- Storing the goods- when there is no demand.
- Releasing the goods – when there is a demand.
Price stabilization:
- It ensures price stabilization.
- It controls the price fluctuations.
- The price of commodities more or less uniform throughout the year by storing the goods, if there is no demand and releasing the goods if they are demanded.
Risk bearing:
When the goods are in the warehouse, in case of damage due to flood fire, theft, etc., the warehouse keepers compensate the loss of the owner of the goods.
Finance:
By pledging warehouse receipt or warehouse warrant, a depositor can get loans from financial institutions.
![]()
Question 5.
How market information is helpful to the invention of a new product in the market?
Answer:
- Strong knowledge of customers.
- Marketing research – process for marketing opportunities- problem-solving collecting- analyzing marketing information.
- Control over fact – the responsibility of the marketing research director.
- Design research carefully and supervise its execution.
- Various combinations of people, technologies for managing marketing information.
- Broader management and strategy decisions.
- Research consumer performance to contribute to improving decision-making performance.
- It is helpful to accurate needs and decision-making by the marketer to be a regular source of information about marketing and trading brand awareness.